
We have curated a comprehensive set of SAP SRM Interview Questions and Answers to empower you in preparing for SAP SRM interviews. Whether you are a fresher or an experienced candidate, this compilation covers the most commonly asked SAP SRM viva questions, ensuring you are well-equipped to respond confidently during your interview. In this extensive list, we have included both fundamental SAP SRM interview questions and more advanced queries to cater to candidates at all experience levels. Each question is accompanied by detailed answers to aid in your understanding and preparation for a successful job interview. With 100 important SAP SRM programming questions, this guide serves as a valuable resource for those seeking to excel in SAP SRM interviews and secure a rewarding position in their careers.
1. What is SRM?
Ans:
Supplier Relationship Management is referred to as SRM. It is an expanded version of ERP in which data is exchanged across the SAP R/3 and SRM screens to improve vendor coordination and completely eliminate paperwork and needless misunderstandings. It works well for businesses with a high volume of users who can buy materials directly from the cart by selecting items from the catalogs that are available.
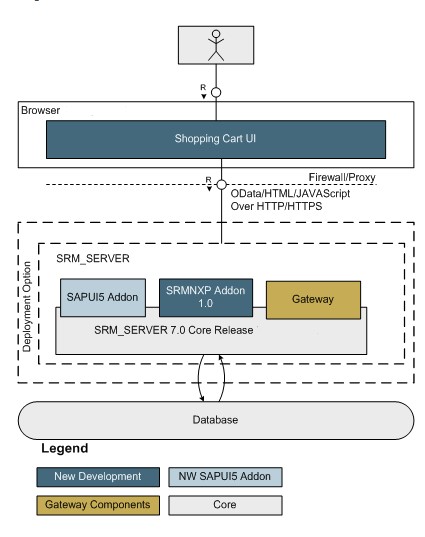
2. Go over the applications of SAP.
Ans:
- Long-term cost reductions: These allow businesses to get a closed loop from source to pay.
- Contract Compliance: It makes enterprise expenditures visible and boosts procurement organization effectiveness.
3. How can a Live Auction Be Created?
Ans:
- Access the auction creation tool in your chosen platform.
- Define auction details such as type, duration, and participants.
- Set bidding rules and increments for transparency.
- Upload item details, specifications, and any relevant documents.
- Invite qualified suppliers and stakeholders to participate.
- Conduct a pre-auction briefing to clarify rules and expectations.
- Launch the live auction at the scheduled time.
- Monitor real-time bids and provide updates to participants.
- Close the auction, declare the winner, and finalize the transaction.
- Document and archive auction results for future reference
4. List the various fields in Central Contact.
Ans:
- Various Tabs – Header Tab, Overview Tab And Distribution Tab in contract.
- Target quantity and value
- Release Value
- Basic Contract
- Item Category
- Normal
- Product Category
5. Do Mappings Need to Be Created Again Every Time?
Ans:
No, mappings do not need to be created again every time. Once mappings are established between different entities or systems, they can be reused unless there are significant changes in the data structures or business requirements.
6. In SRM 7.0, what will be true regarding master data?
Ans:
In SRM 7.0, master data is typically shared between SAP ERP and SRM seamlessly. This ensures consistency and accuracy in information related to suppliers, products, and services. Changes made in one system are reflected in the other, providing a unified view of master data across the procurement landscape.
7. What is the SAP SRM Key Business Process Name?
Ans:
- Procure To Pay
- Catalog Management
- Centralize Sourcing
- Centralized Contract Management
- Supplier Collaboration
8. What are SAP supplier relationship management’s advantages?
Ans:
- Streamlined procurement processes for better efficiency.
- Enhanced collaboration with suppliers through a centralized platform.
- Improved visibility into the supply chain, reducing risks.
- Better control over spend and compliance with procurement policies.
- Increased negotiation power with suppliers. f. Real-time data analytics for informed decision-making.
- Integration with other SAP modules for end-to-end business processes.
- Enhanced supplier performance management.
- Automation of manual procurement tasks for time savings.
- Improved supplier relationships leading to long-term cost savings.
9. How does the SRM organizational structure function?
Ans:
The SRM org structure serves the purpose of organizing and managing procurement-related information within SAP Supplier Relationship Management. It defines the relationships and hierarchy among different organizational elements like purchasing groups, organizational units, and buyers. This structure helps in efficiently managing procurement processes, assigning responsibilities, and ensuring clear communication between different stakeholders involved in the procurement lifecycle.
10. Which multilevel hierarchies are included in regular delivery?
Ans:
- Product Category Hierarchies
- Supplier Hierarchies
- Central Contract Hierarchies
11. How are SAP SRM and SAP MM related?
Ans:
SAP SRM is closely linked with SAP MM (Materials Management) through integration that facilitates seamless procurement processes. This integration ensures real-time data exchange between the two modules, allowing for synchronized information on materials, vendors, and purchase orders. It enables procurement professionals to leverage the functionalities of both systems for comprehensive procurement management.
