
You’ve come to the correct location if you’re seeking for IBM Security QRadar SIEM Interview Questions for Freshers or Experienced. The globe is full of chances from several well-known businesses. Research indicates that IBM Security QRadar SIEM holds a portion of the market. Thus, there is still room for you to advance in IBM Security QRadar SIEM Development as a professional. In order to help you ace the interview and land your ideal job as an IBM Security QRadar SIEM Developer, Mindmajix provides Advanced IBM Security QRadar SIEM Interview Questions.
1. What is QRadar SIEM, and how does it differ from SIM solutions?
Ans:
IBM QRadar Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is a comprehensive solution designed to provide organizations with a robust platform for collecting, correlating, and analyzing security data from various sources. Unlike traditional Security Information Management (SIM) solutions, QRadar SIEM goes beyond log management, offering advanced capabilities such as real-time event correlation, anomaly detection, and incident response.
2. Explain the core components of IBM QRadar architecture.
Ans:
The architecture of IBM QRadar comprises several essential components. The primary ones include the QRadar Console, Event Processor, Flow Processor, Data Nodes, and Search Head. The QRadar Console is the user interface for security analysts to interact with and manage the system. The Event Processor collects, processes, and normalizes raw event data, while the Flow Processor handles network flow data. Data Nodes store and manage the indexed data, providing scalability and redundancy.
3. What is the purpose of the QRadar Console?
Ans:
The QRadar Console is the central point for security analysts to access and manage the QRadar SIEM system. It provides a user-friendly interface for monitoring security events, creating and managing custom rules, investigating offences, and generating reports. The Console acts as the command centre, enabling security professionals to navigate and interact with QRadar’s features efficiently.
4. Describe the role of the QRadar Event Processor.
Ans:
The QRadar Event Processor is a critical component responsible for collecting and processing raw event data. It normalizes disparate log formats into a standardized format, enriches events with additional information, and performs real-time correlation to identify security incidents. The Event Processor plays a pivotal role in the initial stages of event analysis, helping to detect and categorize security threats.
5. What is the function of the QRadar Flow Processor?
Ans:
The QRadar Flow Processor specializes in handling network flow data. It captures and processes information about the connections between devices in the network, providing insights into the communication patterns. This includes source and destination IP addresses, ports, and protocol information. The Flow Processor’s role is crucial in detecting abnormal network behaviour and identifying potential security risks.
6. Explain the significance of QRadar Data Nodes.
Ans:
QRadar Data Nodes are responsible for storing and managing the indexed data generated by the Event and Flow Processors. These nodes ensure the storage infrastructure’s high availability, fault tolerance, and scalability. Data Nodes contribute to the overall performance and resilience of the QRadar SIEM solution by efficiently handling the storage and retrieval of security data.
7. How does QRadar handle log and flow data normalization?
Ans:
QRadar employs a normalization process to convert raw logs and flow data from various sources into a standardized format. This normalization ensures consistency in data representation, making it easier to correlate events and detect security incidents. QRadar facilitates effective analysis and correlation across diverse log sources by normalizing data and enhancing threat detection accuracy.
8. What is the purpose of the QRadar Search Head?
Ans:
The QRadar Search Head is designed for efficient querying and searching within the QRadar system. It allows security analysts to perform searches, create reports, and investigate security events. The Search Head consolidates information from Data Nodes, providing a centralized point for retrieving and analyzing data across the entire QRadar deployment.
9. Describe deploying a QRadar High Availability (HA) environment.
Ans:
Deploying a High Availability (HA) environment in QRadar involves configuring redundant components to ensure continuous operation in case of a system failure. This typically includes setting up redundant Event Processors, Flow Processors, and Data Nodes. HA deployment enhances the system’s reliability, minimizing downtime and ensuring critical security functions remain operational.
10. What is the role of the QRadar System Notification and Health dashboard?
Ans:
The QRadar System Notification and Health dashboard offer a comprehensive view of the overall health and status of the QRadar SIEM deployment. It provides real-time information about system performance, resource utilization, and any potential issues requiring attention. This dashboard is a proactive tool for administrators to monitor the system’s well-being and promptly address any emerging concerns.
11. Explain the difference between QRadar Offense and Incident.
Ans:
| Feature | QRadar Offense | QRadar Incident | |
| Definition | A high-level alert that indicates potential security threats or policy violations based on correlated events. | A detailed and specific security event that has been investigated and confirmed to be a genuine threat or incident. | |
| Trigger | Generated by QRadar’s correlation engine, which analyzes and correlates raw events to identify patterns or anomalies. | Typically created based on the investigation and validation of one or more offenses to confirm a security incident. | |
| Severity | Assigned a severity level (e.g., low, medium, high) based on the perceived threat level of the correlated events. | Severity may be associated with incidents to indicate the potential impact or criticality of the security event. | |
| Investigation Workflow | Serves as the starting point for investigation and analysis. Analysts can drill down into offenses to view correlated events. | Represents a deeper level of investigation, involving additional analysis, validation, and documentation of the incident details. | |
| Lifecycle Management | Offenses may be closed, escalated, or manually marked as offenses to reflect the current state of the investigation. | Incidents have a more structured lifecycle with stages such as open, in progress, resolved, and closed, providing a clearer workflow. | |
| Aggregation | Represents a collection of correlated events that may indicate a potential security issue but does not confirm an actual incident. | Refers to a confirmed and validated security event, often requiring a response or remediation action. |
12. What is a building block in QRadar, and how is it used in rule creation?
Ans:
In QRadar, a building block is a modular component to construct correlation and response rules. It encapsulates specific conditions or actions, such as offence filters, reference sets, or custom properties, providing a customizable and granular approach to rule creation. For example, an offence filter building block allows the creation of rules based on offence criteria, enhancing the platform’s flexibility in detecting and responding to security threats.
