
These Angular 7 Interview Questions have been designed specially to get you acquainted with the nature of questions you may encounter during your interview for the subject of Angular 7 . As per my experience good interviewers hardly plan to ask any particular question during your interview, normally questions start with some basic concept of the subject and later they continue based on further discussion and what you answer.we are going to cover top 100 Angular 7 Interview questions along with their detailed answers. We will be covering Angular 7 scenario based interview questions, Angular 7 interview questions for freshers as well as Angular 7 interview questions and answers for experienced.
1. What is Angular and how does it differ from AngularJS?
Ans:
Angular is a front-end web application framework developed by Google. Unlike AngularJS, which is based on JavaScript, Angular is built using TypeScript, offering better modularity, scalability, and maintainability. TypeScript, a superset of JavaScript, provides static typing, making Angular code more robust.
2. Explain Angular Modules and their significance in an application.
Ans:
Angular Modules are containers for organizing application code into cohesive blocks. They group related components, directives, services, and pipes, facilitating modularity. Modules help manage the application’s complexity, allowing for efficient development, testing, and maintenance. They also enable lazy loading, enhancing performance by loading modules on demand.
3. Differentiate between ngIf and ngSwitch directives in Angular.
Ans:
The ngIf directive conditionally renders HTML elements based on a given expression’s truthiness. On the other hand, ngSwitch evaluates multiple conditions and renders content based on the first true condition, providing a cleaner alternative to nested ngIf statements.
4. Elaborate on Angular Services and their role in the framework.
Ans:
Angular Services are reusable, injectable components that encapsulate logic unrelated to views. They facilitate code sharing and maintain a single instance throughout the application. Services handle tasks such as data retrieval, sharing data between components, and managing application state, promoting a modular and scalable architecture.
5. What is Angular CLI, and how does it simplify project development?
Ans:
Angular CLI (Command Line Interface) is a powerful tool for initializing, developing, and maintaining Angular applications. It automates repetitive tasks, such as project setup, code generation, testing, and deployment. By enforcing best practices and providing a consistent development environment, Angular CLI significantly streamlines the development process.
6. Describe Angular Dependency Injection and its advantages.
Ans:
Angular Dependency Injection is a design pattern that enhances component modularity and testability. It allows components to request dependencies from a higher-level injector, promoting loose coupling. This approach simplifies unit testing, as dependencies can be easily mocked or replaced. Dependency Injection also facilitates code maintenance by making it easier to update or swap out implementations.
7. What is the purpose of the Angular Router, and how does it handle navigation?
Ans:
Angular Router is responsible for managing navigation in Angular applications. It enables developers to define navigation paths and associate them with specific components. The router interprets the browser’s URL and navigates to the corresponding component, allowing for a seamless, SPA (Single Page Application) experience. It also supports lazy loading, optimizing application loading times.
8. Explain the concept of Angular Forms and their types.
Ans:
Angular Forms are a crucial part of building interactive user interfaces. Template-driven forms rely on directives in the template, while Reactive forms use a form model implemented in the component. Template-driven forms are suitable for simpler scenarios, while Reactive forms offer more control, flexibility, and scalability, making them ideal for complex applications.
9. Discuss Angular Lifecycle Hooks and their significance.
Ans:
Angular Lifecycle Hooks are methods that allow developers to execute code at specific points in a component’s life cycle. These hooks, such as ngOnInit and ngOnDestroy, provide opportunities to perform actions like initialization, cleanup, and responding to changes. Understanding and utilizing lifecycle hooks enhance control over component behavior and improve application performance.
10. What are Angular Pipes, and how do they transform data in templates?
Ans:
Angular Pipes are built-in functions that transform data for display in the template. They offer a convenient way to format, filter, and manipulate data before rendering. Pipes can be customized or extended to meet specific requirements, providing a reusable mechanism for data transformation and enhancing the presentation layer of an Angular application.
11. Elaborate on Angular Change Detection and its optimization strategies.
Ans:
Angular Change Detection is a mechanism that tracks changes in the application state and updates the view accordingly. Optimizing change detection is crucial for performance. Strategies like OnPush change detection and Immutable.js help reduce unnecessary checks, improving application responsiveness by updating the view only when needed.
12. Discuss the concept of Angular Guards and their role in route protection.
Ans:
Angular Guards are used to protect routes by controlling access based on certain conditions. Route Guards include CanActivate, CanDeactivate, CanLoad, and CanActivateChild, allowing developers to implement logic for route access, deactivation, lazy loading, and child route activation. By using guards, developers can enforce authentication, authorization, and other security measures in Angular applications.
13. What is Angular HttpClient, and how does it handle HTTP requests?
Ans:
Angular HttpClient is a powerful module for making HTTP requests in Angular applications. It simplifies the process of sending and receiving data from a server, providing features like request/response transformation, error handling, and interceptors. HttpClient promotes a clean and concise syntax for working with HTTP, enhancing code readability and maintainability.
