
- Introduction to ITIL Services Transition
- What is Services Transition?
- Goals of ITIL Service Transition
- Key Principles of ITIL Service Transition
- Transition assessment
- Services approval and testing
- Services Transition arranging and backing
- Processes: ITIL Service Transition
- ITIL 4 Service Transition
- Kinds of Transitions
- Key Definitions
- Services Asset and Configuration Management
- Services progress in the ITSM systems
- Services progress process in YaSM
- Challenges in ITIL Service Transition
- Hazards in ITIL Service Transition
- Conclusion
- Services procedure
- Individuals
- Process
- Innovation
- Providers of the assistance
- Authoritative culture
- Services
- Hazard
- Plan and deal with the progressions in assistance proficiently and viably.
- Deal with the dangers connected with recently presented, adjusted, or ceased Servicess.
- Send the assistance discharges into conditions that help them satisfactorily.
- Set the fitting assumptions for the presentation and use of new or Transitiond Servicess.
- Ensure that the assistance Transitions make the normal incentive for the business.
- Give the fundamental information and data about Servicess and Services resources.
- Approval to construct and test
- Approval to register programming with the authoritative media library (DML)
- Approval to convey
- We ought to assess all Transitions. Be that as it may, for critical Transitions a conventional assessment interaction ought to be conjured. Every association should characterize for itself what “critical Transition” is.
- Assessing the planned impacts of the Transition
- Beyond what many would consider possible, expecting any accidental impacts of the Transition
- Recognizing hazards
- Introducing a suggestion to Transition the executives on whether to continue to the following stage
- The Transition the board cycle can make the go/off limits choice on continuing to the following stage.
- Work with progress arranging and backing to design the assets needed for testing
- Plan and configuration tests
- Plan tests
- Set up the test climate
- Play out the tests
- Assess leave rules and report
- Tidy up and close tests
- Work with limit the executives to guarantee that satisfactory assets are accessible
- Where there is conflict for assets, foster a timetable that meets the prerequisites of the partners
- Guarantee that all gatherings utilize a norm, reusable interaction structure.
- Screen and work on the presentation of the Service Transition lifecycle stage.
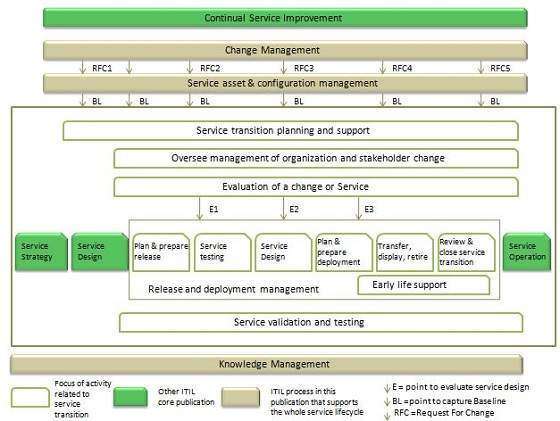
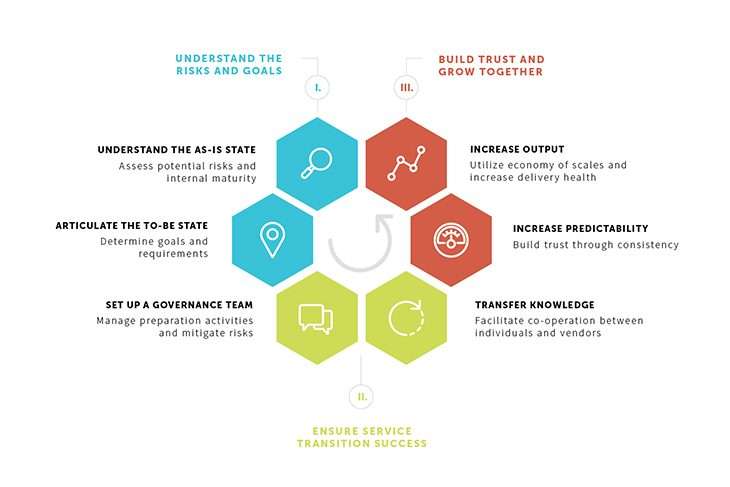
- The Service Transition processes depicted here (fig. 1) follow the particulars of ITIL V3, where Service Transition is the third stage in the Service Lifecycle.
- ITIL V4 has moved from the Service Lifecycle idea to a more all encompassing methodology that incorporates key ideas, the Four Dimensions Model and the Service Value System (SVS).
- Rather than processes, ITIL 4 portrays 34 ‘practices’, and a large number of the 26 cycles indicated in ITIL V3 can be found in ITIL 4 as practices. For instance, ITIL V4 alludes to Transition Management and Configuration Management as practices (Transition Management has been renamed to “Transition Enablement”).