13. Describe the process of updating QRadar DSMs.
Ans:
Updating QRadar DSMs involves keeping Device Support Modules current to ensure compatibility with the latest log source formats. This includes obtaining updated DSM packages from IBM, importing them into QRadar, and deploying the updates across the deployment. Regular updates are crucial for recognizing and parsing log data from new and evolving technologies, ensuring accurate and comprehensive event processing within the QRadar SIEM environment.
14. How does QRadar handle the event and flow retention?
Ans:
QRadar handles event and flow retention by allowing administrators to configure retention policies. By defining retention periods based on organizational needs and compliance requirements, QRadar ensures that historical data is preserved for analysis, compliance reporting, and forensic investigations. Retention settings can be adjusted to balance storage efficiency with retaining data for extended periods.
15. What is QRadar’s role in incident response and forensics?
Ans:
QRadar is pivotal in incident response by providing real-time visibility into security events, automating threat detection, and facilitating swift investigation. Its centralized Console allows security teams to correlate and analyze diverse data sources, aiding in identifying and mitigating security incidents. Additionally, QRadar supports forensic analysis by retaining historical event and flow data, enabling security professionals to reconstruct the timeline of events and conduct detailed investigations to understand the scope and impact of incidents.
16. Explain the purpose of QRadar’s Data Classification Toolkit.
Ans:
QRadar’s Data Classification Toolkit enhances the identification and classification of sensitive information within an organization’s data. It provides a set of rules and algorithms to detect and categorize data based on predefined criteria such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, or custom patterns. Organizations can use this toolkit to strengthen their data protection measures, comply with regulatory requirements, and improve incident detection and response capabilities.
17. How does QRadar handle log source auto-discovery?
Ans:
- Automatic Identification: QRadar employs automatic log source identification to detect and configure new log sources.
- Detection Mechanism: Utilises protocols such as Syslog, SNMP, and others to identify and add new log sources.
- Normalisation: Automatically normalizes log formats to ensure consistency in data representation.
- User Validation: Allows users to validate and customize the auto-discovered log source configurations.
- Efficiency: Enhances operational efficiency by reducing manual configuration efforts for adding log sources.
18. What is the purpose of QRadar Reference Sets?
Ans:
QRadar Reference Sets organize and manage data sets, such as IP addresses, domains, or URLs. Reference Sets enhance offence and flow data by associating additional context for better analysis. Utilized in rules to match and correlate events based on the data contained within reference sets. Reference Sets can be dynamically updated, allowing real-time data enrichment. Used for creating blocklists or allowlists to aid in identifying malicious or trusted entities. Supports the identification of assets by associating IP addresses or other identifiers.
19. Describe creating a custom DSM (Device Support Module) in QRadar.
Ans:
Navigate to the DSM Editor in the QRadar Console. Choose the device type for which the custom DSM is being created. Specify log source parsing rules, including log format, delimiters, and field extractions. Map parsed log fields to QRadar’s normalized event fields. Validate the custom DSM by testing log source parsing and mapping. Save the custom DSM configuration and deploy it to the QRadar deployment.
20. How does QRadar handle distributed log sources across multiple locations?
Ans:
- Log Source Protocols: QRadar supports protocols like Syslog, SNMP, and agents to collect logs from distributed sources.
- Log Source Extensions: Utilises Log Source Extensions (LSX) for specific log sources, facilitating distributed log collection.
- Remote Data Collection: Configures remote data collection settings to gather logs from geographically dispersed locations.
- Multi-Site Deployments: QRadar can be configured for multi-site deployments, allowing centralized management of distributed log sources.
- Load Balancing: Implements load balancing mechanisms for efficient distribution of log processing across components.
21. How does QRadar handle custom log sources that are not supported out of the box?
Ans:
QRadar accommodates custom log sources using the Log Source Extension (LSX) framework. Security administrators can create custom parsers for non-standard log formats, ensuring that diverse and proprietary logs are normalized within the QRadar environment. This flexibility allows organizations to integrate and analyze log data from various sources, even those not initially supported, enabling a more comprehensive approach to security monitoring.
22. What is the significance of the QRadar Network Hierarchy?
Ans:
QRadar Network Hierarchy provides a structured view of an organization’s network, allowing security teams to organize and analyze events based on network segments. This hierarchical representation aids in the identification of security issues specific to different parts of the network. By categorizing devices and subnets, QRadar Network Hierarchy enhances the efficiency of incident investigation and response, enabling security analysts to focus on specific areas of concern and promptly address potential threats.
