
SAS Data Integration (SAS DI) is a powerful ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tool within the SAS software suite. It offers a user-friendly, graphical interface for designing data integration processes without the need for extensive coding. Central to SAS DI is its emphasis on metadata management, facilitating a centralized repository for information about data structures. Users can create reusable job templates and transformations, ensuring consistency and efficiency in handling data integration tasks. The platform supports connectivity to diverse data sources, including databases and flat files, and provides features for data quality assessment and validation. SAS DI allows for scheduling and automating ETL jobs, reducing manual intervention. It seamlessly integrates with other SAS components, enabling advanced analytics on integrated data.
1. What is Data Integration?
Ans:
The process of combining a data from different resources. The combined data is provided to users with unified view. Information from the different enterprise domains are integrated – known as a Enterprise Information Integration. Useful for the merging information from a different technologies among enterprises.
2. What is SAS DI External File Reader transformation?
Ans:
The External File Reader transformation in SAS DI is used to read data from the external files, such as flat files, Excel files, or delimited files. It allows the users to bring external data into the SAS DI for a further processing and analysis.
3. What is change analysis in SAS DI?
Ans:
Change analysis is a process of comparing the one set of metadata to the another set of metadata and identifying the differences between a two sets of metadata.
4. What distinguishes a primary key from a unique key?
Ans:
| Criteria | Primary Key | Unique Key | |
| Purpose |
Identifies each record uniquely in a table. |
Ensures that each value in a column is unique. | |
| Null Values | Does not allow NULL values. | Allows one NULL value per column. | |
| Number of Keys | Only one primary key per table. | Multiple unique keys per table are allowed. | |
| Indexing | Automatically creates a clustered index. | Automatically creates a non-clustered index. |
5. Explain about Pivot – Columns to Rows?
Ans:
Pivoting from columns to rows, commonly known as a ‘Pivot’ operation, is a data transformation technique used to reorganize a dataset by converting values in columns into rows. In this process, unique values in a specific column become new rows, with each original column corresponding to a distinct attribute or category. This transformation is valuable when dealing with datasets structured in a wide format, where information is spread across columns.
6. What are benefits of data integration?
Ans:
- Makes reporting, monitoring, placing the customer information across enterprise flexible and convenient.
- Data usage is efficient.
- Cost Effective.
- Risk adjusted profitability management as it allows the accurate data extraction.
- Allows timely and reliable reporting.
7. Describe how adjust performance of Data Integrator.
Ans:
To enhance the performance of a Data Integrator, several strategies can be employed. Firstly, optimizing the underlying hardware and infrastructure can significantly impact performance. Additionally, tuning the database settings and configurations, such as indexing and partitioning, can improve data retrieval and processing speeds. Efficient job design, involving the use of parallel processing and optimizing transformations, is crucial. Caching frequently accessed data, employing incremental loading techniques, and minimizing data movement between systems also contribute to better performance.
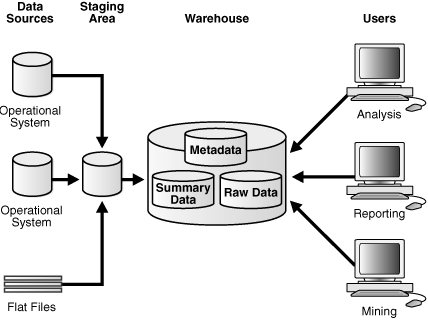
8. What is mean by data staging area?
Ans:
Staging area of data warehouse is both the storage area and set of a process commonly referred as extract transformation load. The data staging area is everything between operational source systems and data presentation area.
9. What is data governance?
Ans:
It is robust, reliable, repeatable and controlled process both at a point of input and through the subsequent downstream control checks. This process exists to manage updates of a business rules to maintain level of consistency.
10. What is data access?
Ans:
Data access refers to ability to read and write data from and to the various sources and destinations within data integration process. SAS DI provides the set of capabilities and transformations that enable the users to access, manipulate, and transform data across the different data storage systems
11. What is slowly changing dimension?
Ans:
This is a technique for tracking changes to dimensional table values in order to analyze the trends. For example, the columns for a customer’s ID, home address, as well as income may be present in a dimension table called customers. Each time address or income changes for customer, a new row could be created for that a customer in dimensional table and old row could be retained.