14. Explain Angular Testing and the different testing strategies available.
Ans:
Angular Testing involves verifying the correctness of application code through unit, integration, and end-to-end testing. Jasmine and Karma are commonly used testing frameworks in the Angular ecosystem. Unit tests focus on individual components, services, and pipes, while integration tests check the collaboration between different parts of the application. End-to-end tests validate the entire application’s functionality.
15. Describe Angular Directives and their role in extending HTML functionality.
Ans:
Angular Directives are markers on a DOM element that tell Angular to attach a specific behavior to that element. They extend HTML by introducing custom functionality. Structural directives, like *ngFor and *ngIf, alter the structure of the DOM, while attribute directives, such as ngModel and ngStyle, modify the element’s appearance or behavior. Directives play a crucial role in creating dynamic and interactive user interfaces.
16. How does Angular handle Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities, and what security measures does it provide?
Ans:
Angular includes built-in security mechanisms to mitigate XSS vulnerabilities. It uses a strict Content Security Policy (CSP) to prevent the execution of malicious scripts. Angular also sanitizes user inputs by default, ensuring that potential harmful content is not executed. Developers can further enhance security by following best practices, such as avoiding the use of innerHTML and using Angular’s data binding features.
17. Discuss the concept of Angular Universal and its benefits.
Ans:
Angular Universal is a technology that allows developers to render Angular applications on the server side, providing server-side rendering (SSR). SSR improves application performance by delivering pre-rendered HTML to the client, reducing the time-to-first-contentful-paint. This approach enhances search engine optimization (SEO) and ensures a better user experience, particularly on devices with slower network connections.
18. Explain the role of Angular Decorators in the framework.
Ans:
Angular Decorators are a set of metadata annotations that provide additional information about classes, methods, and properties. They enhance the functionality of Angular components, services, and modules. Decorators such as @Component, @Injectable, and @NgModule simplify the configuration of various aspects of an application, promoting a declarative and readable coding style.
19. What is the purpose of Angular ngZone, and how does it impact performance?
Ans:
Angular ngZone is a core module that helps developers manage and optimize change detection. It defines a zone where asynchronous operations, such as HTTP requests or setTimeout callbacks, are executed. By controlling the execution context, ngZone improves the efficiency of change detection, reducing the risk of unnecessary updates and enhancing overall application performance.
20. Discuss Angular ViewEncapsulation and its role in styling components.
Ans:
Angular ViewEncapsulation is a mechanism that encapsulates component styles, preventing them from leaking into other components. It provides three encapsulation modes: Emulated, ShadowDom, and None. Emulated uses CSS classes to emulate scoped styles, ShadowDom uses the Shadow DOM to isolate styles, and None disables encapsulation. This feature enhances component reusability and avoids style conflicts in large applications.
21. Elaborate on Angular AOT (Ahead-of-Time) Compilation and its advantages.
Ans:
Angular AOT Compilation is a build process that converts Angular application code into machine code during the build phase rather than at runtime. This pre-compilation improves application startup performance by eliminating the need for runtime compilation. AOT also reduces the bundle size, making the application more efficient and improving the overall user experience.
22. What is the purpose of Angular ng-content, and how does it facilitate component composition?
Ans:
Angular ng-content is a content projection mechanism that allows developers to insert content into a component from its parent component. It enables flexible and reusable component composition, allowing developers to create dynamic templates and layouts. ng-content promotes the creation of customizable and extensible components, enhancing the modularity and maintainability of Angular applications.
23. Explain Angular Observables and their role in handling asynchronous operations.
Ans:
Angular Observables are a key part of the Reactive Extensions for JavaScript (RxJS) library, providing a powerful way to work with asynchronous data streams. They are used for handling events, managing HTTP requests, and dealing with other asynchronous tasks. Observables offer operators for transforming, filtering, and combining data streams, making it easier to manage complex asynchronous code in Angular applications.
24. Discuss the Angular ngModel directive and its role in two-way data binding.
Ans:
Angular ngModel is a directive that facilitates two-way data binding, allowing automatic synchronization between the model and the view. It simplifies the process of capturing user input and updating the application state. ngModel is commonly used in forms to bind input elements to variables in the component, providing a seamless way to manage user interactions and keep the application state in sync.
25. What are Angular Schematics, and how do they streamline project development?
Ans:
Angular Schematics are a powerful tool for automating and streamlining project development tasks. They provide blueprints for generating code, making it easy to create components, modules, services, and other project elements consistently. Schematics enhance project maintainability by enforcing best practices and reducing manual configuration. Developers can create custom schematics to tailor the code generation process to the specific requirements of their projects, improving overall development efficiency.
26. What is Angular Ivy, and how does it enhance performance in Angular 7 applications?
Ans:
Angular Ivy is the latest rendering engine in Angular, introduced to replace the View Engine. It offers improved bundle sizes, faster compilation, and better runtime performance. Ivy achieves these benefits by generating less code, optimizing the change detection mechanism, and enabling features like lazy loading of components. The enhanced tree-shakability and smaller runtime contribute to a more efficient Angular application, making it a valuable upgrade for performance-conscious developers.
