
Service-level management is the monitoring and management of the quality of service(QoS) of an entity’s key performance indicators(KPIs). The key performance indicators range from coarse-grained availability and usage statistics to fine-grained entity-contained per-interaction indicators. Service level management involves comparing actual performance with pre-defined expectations, determining appropriate actions, and producing meaningful reports.
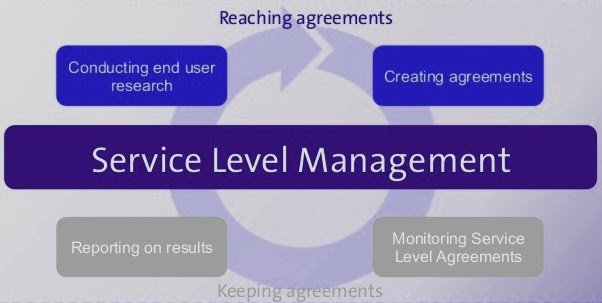
Scope Service Level Management Process:
- Below are the scope of activities that are done under the ITIL V3 Service Level Management Process.
- As described in ITIL V3, Service Level Management Process works closely with Availability Management and Capacity management for the purpose of doing the estimation and planning for the resource requirement.
- The ITIL Service Level Management also has direct corelation with Incident Management and Problem management to ensure that the required quality and levels of service are achieved by using the resources agreed with Financial Management.
- This process also ensures that appropriate Service Continuity Plan is implemented and agreed level of service can be provided to the customers in all circumstances.
- SLM is the primary interface with the customer and works together with Business Relationship Management process to ensure that the agreed IT services are delivered in a cost-effective, secure and efficient approach.
SLM Activities
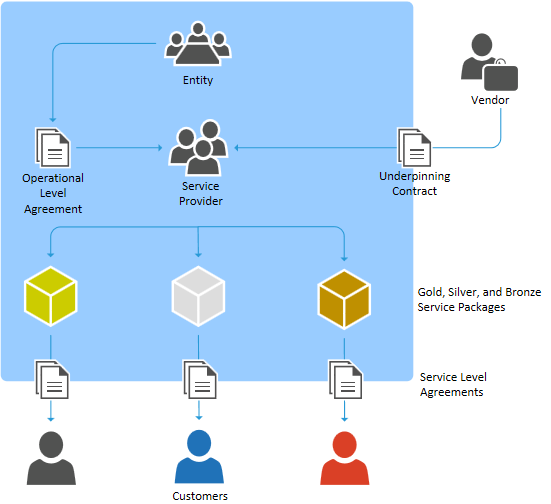
- The following diagram describes activities involved in SLM process −
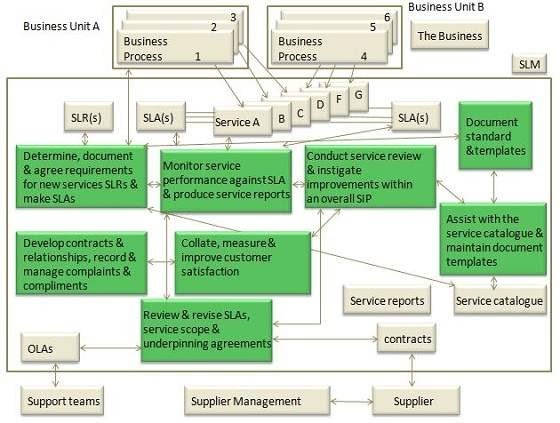
Service Level Management activities include:
- Identifying business requirements by working with business units
- Establishing the scope of services, timeliness, hours of operation, recovery aspects, and service performance
- Translating business requirements into IT requirements
- Developing and maintaining a service catalog, including costs for different tiers of service performance
- Performing gap analysis between business requirements and available services.
