- Role of an RPA Business Analyst
- Required Skills and Qualifications
- Responsibilities in an RPA Project
- Identifying Automation Opportunities
- Process Mapping and Documentation
- Working with Developers and Stakeholders
- Tools Used by RPA Business Analysts
- Gathering Requirements for Automation
- Challenges Faced in RPA Projects
- Best Practices for RPA Analysis
- Certifications and Courses
- Career Growth as an RPA Business Analyst
Role of an RPA Business Analyst
An RPA (Robotic Process Automation) Business Analyst plays a crucial role in connecting business needs with automation solutions. They work closely with stakeholders to identify processes suitable for automation, gathering detailed requirements and ensuring smooth implementation. Unlike traditional business analysts, RPA Business Analysts need a strong understanding of process optimization, automation technologies, and supporting areas like SoftwareTesting Training which can enhance their effectiveness in testing and validating automated workflows. Their responsibilities span from evaluating process feasibility and creating process definition documents (PDDs) to collaborating with developers on the technical implementation. They also support user acceptance testing (UAT) and monitor the automation post-deployment to ensure it functions as intended, recommending improvements and scaling the solution across the organization. This end-to-end involvement, from process discovery to post-deployment support, makes them an essential part of the RPA lifecycle, ensuring that automation initiatives deliver measurable business value.
Required Skills and Qualifications
An RPA Business Analyst requires a unique blend of technical and business skills. Essential skills include strong analytical thinking, excellent communication, a deep understanding of business processes, and familiarity with RPA tools and technologies. While programming knowledge isn’t mandatory, it is highly advantageous. Additionally, the ability to model processes, manage change, and effectively engage stakeholders is crucial. Educational qualifications often include a bachelor’s degree in Business