27. Explain Angular Zone.js and its role in change detection.
Ans:
Angular relies on Zone.js to implement its change detection mechanism. Zone.js is a library that intercepts asynchronous operations, such as event handling and HTTP requests, to trigger change detection. It helps Angular detect and update the UI when the application state changes. Understanding Zone.js is crucial for developers dealing with asynchronous tasks in Angular, as it provides insights into how change detection is orchestrated and how to optimize performance by minimizing unnecessary checks.
28. What is the purpose of Angular ngRx, and how does it manage application state?
Ans:
Angular ngRx is a reactive state management library that implements the Redux pattern. It provides a centralized store to manage the state of an Angular application in a predictable and scalable manner. Developers use actions, reducers, and selectors to update and retrieve state, promoting a unidirectional data flow. ngRx facilitates the development of complex applications by improving code organization, testability, and maintainability through a strict and structured approach to managing application state.
29. Discuss Angular Universal and its role in server-side rendering (SSR).
Ans:
Angular Universal enables server-side rendering (SSR) for Angular applications, enhancing performance and search engine optimization (SEO). SSR involves rendering Angular components on the server, sending pre-rendered HTML to the client, reducing initial load times. This results in improved user experience, especially on slower network connections. Developers can use Angular Universal to build applications that seamlessly switch between client-side and server-side rendering based on the user’s device or network conditions.
30. Explain the concept of Angular DI (Dependency Injection) and its advantages.
Ans:
Angular DI is a powerful design pattern that promotes modularity and testability by providing a way to manage component dependencies. Components, services, and other objects declare their dependencies, and the Angular injector supplies them at runtime. This approach simplifies unit testing, as dependencies can be easily replaced with mocks or stubs. Additionally, DI enhances code maintainability by allowing developers to update or extend functionality without modifying existing code, making it a fundamental concept for building scalable and maintainable Angular applications.
31. Elaborate on Angular Forms, specifically Template-driven forms, and Reactive forms.
Ans:
Angular Forms play a crucial role in capturing and validating user input. Template-driven forms are declarative, relying on directives in the template to create and control the form. They are suitable for simple scenarios but may lack flexibility in complex applications. Reactive forms, on the other hand, are more programmatic, using a form model defined in the component. They offer better control, scalability, and testability, making them ideal for building dynamic and complex forms in Angular applications.
32. What is the role of Angular Resolver in route navigation, and how does it differ from route guards?
Ans:
Angular Resolver pre-fetches data before activating a route, ensuring that the route component has the required data before rendering. This can enhance performance by preventing the component from loading until the necessary data is available. Unlike route guards, which control access to routes based on conditions, resolvers focus on ensuring that the route’s data dependencies are resolved. By using resolvers strategically, developers can optimize the user experience by displaying content only when all required data is ready.
33. Discuss Angular Animations and their integration with components.
Ans:
Angular Animations provide a powerful and flexible way to create smooth and dynamic user interfaces. Developers can define animations for component transitions, state changes, and other UI interactions. Angular’s animation system allows for the creation of complex animations with minimal code. By leveraging keyframes, states, and transitions, developers can bring applications to life with visually appealing and responsive animations. Understanding how to integrate and customize Angular Animations is essential for creating engaging user experiences.
34. What are Angular ViewChildren and ContentChildren, and how do they differ in component interaction?
Ans:
Angular ViewChildren and ContentChildren are decorators used to interact with child components in Angular. ViewChildren query the components declared in the template, while ContentChildren query components projected into the component’s content using ng-content. Understanding the difference between these decorators is crucial for component communication and manipulation of child components. By using ViewChildren and ContentChildren effectively, developers can create more modular and dynamic Angular applications.
35. Explain Angular Lazy Loading and its impact on application performance.
Ans:
35. Explain Angular Lazy Loading and its impact on application performance. Angular Lazy Loading is a technique that defers the loading of certain parts of an application until they are needed. This can significantly improve initial page load times by reducing the amount of code loaded upfront. Lazy loading is commonly applied to modules and components, enabling a more efficient use of resources. By strategically implementing lazy loading, developers can optimize the user experience, especially in larger applications where loading unnecessary code upfront can lead to slower initial load times.
36. Discuss the role of Angular ng IfElse and ngSwitchCase in template logic.
Ans:
Angular ng IfElse and ngSwitchCase are structural directives that enhance template logic. ngIfElse allows developers to conditionally render content based on a true or false condition, providing an alternative template when the condition is false. ngSwitchCase, part of ngSwitch, enables the creation of a switch-like structure in templates, allowing for the selection of a specific template based on the value of an expression. These directives contribute to cleaner and more expressive template code in Angular applications.
37. Elaborate on Angular HostListener and HostBinding and their use in component interaction.
Ans:
Angular HostListener and HostBinding are decorators that facilitate communication between the component and its host element. HostListener allows the component to listen for events on the host element, enabling the execution of custom logic in response to those events. HostBinding, on the other hand, binds a property of the component to a property of the host element, allowing for dynamic updates. These decorators play a crucial role in extending a component’s behavior and appearance in the context of its host element.