- The shift from cycles to rehearses implies ITIL V4 is presently not prescriptive with regards to cycles and gives associations more opportunity to characterize tailor-made Service Transition processes.
- Since the cycles indicated in ITIL V3 have not been negated with the presentation of ITIL V4, associations that need to characterize their Service Transition cycles can in any case utilize the cycles determined in ITIL V3 as layouts.
- Unapproved Transitions
- Impromptu blackouts
- A low Transition achievement rate
- Countless crisis Transitions
- Deferred project executions
- Absence of responsibility for affected frameworks
- Mistaken setup information might bring about helpless effect appraisals
- Bypassing the concurred methodology
- Opposition against an umbrella of Transition Management authority
- The Transition Manager controls the lifecycle of all Transitions.
- Seat Transition Advisory Board (CAB) and ECAB.
- Issue Transition Schedules
- Coordinate structure, testing and execution
- Update the Transition Log
- Audit carried out Transitions
- Audit exceptional RFCs
- Distribute Management Reports
- Guarantee that resources heavily influenced by the IT association are distinguished, controlled and appropriately focused on all through their lifecycle
- Recognize control, record, report, review and check Servicess and other design things (CIs), including adaptations, baselines, constituent parts, their characteristics and connections
- Represent, oversee and secure the respectability of CIs through the help lifecycle by working with Transition the board to guarantee that main approved parts are utilized and just approved Transitions are made
- Guarantee the honesty of CIs and designs needed to control the Servicess by building up and keeping a precise and complete setup the executives framework (CMS)
- Keep up with precise setup data on the verifiable, arranged and present status of Servicess and different CIs
- Optimizing the presentation of Services resources and setups further develops the general help execution and streamlines the expenses and dangers brought about by inadequately oversaw resources, for example Services blackouts, fines, right permit expenses and bombed reviews.
- IT staff to comprehend the arrangement and connections of Servicess and the design things that give them
- Better anticipating and arranging of Transitions
- Fruitful appraisal, arranging and conveyance of Transitions and deliveries
- Goal of episodes and issues inside the help level targets
- Conveyance of Services levels and guarantees
- Progress arranging and backing
- Transition the board
- Services resource and design the executives
- Delivery and organization the executives
- Services approval and testing
- Transition assessment
- Information the board.
- Coordinate turn of events and acquirement exercises
- Foster applications and frameworks
- Acknowledge conveyance of the assistance parts
- Make or update functional documentation
- Test the help parts
- Convey the assistance parts
- Set up the help enactment
- test scripts and test reports, giving a point by point record of testing exercises
- the assistance activity manual, indicating the exercises needed for the activity of a help and its fundamental foundation.
- All of this is very direct. You can observe a total portrayal of the help progress process in this Service Management Wiki, including meanings of the sub-processes, insights concerning the cycle yields, and a RACI network.
- To construct the important connections which are needed to deal with and coordinate the few partners who are a piece of the help progress.
- To organize and focus on the different Servicess which have been presented recently or Transitiond as of late, particularly on the off chance that there have been postponements or disappointments of tests.
- Assuming the connection between the venture and program groups isn’t legitimate, it can bring about help Transition necessities that are absolutely unforeseen.
- An absence of required data from the interest and Services portfolio the board brings about receptive progress arranging and backing with deficient long haul arranging.
- In the event that there is a deferral to one progress, it will have an impact even on future advances also.
- At the point when there are clashing prerequisites, inadequate data obstructs their prioritization.
Introduction to ITIL Services Transition
ITIL Services progress helps plan and deal with the difference in condition of an assistance in its lifecycle. Overseeing hazard for new, Transitiond and resigned Servicess ensure the item climate. This assists the business with conveying worth to itself and its clients.
What is Services Transition?
ITIL Services progress helps plan and deal with the difference in condition of an assistance in its lifecycle. Overseeing hazard for new, Transitiond and resigned Servicess secure the item climate. This assists the business with conveying worth to itself and its clients.
Organizing Services information assists all partners with making educated, solid choices and backing difficulties with Services conveyance. Both overseeing Services hazard and organizing Services information are basic to support progress. During Services progress, the accompanying hierarchical components need support:
No Transition is without hazard. Transition can make additional danger. When changing Servicess, center around correspondence making arrangements for mindfulness and consistence. Perhaps the greatest test in assistance progress is changing individuals’ conduct to oblige some other help. Individuals have a mental need to have a good sense of reassurance and alright with Transitions to them and around them.