23. Describe the role of QRadar Vulnerability Manager (QVM).
Ans:
QRadar Vulnerability Manager (QVM) is crucial in assessing and managing an organization’s infrastructure vulnerabilities. This integration allows security teams to prioritize remediation efforts based on the severity of vulnerabilities and actively respond to potential threats. QVM enhances QRadar’s capabilities by providing a comprehensive view of an organization’s security posture, facilitating proactive vulnerability management.
24. How does QRadar integrate with third-party applications and tools?
Ans:
QRadar supports integration with third-party applications and tools through various mechanisms, including APIs and connectors. This flexibility allows organizations to enhance their security operations by incorporating additional threat intelligence feeds, incident response platforms, or specialized security tools. By integrating seamlessly with third-party solutions, QRadar extends its capabilities, enriches analysis, and enables a more comprehensive and collaborative approach to cybersecurity.
25. Explain the process of tuning QRadar rules for better accuracy.
Ans:
Tuning QRadar rules involves refining the rule criteria to improve accuracy and reduce false positives. Security administrators adjust rule parameters, such as thresholds and conditions, based on the organization’s specific environment and threat landscape. Continuous refinement through tuning ensures that QRadar remains aligned with evolving security needs and effectively detects relevant threats.
26. Explain the concept of QRadar Domain Management.
Ans:
QRadar Domain Management allows the segmentation of QRadar deployments into isolated domains. Enables the creation of separate domains for different organizations, departments, or business units. Administrators can configure settings specific to each domain, including log sources, rules, and users. Ensures security isolation between domains, preventing unauthorized access to domain-specific data. Domains can have independent event and flow processing, enhancing scalability and performance. Provides centralized administration with the ability to manage multiple domains from a single interface.
27. What are the types of QRadar offences, and how are they classified?
Ans:
- Low-Level Offences: Generated for events with lower severity or potential impact.
- Medium-Level Offences: Indicates a moderate level of threat or suspicious activity.
- High-Level Offences: Represent significant security incidents requiring immediate attention.
- Custom Offences: Users can create custom offences based on specific criteria.
- Network Offences: Focuses on offences related to network-based security incidents.
- User Offences: Relates to offences involving user accounts or authentication issues.
28. How does QRadar handle asset discovery and profiling?
Ans:
QRadar automatically discovers assets on the network through various protocols. Integrates with QRadar Vulnerability Manager (QVM) to enhance asset profiling with vulnerability data. Utilises continuous monitoring to dynamically update asset profiles based on network behaviour. Incorporates asset information into offence and incident analysis for risk assessment. Enhances asset discovery by analyzing user behaviour and entity interactions on the network.
29. Describe the significance of QRadar Custom Properties.
Ans:
- Additional Context: Custom Properties in QRadar provide additional context to offences and events.
- User-Defined Information: Enables users to define and associate custom attributes with offences and events.
- Correlation Criteria: Custom Properties can be used as correlation criteria in rules for more specific event correlation.
- Reporting: Custom Properties contribute to creating more detailed and customized reports.
- Tailoring to Organization Needs: Allows tailoring QRadar to specific organizational needs and context.
30. Explain the function of QRadar Log Source Extensions (LSX).
Ans:
Log Source Extensions (LSX) allow the creation of custom parsing logic for non-standard log formats. Enables integration with log sources that do not have pre-built DSMs (Device Support Modules). Enhances the capabilities of custom DSMs by providing additional parsing flexibility. Allows QRadar to support various custom log formats used by different applications. Supports adaptability to changes in log source formats, ensuring continued compatibility as log sources evolve.
31. How does QRadar handle log source and flow source licensing?
Ans:
QRadar employs a licensing model that accounts for both log and flow sources. Each log source and flow source connected to the system requires a licence to contribute to the overall event and flow processing capacity. Administrators manage licensing through the License Management App, where they can allocate and monitor the usage of available log source and flow source licences. This ensures efficient utilization of resources and compliance with licensing agreements.
32. Explain the purpose of QRadar User Behavior Analytics (UBA).
Ans:
QRadar User Behavior Analytics (UBA) detects anomalous user activities and behaviour within an organization’s network. By analyzing patterns of user interactions with systems and data, UBA identifies deviations from normal behaviour that may indicate insider threats or compromised accounts. This proactive approach to user monitoring enhances QRadar’s ability to detect and respond to potential security incidents, providing a valuable layer of defence against insider threats.
33. What is the role of QRadar Tuning Parameters?
Ans:
QRadar Tuning Parameters are configuration settings that allow administrators to adjust the system’s behaviour to align with specific security requirements. These parameters impact various aspects of event processing, correlation, and response. By fine-tuning these parameters, administrators can optimize the performance and effectiveness of QRadar, ensuring that the platform meets the organization’s unique security objectives and operates efficiently in its specific environment.