12. Distinction between the roles of a business partner and a partner.
Ans:
| Feature | |||
| Definition | An entity or person with whom the company has a business relationship | Refers specifically to organizations that engage in procurement activities within SAP SRM | |
| Scope | Extends beyond procurement and can include any business relationship (e.g., customers, vendors, contacts) | Pertains specifically to procurement-related collaborations within the SAP Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) module | |
| Roles | Can play various roles, such as customer, vendor, or contact | Primarily focuses on the vendor or supplier role in the procurement process within SAP SRM | |
| Relationships | Various business relationships | Primarily associated with supplier relationships in SRM | |
| Integration with SRM | Linked to SRM processes but not exclusive | Integral to SRM processes, key in supplier activities |
13. Which SRM number ranges are configure?
Ans:
Number ranges configured in SRM include those for shopping carts, purchase orders, contracts, and other documents. These ranges help in assigning unique identifiers to different types of transactions within the SRM system, ensuring proper tracking and management of procurement activities.
14. What is an associate in business?
Ans:
An associate in business in SAP typically refers to a professional who possesses foundational knowledge and skills in SAP software solutions. This role involves supporting various business processes within an organization by utilizing SAP applications for tasks such as data management, reporting, and system configuration. Associates in business with SAP expertise contribute to the effective utilization of SAP technologies to enhance operational efficiency and decision-making.
15. Do users need to Be considered as authentic members of SRM?
Ans:
Administrators must give suitable responsibilities and authorizations to users in order for them to be legitimate elements of SRM. This guarantees that users have the rights they need to accomplish their jobs inside the SRM system, such as generating shopping carts, executing purchase orders, or managing contracts.
16. How does ERP cover and upload the central contracts?
Ans:
Uploading and covering central contracts in ERP involves transferring contract data from SAP SRM to SAP ERP. This integration ensures that central contracts created in SRM are available and covered in the ERP system, allowing for consistent and coordinated procurement processes across the organization.
17. Why the company should include it in the SAP application?
Ans:
- SRM, or Supplier Relationship Management, is a module in SAP that focuses on optimizing and streamlining procurement processes.
- Companies should add this module to their SAP application to achieve better supplier collaboration, improved procurement efficiency, enhanced spend visibility, and overall cost savings.
- It centralizes procurement activities, providing a unified platform for managing supplier relationships and strategic sourcing.
18. What Is Purchasing Organization?
Ans:
- A Purchasing Organization in SAP is an organizational unit responsible for procurement activities within a company.
- It is allocated a business code and is in charge of making purchase orders, administering contracts, and engaging with vendors on the organization’s behalf.
19. How do integrate sap ERP with sap SRM to upload contracts?
Ans:
SAP ERP integrates with SAP SRM for contract uploads through middleware or direct integration. This integration ensures that contracts created in SAP SRM are seamlessly transferred to SAP ERP, maintaining data consistency and allowing for efficient procurement management.
20. Are number ranges configured in SRM?
Ans:
Configuring number ranges in SRM is essential to ensure that unique identifiers are assigned to different types of documents and transactions. This configuration helps in proper tracking, reporting, and management of procurement-related activities within the SRM system, maintaining data integrity and consistency.
21. Describe some of the tables that are available in the SRM.
Ans:
- BBP_PD: Document Header Data
- BBP_PDBEH: Document Item Data
- BBP_DOCUMENT_TAB: Document Index Table
- BBP_DOCUMENT_TAB: Document Index Table
- BBP_DOCUMENT_TAB: Document Index Table
- BBP_DOCUMENT_TAB: Document Index Table
- BBP_PDBEH: Document Item Data
- BBP_PD: Document Header Data
- BBP_PDHIST: Document Header History Data
- BBP_PD: Document Header Data
22. What does SRM organization structure offer?
Ans:
SRM Org Structure serves to organize and manage procurement-related information. It explains relationships and hierarchy among organizational elements, such as purchasing groups and organizational units. This structure helps in efficiently managing procurement processes, assigning responsibilities, and ensuring clear communication between the stakeholders.
23. Is something stuck in the R/3 queue while replicating from the backend?
Ans:
If something is stuck in queue of R/3 during replication from the backend, check and resolve the underlying issues in the SAP R/3 system, such as network connectivity, system performance or configuration errors to allow smooth data transfer.
24. Is it possible to combine the SAP SRM and ERP procurement functions?
Ans:
Yes, procurement activities between SAP ERP and SAP SRM may be connected. This interface guarantees that data flows seamlessly between the two systems, enabling centralised procurement administration and consistency in information about suppliers, contracts, and purchasing operations.