Goals of ITIL Service Transition
The essential goals of Services Transition are:
Key Principles of ITIL Service Transition
The conventional arrangements for Services progress should be plainly characterized before execution. A portion of the conventional strategies are:
1. Execution of the multitude of vital Transitions to Servicess through assistance progress.
2. Take on a typical system and set of norms for the cycles.
3. Setting up controls and teaches which are powerful.
4. To give frameworks to moving information and backing choices.
5. To design the bundle discharges.
6. Expectation and the executives of the vital course revisions.
7. Ensure that the set up cycles and frameworks are re-used to the greatest degree.
8. The help progress plans and field-tested strategies should be lined up with one another.
9. Building up and keeping up with associations with the partners in question.
10. To deal with the accessible assets across the help handles proactively.
11. Guarantee that there is inclusion almost immediately in the help life-cycle.
12. To give affirmation of the nature of the recently presented or altered help.
13. Work on the nature of the help proactively during Services Transition.
Transition assessment
ITIL Transition assessment investigates Transitions before they move to the following stage in their lifecycle. The lifecycle of a Transition incorporates a few points where a go/off limits choice should be made:
The assessment ought to include:
Services approval and testing
Testing can happen anytime in the help lifecycle however, it by and large happens during Service Transition. The help approval and testing process plans, directs and covers trial of new or Transitiond Servicess. The consequences of testing go to the Transition assessment cycle to help a choice on whether to continue.
The assistance configuration bundle (SDP) traces the tests to perform. Working with Transition assessment, Services approval and testing will:
Services approval and test will perform various kinds of tests, as called for in the help configuration bundle. Sorts of tests include:
Utility testing. Does the assistance convey the necessary usefulness?
Guarantee testing. Will the assistance convey required degrees of accessibility, limit, security, and progression?
Ease of use testing. Will the assistance be usable by all likely clients, incorporating those with confined capacities?
Agreement and guideline testing. Will the assistance adjust to material administrative and agreement necessities?
Functional availability testing. Are the help capacities, including the assistance work area, staffed and prepared to help the new or Transitiond help?
Services Transition arranging and backing
Whenever, there will be a few activities going through the assistance Transition period of the lifecycle. It is the obligation of Transition arranging and backing to facilitate Services progress exercises for this multitude of ventures. In particular, the obligations of Transition arranging and backing include:
Processes: ITIL Service Transition
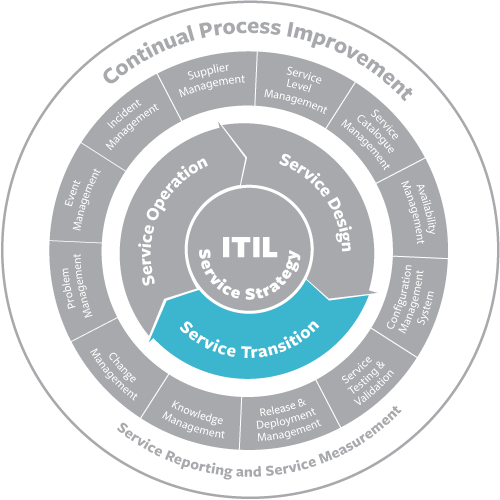
Services Transition assembles and conveys new or adjusted Servicess. The ITIL Services lifecycle phase of Service Transition (see fig. 1) incorporates the accompanying primary cycles:
Transition Management
Strategy Purpose: To manage the lifecycle of all Modifications. The basic goal of Transition Management is to empower gainful Transitions to be made, with least interruption to IT benefits.
Transition Evaluation
Process Objective: To survey significant Transitions, similar to the presentation of another assistance or a significant Transition to a current help, before those Transitions are permitted to continue to the following stage in their lifecycle.
Project Management (Transition Planning and Support)
Process Objective: To plan and facilitate the assets to send a significant Release inside the anticipated expense, time and quality assessments.
Application Development
Process Objective: To cause accessible applications and frameworks which to give the necessary usefulness to IT benefits. This cycle incorporates the turn of events and support of custom applications just as the customization of items from programming sellers.
Delivery and Deployment Management
Process Objective: To plan, timetable and control the development of deliveries to test and live conditions. The essential objective of Release Management is to guarantee that the honesty of the live climate is ensured and that the right parts are delivered.
Services Validation and Testing
Process Objective: To guarantee that sent Releases and the subsequent Servicess meet client assumptions, and to check that IT tasks can uphold the new help.
Services Asset and Configuration Management
Process Objective: To keep up with data about Configuration Items needed to convey an IT Services, including their connections.
Information Management
Process Objective: To assemble, break down, store and offer information and data inside an association. The main role of Knowledge Management is to further develop effectiveness by diminishing the need to rediscover information.