34. Describe the process of integrating QRadar with threat intelligence feeds.
Ans:
Integrating QRadar with threat intelligence feeds involves incorporating external threat intelligence data into the SIEM platform. QRadar supports standard formats like STIX/TAXI and integrates with popular threat intelligence providers. Through this integration, QRadar enriches its understanding of potential threats by cross-referencing incoming events and flows with known indicators of compromise.
35. How does QRadar handle incident correlation and prioritization?
Ans:
QRadar excels in incident correlation and prioritization by aggregating and correlating events based on predefined rules. The platform assigns offences to correlated events, allowing security teams to prioritize their investigations based on the severity and relevance of the incidents. QRadar’s correlation engine identifies patterns indicative of security threats, helping analysts focus on critical incidents and respond promptly to mitigate potential risks.
36. Explain the concept of QRadar Log Source Types.
Ans:
QRadar Log Source Types represent predefined configurations for specific log sources, defining how QRadar processes and interprets incoming log data. Each Log Source Type is tailored to a particular device or application, streamlining the integration process. QRadar supports many out-of-the-box Log Source Types, including common network devices, operating systems, and security appliances.
37. Describe the role of QRadar Custom Actions.
Ans:
QRadar Custom Actions enable security analysts to define specific responses and workflows based on rule outcomes. For example, custom actions can include sending notifications, triggering automated remediation scripts, or integrating with external systems. This flexibility enhances the effectiveness of incident response in QRadar, enabling organizations to customize their security operations based on unique requirements.
38. How does QRadar handle log source identification and categorization?
Ans:
QRadar handles log source identification and categorization using predefined Log Source Types and Log Source Extensions (LSX). Log Source Types facilitate the automatic recognition and configuration of supported log sources, while LSX allows the creation of custom parsers for non-standard log formats. This combination ensures that diverse log sources are accurately identified, categorized, and normalized within the QRadar SIEM environment, enabling comprehensive security event analysis.
39. What are QRadar Custom Event Properties, and how are they used?
Ans:
QRadar Custom Event Properties allow users to define additional attributes associated with events, enriching the context of security data. Users can create custom event properties to capture specific information not covered by standard event fields. These properties can then be used in rule creation, offence filters, and report generation, providing a more detailed and tailored analysis of security events. By leveraging Custom Event Properties, organizations enhance their ability to correlate events and gain insights into unique aspects of their security landscape.
40. Explain the significance of the QRadar Risk Manager.
Ans:
QRadar Risk Manager plays a significant role in enhancing the overall security posture of an organization by providing comprehensive risk management capabilities. It allows security teams to visualize and analyze network topology, identify vulnerabilities, and assess potential risks. By correlating vulnerability data with real-time security events, the QRadar Risk Manager helps prioritize remediation efforts and effectively allocates security resources.
41. What are the common challenges in QRadar deployment, and how can they be mitigated?
Ans:
- Limited Resources:
- Challenge: Insufficient hardware resources may lead to performance issues.
- Mitigation: Properly assess system requirements and allocate adequate CPU, memory, and storage resources.
- Scaling Issues:
- Challenge: Difficulty in scaling the solution to accommodate growing data volumes.
- Mitigation: Design a scalable architecture, consider distributed deployments, and optimize data retention policies.
- Integration Complexities:
- Challenge: Integrating QRadar with existing security infrastructure can be complex.
- Mitigation: Follow documentation, leverage available integrations, and use QRadar’s flexible APIs for custom integrations.
42. Describe the process of integrating QRadar with Active Directory for user and asset information.
Ans:
Integrate QRadar with Active Directory using LDAP configuration. Configure LDAP parameters, such as server details, bind credentials, and search base. Map LDAP attributes to QRadar fields to import user and asset information. Utilize this information for correlation, reporting, and user behaviour analytics. Implement scheduled syncs to update QRadar’s user and asset data. Enhance incident response by correlating security events with Active Directory information.
43. How does QRadar handle encrypted traffic and SSL decryption?
Ans:
Utilise SSL/TLS inspection tools to gain visibility into encrypted traffic.QRadar can ingest logs from SSL decryption appliances to analyze decrypted content. Define decryption policies based on organizational requirements and compliance.Configure QRadar to handle both encrypted and decrypted logs for comprehensive analysis. Integrate QRadar with proxy devices or decryption tools to obtain decrypted logs. Enable analysis of the full content of network traffic for improved threat detection.
44. Explain the concept of QRadar Custom Rules.
Ans:
- Rule Customization: Create rules tailored to specific security requirements or unique organizational contexts. Define custom criteria, thresholds, and response actions in QRadar rules.
- Specialized Use Cases: Address specific use cases or compliance requirements using custom rules. Regularly review and update custom rules to adapt to evolving threats.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test custom rules in a controlled environment before deploying them. Validate rule effectiveness through simulation or controlled testing scenarios.
45. What is the purpose of the QRadar Log Activity tab?
Ans:
The Log Activity tab provides a real-time view of log and event data in QRadar.Allows security analysts to monitor incoming logs, investigate anomalies, and respond to security incidents. Users can filter and search logs based on various criteria.Enhances the efficiency of log analysis and accelerates incident response. Customizable views enable users to focus on specific log sources, severity levels, or time frames.Provides flexibility in tailoring the display to individual or organizational needs.
