
We have compiled a comprehensive set of SAP EWM Interview Questions and Answers to aid in your preparation for the SAP EWM interview process. These questions cover a range of topics, ensuring you are well-equipped to handle the viva questions that an interviewer may pose. The SAP EWM domain offers abundant opportunities with many reputable companies globally, and the market share for SAP EWM stands at approximately 3.25%, indicating a significant demand. With this SAP Extended Warehouse Management certification guide, you can position yourself for success in your career. ACTE provides advanced SAP EWM Interview Questions, enabling you to excel in your interview and realize your aspirations as an SAP EWM Developer.
1. Explain SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM).
Ans:
SAP EWM is used to streamline the procedures involved in moving items and efficiently manage inventories in the warehouse, which allows the company to keep an eye on the flow of goods through warehouse as well as inbound and also outgoing procedures.
2. How does SAP EWM different from SAP Warehouse Management?
Ans:
- Similar to the warehouse management system, SAP EWM is a component of SAP supply chain management, but it offers more sophisticated and reliable capabilities to regulate critical warehouse operations.
- Extended Warehouse Management for SAP While EWM and warehouse management are the same, EWM provides additional features, including RF framework pickup and storage, warehouse organization, and more adaptable solutions for handling warehouse operations.
- SAP EWM creates additional features are not available in WM, resource areas activity areas labor management and work centers. An even more complete option for managing warehouse duties within the business is SAP EWM.
3. What are the main characteristics of SAP Warehouse management?
Ans:
- Using SAP EWM, can control Warehouse activities such as picking, posting, and managing storage Bins and good receipts.
- Can set an alert for changed data before the goods are received from EWM to the ERP system, reverse or correct the receipt of goods from EWM to the ERP system, and set an inbound delivery split from the EWM to ERP system.
- Perform deconsolidation of handling units containing various products before putting them away in the different storage sections.
- Find storage concepts using slotting for products and optimize the arrangement of the goods warehouse automatically.
4. What are the various deployment options in EWM?
Ans:
SAP EWM can be deployed on ERP server as a component within the supply chain management domain. SAP EWM is linked to the ERP to transactional and master data. CRM connectivity is required for utilising features like slotting and availability checks. Despite being hosted on the same server as SCM apps, SAP EWM is considered a distinct application. To enhance the performance, SAP EWM can be operated in a separate SCM environment as an alternative.
5. How does the SAP ERP system relate to the APO system via EVM or CM?
Ans:
SAP ERP and EWM are connected to facilitate the transfer of transactions and master data. The Core Interface (CIF) is the fundamental component. The core interface serves as standardised means of communication between the SAP SCM system and SAP Advanced Planning and Optimization APO. The ERP system contains master data like customer, material, and vendor information.
6. How do check the various menu structures of the EWM system?
Ans:
- Warehouse Monitor: Tcode – /SCWM/MON
- Maintain Inbound Delivery: Tcode -/SCWM/PRDI
- Maintain Outbound Delivery: Tcode SCWM/PRDO
- RF Environment: Tcode-/SCWM/RFUI
- Creating Storage Bin: Tcode- /SCWM/LS01
- Confirm Warehouse Task: Tcode- /SCWM/TO_CONF
- Warehouse Product Maintenance: Tcode- /SCWM/MAT1
7. Which organisational units make up warehouse management?
Ans:
- Warehouse Number
- Storage Type
- Storage Section
- Storage Bin
- Activity Areas
- Quant
8. What is a Storage Bin?
Ans:
Storage bins are physical locations within a warehouse where products are saved. They are situated at most basic level of the organizational system. When depositing an item in warehouse, it is imperative to offer a precise position.
9. What is the use of Activity areas in the Storage Bin?
Ans:
Storage bins are classified into distinct activity zones. It encompasses tasks such as selecting, storing, doing a physical count of goods. And can allocate the same Storage Bin to activity sections inside an activity.