Administration, Computer Science, or related fields. Certifications in popular RPA platforms such as UiPath, Automation Anywhere, or Blue Prism are commonly preferred, and resources like a UiPath Tutorial Guide can be incredibly helpful for building hands-on expertise. This combination of skills and qualifications enables RPA Business Analysts to successfully identify, design, and implement automation solutions that drive business efficiency and innovation.
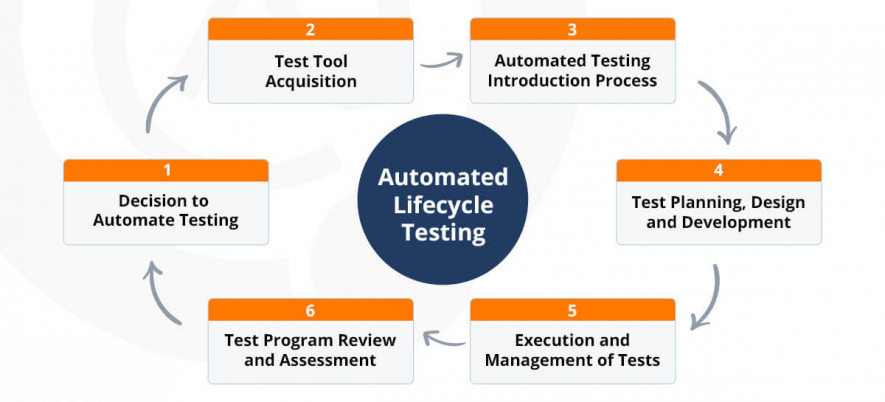
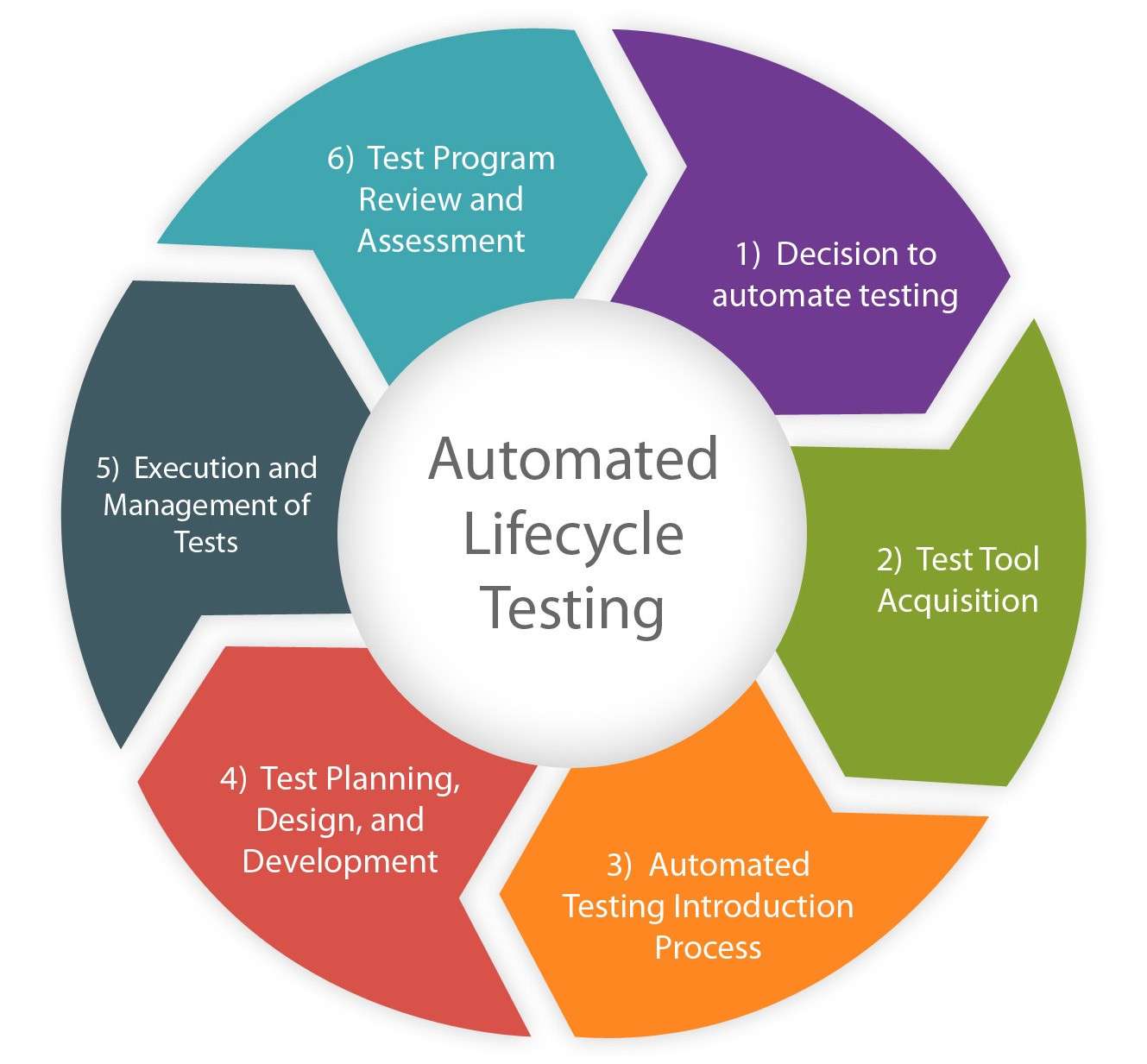
Responsibilities in an RPA Project
The responsibilities of an RPA Business Analyst span multiple stages of an RPA project, from initial assessments to post-deployment monitoring. They play a crucial role in ensuring that the automation solutions align with business objectives and deliver measurable results. Below are the key responsibilities:
- Process Assessment: Evaluate processes to determine their suitability for automation based on factors such as volume, complexity, and business impact.
- Preparation of Process Design Documents (PDDs): Document detailed process workflows and define automation requirements to guide the development phase.
- Prioritization of Processes: Rank processes based on their potential business impact and feasibility for automation.
- Collaboration with Developers: Work closely with RPA developers to ensure that the automation solution meets the business needs and technical specifications.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Validate automated solutions by testing them with end-users to ensure they function as expected and meet business requirements.
- Change Management Support: Assist in managing organizational change by supporting training, communication, and transition strategies to ensure smooth adoption of the automation.
- Post-Deployment Monitoring: Track the performance of bots after deployment, identify areas for improvement, and recommend optimizations to enhance efficiency.
- Creating As-Is Process Maps: Develop detailed diagrams that capture every step, decision point, and exception in the current process. These maps serve as the foundation for automation.