ITIL 4 Service Transition
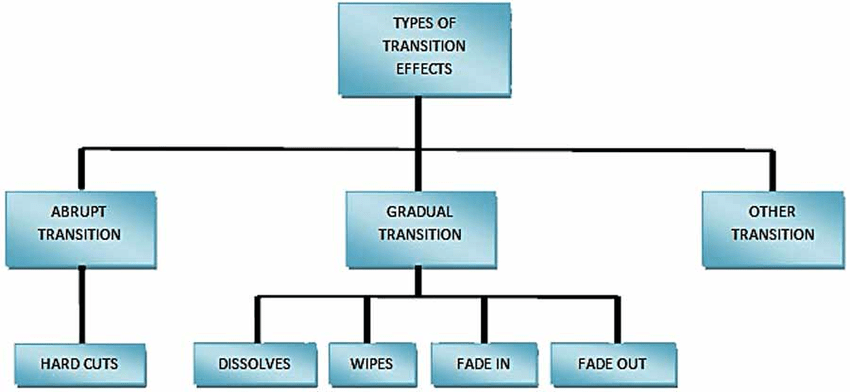
Kinds of Transitions:
1. Ordinary Transition are Transitions that should go through appraisal, approval and may require Transition Advisory Board (CAB) arrangement before execution.
2. Crisis Transition are just for exceptionally basic Transitions expected to reestablish flopped high accessibility or far and wide assistance disappointment, or that will keep such a disappointment from inescapably happening. Crisis Transitions are dealt with through ECAB (Emergency CAB).
3. Standard Transition are utilized for pre-approved tedious, generally safe, all around tried Transitions. Regularly these will be utilized for Services functional support Transitions.
Key Definitions:
Services Transition is the expansion, alteration or expulsion of whatever might affect IT Services. The Scope ought to incorporate all IT Services, Configuration Items, Processes, Documentation and so forth
Design Item (CI) is any part that should be overseen to convey an IT Service Transition Advisory Board is a body that exists to help the approval of Transitions and to help Transition Management in the appraisal and prioritization of Transitions
Key Metrics for Transition the executives are:
Key Challenges with Transition the board are:
The job of progress chief is as per the following:
Services Asset and Configuration Management
The reason for the SACM cycle is to guarantee that the resources needed to convey Servicess are appropriately controlled, and that exact and solid data concerning those resources is accessible when and where it is required. This data incorporates subtleties of how the resources have been designed and the connections between resources.
Objectives:The targets of SACM are to:
SACM gives perceivability of precise portrayals of a help, delivery or climate that empowers:
Services progress in the ITSM systems
Services progress has been an unmistakable subject in help the executives since the approach of ITIL v3, where Services Transition is one of the five assistance lifecycle stages.
The ITIL v3 center distribution about help Transition portrays Services progress as the stage that takes the results from Services plan, the first phase of the assistance lifecycle, and utilizes them to guarantee that assistance arrangements easily moved to live activity. Services progress as depicted in ITIL v3 incorporates seven cycles:
ITIL® 4 has dropped the assistance lifecycle idea for a more comprehensive methodology. ITIL v4 does never again characterize explicit cycles that associations should carry out, yet most recognizable ITIL processes from the help Transition book have tracked down their direction into ITIL 4 as “rehearses”. Accordingly, ITIL v4 alludes to Transition the executives, arrangement the board and Services approval and testing as practices (in spite of the fact that Transition the executives has been renamed to “Transition enablement”).
Other help the executives structures, like CMMI-SVC®, USMBOK™ and COBIT®, additionally incorporate cycles for managing Services Transition, in spite of the fact that with somewhat various names (in CMMI-SVC®, for example, there’s an interaction region named “SST (Service System Transition)”.
VeriSM™ presents the VeriSM model as “an assistance the executives working model for an association”. VeriSM portrays “significant level stages” for the turn of events and arrangement of items and Servicess. One of these stages, “produce”, looks like the assistance Transition stage in the ITIL Services lifecycle and is answerable for building, testing and executing items or Servicess.
Lastly, ISO 20000, the worldwide norm for Services the executives, incorporates explicit prerequisites for Services fabricate and progress.
Services progress process in YaSM
The YaSM Services the executives model deciphers the direction from the different ITSM systems into a smoothed out assistance progress process. It gets set off by the assistance configuration process once a help definition and a help execution outline have been made. Toward the finish of the help fabricate process, the assistance that is “prepared for enactment”, and that implies clients can now be welcome to consent to a help arrangement for the help and begin utilizing it. The help Transition process is comprised of the accompanying sub-processes:
For each sub-process, YaSM gives a definite layout that portrays the interaction exercises, jobs, information sources and results. Likewise, the YaSM model contains archive layouts for the critical results from the help assemble process:
Challenges in ITIL Service Transition
The Challenges in ITIL Service Transition are:
Hazards in ITIL Service Transition
The Risks in ITIL Service Transition are:
Conclusion:
ITIL Service Transition hence assists with arranging and deal with the progressions in help proficiently and adequately. By dealing with the dangers connected with recently presented, altered, or suspended Servicess helps in conveying the assistance discharges into conditions. Allow yourself an opportunity to fill in your Service Management profession with the ITIL 4 Foundation affirmation preparing, and gain valuable abilities and best practices.