10. What is Quant?
Ans:
A quantity of products in the Storage Bin is mentioned by the variable Quant. The quant is employed for an inventory management within the Storage Bin.
11. What are structural elements in Warehouse management?
Ans:
- Warehouse Number
- Storage Type
- Storage Section
- Storage Bin
- Activity Area
12. In a warehouse construction, what are the highest and lowest units?
Ans:
Highest Units:
- Executive Offices: The top levels of a warehouse structure often house executive offices, providing a strategic vantage point for management.
- Administrative Spaces: Headquarters and administrative areas are typically located on higher floors to oversee overall warehouse operations.
Lowest Units:
- Loading Docks: Ground-level loading docks provide for more efficient loading and unloading of products from trucks and vehicles.
- Storage and Warehousing Space: The main warehouse floor at or near ground level houses storage areas for inventory, utilizing various storage systems.
13. What is a storage section?
Ans:
This is the Storage category and signifies a collection of Bins that share identical attributes. Typically utilized storage sections include the categories are high-velocity or low-velocity goods, etc.
14. What is the work centre in a warehouse?
Ans:
A work centre in a warehouse is assigned to the Storage type and physical unit to perform packing, deconsolidation, or weighing activities. Storage type assigned to the work centre has a role of the work center, pick a point or pick point and identification. And can also more than one work center in storage type.
15. In what warehouse procedures do work centers?
Ans:
- Counting
- Quality check
- Deconsolidation
- Packing
16. In the SAP EWM system, how may a packing work center be created?
Ans:
- Warehouse
- Storage Type
- Inbound Section
- Outbound Section
17. Which are the different kinds of SAP EWM warehouse processes?
Ans:
- Stock Removal
- Putaway
- Internal Movement
- Goods receipt posting
- Goods issue posting
- Physical Inventory
- Cross Line Putaway
18. What is Value Added Services in Warehouse management?
Ans:
Value-Added Services (VAS) in warehouse management refer to additional activities or enhancements beyond the basic storage and distribution functions that can add value to products and improve overall customer satisfaction. These services go beyond traditional warehousing and involve customization, manipulation, or processing of products to meet specific customer requirements.
19. How do communicate the shipping and packing standards to employees?
Ans:
Effectively communicating shipping and packing standards to employees is crucial for maintaining consistency, efficiency, and quality in warehouse operations.
Documented Standards:
Develop comprehensive documentation outlining shipping and packing standards. This can include written procedures, checklists, and visual guides.
Training Programs:
Conduct employee training programmes to ensure they grasp the established criteria. Utilise a mix of textual information, hands-on demonstrations, and multimedia presentations.
20. What are the various constituents of Value-Added Order?
Ans:
- Order Header
- VAS activities to be performed
- Items
- Auxiliary Products
21. Where does manage Packaging specifications?
Ans:
To gain the packaging specification, follow this path:
- Simple access → EWM → Master Data → Packaging Specification → Maintaining Packaging Specification
22. How can direct Goods Issues in the SAP EWM system?
Ans:
The goods issue procedure in an expanded Warehouse management commences with an outward delivery request. The process of creating an outward delivery document starts in the ERP system. In the context of EWM, the delivery document is duplicated in the SAP EWM system for a pertinent items.
23. What is a Stock Removal Strategy?
Ans:
- The stock removal strategy is the method used to examine the storage bins for one or more products that require to be picked.
- In customizing for SCM extended Warehouse management, can customize a stock removal rule definition table.
24. What is a Denial Scenario?
Ans:
A denial scenario refers to a situation in which a user or entity is denied access to a particular resource, system, or service. This often occurs due to security measures, access controls, or authentication failures. In cybersecurity, denial scenarios can result from incorrect login credentials, unauthorized access attempts, or deliberate security measures to protect sensitive information.
25. When is the Denial scenario utilized in the EWM system for outbound delivery?
Ans:
If the Warehouse job is unable to fulfil the requested quantity in an outbound delivery request, system can be set up to create a pick denial. If an employee picks a lower quantity than what is specified in outgoing delivery and there is no extra stock available in the Warehouse,, have the option to configure a system to automatically deny the choice.
