
Continuous Service Improvement (CSI) deals with measures to be taken to improve the quality of services by learning from past successes and failures.
- Its purpose is to align and realign IT Services to the changing needs by identifying and implementing improvements to the changing business needs.
What Is Continual Service Improvement (CSI) In ITIL ITSM?
- ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) is the fifth and final Process-group of ITIL Service Management Lifecycle under ITIL’s IT Service Management Framework (ITSM).
- It aims to deal with measures to be adopted to improve the service quality by learning from past successes and failures.
- CSI also aligns and realigns IT Services to the changing business requirements by identifying and implementing changes for improvements.
- For doing this, it takes the similar approach described in Deming Cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act).
- The ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) actually describes the best practices for achieving incremental and large-scale improvements in services quality, operational efficiency, and business continuity.
- It effectively describes and utilizes the concept of Key Performance Indicator (KPI), which is a metrics-driven process, for reviewing, evaluating, and benchmarking performance of services.
ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) Objective:
According to ITIL v3, the primary objective of ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) stage is to continually improve the quality, effectiveness, and efficiency of IT processes and services. Some other objectives of CSI are as follows:
- Review and analyze improvement opportunities in every lifecycle phase
- Analyze and evaluate Service Level achievement results.
- Improve cost-effectiveness of delivered IT services without impacting on customer satisfaction.
- Ensures alignment with quality management methods to support improvement activities.
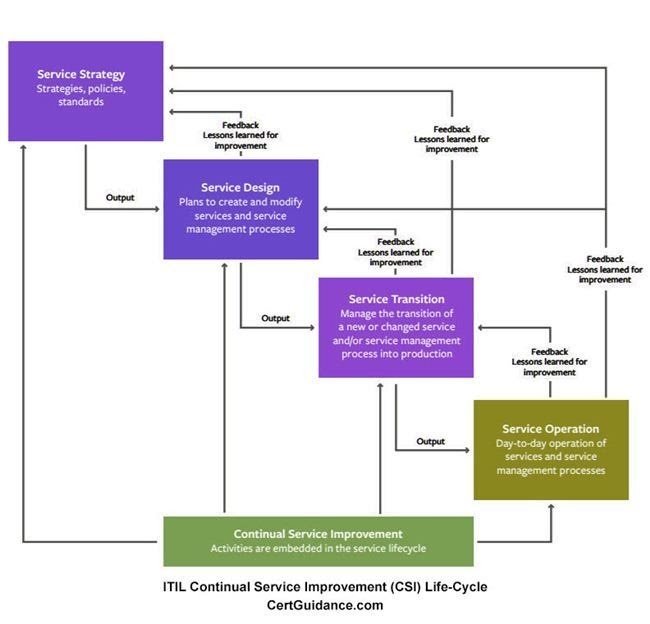
This CSI process group (Stage) acts as a guide and provide continual feedback to every process groups (Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, and Service Operation) of Service Management Life-Cycle.
- The Below Image shows the Flow of information between CSI & other processes and how it provides feedback to each of the processes.
- This is very important to remember that, this is not a static one-time process. Instead, as the name suggests, it is a continual process which runs in periodic cycles.
ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) Approaches:
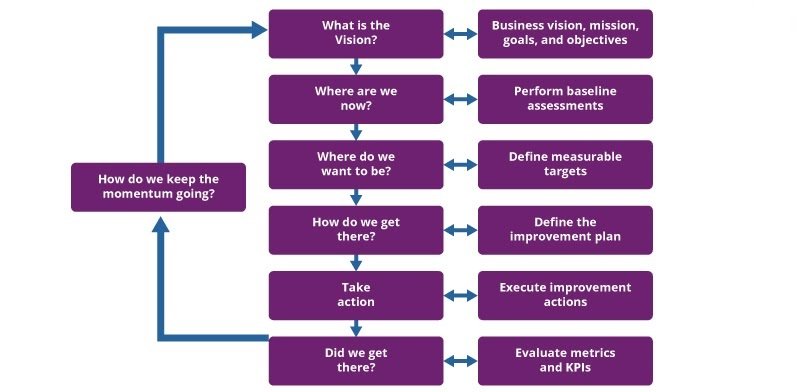
- This process follows a six-step approach for reviewing, evaluation, planning, and implementing the Improvement process.