46. Describe the role of QRadar Custom Offense Rules.
Ans:
Custom Offence Rules enable users to define criteria for generating offences.Enhances the platform’s ability to correlate events and identify specific security incidents. Users can prioritize offences based on custom criteria, ensuring relevant incidents receive
attention.Supports a more nuanced approach to incident response and risk management. Custom Offence Rules allow organizations to tailor offence generation to unique security policies.Provides flexibility in adapting QRadar to specific threat landscapes and compliance requirements.
47. How does QRadar handle log source parsing and normalization for non-standard log formats?
Ans:
Utilise LSX to create custom parsers for non-standard log formats.Allows QRadar to handle diverse log sources, ensuring effective normalization. Develop custom Device Support Modules (DSMs) to support unique log sources.Enhances QRadar’s ability to parse and normalize data from various sources. Keep custom parsers and DSMs updated to align with changes in log formats. Regularly test and validate parsing configurations for accuracy.
48. What is the purpose of QRadar Community Edition, and how does it differ from the full version?
Ans:
QRadar Community Edition is a free version of the QRadar SIEM solution.Provides a limited but functional version of the platform for small deployments and non-production use. Ideal for learning QRadar features, testing configurations, and gaining hands-on experience.Allows users to explore the capabilities of QRadar without a full-scale deployment. Suited for individual practitioners, security enthusiasts, and small businesses with modest security needs.Offers an opportunity to familiarise oneself with QRadar’s features and functionality.
49. Explain the process of creating a custom dashboard in QRadar.
Ans:
Access the QRadar Console and navigate to the Dashboard tab. Choose the “New Dashboard” option and configure the layout and widgets. Select and configure widgets based on the desired information or visualizations. Customize the dashboard with relevant data, graphs, and charts. Choose appropriate data sources for widgets, such as offences, logs, or network flows. Tailor the dashboard to specific security use cases or monitoring requirements. Personalize the dashboard to align with individual or team preferences. Save and share custom dashboards for collaborative use within the organization.
50. Describe the role of QRadar Domain Managers and their significance in a multi-tenant environment.
Ans:
Domain Managers facilitate the creation of isolated environments within QRadar.Each domain operates independently, allowing for the segregation of data and configurations. Administrators can configure settings specific to each domain, including log sources, rules, and users.Enhances customization and management flexibility in a multi-tenant environment. Provides centralized administration for managing multiple domains from a single interface. Streamlines the overall management of a complex, multi-tenant QRadar deployment. Ensures security isolation between domains, preventing unauthorized access to domain-specific data.Enhances data privacy and compliance in multi-tenant environments.
51.Describe the process of updating QRadar software and firmware.
Ans:
Before updating, backup QRadar’s configuration, including rules, custom properties, and reference sets. Visit IBM Fix Central to download the latest software and firmware updates for QRadar. Install updates using the provided installer, following IBM’s documentation for the specific version. After the update, validate system health, ensuring no critical issues or disruptions. Regularly apply patch updates to address vulnerabilities and bugs. Monitor system performance post-update to identify and address any unexpected issues.
52. How does QRadar handle event and flow data compression?
Ans:
QRadar automatically compresses event and flow data by default to optimize storage.
Utilises compression algorithms to reduce data size while maintaining integrity. Compressed data enhances storage efficiency, allowing historical data retention for longer periods. QRadar can decompress data for analysis and reporting.
53. What is the purpose of QRadar Log Source Extension (LSX) for Windows events?
Ans:
- Custom Parsing: LSX for Windows Events enables custom parsing of Windows log sources.
- Normalisation: Facilitates normalization of Windows event data for consistent representation.
- Field Extraction: Allows extraction of specific fields from Windows events for correlation and analysis.
- Handling Non-Standard Formats: Supports handling non-standard log formats associated with Windows events.
54. Explain the concept of QRadar Custom Functions.
Ans:
Custom Functions enable users to define unique processing logic for events and flows.
Enhances rule criteria by introducing user-defined functions for correlation. Enables adaptation to specific organizational needs and diverse security landscapes. Custom Functions can be utilized within custom rules to tailor QRadar to unique requirements.
55. Describe the role of QRadar Auto-Update in maintaining the system’s health.
Ans:
- Automatic Updates: QRadar Auto-Update automates applying software updates and patches.
- Maintaining Health: Ensures the system remains up-to-date with the latest fixes, improvements, and security patches.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Allows administrators to schedule updates during maintenance windows for minimal disruption.
- Health Monitoring: Monitors system health and automatically applies updates to maintain optimal performance.
56. How does QRadar handle network and asset discovery in a dynamic environment?
Ans:
QRadar monitors the network for new assets and environmental changes. Utilises protocols like SNMP and other discovery mechanisms to identify assets. Profiles assets dynamically based on network behaviour for accurate representation. Integrates with QRadar Vulnerability Manager for enhanced asset discovery and profiling.
57. What is the significance of QRadar Custom Event Processor Rules?
Ans:
Custom Event Processor Rules enable users to define custom event processing logic. Allows for specialized event handling based on user-defined criteria. Facilitates fine-tuning of the event processing flow within QRadar. Enables adaptation to unique security scenarios or specialized event requirements.