26. What is Storage Control?
Ans:
- A Storage control is employed to ascertain the motions of the products within the warehouse.
- It is used to carry out the procedure of storing or removing items in Warehouse.
27. What are the different types of Storage Control?
Ans:
- Access Control
- Data Lifecycle Management (DLM)
- Quality of Service (QoS) Control
- Volume and Capacity Control
- Backup and Recovery Control
- Data Compression and Deduplication
28. Which component is prioritized in the execution sequence of ComBined Storage Control?
Ans:
In SAP Extended Warehouse Management, process-oriented storage control is performed initially, followed by a layout storage control. The layout storage control examines if the put-away step is feasible in the warehouse layout view and adjusts a put-away or stock eliminate accordingly.
29. Which transactions lead to transfer orders for the internal transfer of partial product quantities?
Ans:
Stock Transfer Posting:
Transaction Code (SAP): MB1B
Description: Transfers stock between different storage locations within the same plant, allowing for partial quantities.
Transfer Order Creation:
Transaction Code (SAP): LT01
Description: Initiates the creation of a transfer order for the internal movement of materials, including partial quantities.
30. What is system-controlled pick, pack, and pass of items distinct from user – controlled?
Ans:
Need a Warehouse order generation rule that facilitates a prioritized development of Warehouse orders for pick, pack, and pass procedure. The classification groups for this are:
Automated:
- The system-driven choice finds the sequence of Warehouse orders in the top Warehouse.
- The order is decided based on the assigned sort sequence in configuration.
- Configuration options for accessing activity zones.
Driven by user:
- In the user-driven option, the sequence is found manually during execution.
- This implies that the material flow system is capable of performing the task.
31. What are the different components of VAS order?
Ans:
- Order header
- VAS Activities to be performed
- Items
- Auxiliary products
32. What are common Control fields in Replenishment?
Ans:
- Minimum stocking quantity
- Maximum stocking quantity
- Replenishment quantity
33. In the EWM system, what are pick pack and pass of goods?
Ans:
This is utilized to control the selection, packaging, and movement of items in the warehouse’s activity zones. The process flow is the same as for a typical RF process, and it can be used in an RF environment. Goods are transferred from activity area to activity area in pick, pack, and pass until they reach the system’s target point.
34. What is the definition of automatic and direct replenishment?
Ans:
The automatic replenishment process is initiated once the Warehouse task is confirmed. Direct Replenishment is initiated when a pick request is canceled and can only be carried out in situations when bins are fixed. The system determines the replenishment based on the highest and the lowest quantities. Picket-based direct replenishment is executed on the assumption of a Storage Bin amount of null.
35. What is utilizing Physical Inventor in SAP EWM?
Ans:
To comply with the financial accounting and tax rules, may need to conduct an accurate inventory to find the worth of inventory in the Warehouse. The physical inventory process is concerned with the counting warehouse’s physical inventory and obtaining counting results. Management can utilize physical inventory to count inventory so products can be supplied or corrected.
36. What are the different types of Physical inventory?
Ans:
- Periodic Physical Inventory
- Continuous (Cycle) Counting
- ABC Analysis
- Selective Inventory
- Perpetual Inventory
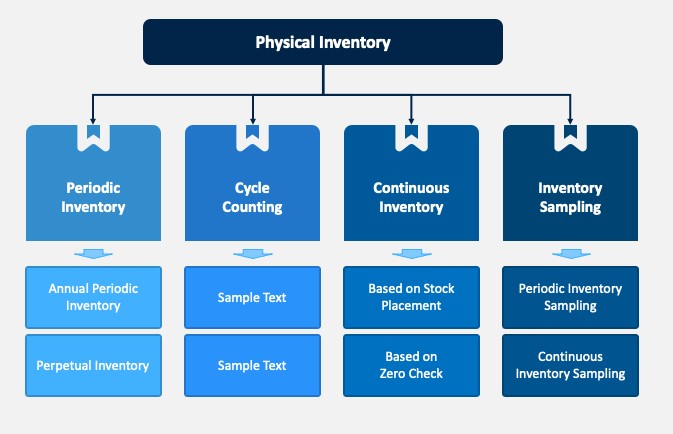
37. Which physical inventory processes does the SAP system support?
Ans:
Mobile Data Entry:
- Enabling the use of mobile devices for data entry during physical inventory counts, improving accuracy and efficiency.