12. What is snow flake schema?
Ans:
Snow flake schema is defined in which single fact table is connected to the multiple dimension tables. The dimension are structured to be minimize update anomalies and to address a single themes.
- CREATE TABLE Sales (SalesID INT PRIMARY KEY, ProductID
- INT, CustomerID INT, SaleDate DATE, Quantity INT, Amount DECIMAL(10, 2));
- CREATE TABLE Products (ProductID INT PRIMARY KEY, ProductName VARCHAR(255), CategoryID INT);
- CREATE TABLE Categories (CategoryID INT PRIMARY KEY, CategoryName VARCHAR(255));
- CREATE TABLE Customers (CustomerID INT PRIMARY KEY, CustomerName VARCHAR(255), City VARCHAR(255), Country VARCHAR(255));
13. What is star schema?
Ans:
A Star schema is defined as a database in which single fact table is connected to the multiple dimension tables. This is called a star schema.
14. What does SAS application server, database server, SAS OLAP server and SAS metadata server?
Ans:
SAS application server provides the SAS services to a client. On other hand database server provides a relational database service to a client. Oracle, DB2, and Teradata are examples of a relational databases. SAS OLAP server provides the access to multidimensional data. SAS metadata server provides a metadata management services to a one or more client application.
15. What is operational data and operational system?
Ans:
Operational data is used as a source data for data warehouse. An operational system is one or more programs that provide a source data for a data warehouse.
16. What is use of SAS management console?
Ans:
The SAS Management Console is the centralized administrative application that provides unified interface for managing and configuring SAS environments. It serves as control center for administering various components of SAS platform. The SAS Management Console is the key tool for SAS administrators, enabling them to perform wide range of tasks related to configuration, monitoring, and maintenance of SAS environments
17. Name some data transformation used in SAS DI.
Ans:
Data transformations can take various forms, such as appending, applying lookup standardisation, creating a match code transformation, data transfer, data validation, extracting, lookup in fact tables, important data transformations, lookup, SAS rank, Sort, SCD type 2 loader, SQL join, and standardising a transformation. Create a surrogate key generator, translate a transformation, and change user-written code.
18. Describe about metadata object.
Ans:
Metadata objects in context of SAS (Statistical Analysis System) refer to structured information about data, processes, and resources stored in a metadata repository. Metadata is essential for the managing, organizing, and understanding a components and relationships within a SAS environment. Each metadata object represents specific entity or aspect of SAS system
19. Name scheduler for scheduling job and explain the scheduler.
Ans:
CONTROL_m is the scheduler used to schedule jobs. It also allows the user to view process flow and dependencies, facilitating easy and efficient business process optimization, even in data centers with multiple platform types (e.g., Unix, Microsoft Windows, and MVS).
20. What is change analysis in SAS DI?
Ans:
The process of matching one set of metadata to another and determining the differences between the two sets of metadata is called change analysis.
21. Describe the interaction table in SAS DI.
Ans:
Table that explains the connections between two or more tables. An intersection table, for instance, could explain the many-to-many connections between a group table and a user table.
22. What are prime responsibilities of Data Integration Administrator?
Ans:
The prime responsibilities of a Data Integration Administrator include managing and maintaining data integration tools, overseeing the deployment and execution of ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, ensuring data quality and integrity, monitoring system performance, troubleshooting issues, implementing security measures, collaborating with data stakeholders, and staying updated on industry best practices.
23. Explain the difference between retained key and surrogate key.
Ans:
Generated keys are employed in the implementation of retained keys and surrogate keys, as well as in one or more columns that serve as a unique row identification in a table. There can only be one primary key per table.
A surrogate key is a column that holds distinct integer values that are produced in a sequential manner upon the addition and modification of rows.
24. Explain about Data Integrator Metadata Reports.
Ans:
Data Integrator metadata reports provide detailed insights into the metadata associated with ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes. These reports offer a comprehensive view of the data integration environment, including information about data sources, transformations, target systems, job execution details, and dependencies. Metadata reports aid administrators and developers in understanding the data lineage, impact analysis, and the overall health of the ETL processes.
25. Explain various caches available in Data Integrator.
Ans:
SAP Data Integrator provides different types of caches to enhance performance. The Lookup Cache is utilized to store and retrieve data during lookup operations, minimizing the need to access the database repeatedly. The Data Cache is employed for temporary storage of data during transformation processes, optimizing performance by reducing redundant data retrievals. Global Cache allows sharing data across multiple data flows within a job.
