
ITIL Change Evaluation Process
Change Evaluation is one of the main processes under the Service Transition Module of the ITIL best practice framework. We already learned about the Change Management process. We may think of this process as an extension of Change Management.
This ITIL Change Evaluation Process comes into the picture, whenever the organization decided to make major changes to their existing infrastructure or services. This process is undertaken separately for managing risks associated with major changes to reduce the chances of failures.
As described in ITIL V3, Change Evaluation Process is initiated from & controlled by change management and taken care of by Change Manager.
This process is tightly bound with some other processes, such as Design Coordination, Transition Planning & Support, and some part of Incident Management.The purpose of change evaluation is to provide a uniform and structured means of determining the performance of a change relating to the likely impact on the business, on any existing or proposed services, the current and future IT infrastructure.
Why ITIL?
Following are the various reasons which allows the IT and Business managers to use this method:
- It is used to enhance the resource and capabilities.
- It is used for planning the processes with particular goals in mind.
- It helps in integrating business and service strategies.
- It also helps to control the IT budget and investment.
- This framework also helps in changing the organizational culture.
- It also helps in developing the IT and business partnerships.
- It also offers the maximum values to the customers.
- It also improves the relationship with the customers by delivering the services.
- It also offers good management of services.
- It also helps in measuring, optimizing, and monitoring the performance of the service provider.
- It allows them to define the roles for each task.
- It manages the service failure.
- It helps managers by providing the service which is reliable and useful.
Why is ITIL required?
ITIL helps business managers and IT managers to deliver services to the customers in an effective manner and hence gaining the customer’s confidence and satisfaction. The areas where ITIL plays an effective role are as given below :
- IT and business strategic planning
- Integrating and aligning IT and business goals
- Implementing continuous improvement
- Acquiring and retaining the right resources and skill sets
- Reducing costs and the Total Cost of Ownership
- Demonstrating the business value to IT
- Achieving and demonstrating Value for Money and Return on Investment.
- Measuring IT organization effectiveness and efficiency
- Developing business and IT partnerships and relationships
- Improving project delivery success
- Managing constant business and IT change
ITIL Change Evaluation Sub-Process:
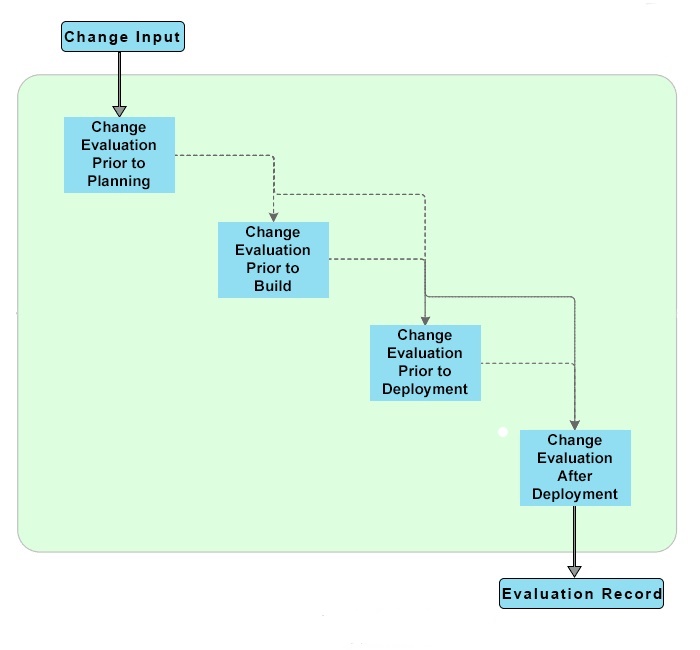
As defined by ITIL v3, there are four sub-processes of this process. Below are the objectives and descriptions of those sub-processes, followed by a diagram to explain the ITIL Change Evaluation Process flow:
- Change Evaluation prior to Planning: To assess & evaluate a proposed major Change before authorizing the Change planning phase.
- Change Evaluation prior to Build: To assess & evaluate a proposed major Change before authorizing the Change build phase.
- Change Evaluation prior to Deployment: To assess & evaluate a proposed major Change before authorizing the Change deployment phase.
- Change Evaluation after Deployment: To assess & evaluate a major Change after it has been implemented, to verify if the Change has met its objectives and to record any lessons learned from this change.
Important Terms used in the ITIL:
There are various following terms used in the ITIL which are required to learn:
Capabilities: Capability or capacity is the level of strength of the services and infrastructure of IT. It is an intangible asset of any organization or business.
Resources: It is a term that includes the people, infrastructure, money, applications, etc which may help in delivering IT services.
Baseline: It is referred to as a (starting) initial point of a service or project. In this framework, it is used for measuring how the operations of IT are performing.