Statistical Inventory Sampling:
- Using statistical methods to select a representative sample of items for counting, providing an estimate of overall inventory accuracy.
Batch Input Processing:
- Allowing for the processing of large volumes of physical inventory data using batch input techniques to streamline the input process.
38. What is Ad-hoc Physical inventory?
Ans:
Ad-hoc physical inventory refers to a spontaneous or unscheduled physical counting of inventory that is not part of the regular or periodic inventory cycle. Unlike planned physical inventory processes, which are scheduled at predetermined intervals, ad-hoc physical inventory is conducted on an as-needed basis, often in response to specific situations or requirements.
39. What is the Slotting process in EWM?
Ans:
Slotting is the process in EWM to explain the most suitable parameters- Storage type, section, etc. Slotting places the goods in the Warehouse in a manner that offers the most optimal Storage and picking of goods.
40. What considerations should be taken into account when dealing with serial numbers?
Ans:
When working with products that necessitate serial numbers, it is essential to activate the quantity role SN (number of serial numbers). Failure to do so may result in errors when adjusting the delivery quantity. Additionally, an Item type designed for products requiring serial numbers for all items can be employed.
41. What are Expected Good Receipts?
Ans:
Expected good receipts are used to generate the inbound deliveries. And can also generate goods receipts in the EWM system without an inbound delivery.
Advantages of using good receipt:
- This process occurs in EWM system only.
- If the ERP system is down, the expected goods receipt can still be executed in EWM.
- Anticipated goods receipt can be used as a preview of goods receipt as it is based on information from the production order.
42. What is Cross docking in the SAP EWM system?
Ans:
Using cross-docking may reduce the costs related to transporting goods in a warehouse and minimize the time it takes to deliver them. Cross docking entails a solitary movement of merchandise from the Goods Receipt Zone to the Goods Issue Zone. It is applicable only when the sequence in which the stock is taken out is not explained by the First in, First out concept.
43. What are the different types of cross-docking?
Ans:
- Transportation cross-docking
- Merchandise Distribution
- Push deployment
- Pick from goods receipt
- Opportunistic Cross-docking
44. What is the use of the RF framework in the EWM system?
Ans:
RF is a radio frequency mobile data entry in SAP EWM. It facilitates quick contact between the warehouse staff and EWM system. The RF framework offers options for connecting to the SAP system, both browser-based and GUI devices. It is possible to create screen templates and merge them into a display profile.
45. What occurs if the order item has no storage location for picking?
Ans:
- When no storage location for picking is specified in an order item, it can lead to operational challenges within a warehouse or distribution centre.
- Storage locations play a crucial role in the logistics process, determining where goods are stored and picked within a facility.
46. What is the SAP EWM system?
Ans:
SAP EWM is the element of SAP offer Chain Management (SAP SCM) and encourages inventory management and movement of products in warehouses. The multi-client warehouse management resolution was designed for giant distribution centers with difficult and extremely machine-driven processes.
47. Is SAP EWM good?
Ans:
The best-of-breed warehouse solutions well in more turnout, standalone, automated, specialist operations, wherever more performance is crucial. In distinction, SAP EWM scores well wherever there’s a desire for a higher level of integration between the warehouse, production, internal control and transport.
48. Justify the configuration of the organizational structure SAP EWM.
Ans:
When no storage location for picking is specified in an order item, it can lead to operational challenges within a warehouse or distribution center. Storage locations play a crucial role in the logistics process, determining where goods are stored and picked within a facility. Take new answer.