- Determining the costs related to services such that service goals satisfy business needs at a price the business can afford
- Drafting, negotiating and refining SLAs with the business units, ensuring business requirements are met and agreement from all parties involved
- Implementing SLAs
- Measuring SLA performance, reporting results and adjusting as necessary
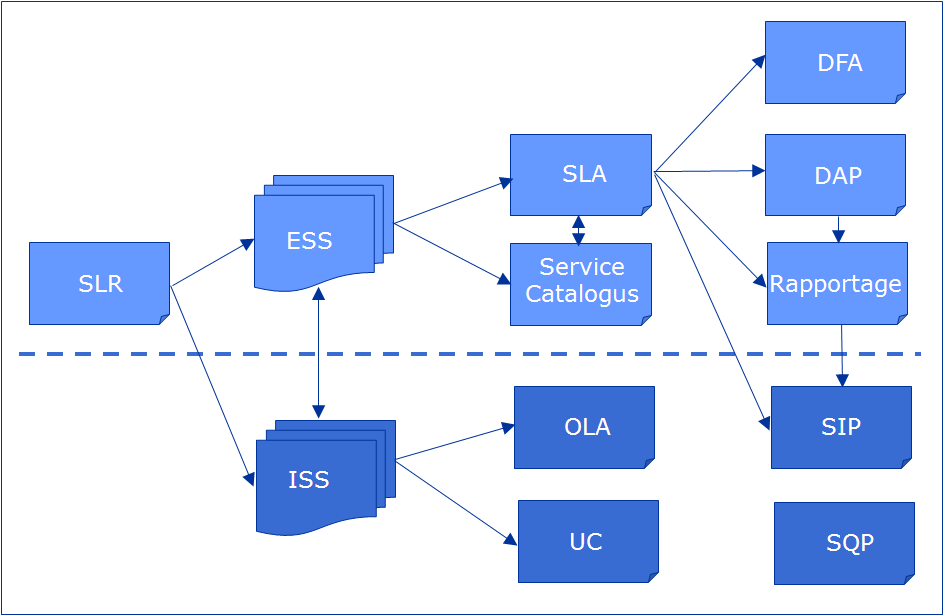
SLM deals with following two kinds of agreements:
1. Service Level Agreement SLA
2. Operational Level Agreement OLA
- Service Level Agreement SLA It is agreed document assuring the warranty with regard to level of service quality delivered by the service provider. It is between service provider and the customer.
- Operational Level Agreement OLA Unlike SLA it is agreement within the organization.
Service Level Management Process
- Service Level Management (SLM) is one of the well-defined main processes under Service Design process group of the ITIL best practice framework.
- According to ITIL V3 definition, it is the process responsible for the continual identification, monitoring, and review of the IT Service benchmarks specified in the service-level agreements (SLAs).
- ITIL Service Level Management Process (ITIL SLM) helps to achieve the target service level by ensuring that proper agreements are in place with internal IT support providers and external suppliers in the form of Operational Level Agreements (OLAs) and Underpinning Contracts (UCs), respectively.
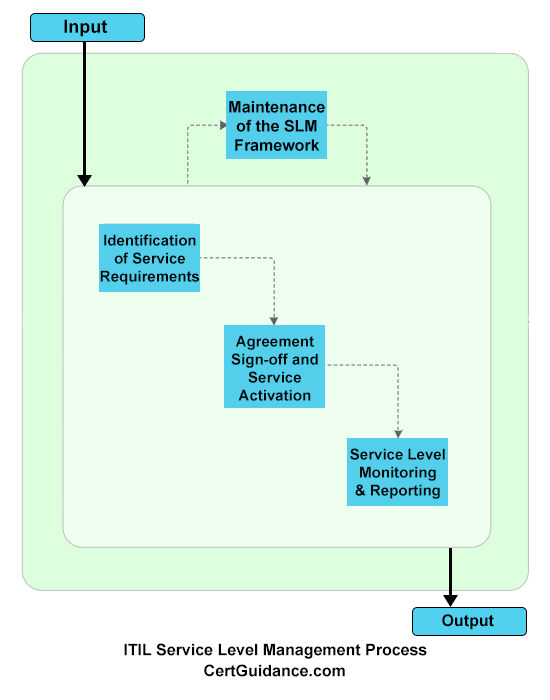
Service Level Management Sub-Process:
- As defined in ITIL V3, Service Level Management process has Four Sub-Processes operating under it.
- Below are the description and objective of those sub-processes, followed by a diagram illustrating the ITIL Service Level Management Process Flow:
1) Maintenance of the SLM Framework:
- Maintainance of SLM Framework sub-process is responsible for maintaining the underlying Service Level Management Framework.
- More specifically, it has the responsibility to design and maintain the underlying structure of the Customer Agreement Portfolio and also to provide templates for the various SLM documents.
2) Identification of Service Requirements:
- Used to document the desired outcomes, or requirements from the customer viewpoint, for any new services or major service modifications.
- This sub-process identifies the much-needed service requirements that are required to be documented and submitted for an initial evaluation, to check if the requirements are technically and/or economically viable, and to find alternatives if possible.