Process: This term is a set of activities, which are designed to perform a particular objective. It accepts one or more defined inputs and transforms them into an output which is defined. Process is a term which is triggered by the particular events.
Service: It is a means of delivering the values to the customers by achieving the customer’s result without defining the costs and risks. Sometimes, this term is also a synonym for IT service, service package or core service.
ITIL Role: Role is a term, which is a collection of specific activities, authorities, and responsibilities granted to an individual or team.
Business Case: The business case is a term describing the expected expense and profit which can be achieved as the result of a change.
Function: In the ITIL framework, function is a group of tools and people which is used to perform one or more activities or processes.
Process Owner: A Process Owner has a responsibility to manage the overall performance, design, integration, improvement of a single process.
Process Manager: In large organizations, there are separate Process Managers and Process Owners for the better management. In any organization, the role of a Process Manager is to manage the processes operationally.
Service Owner: The service owner is a person in an organization, whose role is to deliver the specific service as per the SLA (Service Level Agreement). Also, he is responsible for managing the overall performance, design, and integration of a single service.
ITSM (IT Service Management): It is a term in the ITIL framework, which provides the services of IT in a focused and client-friendly manner. The main component of ITSM is a framework which design the services according to the SLA. And, that framework is known as SLM (Service Level Management).
CI (Configuration Item): It is a component having a direct impact on the delivering IT services. The information for each Configuration Item is automatically stored in the configuration record within the CMS (Configuration Management system).
This term includes the services of IT, software, hardware, building, and the formal documentation such as SLAs (Service Level Agreement).
CMDB (Configuration Management Database): This component is used for storing the configuration records, which contains the attributes and the relationships of CI. It is a term, which also tracks the inter-relationship between all the Configuration Items.
CMS (Configuration Management System): A CMS is a collection of tools and databases, which manages the configuration data of IT services providers. It is a component, which also contains the information about the problems, changes, known errors, and incidents. It may also contain data about suppliers, business units, customers, employees and the end-users.
The CMS is used by all the processes of ITSM and maintained by the configuration management.
Change: Change is the modification of anything, which may affect the services of IT.
Service Manager: The Service Manager is responsible for the development and improvement of all the IT services.
Access: This term in ITIL allows the users to access the level and scope of the functionality of a service or data.
Product Manager: The Product Manager is responsible for the performance, improvement, and quality check of the group of related IT services.
Risk: This term is defined as an uncertain event. If it occurs, there is an effect on the IT services positively or negatively.
Problem: In the ITIL framework, this term is defined as the unknown causes of one or more incidents.
Known Error: The Known Error is stored in the KEBD i.e., Known Error Database. These errors are created and managed by Problem Management.
Incident: It is a component in ITIL, which is the reduction in the quality of the IT service or an unplanned interruption to the organization’s IT services. It is also defined as the failure of a configuration item.
Service Level Agreement (SLA): In the ITIL framework, there is an SLA agreement in an organization between the customer and the IT service provider. This agreement describes the services of IT and defines the responsibilities of the customer and the provider. Service Level Agreement also describes the document level service targets.
Operational Level Agreement (OLA): In ITIL, there is also an Operational Level Agreement in an organization of IT between the service provider and other parts of that organization. This term defines the services or goods which are to be provided. And, it also defines the responsibilities of both the parties.
Service Lifecycle in ITIL:
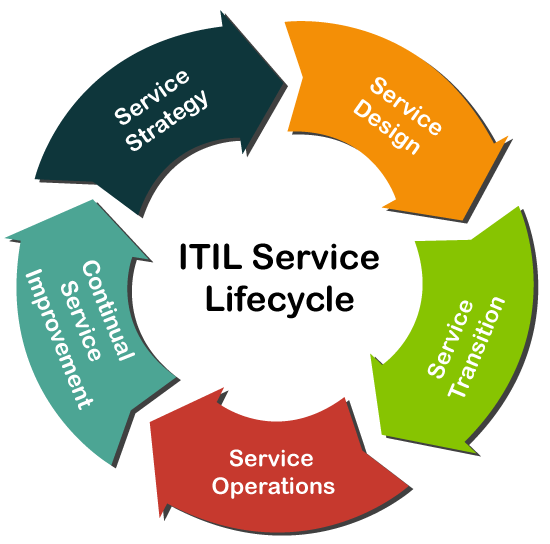
The ITIL framework is completely based on the lifecycle of a service. The lifecycle of IT Service Management is also called a ‘Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA)’ or ‘Deming Cycle’. It helps the service providers to achieve a better understanding of its structure. It also defines the process of how the services are started and maintained.
The lifecycle of a service in the framework of ITIL is broadly classified into the following five stages:
- Service Strategy
- Service Design
- Service Transition
- Service Operations
- Continual Service Improvement
Each stage in this life cycle contains the various processes of ITIL and all the stages are interconnected. Now, we will learn about each stage of the service lifecycle one by one.