49. Justify SAP Extended Warehouse Management EWM.
Ans:
SAP EWM is employed to efficiently manage inventory in the Warehouse and to support the process of product movement. It permits the corporations to regulate their Warehouse inward and departing processes and the movement of products in a Warehouse.
50. How do SAP Warehouse Management’s core options measure up?
Ans:
Using SAP EWM Will be able to maintain warehouse activities- choosing, posting and managing storage bins and receipts. Can set alerts for changed information before product receipt from EWM to ERP system, correction of the products receipt from EWM to the ERP system and an inward delivery split from the EWM to the ERP system.
51. What square measures the different preparation choices in EWM?
Ans:
SAP EWM is considered to be installed in an ERP server; it is also considered an application within the context of offer chain management. In order to access master information and group actions, SAP EWM is coupled with ERP. Additionally, connectivity with CRM is required for slotting and availability check.
52. What is the employment of Activity areas in Storage bins?
Ans:
Storage bins square measure more classified within activity space. It includes activities such as choosing, golf shot away or a physical inventory. As per activity, able to assign a similar storage bin to more activity areas.
53. What is SAP EWM in combination with SAP S/4?
Ans:
A basic embedded EWM practicality is accessible to anyone with SAP S/4HANA license with advanced options on the market via extra license. Shoppers could select an embedded EWM for several reasons.
54. What is a piece Center in a Warehouse?
Ans:
A work center in the Warehouse is assigned to the storage sort and a physical unit to perform packing, deconsolidation or advisement activities. Storage sort assigned to the work center encompasses the role of labor center, choose purpose or choose purpose and identification. Able to additionally put together quite a piece center during storage sort.
55. Where does one use Work Centers in Warehouse processes?
Ans:
The work center will be used for a subsequent the subsequent:
- Packing
- Deconsolidation
- Counting
- Quality check
56. Differentiate Direct and Indirect labor.
Ans:
| Feature | |||
| Definition | Tasks directly related to physical handling of goods | Tasks supporting warehouse operations, not directly handling goods | |
| Nature of Work | Hands-on activities impacting inventory movement | Broader responsibilities indirectly contributing to operations | |
| Performance Metrics | Metrics include pick rates, accuracy, on-time delivery | Metrics involve team management, process adherence | |
| Resource Utilization | Direct involvement in resource-intensive physical tasks | Focus on efficient resource utilization through oversight | |
| System Integration | Integrated into SAP EWM processes with real-time monitoring | Utilizes SAP EWM for reporting but not direct process integration | |
| Examples | Picking, packing, loading, replenishment | Supervision, quality control, administrative tasks |
57. Which area unit is entirely separate from the storage method variations?
Ans:
- Stock Removal
- Putaway
- Internal Movement
- Goods receipt posting
- Goods issue posting
- Physical Inventory
- Cross Line putaway
58. What area unit the various elements during additional Order?
Ans:
A Value additional services order consists of the following:
- Order Header
- VAS activities to be performed
- Items
- Auxiliary product (Packing material, labels, oil, etc.)
59. Does one perform direct merchandise issues in the SAP EWM system?
Ans:
The goods issue method in extended warehouse management starts with the outward delivery requests. The Unit -relevant in EWM, delivery documents are replicated within SAP EWM system.
60. What does one perceive by the Stock Removal Strategy?
Ans:
Stock removal strategy could be the technique of deciding storage bins for one or additional product to be picked. Able to customize a stock removal rule definition table in customizing for SCM extended warehouse management.
61. What area unit is the dealing obtainable?
Ans:
LT01: Create A Transfer Order while not supplying an Object (transaction code LT01).
LT10: Produce the Transfer Order from the listing (transaction code LT10).
62. In external delivery system, what is the condition of denial that one observes?
Ans:
In the outward delivery system, a denial scenario refers to situations where the system or users encounter issues preventing the successful completion of a delivery process.