38. What is Angular TestBed, and how does it support unit testing in Angular applications?
Ans:
Angular TestBed is a utility provided by Angular’s testing framework for configuring and creating isolated testing environments. It allows developers to set up components, services, and modules for testing, providing a controlled environment for unit tests. By using TestBed, developers can configure dependencies, simulate module configurations, and create instances of components for testing purposes. This facilitates effective unit testing, ensuring that each test is isolated and reproducible, leading to more robust and maintainable Angular applications.
39. Explain Angular ngZone and its role in managing asynchronous tasks.
Ans:
Angular ngZone is a crucial part of managing the Angular application’s change detection and handling asynchronous operations. It defines execution zones where Angular can track asynchronous tasks and trigger change detection when necessary. Developers can use ngZone.run() to execute code within the Angular zone, ensuring proper synchronization with the change detection mechanism. Understanding ngZone is essential for optimizing application performance, particularly when dealing with third-party libraries or asynchronous operations that might occur outside the Angular zone.
40. What is the purpose of Angular ngClass and ngStyle directives, and how do they enhance dynamic styling in templates?
Ans:
Angular ngClass and ngStyle are directives that facilitate dynamic styling in templates. ngClass allows developers to conditionally apply CSS classes based on expressions, providing a flexible way to manage the appearance of elements. ngStyle enables the dynamic application of inline styles based on component properties. By leveraging these directives, developers can create responsive and interactive user interfaces with styles that adapt to changing conditions, enhancing the overall user experience in Angular applications.
41. Discuss Angular Compiler and its role in the compilation process.
Ans:
Angular Compiler is a key component in the Angular framework responsible for translating application code into executable JavaScript. It operates during the build process, converting TypeScript and Angular templates into optimized JavaScript code. Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation is a feature of the Angular Compiler that further improves performance by pre-compiling components before runtime. Understanding the Angular Compiler and its optimizations is crucial for developers seeking to enhance application speed and efficiency.
42. What are Angular ContentChild and ViewChild, and how do they differ in component interaction?
Ans:
Angular ContentChild and ViewChild are decorators used to interact with child components in Angular. ContentChild queries components projected into the component’s content using ng-content, while ViewChild queries the components declared in the template. The distinction between these decorators is essential for effective component communication and manipulation of child components. By using ContentChild and ViewChild appropriately, developers can create more modular and dynamic Angular applications.
43. Explain Angular ngRx Effects and their role in managing side effects in state management.
Ans:
Angular ngRx Effects are used to manage side effects, such as asynchronous operations, in NgRx-based state management. Effects are responsible for handling actions that have side effects, such as making HTTP requests or interacting with external services. By isolating side effects in Effects, developers can keep the reducer functions pure and testable. Understanding how to use ngRx Effects is crucial for building scalable and maintainable Angular applications with complex state management requirements.
44. Discuss Angular ng-container and its role in template organization.
Ans:
Angular ng-container is a structural directive that does not create any element in the DOM. It serves as a grouping element for other directives like *ngIf and *ngFor, allowing developers to apply these directives without introducing an extra wrapper element in the DOM. ng-container enhances template organization by providing a cleaner and more semantic structure. It is particularly useful when multiple structural directives need to be applied to a single section of the template, contributing to more readable and maintainable Angular templates.
45. What is Angular ChangeDetectionRef, and how does it enable manual triggering of change detection?
Ans:
Angular ChangeDetectionRef is a service that provides a way to manually trigger change detection in Angular applications. By injecting ChangeDetectionRef into a component, developers gain control over when change detection is executed. This can be useful in scenarios where change detection needs to be explicitly triggered, optimizing performance by avoiding unnecessary checks. Understanding how to use ChangeDetectionRef effectively allows developers to fine-tune change detection in specific parts of the application, contributing to a more responsive and efficient user interface.
46. Elaborate on Angular Dynamic Components and their use cases.
Ans:
Angular Dynamic Components allow developers to create and manipulate components at runtime, providing flexibility and extensibility to the application. These components can be dynamically added, removed, or modified based on user interactions or dynamic data. Dynamic Components are particularly useful in scenarios where the structure of the user interface needs to adapt to changing requirements. By leveraging Dynamic Components, developers can build more dynamic and interactive Angular applications that can evolve and respond to user actions in real-time.
47. What is Angular ElementRef, and how is it used in Angular applications?
Ans:
Angular ElementRef is a service that provides access to the host element of a directive or component. By injecting ElementRef into a directive or component, developers can interact directly with the underlying DOM element. This can be useful when imperative actions, such as manipulating the DOM or accessing specific properties of the host element, are required. However, it’s essential to use ElementRef judiciously, as direct manipulation of the DOM can bypass Angular’s change detection and introduce potential performance issues. Understanding when and how to use ElementRef ensures proper integration with Angular’s architecture.
48. Explain Angular CDK (Component Dev Kit) and its role in building reusable UI components.
Ans:
Angular CDK is a set of tools and utilities provided by Angular for building common user interface components. It offers a collection of pre-built components, directives, and utilities that facilitate the creation of accessible, responsive, and reusable UI components. Developers can leverage Angular CDK to build custom components with consistent behavior and interactions, ensuring a cohesive user experience across different parts of an application.