26. What is Hierarchy Flattening?
Ans:
Hierarchy flattening is the process of building a hierarchy of parent-child relationships. A description of hierarchy in vertical or horizontal format is produced. The hierarchy pattern includes the Parent column, Child Column, Parent Attributes and Child Attributes. Hierarchy Flattening allows to understand a basic hierarchy of BI in a lucid manner.
27. Is Data integration And ETL programming is same?
Ans:
No, Data Integration and ETL programming are the different. Passing of data to the different systems from other systems is known as a data integration. It may integrate data within same application. On the other hand, ETL involves removing data from various sources. Transforming data and transferring it into other objects or tables is the main task of an ETL tool.
28. Describe about Physical Data Integration?
Ans:
Physical Data Integration is all about creating a new system that replicates data from source systems. This process is done to manage data independent of the original system. Data Warehouse is example of Physical Data Integration. Data version management and the combining of data from multiple sources, such as mainframes, flat files, and databases, are two advantages of PDI.
29. Why is SAS Data Integration Studio important?
Ans:
Companies are beginning to understand that they must have an integrated view of their data in order to succeed, and SAS Data Integration Studio is a single tool that offers the adaptability, dependability, and agility required to meet evolving data integration challenges. Users of SAS Data Integration Studio can react quickly and effectively on any project, which lowers the overall cost of data integration.
30. For whom is SAS Data Integration Studio designed?
Ans:
The SAS Data Integration Studio enables data integration managers and designers to produce high-quality results more quickly, manage change more skillfully, and work more productively.
31. Explain Data Dimension.
Ans:
Data Dimension in SAS DI is defined as a data in between the customers, products, and organization that can be accessed with governance of data. Generally, we need to acquire best support of all the business data views with the great self-service reporting.
32. Explain Data Access.
Ans:
For the purpose of handling massive data loads, the approval chosen by specific business users is known as Data Access in SAS Data Integration.
33. Define Data Governance.
Ans:
Data Governance in Data Integration is a repeatable, affordable, and robust process, which downstream all down checks. This procedure will be able to handle all updates necessary to keep the data consistent.
34. Explain multi-dimensional reporting.
Ans:
The DI’s multidimensional reporting feature enables users to perform an aggregate analysis of business metrics spanning numerous business dimensions.
35. What do dimension tables in DI mean?
Ans:
In SAS Data Integration, the dimension table is defined as an integral component for the fact table because it contains more textual explanations about the business. These dimension tables in DI is a well-designed model that may contain the more attributes and columns, as will describe the dimension of row table and serves as a main source of reporting labels.
36. What is meant by SAS metadata server, SAS application server?
Ans:
In data integration, the SAS metadata server will be able to offer all metadata management services based on the requests made by a client application. Whereas the SAS application will hassle-free and directly offer the customers enormous services.
37. Describe the importance of SAS Management Console.
Ans:
In Data Integration, the primary purpose of the SAS Management Console is to offer an excellent user interface for carrying out all of the tasks carried out by the SAS administration.
38. Describe the SAS DI’s benefits and drawbacks.
Ans:
The time required to develop an SAS data integration is decreased by enabling the quick creation of data streams, data marts, and warehouses. Occasionally, the SAS DI may experience performance problems and produce extremely complex, difficult-to-decode code.
39. What is mean by fact table in dw?
Ans:
A fact table shows the subject matter and analysis’s main focus. Typically, it includes analysis components like quantity sold, cost, and sales. The specific aspects can be understood by averaging or summarising these attributes. In order to analyse the fact measures from various scenarios, the fact table can also be summarised as a union of the dimension tables.
40. What is data reconciliation?
Ans:
It Is correction of the data inconsistency If data is loaded incorrectly from a source system and if there is inconsistency between the source system and loaded data then source system is a treated authoritative.
41. What is History Preserving?
Ans:
History Preserving is for providing a new row in the target instead of updating existing row. The columns are indicated for a transforming the changes that are to be preserved. New rows are created when value of certain column changes. Each of these rows is flagged as a UPDATE. The UPDATE flag is applied for input data set.
42. Describe deployment of SAS Data Integration studio jobs as a SAS stored process.
Ans:
To deploy SAS Data Integration Studio jobs as SAS stored processes, create and test ETL jobs in the Studio, then use the “Deploy as Stored Process” option. This converts the job into a reusable stored process, accessible through the SAS Stored Process Server for consistent execution across SAS applications.