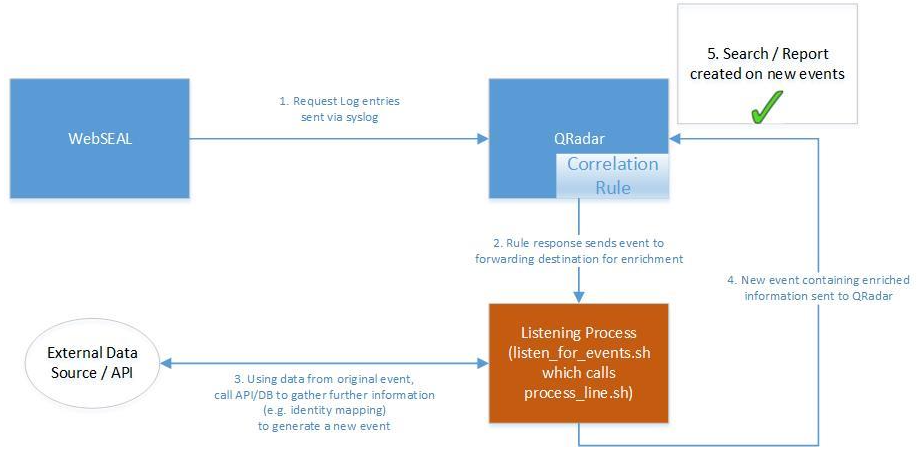
58. Explain the process of integrating QRadar with incident response platforms.
Ans:
- API Integration: Utilise APIs to integrate QRadar with incident response platforms.
- Event Forwarding: Configure QRadar to forward relevant events to incident response tools.
- Automated Workflows: Define automated response workflows based on QRadar events.
- Bi-Directional Communication: Establish bi-directional communication for real-time incident response.
59. How does QRadar support cloud-based log sources and flows?
Ans:
QRadar supports cloud log sources using standard protocols like Syslog, API, or custom connectors. Utilises flow logs from cloud environments for comprehensive visibility. Normalizes and correlates cloud-based logs and flows with on-premises data. Integrates with cloud APIs to pull relevant log and flow information.
60. Describe the role of QRadar Data Classification Rules.
Ans:
Data Classification Rules identify and categorize sensitive information within logs. Rules allow customization of criteria for recognizing specific data patterns. Supports creating security policies based on classified data. Assists in compliance efforts by identifying and managing sensitive data.
61. What is the purpose of the QRadar Community Forum, and how can it be beneficial?
Ans:
The QRadar Community Forum is an online platform for users, administrators, and security professionals to collaborate, share knowledge, and seek assistance regarding IBM QRadar. The forum fosters a community-driven approach where users can discuss best practices, troubleshoot issues, and exchange insights on deploying and managing QRadar. It provides a space for users to pose questions, share solutions, and engage with experts and peers in the field.
62. Explain the concept of QRadar Custom Log Source Types.
Ans:
QRadar Custom Log Source Types allow users to define and configure log sources that may not be supported by default Device Support Modules (DSMs). This capability is particularly useful when dealing with unique or proprietary systems that generate log data. By defining custom log source types, QRadar ensures accurate interpretation and correlation of events, enabling a more comprehensive and adaptable approach to log management within diverse IT environments
63. How does QRadar handle log source failures and troubleshooting?
Ans:
In QRadar, managing log source failures and troubleshooting is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the security information and event management (SIEM) system. Administrators can utilize the QRadar interface when log source failures occur to identify the specific issues causing the failures. The system provides detailed information on the failed log sources, including error messages and diagnostic data. Troubleshooting involves examining log source configurations, validating connectivity, and ensuring proper log format parsing.
64. Describe the role of QRadar Custom Flow Processors.
Ans:
QRadar Custom Flow Processors play a pivotal role in tailoring the analysis and processing of network flow data within the QRadar SIEM. These custom processors allow users to define specific flow processing rules and logic based on unique organizational requirements. The level of customization enhances the SIEM’s ability to detect and respond to network-related security incidents, ensuring that the flow processing capabilities align closely with the specific needs and intricacies of the organization’s network infrastructure.
65. What is the purpose of QRadar Asset Profiles?
Ans:
QRadar Asset Profiles provide a detailed and organized view of assets within an organization’s network—these profiles aggregate information about individual assets, including network and vulnerability data. Asset Profiles offer insights into the relationships between assets, their configurations, and associated vulnerabilities. This feature enhances the effectiveness of risk management, allowing organizations to focus on mitigating vulnerabilities that pose the greatest threat to their infrastructure.
66. How does QRadar handle correlation across different log sources?
Ans:
QRadar excels at correlation across log sources using a flexible and rule-driven correlation engine. Security administrators can create correlation rules that define conditions for correlating events from diverse log sources. By establishing correlations across different log sources, QRadar enhances the detection of sophisticated attacks and provides a more holistic view of the security landscape, allowing organizations to respond proactively to potential threats.