49. What is Angular NgModel and how does it facilitate two-way data binding in forms?
Ans:
Angular NgModel is a directive that facilitates two-way data binding in forms, allowing for seamless synchronization between the view and the model. By using NgModel in form controls, developers can bind input elements to properties in the component, ensuring that changes in the view immediately update the underlying model and vice versa. This simplifies the handling of user input in forms, providing a convenient and declarative way to manage form data. Understanding the intricacies of NgModel is essential for building interactive and data-driven forms in Angular applications.
50. Discuss Angular Interceptors and their role in handling HTTP requests and responses.
Ans:
Angular Interceptors are a powerful feature that allows developers to intercept and modify HTTP requests and responses. By implementing interceptors, developers can add custom logic, such as authentication, logging, or error handling, to the HTTP pipeline. Interceptors provide a centralized and reusable way to manage cross-cutting concerns related to HTTP communication. Understanding how to leverage Angular Interceptors is crucial for enhancing the robustness and security of Angular applications by adding global behaviors to HTTP requests and responses.
51. What are the key features introduced in Angular 7?
Ans:
Angular 7 brought significant improvements, including enhanced Angular CLI tools for streamlined development and updated Angular Material with new components and features. The introduction of virtual scrolling in Angular CDK optimized the rendering of large lists, while CLI prompts guided developers through tasks. Dependency updates, such as TypeScript 3.1 and RxJS 6.3, ensured compatibility with the latest technologies. Angular Elements, facilitating the packaging of Angular components as custom elements, also received improvements. These updates collectively aimed at improving the developer experience and boosting application performance.
52. Explain Angular CLI and its significance in Angular development.
Ans:
Angular Command Line Interface is a powerful tool for Angular development. It simplifies various tasks such as project scaffolding, code generation, testing, and deployment. Developers use CLI commands to create components, services, modules, and more. Its significance lies in providing a standardized and efficient way to initiate, build, and maintain Angular applications, enhancing productivity and enforcing best practices.
53. Can you describe the improvements made to Angular Material and CDK in Angular 7?
Ans:
In Angular 7, Angular Material and the Component Dev Kit (CDK) saw enhancements with the addition of new components, including a date range picker and virtual scrolling. The update also introduced starter components for Angular Material, streamlining the development of common UI patterns. These improvements aimed to provide developers with a richer set of tools for creating more feature-complete and visually appealing Angular applications.
54. What is the significance of Virtual Scrolling in Angular CDK?
Ans:
Virtual Scrolling in Angular CDK is significant for efficiently rendering large lists by only rendering the items that are currently visible to the user. This improves performance by reducing the number of DOM elements created, resulting in faster loading times and smoother user experiences, especially in applications with extensive data lists.
55. How does Dependency Injection work in Angular 7?
Ans:
Dependency Injection in Angular 7 is a design pattern where a class receives its dependencies from an external source rather than creating them itself. Angular’s dependency injection system provides a way to manage and inject dependencies into components, services, and other objects. This promotes modular and testable code by allowing components to be more loosely coupled and easily replaceable.xplain the concept of Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation in Angular 7.
56.Explain the concept of Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation in Angular 7.
Ans:
Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation is the process of converting Angular application code into efficient JavaScript code during the build phase, before the application is served to the client’s browser. In Angular 7, AOT compilation offers benefits such as smaller bundle sizes, faster rendering, and improved runtime performance, contributing to a more optimized and faster user experience.
57. What are some of the CLI commands that you frequently use in Angular development?
Ans:
In Angular development, frequently used CLI commands include ng new for creating a new project, ng generate for generating various elements, ng serve for running a development server, ng build for deployment-ready builds, ng test for running unit tests, and ng lint for code analysis. These commands streamline development tasks and are integral to the Angular CLI’s efficiency.
58. How does Angular 7 support the development of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)?
Ans:
Angular 7 supports the development of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) through built-in features. The Angular Service Worker, in conjunction with the Angular CLI, facilitates the seamless addition of PWA capabilities. This includes offline functionality, background synchronization, and improved performance, enhancing the user experience across various devices.
59. Discuss the updates and improvements in TypeScript support in Angular 7.
Ans:
Regarding TypeScript support in Angular 7, updates include compatibility with TypeScript 3.1. This ensures that Angular projects can leverage the latest features and improvements introduced in TypeScript, enhancing the development experience with better type checking, improved tooling, and overall language enhancements. These TypeScript updates contribute to the maintainability and robustness of Angular applications.
60. What is the purpose of the Angular Router and how is it used in Angular 7 applications?
Ans:
The Angular Router is a powerful navigation library that allows developers to manage navigation in Angular applications. Its purpose is to enable the creation of Single Page Applications (SPAs) by providing a way to navigate between different views or components without requiring a full page reload. In Angular 7 applications, the router is configured using routes, each associated with a specific component. It plays a crucial role in creating a seamless and responsive user experience by enabling navigation and deep linking.