43. What is Uniform Data Access Integration?
Ans:
Uniform Data Access Integration is a systematic approach that establishes a standardized method for integrating and accessing data from diverse sources. It ensures a consistent interface for applications to interact with various data repositories, fostering interoperability and simplifying the overall integration process across different systems and formats.
44. Difference between Data integration And ETL programming.
Ans:
Passing of data to different systems from the other systems is known as data integration. It may integrate a data within the same application. ETL, on other hand, is to extract the data from a different sources. The main function of an ETL tool is to transform data before loading it into other objects or tables.
45. Explain about Manual Integration and Application Based Integration.
Ans:
Manual integration involves human intervention to transfer or synchronize data between different applications or systems. This often requires manual data entry, file transfers, or other manual processes to ensure data consistency. Application-based integration leverages predefined interfaces and communication protocols to enable smooth data flow and synchronization between connected systems, enhancing overall system interoperability and workflow automation.
46. What are main components of SAS DI Studio?
Ans:
The main components of SAS Data Integration Studio are used in the design, implementation, and management of Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) processes. The metadata repository, which houses data and process information, the DI Studio client, which offers a graphical job design interface, job flows, which show the order and dependencies of job executions, transformations like Extract, Transform, and Load transformations, and the capacity to deploy jobs as SAS stored processes for more extensive integration throughout the SAS ecosystem are the main components.
47. Explain purpose of a SAS DI job flow.
Ans:
A job flow in SAS DI represents a sequence of steps in a data integration process. It defines order in which transformations and tasks are executed. The job flow is created in Diagram Workspace and represents overall structure of the ETL job.
48. What is difference between a transformation and table in SAS DI.
Ans:
A transformation in SAS DI represents the data processing operation, such as filtering, sorting, or aggregating data. A table, on other hand, is a result set or a physical data table. Transformations are used to manipulate and transform a data, while tables store results of these transformations.
49. How can handle errors in SAS DI Studio?
Ans:
SAS DI Studio provides the error handling through use of various options, such as conditional processing, alerts, and log inspection. Transformations can be configured to handle the errors by directing the flow based on success or failure of preceding steps.
50. Explain SAS DI Repository.
Ans:
The SAS DI Repository is the centralized storage location for metadata in SAS DI Studio. It stores an information about jobs, tables, transformations, libraries, and other objects. The repository allows for a version control, sharing of metadata, and managing dependencies between the different components.
51. What are different types of transformations available in SAS DI Studio?
Ans:
SAS Data Integration Studio provides a variety of transformations for manipulating and processing data within ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) jobs. Common transformations include Extract, which retrieves data from source systems; Filter, which selects specific rows based on conditions; Sort, arranging data in a specified order; and Aggregate, summarizing data. Other transformations include Lookup for merging data, Data Validation for quality checks, and Data Transpose for restructuring data.
52. How do parameterize a job in SAS DI Studio.
Ans:
Parameters in SAS DI Studio allow for a dynamic values to be passed to job components. Parameters can be defined at a various levels, including job level, job flow level, or even at transformation level. They can be used to make a jobs more flexible and reusable.
53. Explain concept of change management in SAS DI Studio.
Ans:
Change management in SAS DI Studio involves the tracking and managing changes to a metadata objects. This includes versioning, comparing versions, and promoting objects between the development, test, and production environments. It ensures a controlled and audited development processes.
54. What is purpose of SAS DI Transformation Generator?
Ans:
The Transformation Generator in SAS DI Studio is used to create a custom transformations by writing the custom SAS code. It allows the users to extend the capabilities of SAS DI Studio by incorporating a specialized data processing logic.
55. How does SAS DI support loading of large datasets efficiently?
Ans:
SAS DI Studio supports the efficient loading of large datasets through techniques like a parallel processing, bulk loading, and data partitioning. Parallel processing allows distribution of work across the multiple nodes, while bulk loading techniques optimize loading of data into tables.
56. Explain concept of Change Data Capture (CDC) in SAS DI.
Ans:
Change Data Capture in SAS DI involves the identifying and capturing changes made to source data since a last extraction. It allows for the incremental loading of only changed data, reducing the processing time and resources needed for a data integration jobs.