- These approaches are nothing but some pre-defined questions, for which the CSI process tries to find answers. Those questions or approaches are as follows:
(i) What is the vision?
Describes and defines the long-term objective of the organization.
(ii) Where are we now?
Analyze the current position of the organization in terms of Business, organization, people, Process, and measures the present values of defined KPI.
(iii) Where do we want to be?
Describes the baseline objectives of the organization and defines the desired KPI values to be achieved.
(iv) How do we get there?
Define Plans for achieving those objectives & KPI targets.
(v) Did we get there?
After implementing the plan, it is the self-assessment to be done to check whether we have touched those defined KPI benchmarks.
(vi) How do we keep up the momentum?
This is the state where the process control is again passed to the beginning for evaluation and re-planning of objectives.
Steps Of The Continual Improvement Model
The continual improvement uses the continual improvement model depicted below, which provides the required approach for continual improvement, which applies to SVS in entirety.
Continual improvement model
Processes: ITIL Continual Service Improvement
- CSI continually improves the effectiveness and efficiency of services and processes.
- ITIL V3 defines one process in the CSI stage of the service lifecycle: The “Seven-Step Improvement Process”.
- These seven steps describe a generic approach to continual improvement that can be applied in many situations, rather than a process that organizations would implement in practice.
- Specific CSI methods and techniques are mostly discussed in other parts of the ITIL CSI publication.
ITIL Continual Service Improvement (ITIL CSI)
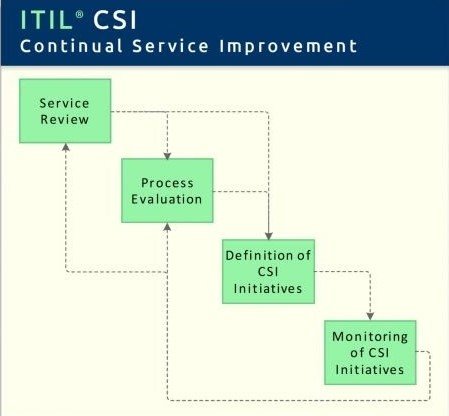
Therefore, organizations seeking to introduce an ITIL-aligned Continual Service Improvement (CSI) process will typically define a set of service improvement processes to ensure that ideas for improvement are identified and implemented, as described below:
Service Review
Process Objective: To review business services and infrastructure services on a regular basis. The aim of this process is to improve service quality where necessary, and to identify more economical ways of providing a service where possible.
Process Evaluation
Process Objective: To evaluate processes on a regular basis. This includes identifying areas where the targeted process metrics are not reached, and holding regular benchmarkings, audits, maturity assessments and reviews.
Definition of CSI Initiatives
Process Objective: To define specific initiatives aimed at improving services and processes, based on the results of service reviews and process evaluations. The resulting initiatives are either internal initiatives pursued by the service provider on his own behalf, or initiatives which require the customer’s cooperation.
Monitoring of CSI Initiatives
Process Objective: To verify if improvement initiatives are proceeding according to plan, and to introduce corrective measures where necessary.
ITIL Continual Service Improvement – 7 Step Improvement Process
Continual Service Improvement (CSI) focuses on service improvement that supports business processes. CSI uses a seven step improvement process plan which is critical for itself and other stages of the ITIL lifecycle.
Seven step improvement process of CSI starts as follows –
- Identify the approach for improvement
- State what will you measure
- Collect the Data
- Process the data
- Analyze the data and information
- Present and use the information
- Implement corrective or remedial activities
- Identify the approach for improvement
Before an improvement plan is executed it is really necessary to understand the need for improvement.
- The information related to what all services need to be measured is gathered in the initial phase of ITIL service lifecycle i.e. in service strategy and service design the information.
- A thorough understanding of business objectives is done and areas are identified that needs enhancement.