61. Can you explain the concept of Lazy Loading in Angular 7?
Ans:
Lazy Loading is a technique in Angular 7 where modules are loaded on-demand, as needed, rather than upfront when the application is initially loaded. This can significantly improve the application’s initial load time, as it loads only the essential modules for the current view. In Angular, Lazy Loading is achieved by configuring the router to load specific modules asynchronously. This helps in optimizing the performance of large applications by loading resources only when they are required.
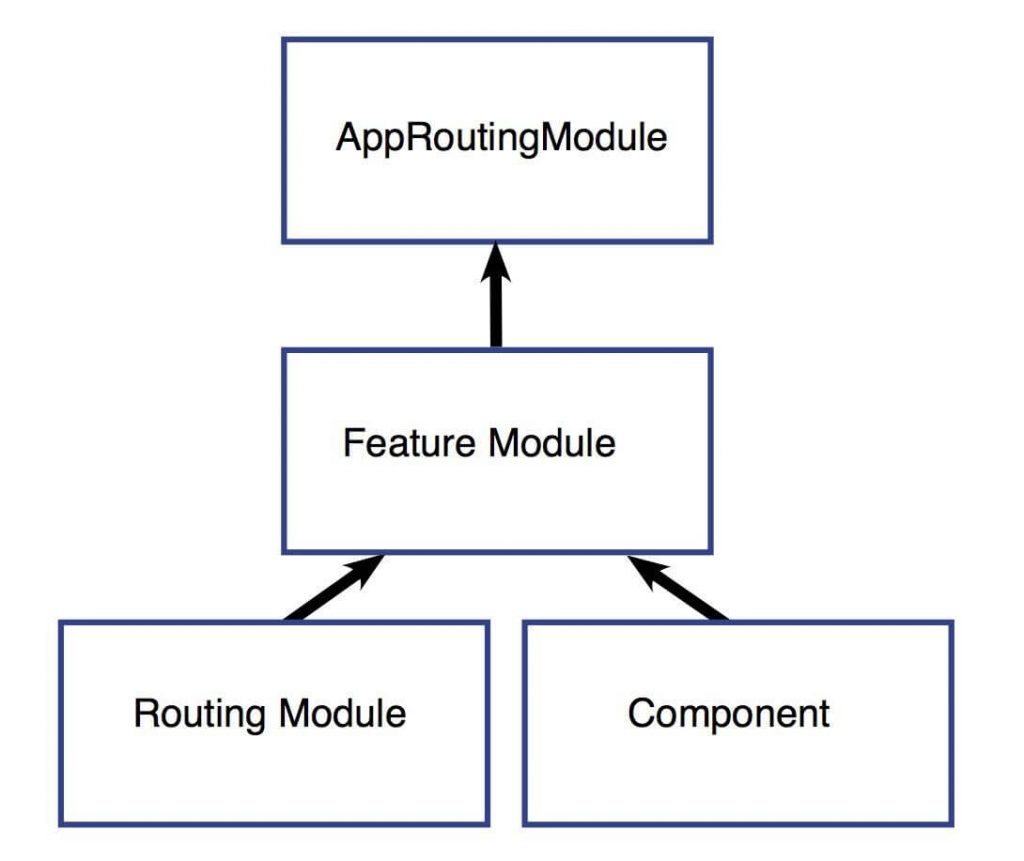
62.What are Angular Guards, and how do they enhance the security of Angular applications?
Ans:
Angular Guards are a set of interfaces that allow developers to implement logic before a route is activated or even after it has been deactivated. They enhance the security of Angular applications by controlling access to certain routes based on predefined conditions. They are different types of guards, including CanActivate, CanActivateChild, CanDeactivate, and CanLoad. Developers can use these guards to enforce authentication, authorization, or any custom logic to ensure that users have the necessary permissions before navigating to a specific route. This helps in preventing unauthorized access to parts of the application and ensures a secure and controlled navigation flow.
63. Explain the concept of Change Detection in Angular and its importance in the framework.
Ans:
Change Detection in Angular is the automatic process of tracking changes in the application’s state and updating the UI accordingly. This ensures a dynamic and responsive user interface, keeping the view in sync with the underlying data.
64. How can you communicate between components in Angular 7?
Ans:
Communication is achieved through input/output properties for parent-child interactions, ViewChild/ContentChild for accessing child components, services as a centralized communication hub, and event emitters for custom event notifications. These mechanisms enable effective data flow and interaction between different parts of an Angular application.
65. What is ng-content in Angular 7 and how is it used?
Ans:
ng-content is an Angular directive used for content projection. It allows a component to accept content from its parent component, making it a versatile tool for creating reusable components. With ng-content, the parent component can inject content into specific areas within the child component’s template, providing flexibility and enabling the creation of dynamic components.