67. Explain the concept of QRadar Payload Protection.
Ans:
QRadar Payload Protection is a feature designed to enhance security by inspecting and analyzing the payload content of network traffic. This capability enables QRadar to identify malicious or suspicious content within the data payload of network communications. QRadar can detect threats such as malware, command and control communications, or data exfiltration attempts by analyzing the payload. Payload Protection is a crucial component of QRadar’s overall threat detection strategy, providing an additional layer of defence against advanced and evasive cyber threats.
68. Describe the role of QRadar Global Event and Flow Filters.
Ans:
QRadar Global Event and Flow Filters are vital in managing and controlling the data that enters the QRadar system. By configuring these filters, organizations can enforce consistent data normalization, apply data masking for privacy compliance, and focus on ingesting only the most relevant information. Global Event and Flow Filters optimize QRadar’s performance, reduce noise, and ensure that the SIEM platform processes and stores data efficiently.
69. How does QRadar handle DNS and DHCP logs for network visibility?
Ans:
QRadar effectively handles DNS (Domain Name System) and DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) logs to enhance network visibility. QRadar gains insights into domain resolutions, potential malicious domains, and abnormal DNS activities by ingesting and analyzing DNS logs. QRadar’s ability to correlate DNS and DHCP data contributes to comprehensive network visibility, allowing security teams to detect and respond to potential security incidents with a deeper understanding of network dynamics.
70. What is the significance of the QRadar Threat Intelligence app?
Ans:
The QRadar Threat Intelligence app significantly augments the SIEM’s capabilities with external threat intelligence feeds. This app enables QRadar to leverage up-to-date threat intelligence data, including indicators of compromise (IoCs) and known malicious entities. QRadar enhances its ability to detect and prioritize potential security threats by integrating threat intelligence into the analysis and correlation processes.
71. Explain the process of integrating QRadar with ticketing and remediation systems.
Ans:
- Ticketing System Integration: QRadar integrates with ticketing systems through APIs or syslog forwarding.
- Automated Incident Handling: Define rules to trigger automated responses and create tickets for incidents.
- Remediation Workflow Integration: Incorporate remediation workflows into ticketing systems for streamlined incident resolution.
- Bi-Directional Communication: Establish bi-directional communication for real-time updates between QRadar and ticketing systems.
72. How does QRadar handle multi-tenancy and data isolation?
Ans:
QRadar utilizes Domain Managers to create isolated environments for multi-tenancy. Each domain has its separate configurations, log sources, rules, and users. Ensures security isolation between tenants, preventing unauthorized access. Provides centralized administration for managing multiple domains from a single interface.
73. Describe the role of QRadar Custom Log Source Extensions.
Ans:
Custom Log Source Extensions allow parsing of non-standard log formats. Enables integration with log sources lacking predefined DSMs. Facilitates extraction of specific fields from logs for normalization. Supports a wide range of custom log formats used by various applications.
74. What is the purpose of QRadar Custom Reference Data?
Ans:
- Additional Context: Custom Reference Data adds context to events, enhancing analysis.
- User-Defined Attributes: Allows users to define and manage custom attributes for reference data.
- Enrichment of Data: Enhances the enrichment of event and flow data with organization-specific information.
- Integration with Threat Intelligence: Integrates with threat intelligence feeds to augment QRadar’s understanding of threats.
75. Explain the concept of QRadar Domain Log Activity.
Ans:
Domain Log Activity provides domain-specific views of logs and events. Enables security analysts to focus on logs relevant to their domain. Allows customization of log views based on individual or domain-specific needs. Enhances data privacy by restricting log access to domain-specific information.
76. How does QRadar handle distributed deployments for scalability?
Ans:
Distributed processing load through load balancing across multiple appliances. Deploy Event and Flow Processors in distributed configurations for optimal resource utilization. Utilise High Availability configurations to ensure continuity in case of appliance failure. Centralized Console provides a single point for managing and monitoring distributed deployments.
77. What is the significance of QRadar Network Insights?
Ans:
QRadar Network Insights provides enhanced visibility into network traffic. Utilises behavioural analysis to detect anomalous network activities. Aids security teams proactively hunt for network threats. Integrates seamlessly with QRadar for comprehensive security event correlation.
78. Describe the role of QRadar Custom Offense Building Blocks.
Ans:
- Customised Offence Generation: Custom Offense Building Blocks enable users to customize offence generation criteria.
- Tailored Offense Prioritization: Allows prioritization of offences based on user-defined parameters.
- Incident Customization: Facilitates customization of offence generation based on unique security policies.
- Fine-Tuning Offence Generation: Enhances fine-tuning of offence generation to align with evolving security needs.
79. How does QRadar handle log source override and event modification?
Ans:
QRadar allows administrators to override default log source configurations. Custom Log Source Extensions can be used for specific parsing requirements. Event Modification Rules enable users to modify event properties based on specific conditions. Enhances flexibility in normalization and ensures accurate representation of log data.
80. Explain the process of creating and managing QRadar Data Nodes.
Ans:
Define Data Nodes to distribute storage and processing across multiple appliances. Distributed data processing load through Data Nodes for optimal performance. Implement High Availability configurations for Data Nodes to ensure data availability. Manage data storage and retention policies across distributed Data Nodes.