57. What is SAS DI Prompt, and how is it used?
Ans:
A SAS DI Prompt is a user-defined variable that allows the users to enter values at runtime. Prompts can be used in the SAS DI Studio to make jobs more flexible and interactive, enabling the users to provide an input values when executing a job.
58. How can perform data validation in SAS DI Studio?
Ans:
Data validation in SAS DI Studio can be performed using the various techniques, including use of data audit transformations, table comparison transformations, and validation rules feature. These methods help ensure a data integrity and accuracy during ETL process.
59. What is purpose of SAS DI External File Writer transformation?
Ans:
The External File Writer transformation in SAS DI is used to write a data to external files, such as flat files, XML files, or delimited files. It allows the users to export data from a SAS DI Studio to external systems or formats.
60. Explain concept of parallel processing in SAS DI Studio.
Ans:
Parallel processing in SAS DI Studio involves simultaneous execution of the multiple tasks or steps to improve performance. It is achieved by a distributing data and processing tasks across the multiple nodes or resources, making ETL process more scalable and efficient.
61. What is significance of SAS DI Log Manager?
Ans:
The SAS DI Log Manager is used to view and manage logs generated by a SAS DI jobs. It provides details about the job execution, errors, and warnings. Log Manager helps in the troubleshooting, auditing, and monitoring performance of data integration processes.
62. What is purpose of SAS DI Loop transformations?
Ans:
SAS DI Loop transformations allow for iteration over a set of values or a conditions within a job. They enable repetitive execution of the specific set of tasks, providing flexibility in handling scenarios where the process needs to be repeated.
63. Explain SAS DI Data Validation transformation.
Ans:
The Data Validation transformation in SAS DI is used to compare a data from different tables or sources to identify the discrepancies. It checks for data integrity and ensures that data being processed meets a specified validation criteria.
64. What is SAS DI Surrogate Key Generator transformation?
Ans:
The Surrogate Key Generator transformation in the SAS DI is used to generate a surrogate keys for dimension tables. Surrogate keys are the artificial keys assigned to rows in a table to provide unique identifier, often used in the data warehousing scenarios.
65. How does SAS DI Studio support creation and maintenance of reference tables?
Ans:
SAS DI Studio supports creation and maintenance of reference tables through the transformations like the Surrogate Key Generator and Slowly Changing Dimension (SCD) transformation. These transformations help manage keys and changes in the dimension tables over time.
66. Explain SAS DI Data Masking transformation.
Ans:
The Data Masking transformation in SAS DI is used to replace the sensitive data with masked or anonymized values. It is commonly used in the scenarios where privacy and security considerations require protection of personally identifiable information (PII).
67. Explain the role of the SAS DI User Written Code transformation.
Ans:
The User Written Code transformation in the SAS DI allows users to include the custom SAS code within a DI job. It provides the flexibility for incorporating specialized logic or functionality that is not available through the standard SAS DI transformations.
68. What is SAS DI Hadoop Data Integration transformation?
Ans:
The Hadoop Data Integration transformation in the SAS DI Studio facilitates the integration of data between the SAS and Hadoop environments. It allows users to read a data from and write data to Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and execute a HiveQL statements.
69. How does SAS DI handle metadata propagation in a job?
Ans:
SAS DI propagates a metadata automatically. When a transformation or table is added to the job, its metadata is automatically registered in repository. If changes are made to metadata, they are automatically reflected in all the job instances using that metadata.
70. Explain SAS DI Case Converter transformation.
Ans:
The Case Converter transformation in SAS DI is used to change case of character strings. It allows for converting a strings to uppercase, lowercase, or mixed case based on a specified rules.
71. What are options available for deploying SAS DI jobs to different environments?
Ans:
SAS DI jobs can be deployed to the different environments using export/import functionality, which allows for a moving jobs between repositories. Additionally, jobs can be deployed to the different SAS servers, and scheduling can be managed using SAS job scheduler.
72. How can perform data profiling in SAS DI Studio?
Ans:
SAS DI Studio provides a data profiling transformations, such as Summary Statistics transformation, which can be used to be analyze and profile data. These transformations help in understanding a data characteristics, distributions, and identifying the potential data quality issues.
73. Explain SAS DI Data Encryption transformation.
Ans:
The Data Encryption transformation in the SAS DI is used to encrypt sensitive data, ensuring confidentiality and security of information. It is commonly used in scenarios where data needs to be protected during the transmission or storage.