3) Agreements Sign-Off and Service Activation:
- Makes sure to have all relevant contracts signed off after completion of Service Transition and to check if Service Acceptance Criteria are fulfilled. This includes but not limited to sign-off SLAs, OLAs, underpinning contracts by both the Service Owners and the customers.
4) Service Level Monitoring and Reporting:
- Used to monitor the achieved service levels and compare them with agreed service level targets for preparing Service Level Reports. Those reports are then circulated to customers and other stakeholders to highlight the service quality.
Important Terminologies & Definitions: Customer Agreement Portfolio:
It is the database which contains information about all Service Agreements done with customers to provide the framework for delivering services.
Outline of Service Requirements:
- This is the desired outcome of a service, stated in terms of required service functionality (utility) and service levels (warranty).
Service Acceptance Criteria (SAC):
- A set of criteria or benchmark used for service acceptance testing to ensure that an IT service meets its functionality and quality requirements as per the customer requirement.
Service Level Agreement (SLA):
- SLA (A.K.A Service Level Agreement) is an agreement or contract between an IT service provider and a customer.
- In ITIL, SLA specifically describes the IT service, the responsibilities of the IT service provider and the customer, and documents the service level targets.
Service Level Report:
- The Service Level Report is the document of assessment of service provider’s ability to deliver the agreed service quality.
- It compares the agreed SLA with the actually achieved service levels and also includes other information, such as usage statistics of services, ongoing measures for service improvement, and any exceptional events.
- A Service Level Report is issued by the service provider for its customers, IT management and other Service Management processes.
Service Level Requirements (SLR):
- The Service Level Requirements (SLR) are documents containing the requirements for a service from the client viewpoint.
- In ITIL, SLR defines detailed service level targets, mutual responsibilities, and other requirements specific to a group of similar customers.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) is a derived form of SLR, created whenever any service enters a new stage of its life-cycle.
Operational Level Agreement (OLA):
- In ITIL, OLA (A.K.A. Operation Level Agreement) is an internal agreement between an IT Service Provider and other units of the same organization.
- An OLA supports the IT service provider in the delivery of services to customers.
- The OLA defines the goods or services to be provided and the responsibilities of both parties within the same organization.
- Operation Level Agreement (OLS) is not visible or communicated to customers.
- Few examples of OLA: There could be an agreement between the IT service provider and the procurement department to purchase hardware in agreed times, or it may be between the Service Desk and an IT Infra support team to provide Incident resolution in agreed time.
Underpinning Contracts (UC):
- In ITIL, Underpinning Contract is an agreement or contract between a Service Provider and a Third Party Provider for receiving some specialized services.
- The third party provides supporting services, which enables the service provider to deliver a service to a customer.
- An Underpinning Contract must be aligned with the customer-facing Service Level Agreements. For Example, A Service Provider may make an agreement with a third party supplier for servicing computer hardware in time of critical hardware failure.
SLM Document Templates:
- It broadly points to all the templates used for various documentation purposes under service level management process.
- A few examples are Service Level Requirements template, Service Level Agreement document, Operational Level Agreement document, Underpinning Contracts, Service Acceptance Criteria etc.
Service Level Management Roles & Responsibilities:
- Service Level Manager:
- This role is the Process Owner for ITIL Service Level Management Process.
- The Service Level Manager is responsible for negotiating Service Level Agreements and ensuring that these are met.
- This role is also responsible for ensuring that all ITIL Service Management processes, Operational Level Agreements and Underpinning Contracts are appropriate, and aligned for meeting the agreed service level targets.
- The Service Level Manager also monitors and reports the achieved service levels to all stakeholders.
- Service Owner:
- The Service Owner has the responsibility to deliver a particular service within the agreed service levels.
- Typically, this role acts as the counterpart of the Service Level Manager at time of negotiating Operational Level Agreements (OLAs).
- Often, the Service Owners are observed as the leader of a team of technical specialists or an internal support unit.
Benefits to implementing SLM processes
Immediate benefits to implementing SLM processes include:
- Enabling a better understanding between business units and IT
- Setting more accurate service quality expectations and effectively measuring, monitoring and reporting service quality
- Clearly delineating roles and responsibilities
- Providing the necessary flexibility for business to react quickly to market conditions
- Creating more accurate infrastructure sizing based on clearly defining service levels
- Avoiding or mitigating the costs of excess or insufficient capacity
- Providing discipline in supporting internal or external sourcing of IT services
- Service Level Management teams have close ties to business processes and customer management, Financial Management for IT Services, and Capacity Management. Capacity Management provides performance data to the SLM team for SLA sizing. Service Level Management passes information about service gaps and interruptions back to Capacity Management for capacity assessment and implementation of required changes.