81. What is the purpose of QRadar Data Retention Policies?
Ans:
QRadar Data Retention Policies define how long different types of data should be retained within the SIEM system. These policies help organizations align their data retention practices with regulatory requirements, compliance standards, and internal data management needs. By configuring retention policies, administrators can optimize storage usage, manage historical data for forensic analysis, and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
82. How does QRadar handle user and entity behaviour analytics (UEBA)?
Ans:
QRadar addresses User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) by employing advanced analytics to detect abnormal behaviours and potential insider threats. QRadar can identify deviations and anomalies that may indicate security incidents by establishing baselines of normal user and entity activities. UEBA capabilities include monitoring user behaviour, tracking privileged access, and identifying patterns indicative of malicious actions.
83. Describe the role of QRadar Custom Rule Responses.
Ans:
QRadar Custom Rule Responses allow security administrators to define specific actions to take when a correlation rule is triggered. These responses go beyond default actions and enable organizations to tailor their incident response processes. Custom Rule Responses may include automated actions, notifications, or integrations with external systems for orchestrated incident response. Organizations can ensure that their QRadar deployment aligns with their unique security policies and operational requirements by customizing rule responses.
84. What is the significance of QRadar Asset Discovery and Profiling Rules?
Ans:
QRadar Asset Discovery and Profiling Rules play a significant role in maintaining an accurate and up-to-date inventory of network assets. These rules enable QRadar to discover new assets automatically and profile their characteristics, including open ports, services, and vulnerabilities. By continuously updating asset profiles, organizations can enhance their overall security posture, prioritize vulnerability management, and ensure that the SIEM system reflects the current state of the network.
85. Explain the concept of QRadar Custom Flow Sources.
Ans:
QRadar Custom Flow Sources allow users to integrate and analyze flow data from custom or non-standard sources that may not be supported by default. Organizations can extend QRadar’s visibility into network traffic beyond conventional sources by defining custom flow sources. This flexibility enables security teams to capture and analyze flow data from diverse network elements, supporting a more comprehensive understanding of communication patterns and potential security risks.
86. How does QRadar handle log source exclusion and inclusion filters?
Ans:
QRadar allows administrators to manage log sources effectively through exclusion and inclusion filters. These filters allow organizations to tailor the types of logs ingested by QRadar, optimizing resource usage and focusing on relevant data. Exclusion filters enable the exclusion of specific logs or log sources that may not be critical for analysis. In contrast, inclusion filters ensure that only specified logs meeting certain criteria are processed.
87. Describe the process of integrating QRadar with endpoint protection solutions.
Ans:
Integrating QRadar with endpoint protection solutions involves configuring the SIEM system to ingest and analyze data from endpoint security tools. By integrating with these solutions, QRadar gains visibility into endpoint activities, threat detections, and security events at the device level. By leveraging information from endpoint protection solutions, QRadar provides a more comprehensive view of the security landscape, facilitating proactive threat hunting and rapid response to potential threats.
88. What is the purpose of QRadar Advanced Search?
Ans:
QRadar Advanced Search is a feature that empowers users to conduct highly specific and targeted searches within the SIEM system. This functionality goes beyond standard search capabilities, allowing users to define complex search queries based on multiple criteria, time frames, and data sources. It enables security analysts to retrieve precise information from vast datasets, facilitating in-depth exploration of security events and aiding in identifying patterns or anomalies that may require further investigation.
89. Explain the concept of QRadar Incident Forensics.
Ans:
QRadar Incident Forensics is a feature designed to streamline and enhance the investigative process following a security incident. This capability allows security analysts to reconstruct the timeline of events, visualize attack paths, and explore the details of a security incident in a granular manner. By combining advanced search capabilities with visualization tools, QRadar Incident Forensics empowers security teams to conduct thorough post-incident analysis and strengthen their cybersecurity defences.
90. How does QRadar handle log source auto-update and DSM versioning?
Ans:
QRadar simplifies the management of log sources and their associated Device Support Modules (DSMs) through automated updates and versioning. The Log Source Auto-Update feature ensures that QRadar remains current with the latest DSM versions, providing support for new log sources and improved parsing capabilities. Automated updates streamline the maintenance of DSMs, reducing the manual effort required for compatibility management. This approach enhances the overall efficiency and accuracy of log source management in QRadar.
91. Describe the role of QRadar Custom Offense Filters.
Ans:
- Customised Offence Filtering: QRadar Custom Offense Filters allow users to define specific criteria for filtering and organizing offences based on their unique requirements.
- Tailored Offense Prioritization: Users can customize filters to prioritize offences based on severity, specific rules, or other parameters relevant to their security policies.
- Focused Analysis: Custom Offence Filters enable security analysts to focus their analysis on specific offences, streamlining the investigation process.
- Automation Triggers: Custom Offence Filters can be associated with automated response actions, ensuring that specific responses are triggered based on defined offence characteristics.
- Enhanced Visibility: These filters enhance visibility into the security landscape by allowing organizations to categorize and prioritize offences that align with their unique security objectives.