Authorization Issues:
Denial scenarios may arise due to authorization problems, restricting users from executing certain actions or completing the delivery process without proper permissions.
Stock Unavailability:
The denial situation can occur when there is insufficient stock available to fulfill the delivery, leading to delays or rejections in the outbound delivery process.
63. Does the EWM system’s Denial state of affairs apply to external delivery?
Ans:
When a warehouse task cannot meet the amount requested in associate degree outward delivery requests, the system will be organized to lift a choose denial. Just in case of stock discrepancy picked by associate degree worker, a smaller amount as per outward delivery and no various stock is on the market within the warehouse, able to set the system to execute choose denial.
64. What is the SAP EWM material flow system?
Ans:
The material flow system (MFS) permits to attachment of an associate degree automatic warehouse to SAP Extended Warehouse Management (SAP EWM) while not requiring further warehouse management unit. The SAP EWM system then holds back tasks for PLC as presently as these limits are exceeded.
65. Which area unit are SAP S/4HANA EWM readying options?
Ans:
Clients will choose from 2 reading choices loosely. They will choose either associate degree embedded EWM resolution or decentralized EWM. With 1610 unharness, SAP EWM was provided as an associate degree embedded application element.
66. Is Ewm activity space determined?
Ans:
EWM generates warehouse orders for each activity space. Once EWM generates warehouse tasks, it considers the activity space and copies attributes from this activity space, like deconsolidation cluster.
67. What is deciding pack and pass of products within the EWM system?
Ans:
This is accustomed to managing the selection, packing and transportation of products in activity areas in the warehouses. This will be utilized in RF environments normally and the method flow is the same as for traditional RF processes. In pick, pack and pass merchandise area unit captive from activity space to activity space until it arrives at destination purpose within system.
68. What is the SAP EWM layout?
Ans:
For this activity, SAP Extended Warehouse Management (SAP EWM) splits warehouse order into two: one from storage bin A to identification purpose, and a second from identification purpose to storage bin B. Move the merchandise employing a decided purpose throughout selection.
69. What is a replacement for SAP EWM?
Ans:
Replenishment is outlined as the movement of the products from warehouse to cargo locations. In SAP EWM, use predefined techniques for the replacement of storage bins. There are unit completely various replacement management fields outlined at the storage sort level or storage bin level. The information for management fields is entered manually within the system otherwise, a slotting method to outline these fields.
70. What area unit common management fields in Replenishment?
Ans:
- Minimum stocking amount
- Maximum stocking amount
- Replenishment amount
71. What happens outgoing process in SAP s 4HANA-embedded EWM?
Ans:
The outbound method is employed to ship ordered merchandise to the customers. This method initiate with the creation of a sales order associate who degreed an outgoing delivery. The outgoing delivery is replicated to the Embedded EWM system, wherever an associate degree outgoing delivery order is formed.
72. What is ODO in EWM?
Ans:
The outgoing Delivery Order (ODO) is formed mechanically from outgoing delivery requests. This can be a document containing all the information needed for triggering and observing the whole outgoing delivery method. From the ODO, outgoing Delivery is formed.
73. Why does one use Physical inventory in SAP EWM?
Ans:
To perform monetary accounting and tax laws will perform accurate inventory to urge the worth of a listing within the warehouse. The physical inventory method deals with the reckoning physical inventory of a warehouse and urges reckoning results. Physical inventory is utilized by the management to count inventory so that product is furnished or corrected.
74. What is Associate in Nursing Ad-hoc Physical inventory?
Ans:
The Ad-hoc physical inventory may be a style of continuous physical inventory and dead anytime throughout the financial year, an advertisement hoc physical inventory might become necessary.
75. What is the warehouse request in SAP EWM?
Ans:
The warehouse request may be a document that permits the process of warehouse activities for selected products. The warehouse activities for products embrace the following: selecting. Putaway. Stock transfer (within a warehouse).