74. How does SAS DI Studio handle version control for jobs?
Ans:
SAS DI Studio supports the version control through the use of SAS Source Management System (SMS). Users can check out and check in the jobs, allowing for collaboration, tracking changes, and managing versions of a DI jobs.
75. What is SAS DI Impact Analysis feature, and how is it useful?
Ans:
The Impact Analysis feature in SAS DI Studio allows the users to assess the impact of changes to a metadata objects. It helps in understanding how modifications to the tables, columns, or transformations may affect the other components within a DI job or across jobs.
76. Explain SAS DI Data Validation and Quality Library.
Ans:
The Data Validation and Quality Library in SAS DI provides the set of pre-built transformations and rules for a data quality and validation. It includes transformations for a checking data completeness, consistency, and conformity to the predefined rules.
77. Explain SAS DI Change Tracking transformation.
Ans:
The Change Tracking transformation in SAS DI is used to identify and capture changes made to source data. It can be configured to track changes at the row or column level and is often used in scenarios where auditing and change history are important.
78. How does SAS DI handle data lineage and impact analysis?
Ans:
SAS DI Studio maintains a metadata that includes the data lineage information. The metadata repository records the relationships between tables, transformations, and other objects. The Impact Analysis feature uses this metadata to assess impact of changes on a dependent objects.
79. What is SAS DI Summary Table Loader transformation.
Ans:
The Summary Table Loader transformation in the SAS DI is used to create and load summary tables. It enables summarization of data at different levels of granularity and is commonly used to improve the query performance in a data warehousing scenarios.
80. Explain SAS DI External Database Loader transformation.
Ans:
The External Database Loader transformation in the SAS DI is used to load data directly from external database into the target table in SAS. It streamlines the process of importing a data from external sources without need for intermediate staging tables.
81. What is SAS DI Case Statement transformation?
Ans:
The Case Statement transformation in SAS DI is used to create a conditional logic based on the specified conditions. It allows the users to define rules and criteria to evaluate and make decisions, enabling the dynamic transformations within a job.
82. Explain SAS DI Copy Files transformation.
Ans:
The Copy Files transformation in SAS DI is used to copy the files froma one location to another. It facilitates the file management within data integration processes, allowing the users to move or duplicate files as part of ETL workflow.
83. How does SAS DI Studio support integration with cloud-based storage systems?
Ans:
SAS DI Studio can integrate with the cloud-based storage systems using an appropriate libraries or connectors. For example, SAS provides the libraries and connectors for integrating with the cloud storage platforms like an Amazon S3 or Microsoft Azure Blob Storage.
84. Explain SAS DI Data Set Comparison transformation.
Ans:
The Data Set Comparison transformation in the SAS DI is used to compare a two datasets and identify differences. It can be configured to be detect additions, deletions, or changes in the data records between compared datasets.
85. How can parameterize SAS DI job properties?
Ans:
SAS DI job properties can be parameterized by defining and using the parameters at different levels, like job level, job flow level, or transformation level. Parameters allow the users to make jobs more flexible by providing a dynamic values at runtime.
86. What is SAS DI LDAP transformation?
Ans:
The LDAP transformation in the SAS DI is used to integrate with the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) servers. It allows the users to retrieve information from and update data in the LDAP directories, commonly used for a managing user authentication and authorization.
87. Explain SAS DI Date and Time Generation transformation.
Ans:
The Date and Time Generation transformation in the SAS DI is used to generate date and time values based on the specified rules. It is useful for creating a date-related dimensions or for generating a test data with the specific date and time characteristics.
88. How can implement version control for SAS DI jobs using external tools?
Ans:
Version control for SAS DI jobs can be implemented using the external tools such as Git or SVN. Users can export the SAS DI job files, store them in the version-controlled repository, and manage changes, branches, and releases using the standard version control practices.
89. What is SAS DI Random Sample transformation?
Ans:
The Random Sample transformation in SAS DI is used to create the random subset of data from the larger dataset. It is useful for scenarios where a representative sample is needed for a testing, analysis, or quality assurance.
90. Explain SAS DI Export Data transformation?
Ans:
The Export Data transformation in SAS DI is used to the export SAS datasets to external file formats, like CSV, Excel, or delimited files. It facilitates the exchange of a data between the SAS and other systems.