Service Strategy
Service Strategy is the first and initial stage in the lifecycle of the ITIL framework. The main aim of this stage is that it offers a strategy on the basis of the current market scenario and business perspective for the services of IT.
This stage mainly defines the plans, position, patterns, and perspective which are required for a service provider. It establishes the principles and policies which guide the whole lifecycle of IT service.
Following are the various essential services or processes which comes under the Service Strategy stage:
- Financial Management
- Demand Management
- Service Portfolio Management
- Business Relationship Management
- Strategy Management
Service Design
It is the second phase or a stage in the lifecycle of a service in the framework of ITIL. This stage provides the blueprint for the IT services. The main goal of this stage is to design the new IT services. We can also change the existing services in this stage.
Following are the various essential services or processes which comes under the Service Design stage:
- Service Level Management
- Capacity Management
- Availability Management
- Risk Management
- Service Continuity Management
- Service Catalogue Management
- Information Security Management
- Supplier Management
- Compliance Management
- Architecture Management
Service Transition
Service Transition is the third stage in the lifecycle of ITIL Management Framework.
The main goal of this stage is to build, test, and develop the new or modified services of IT. This stage of service lifecycle manages the risks to the existing services. It also certifies that the value of a business is obtained.
This stage also makes sure that the new and changed IT services meet the expectation of the business as defined in the previous two stages of service strategy and service design in the life cycle.
It can also easily manage or maintain the transition of new or modified IT services from the Service Design stage to Service Operation stage.
There are following various essential services or processes which comes under the Service Transition stage:
- Change Management
- Release and Deployment Management
- Service Asset and Configuration Management
- Knowledge Management
- Project Management (Transition Planning and Support)
- Service Validation and Testing
- Change Evaluation
Service Operations
Service Operations is the fourth stage in the lifecycle of ITIL. This stage provides the guidelines about how to maintain and manage the stability in services of IT, which helps in achieving the agreed level targets of service delivery.
This stage is also responsible for monitoring the services of IT and fulfilling the requests. In this stage, all the plans of transition and design are measured and executed for the actual efficiency. It is also responsible for resolving the incidents and carrying out the operational tasks.
There are following various essential services or processes which comes under the stage of Service Operations:
- Event Management
- Access Management
- Problem Management
- Incident Management
- Application Management
- Technical Management
Continual Service Improvement
It is the fifth stage in the lifecycle of ITIL service. This stage helps to identify and implement strategies, which is used for providing better services in future.
Following are the various objectives or goals under this CSI:
- It improves the quality services by learning from the past failures.
- It also helps in analyzing and reviewing the improvement opportunities in every phase of the service lifecycle.
- It also evaluates the service level achievement results.
- It also describes the best guidelines to achieve the large-scale improvements in the quality of service.
- It also helps in describing the concept of KPI, which is a process metrics-driven for evaluating and reviewing the performance of the services.
There are following various essential services or processes which comes under the stage of CSI:
- Service Review
- Process Evaluation
- Definition of CSI Initiatives
- Monitoring of CSI Initiatives
Advantages of ITIL:
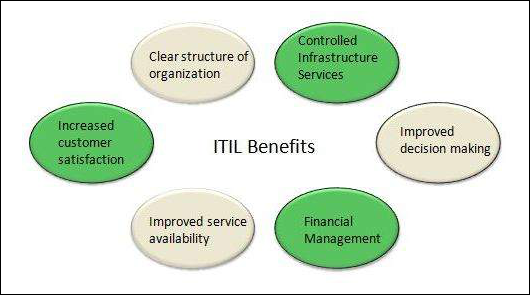
Following are the various advantages or benefits of ITIL:
- One of the best advantages of ITIL is that it helps in increasing the customer satisfaction.
- It allows managers to improve the decision-making process.
- It is also used for creating the clear structure of an organization.
- It also helps managers by controlling the infrastructure services.
- It improves the interaction between the customers and the service provider.
- With the help of this framework, service delivery is also improved.
- It establishes the framework of ITSM for the organization.
Conclusion
A solid ITIL change management process means IT can safely say “yes” to more requests for change from the business and IT might shake off its image as “The No Department.” Through change management, IT can quickly improve infrastructure quality, reduce service disruption, and be more responsive to the business. The business will undoubtedly notice the difference.
By following this 6-step process of implementation, you can improve your chances of a successful implementation, shorten the time-to-value, and gain support for further ITSM process work.
- Identify why you want to implement ITIL change management
- Understand the importance of change management
- Identify what is ITIL change management & its types
- Define change management roles & responsibilities
- Design the ITIL change management process flow
- Measure change management KPI