Capacity Management supports Service Level Management by:
- Gathering historical and real-time data on service performance
- Determining current levels of service to use as a starting point in SLA negotiations
- Providing the performance data required to make informed decisions regarding SLAs
- Allowing you to experiment with multiple scenarios to determine resources needed to meet business unit goals
- Determining whether SLAs are sustainable on current hardware or if upgrades are required
- Tracking and reporting service performance against SLAs on an ongoing basis
- Proactively alerting IT of impending bottlenecks so they can be resolved before impacting service performance
As with all major projects, proper planning is key. HelpSystems recommends following these steps for implementing ITIL Service Level Management:
- Gather the data
Identify a SLM manager and form a team to spearhead the implementation. The team must perform several duties:
- Assess current state. Discover where and to what extent CM work is being performed today and document current reports, distribution lists, policies and procedures.
- Inventory tools and software currently used for monitoring, capacity planning, performance management, and charge back, all of which support SLM processes.
- Collect budget details that pertain to capacity management work.
- Perform a gap analysis to reveal areas that require process improvements, training, or software.
- Develop a project plan to migrate to the new organization based on required changes you uncovered.
- Build the plan
The implementation plan should:
- Establish the three major components of capacity management – people, processes and tools.
- Outline the costs necessary to sustain the new organization and build a preliminary budget.
- Determine where the service level manager should be placed in the organization, ideally reporting directly to the CIO, IT Director or within the service management group.
- Describe workflow, including data inputs, information outputs, and work processes.
- Allocate sufficient time for training the people performing the work.
- Identify any necessary work to acquire, consolidate and/or implement capacity and performance tools.
- Execute the plan.
You will want to execute the project plan in a series of steps:
- Assign the staff.
- Document and publish the processes. This is an important step that will likely take considerable time during initial implementation.
- Acquire and implement the tools. Ideally, a single tool would be used to provide the data and reporting necessary for accurate reporting of service performance.
- Inventory IT services and build a service catalog. Be sure service definitions meet Financial Management’s requirements, such that utilization data can be obtained and associated to a particular service.
- Identify, develop, negotiate and implement SLAs and OLAs. Close work with business units is required. SLAs and OLAs should be a page or two in length and include:
- Parties involved
- Start, end and review dates
- Scope of the agreement
- Description of the services provided
- Roles and responsibilities of each party involved
- Hours of operation
- Service availability
- Service reliability
- Support
- Throughput, transaction times and/or response times
- Change turnaround targets
- Security requirements and considerations
- Service continuity
- Service costs and how they are charged
- Service reporting
- Service incentives and penalties
- Identify any required services not currently provided by IT and resolve any contradictions in service requirements vs contingency recovery time, for example.
- Define metrics to measure success. Be sure to tie your metrics to business value, not technical measures. Metrics should be few in number, yet succinct and to the point.
- Build training materials and execute the training plan. Develop the training materials based on the processes you drafted and test staff members to ensure retention.
- Implement reporting and exception processes and procedures. Two types of reporting are necessary. High-level reporting, used to keep management informed, often takes the form of a dashboard, using colors to depict service quality. Be sure to report both current status and how it is trending. The second type of reporting is more detailed for use by the SLM team to identify problematic service areas.
- Initiate the ongoing work of SLM.
Begin the reporting process. Include the ability to:
- Automatically alert the SLM team when services are in danger of missing performance targets due to bottlenecks or sudden spikes in demand.
- Automatically alert the SLM team when trends show performance is approaching agreed-upon limits, so that corrective actions can be taken to prevent service outages or poor service performance.Schedule monthly or quarterly review meetings to discuss service performance results. Initiate any changes required as a result of unforeseen business events or changes in business priorities.
- Post implementation review.>
Document lessons learned and identify any changes that should be made to the process to facilitate future process migrations. Perform a post-implementation audit 6-12 months after completion to determine if the new processes are being adhered to and if you’re getting expected results.
CONCLUSION:
We hope that you have enjoyed the above article describing the ITIL Service Level Management Process, along with SML, SLA, OLA, and Underpinning Contract. Be with us to explore free training on Leading Technologies and Certifications.
Leave us some comments if you have any questions about Service Level Management – ITIL V3 Process, we would be very happy to help you.