- It also focuses on the effectiveness of the improvement plan. This data is then fed into the CSI improvement plan cycle.
Why do we measure Continual Service Improvement?
- It would be easy to find out the areas to measure by knowing the new service level requirement, available funds and IT capabilities.
- IT capabilities are identified in service design and implemented via service transition.
- CSI conducts gap analysis to identify the opportunities for improvement.
- If CSI finds that the available tools and resource are not capable enough or if the cost is non-affordable to deliver the desired data then the measure identified in earlier step needs to be revisited.
Collect the Data
Data is gathered according to the goals and objectives of service operation. In order to have raw and quantitative data, monitoring should be in place. The quality of data is critical and it can be gathered through various means – manual or automatic.
Process the data
Once the data is collected it is important to provide it to the audience in required format. Critical Success Factor (CSF’s) and Key Performance Indicator’s (KPI’s) plays a vital role in processing the data. The raw data is organized and divided according to its categories and operation which makes it easy to process and transform the data into information.
Analyze the data and information
The data which is finally information now is carefully analyzed to find missing gaps and its impact on business. The information is thoroughly evaluated taking into consideration all relevant – internal and external factors that can directly or indirectly impact the data. The information is converted into knowledge or facts.
Challenges of Continual Service Improvement
Present and use the information
The analyzed data is shared with the business stakeholders in a clear and defined manner, presenting them an accurate picture of the results of the improvement plan that is implemented. CSI works closely with senior management and assist them to make strategic decisions and determine the next step to optimize and improve the service.
Implement corrective or remedial activities
- As CSI has identified the areas that need a change, solutions and remedial plans are communicated to the management to improve the service.
- A change, thus implemented for the improvement sets a new baseline and the cycle begins again.
- The seven step process is the vital process of CSI. It enables an organizational resource to identify and understand which process and function of their service operations needs major enhancement.
Implementation of CSI
- For the application of CSI to services and service management processes.
- At implementation all four stages of the PDDCA cycle are used.
- With ongoing improvement, CSI draws check and act stages to monitor, measure, review and implement initiatives.
- After these four stages a phase of consolidation prevents the circle from rolling back down the hill as shown in the figure.
- Our goal in using the Deming cycle or PDCA cycle is steady, ongoing improvement.
- It is a fundamental tenet of Continual Service Improvement (CSI).
- PDCA should be repeated multiple times to implement Continual Service Improvement (CSI).
- Handling of cultural change is required to implement CSI for improvement.
- It should be noted that the PDCA cycle is a fundamental part of many quality standards including ISO/IEC 20000.
CSI And Service Lifecycle
- Service strategy establishes policies some principles that provide guidance for the whole service lifecycle. The service portfolio is defined in this lifecycle stage and new or changed services are chartered. During the service design stage of the lifecycle, everything needed to transition and operate the new or changed service is documented in a service design package.
- This lifecycle stage also designs everything needed to create, transition and operate the services, including management information systems and tools, architectures, processes, measurement methods and metrics. The activities of the service transition and service operation stages of the lifecycle a defined during service design.
- Service transition ensures that the requirements of the service strategy, which developed in service design are effectively realized in service operation our controlling the risks of failure and disruption.
- The service operation stage of the service lifecycle carries out the activities and processes required to deliver the agreed services.
- During this stage of the lifecycle, the value defined in the service strategy is realized. Continual Service Improvement (CSI) acts in tandem to the lifecycle stages.
- Who processes, activities, roles, services and technology should be measured and subjected to continual improvement. The strength of the service lifecycle rests upon continual feedback throughout each stage of the lifecycle.
- This feedback ensures that service optimization is managed from business perspective and measured in terms of the value the business drivers from services at any point in time during the service lifecycle.
- At every point in the service lifecycle, the process of monitoring, assessment and feedback between each stage drives decisions about the need for minor course corrections or major service improvement initiatives.
- Adopting appropriate technology to automate the processes and provide management with the information that supports the processes is also important for effective and efficient service management.