76. What square measure Expected smart Receipts?
Ans:
Expected smart receipts square measure accustomed to the produce incoming deliveries. Able to conjointly produce product receipts within the EWM system while not associated with a Nursing incoming delivery.
Advantages of mistreatment smart receipt:
- This method performs within the EWM system solely.
- If the ERP system is down, able to still execute the expected product receipt in EWM.
- Expected product receipt relies on the information in order therefore it is used as a preview of product receipt.
77. What is cross-moorage in the SAP EWM system?
Ans:
Cross moorage allows scaling back the prices of product transportation within warehouse and shortening the time required for delivery. Cross moorage solely creates a one-movement GR Zone to GI Zone and may solely be used if stock for removal is not determined by 1st in 1st out.
78. What is the utilization of the RF framework in the EWM system?
Ans:
- In SAP EWM, RF stands for frequent mobile information entry that enables real-time communication between the warehouse workers and also the EWM system.
- RF framework supports every browser-based mostly graphical user interface device to attach to the SAP system. Able to produce screen templates and merge them to the alleged show profile. This show profile is appointed to a presentation device.
79. Is the case for affiliation theme between EWM and PLC?
Ans:
- Any warehouse employing a heritage PLC system will originate SAP MFS in a very manner that everyone its.
- Adapt message traffic between the SAP EWM and PLCs.
80. Is SAP EWM a part of Hana?
Ans:
SAP EWM is a NEW practicality that SAP provides for the management of inventory in several specific locations within new unleash S/4 HANA. Though not required altogether by organizations, it’s a module every supply authority or professional person ought to comprehend.
81. Is SAP EWM a part of ECC?
Ans:
While SAP WM was WMS core a part of the computer code Suite, EWM was perceived as a specialized product tailored towards more volume warehouses requiring a lot of advanced processes the perception was conjointly fed by a lot of complicated decentral designs requiring EWM to run severally and interfacing with computer code backend.
82. What is Ewm within the offer chain?
Ans:
SAP EWM is the component of SAP AG’s offer Chain Management Suite of solutions. The Extended Warehouse Management product is an Associate in Nursing integrated software system platform for versatile, machine-controlled support for process product movements and for managing inventory within the warehouse.
83. What is the SAP warehouse Number?
Ans:
In SAP ERP, warehouse variety is employed to represent a physical warehouse wherever all the fabric is held. Warehouse numbers square measure created within the ERP system and to activate it, employ a mixture of plant and storage location appointed to present plant with the individual warehouse variety.
84. What is the storage kind in SAP EWM?
Ans:
- High rack cargo area.
- Bulk cargo area.
- Fixed bin cargo area.
- General cargo area.
- Pallet cargo area.
85. What is the activity space in SAP EWM?
Ans:
An activity space may be a logical grouping of storage bins for the aim of away, picking, inventory or renewal. For example, a warehouse may choose outgoing orders employing a “U” chosen path and an “S” or “Z” chosen path for stock putaway and renewal.
86. What is SAP basic knowledge?
Ans:
One of the top enterprise resource planning programmes is SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products), which combines different business operations to optimise data and procedures inside a company.
87. Why select the SAP EWM strategy?
Ans:
The SAP EWM application provides more repositioning solutions for placing away, picking, packing, internal movement in the warehouse, etc. These areas help manage a high volume of product movements in and out of the warehouse.
88. What is SAP straightforward Access?
Ans:
This is a user-specific purpose of entry into the SAP system. The user menu contains solely those things that just ought to perform the daily tasks, like transactions, reports, and net addresses.
89. What is Fiori?
Ans:
- Fiori is an efficient application, delivering a role-based user expertise that may be personalized across all lines of business, tasks and devices.
- It uses tiles to encapsulate commonplace tasks such as viewing sales orders or approving timesheets.
90. What is capacity check in EWM?
Ans:
Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) can check the capacity of the storage bin using the following factor. The system checks the weight of the product to be put away against the available weight of a storage bin.