66. Explain the concept of ViewEncapsulation in Angular and its types.
Ans:
| Concepte | Description | |
| ViewEncapsulation |
A mechanism in Angular to encapsulate styles in a component, preventing global style leakage. | |
| Types | Three types: Emulated (default), Native, and None. | |
| Emulated (default) | Styles are encapsulated to the component, but a part of them is emulated globally using shadow DOM or other techniques. | |
| Native | Utilizes the browser’s native shadow DOM to encapsulate styles, ensuring a more isolated scope. |
67. How does Angular 7 handle forms, and what are the advantages of using Reactive Forms?
Ans:
Handling Forms in Angular 7 :
Angular 7 supports template-driven and reactive forms. Template-driven forms utilize HTML directives, suitable for simpler scenarios. Reactive forms, created programmatically, offer enhanced testability, dynamic controls, scalability, and seamless integration with observables.
Advantages of Reactive Forms :
Reactive forms in Angular 7 provide enhanced testability, support dynamic controls, improve scalability for larger forms, and seamlessly integrate with asynchronous data through Angular’s reactive programming features.
68.Can you describe the Angular Universal and its role in Angular 7 applications?
Ans:
Angular Universal enables server-side rendering in Angular 7, improving performance and SEO. It facilitates faster initial page loads, enhances user experiences, and supports the execution of Angular applications on various server environments like Node.js or .NET.
69. Explain the concept of Angular Dependency Injection and provide an example.
Ans:
Angular Dependency Injection (DI) is a design pattern where components and services receive their dependencies from an external source rather than creating them themselves. It promotes code modularity, maintainability, and testability.
An example is injecting a service into a component:
- // Service
- @Injectable()
- class DataService {
- getData() {
- return ‘Angular Dependency Injection Example’;
- }
- }
- // Component
- @Component({
- selector: ‘app-example’,
- template: ‘{{ data }}’,
- })
- class ExampleComponent {
- constructor(private dataService: DataService) {}
- ngOnInit() {
- this.data = this.dataService.getData();
- }
- }
70. What is ngZone in Angular, and why is it used?
Ans:
NgZone in Angular is a service that provides a zone where Angular can run tasks. It is used to manage asynchronous operations and change detection. Angular relies on zones to capture asynchronous events and trigger change detection appropriately. NgZone is particularly useful when dealing with third-party libraries or APIs that run outside Angular’s knowledge. It helps ensure that Angular is aware of changes and updates the UI accordingly, preventing issues like “ExpressionChangedAfterItHasBeenCheckedError.”
71. Explain the concept of Zones in Angular and their significance.
Ans:
Zones in Angular are execution contexts that allow developers to intercept and track asynchronous operations. They play a crucial role in Angular’s change detection mechanism. Zones help Angular to capture asynchronous tasks and ensure that change detection runs appropriately. This is significant for managing events, promises, and other asynchronous operations within Angular applications.
72. How does Angular handle HTTP requests, and what improvements were made in Angular 7 in this context?
Ans:
Angular handles HTTP requests through the HttpClient module. In Angular 7, improvements were made in the form of enhanced support for interceptors, allowing developers to modify HTTP requests globally. Additionally, the HttpClient module now supports the configuration of an HTTP client with a base URL, simplifying the management of API endpoints.
73. What is the purpose of the trackBy function in Angular ngFor directive?
Ans:
The trackBy function in Angular’s ngFor directive is used to improve the efficiency of rendering lists. It helps Angular identify which items have changed, added, or removed in a list, minimizing unnecessary DOM manipulations. By providing a unique identifier for each item, the trackBy function allows Angular to optimize the rendering process, resulting in better performance, especially in scenarios where the list frequently updates.
74. How does Angular 7 support internationalization (i18n) and localization?
Ans:
Angular 7 provides robust support for internationalization and localization. Developers can use the Angular i18n tooling to mark text for translation, extract messages, and generate translation files. The @angular/common library includes the LOCALE_ID token for setting the application’s locale dynamically. Angular CLI simplifies the extraction and compilation of translations, making it easier to build multilingual applications.
75. Can you explain the Angular ngZone and its role in change detection?
Ans:
NgZone in Angular is a service that enables the management of asynchronous operations and the execution of tasks within a specific zone. Zones play a crucial role in Angular’s change detection mechanism. When an asynchronous task is executed outside the Angular zone (e.g., a callback from a third-party library), NgZone ensures that Angular is aware of the task’s completion. This helps trigger the change detection cycle, updating the UI to reflect the changes made by the asynchronous operation. NgZone is vital for maintaining the integrity of Angular applications and ensuring that changes in the application state are reflected in the user interface.
76.How does Angular handle error handling, and what improvements were introduced in Angular 7 in this context?
Ans:
Angular manages errors using observables, with Angular 7 introducing the catchError operator for more effective error handling in observable pipelines. This improvement enhances the clarity and robustness of error management in Angular applications.
77. Can you elaborate on the Angular ChangeDetectionStrategy and its different options?
Ans:
Angular’s ChangeDetectionStrategy dictates how the framework detects and responds to changes in the application state. The OnPush option, introduced in Angular, optimizes performance by checking components only if their inputs change or if triggered by an event. This is particularly beneficial for improving responsiveness when working with immutable data and pure components.