- Utilizing Visualization Tools: Use tools like Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, or process mining tools to create visual representations of workflows, helping to clarify process flows for developers.
- Providing Insight into Process Complexities: Ensure that the process maps include all necessary details to allow developers to understand the intricacies and potential challenges of the process.
- Preparing the Process Design Document (PDD): Document all the process details and automation requirements in the PDD, which serves as a guide for RPA development.
- Creating the Solution Design Document (SDD): Prepare the SDD, which outlines the technical solution, architecture, and how the automation will be implemented based on the process design.
- Process Mapping and Documentation Tools: Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, and Bizagi are commonly used to create detailed process maps, helping visualize workflows and document business processes for automation.
- Requirement Management Tools: JIRA and Confluence are essential for tracking and documenting user stories, defining acceptance criteria, and managing the overall project requirements. These tools help ensure that business needs are clearly communicated and met.
- RPA Development Tools: Familiarity with RPA development environments such as UiPath Studio, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism is beneficial for an RPA Business Analyst. Although they may not directly develop automation solutions, knowledge of these tools aids in understanding technical aspects and collaborating effectively with developers.
- Process Mining Tools: Tools like Celonis and UiPath Process Mining are valuable for identifying potential automation opportunities by analyzing existing processes and highlighting inefficiencies that can be automated.
- Project Management Tools: To track progress and coordinate tasks, RPA Business Analysts often rely on project management tools like Trello, Asana, or Microsoft Project. These platforms help organize workflows, track deadlines, and ensure that all stakeholders are aligned.
- Conduct Thorough Process Assessments and Feasibility Studies: Before initiating automation, evaluate processes carefully to determine their suitability and potential for automation.
- Early Involvement of IT and Compliance Teams: Collaborate with IT and compliance teams early to address technical challenges and regulatory concerns, ensuring smooth implementation.
- Clear and Detailed Documentation: Create clear, detailed documentation to avoid misunderstandings during development and ensure all stakeholders are aligned on the process and requirements.
- Adopt an Agile Approach: Use an agile methodology to enable iterative development, allowing for continuous feedback and adjustments throughout the RPA project.
- Engage End-Users Early: Involve end-users early in the process and prepare them for changes to minimize resistance and ensure smoother adoption of the automated solution.
By adhering to these best practices, RPA Business Analysts can help ensure that automation initiatives are well-executed, effective, and widely accepted within the organization.
These responsibilities ensure that RPA projects are executed effectively, aligning with business goals and driving continuous improvement.
Identifying Automation Opportunities
Identifying the right processes for automation is a key responsibility of an RPA Business Analyst. This process begins with conducting workshops with business teams to thoroughly understand end-to-end workflows and identify opportunities for automation. Analysts evaluate processes based on criteria like volume, complexity, stability, and potential return on investment (ROI). Ideal candidates for automation are processes that are repetitive, rule-based, and involve structured data. Knowledge of tools and concepts like SoftwareTesting Training can further enhance an analyst’s ability to validate process stability and ensure automation readiness. By analyzing these factors, the RPA Business Analyst creates a prioritized pipeline of automation opportunities. They use various assessment tools and methodologies to ensure that the automation program aligns with business goals and delivers measurable benefits. This careful selection process is critical in making sure that RPA initiatives provide tangible value to the organization while optimizing efficiency.
Boost your confidence for interviews by reading this Automation Testing Interview Questions and Answers
Process Mapping and Documentation
Accurate process mapping and documentation are essential for successful RPA implementation. RPA Business Analysts play a vital role in creating clear, detailed process maps that guide the development of automation solutions. Below are the key responsibilities related to process mapping and documentation:
These tasks ensure that the RPA implementation is well-documented, which is crucial for creating efficient and accurate automation solutions.
Want to lead in Automation Testing? Enroll in ACTE’s Automation Testing Master Program Training Course and start your journey today!
Working with Developers and Stakeholders
Effective collaboration between technical teams and business stakeholders is crucial for an RPA Business Analyst. They serve as the intermediary, ensuring that the automation solutions developed align closely with the business needs. Acting as the voice of the business for developers, RPA Business Analysts provide clear guidance on the expectations, requirements, and priorities from a business perspective. They also facilitate communication between various stakeholders, including project managers, IT teams, compliance officers, and end-users, ensuring that everyone remains aligned throughout the RPA project lifecycle.
Their strategy for interaction typically involves regular meetings with stakeholders to ensure ongoing engagement and validation of requirements. These sessions help confirm that the automation goals are clearly understood and that any changes or updates are quickly communicated. Additionally, RPA Business Analysts conduct demonstrations of automation progress to showcase how solutions are evolving and to gather feedback from users early on. This collaborative approach ensures transparency, promotes continuous feedback, and helps to identify potential risks or misunderstandings early, reducing the likelihood of project delays or misaligned expectations. For those looking to expand their understanding of How to Get Started as an RPA Developer can provide valuable insight into the technical aspects of solution building and the necessary skills. By maintaining open channels of communication, the RPA Business Analyst ensures that the automation solutions effectively meet the business requirements, while also fostering a smooth development and deployment process. Their role in facilitating these interactions and managing stakeholder expectations is vital in keeping the project on track and ensuring that the automation delivers measurable value.
Tools Used by RPA Business Analysts
RPA Business Analysts leverage a wide range of tools to carry out their responsibilities efficiently and ensure successful project delivery. Below are the key tools they typically use:
These tools enable RPA Business Analysts to manage the various stages of the RPA project lifecycle, ensuring that automation initiatives are successfully planned, executed, and monitored.
Gathering Requirements for Automation
Requirement gathering is a meticulous process that lays the foundation for successful RPA deployment. RPA Business Analysts conduct interviews, workshops, and observation sessions to collect detailed information about the current state of processes. They must identify inputs, outputs, business rules, exceptions, and hand-offs involved in a process. Creating detailed user stories, defining clear acceptance criteria, and validating requirements with stakeholders are essential steps. As automation technologies evolve, understanding emerging concepts about the fundamentals of What is Hyper Automation Tech becomes crucial for RPA professionals. Thorough documentation ensures developers clearly understand what needs to be automated and helps avoid costly rework.
Challenges Faced in RPA Projects
RPA projects are not without their challenges. One major challenge is identifying processes that are genuinely suitable for automation. Poorly selected processes can result in low ROI or failed automations. Another common challenge is resistance to change from employees, who may fear job loss due to automation. RPA Business Analysts must also deal with incomplete or inconsistent process documentation, frequent changes in business processes, and technical limitations of RPA tools. Addressing these challenges requires strong stakeholder engagement, robust change management strategies, and continuous communication.
Best Practices for RPA Analysis
To ensure the success of RPA initiatives, RPA Business Analysts should follow best practices throughout the project lifecycle. Below are the key practices to ensure effective implementation:
Certifications and Courses
Several certifications and courses can help aspiring RPA Business Analysts build credibility and expertise. Certifications from leading RPA vendors like UiPath (UiPath RPA Business Analyst Training), Automation Anywhere (Certified Advanced RPA Professional), and Blue Prism (Blue Prism Business Analyst Certification) are highly recognized. Additional certifications in Business Analysis (such as CBAP, CCBA from IIBA) and Process Improvement (such as Lean Six Sigma) can also enhance an analyst’s skill set. For those interested in expanding their knowledge about the development side of automation, resources like Primary Roles and Responsibilities of RPA Developers can provide valuable insights. Online platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and edX offer specialized RPA Business Analyst courses for beginners and experienced professionals.
Career Growth as an RPA Business Analyst
The career prospects for RPA Business Analysts are rapidly expanding as organizations increasingly adopt automation to enhance efficiency and reduce costs, driving a rising demand for skilled professionals. Career growth can lead to various roles such as RPA Consultant, where they offer expert guidance, RPA Solution Architect, responsible for designing end-to-end automation solutions, RPA Project Manager, overseeing project delivery, or Automation Center of Excellence (CoE) Lead, driving RPA best practices within the organization. Additionally, experience in RPA especially when complemented by SoftwareTesting Training which strengthens testing and validation expertise can open doors to broader digital transformation roles, including those focused on intelligent automation technologies like AI, machine learning, and cognitive automation. As the field evolves, RPA Business Analysts who continually update their knowledge and adapt to new technologies will be well-positioned for long-term career success. With automation becoming a core part of business operations, RPA professionals have significant opportunities for advancement and career development in this dynamic industry.