78. What is the Angular Renderer2, and when might it be used in Angular 7 applications?
Ans:
Renderer2 in Angular is a service that provides a platform-independent interface for manipulating elements in the DOM. In Angular 7, it is used for direct DOM manipulation, offering a consistent approach regardless of the underlying rendering engine. Renderer2 enhances portability and is valuable when dynamically creating or updating elements while maintaining Angular’s abstraction over the platform.
79. Explain Angular Zones and how they impact change detection in Angular applications.
Ans:
Angular Zones define execution contexts that enable tracking of asynchronous operations. They play a pivotal role in Angular’s change detection by allowing the framework to intercept and manage asynchronous tasks. When tasks occur within a zone, Angular is aware of them and triggers change detection to update the UI. This ensures consistency between the application state and the user interface. If tasks occur outside the zone, Angular won’t automatically detect changes, emphasizing the significance of Zones for maintaining synchronization and responsiveness in Angular applications.
80. What is the Angular Router Outlet, and how is it different from RouterLink?
Ans:
Angular Router Outlet :
The Angular Router Outlet is a directive serving as a placeholder in the template where the router injects the component based on the current route, enabling dynamic component rendering.
RouterLink in Angular :
RouterLink is a directive used for navigation, providing a declarative way to navigate to a specific route when attached to an HTML element. It differs from Router Outlet, which is a container for dynamically loading routed components.
81. Can you discuss the role of Angular Services and when to use them in Angular 7?
Ans:
Angular Services facilitate code modularity and reusability by encapsulating shared functionality and data. They play a pivotal role in promoting a separation of concerns and providing a centralized place for managing business logic, data, and communication between components. Services are ideal for tasks such as data retrieval, business logic, and inter-component communication, making them a cornerstone for building scalable and maintainable Angular applications.
82. How does Angular 7 handle module loading, and what is the significance of lazy loading in this context?
Ans:
Angular 7 Module Loading :
Angular 7 adopts a modular architecture with dynamic import for on-demand module loading, managed by the Angular CLI.
Lazy Loading Significance :
Lazy loading is crucial for optimizing Angular applications as it allows modules to be loaded only when required, reducing initial loading times and improving the overall application performance. /p>
83. Explain the concept of Angular Forms Validators and provide an example of their usage.
Ans:
Angular Forms Validators are functions used to validate the input of form controls. They can be applied to form controls to ensure that the entered data meets specific criteria.
For example, to require a field, use the Validators.required function:
- import { Validators, FormBuilder, FormGroup } from ‘@angular/forms’;
- // Creating a form group with a required field
- const formGroup = this.formBuilder.group({
- username: [”, Validators.required],
- });
84. What are Angular Resolvers, and how do they contribute to data fetching in Angular routes?
Ans:
Angular Resolvers are services used to fetch data before a route is activated. They ensure that the required data is available before rendering the associated component, preventing issues with incomplete data. Resolvers are defined in route configurations and associated with a specific route.
For example:
- // In route configuration
- {
- path: ‘profile’,
- component: ProfileComponent,
- resolve: { userData: UserDataResolver }
- }
- // Resolver implementation
- @Injectable({ providedIn: ‘root’ })
- export class UserDataResolver implements Resolve
{ - resolve(route: ActivatedRouteSnapshot, state: RouterStateSnapshot): Observable
{ - return this.userService.getUserData();
- }
- }
85.Discuss the role of Angular Directives and provide examples of built-in and custom directives.
Ans:
Angular Directives are markers on the DOM elements that tell Angular to attach a particular behavior to that element or transform it. They play a key role in extending HTML with custom functionalities. Built-in directives include *ngIf and *ngFor.
86. Can you explain Angular’s ContentChild and ContentChildren decorators, and when to use them in components?
Ans:
ContentChild and ContentChildren :
ContentChild and ContentChildren decorators in Angular are used to query and access content projected into a component. ContentChild retrieves the first matching element or directive, while ContentChildren retrieves a QueryList of matching elements or directives.
When to Use :
Use ContentChild and ContentChildren when you need to access and manipulate content projected into a component. They are particularly useful for creating flexible and reusable components that can work with varying content structures.
87. What is the purpose of Angular Animations, and how are they implemented in Angular 7?
Ans:
Angular Animations enhance UI by creating visually appealing transitions. In Angular 7, animations are implemented using the @angular/animations module, defining transitions with functions like trigger and animate.
88. Can you explain the concept of Angular Pipes and provide an example of their usage?
Ans:
Angular Pipes transform data in templates, offering a convenient way to format or manipulate it. For instance, using the Date Pipe to format currentDate.
89. How does Angular 7 support the creation of dynamic components, and what is their significance?
Ans:
Angular 7 supports dynamic components through the ComponentFactoryResolver and ViewContainerRef. Dynamically creating and adding components at runtime is significant for building flexible and extensible applications.
90. Can you describe the role of Angular Life Cycle Hooks?
Ans:
Angular Life Cycle Hooks allow developers to tap into different phases of a component’s life cycle. ngOnInit is used for initialization tasks, like fetching initial data from a service.