25. With a powerful ECC, why does the client develop EC but not classic?
Ans:
The decision to develop in Extended Classic (EC) or Classic deployment in SAP SRM depends on specific business requirements. If strong integration with SAP ECC (Enterprise Core Component) is needed, EC is preferred as it provides real-time integration between SRM and ECC.
26. In a standalone scenario, where does AI processing occur for shopping carts?
Ans:
In a standalone scenario, AL (Application Layer) processing for the shopping cart occurs within the SRM system itself. The standalone scenario implies that SRM operates independently without direct integration with other SAP systems.
27. What Is the Process of Supplier Self-Service?
Ans:
Supplier Self-Service Process involves providing suppliers with access to a portal where they can perform various tasks, such as updating their information, submitting bids, and managing contracts. This process enhances collaboration, reduces manual efforts, and improves the overall efficiency of the procurement cycle.
28. Why is there a tab for import status?
Ans:
The Import Status tab in SRM is used to track and monitor the status of data imports. It provides information about the success or failure of data imports, helping administrators identify and address issues related to data consistency and accuracy.
29. What is an ITS URL?
Ans:
- ITS URL (Internet Transaction Server Uniform Resource Locator) is the web address used to access the Internet Transaction Server.
- It provides a link to the ITS, allowing users to interact with SAP applications through a web browser.
30. Describe supply management works in an organization.
Ans:
- Supply Management in an organization involves strategic planning and execution of processes related to sourcing, procurement, and supplier relationship management.
- It aims to optimize the supply chain, ensure the availability of goods and services, and achieve cost-effective and sustainable procurement practices.
31. Why would local bid invitation with an internal number range?
Ans:
Obtaining an internal number range for local bid invitations ensures systematic and traceable identification of each invitation. It helps in maintaining order and clarity in the procurement process, enabling effective tracking, reporting, and auditability of bid-related activities.
32. How do we use SRM?
Ans:
SRM, or Supplier Relationship Management, is used for streamlining and automating procurement processes. It acts as a centralised platform for managing supplier contacts, sourcing products and services, creating purchase orders, and optimising the procurement lifecycle.
33. What is the use of company code?
Ans:
The Company Code in SAP is a key organizational element that represents an independent legal entity within the enterprise. It is used for financial accounting and reporting purposes, allowing businesses to track and manage financial transactions separately for different legal entities.
34. When will live auction replace Rfx?
Ans:
The transition from RFX (Request for Quotation) to live auction typically occurs when organizations seek to foster competitive bidding in real-time. Live auctions provide a dynamic platform for suppliers to submit immediate bids, allowing buyers to achieve better prices and terms for goods and services.
35. How do SRM and MM Relate to one another?
Ans:
SRM and MM (Materials Management) are closely related modules within SAP. While MM focuses on internal procurement processes, SRM extends these capabilities to external procurement, emphasizing collaboration with suppliers, strategic sourcing, and contract management.
36. In the supplier evaluation process, which evaluation categories are included?
Ans:
- Various evaluation categories in supplier evaluation include performance, delivery, quality, and overall reliability.
- These categories provide a structured framework for assessing and measuring the effectiveness of suppliers in meeting business requirements.
37. What are SAP supplier relationship management workflows’ benefits?
Ans:
Workflows in SAP Supplier Relationship Management facilitate automated routing of documents and approval processes. The benefits include improved process efficiency, reduced cycle times, enhanced transparency, and better adherence to organizational policies and procedures.
38. SRM sub modules: What are they?
Ans:
SRM sub-modules include Supplier Self-Services (SUS), Sourcing, Contract Management, Procurement, and Catalog Management. Each submodule addresses specific aspects of the procurement process, contributing to overall efficiency and effectiveness.
39. What does the shopping cart wizard’s different steps involve?
Ans:
Steps in the Shopping Cart Wizard include:
- Entering item details
- Specifying delivery information
- Assigning cost centers
- Selecting suppliers
- Defining accounting details
- Confirmation
40. In SAP SRM, which are the main business processes?
Ans:
Key business processes in SAP SRM include:
- Supplier Identification and Onboarding
- Sourcing and RFx Management
- Contract Management
- Purchase Order Processing
- Catalogue Management
- Supplier Performance Management
- Procure – to-Pay (P2P)
41. What is Purchasing organization?
Ans:
In SAP, a Purchasing Organisation is an organisational entity in charge of a company’s procurement activities. It is allocated a distinct business code and is responsible for making purchase orders, maintaining contracts, and engaging with vendors on the organization’s behalf.
42. How can conduct a specific product or supplier search?
Ans:
To search for a particular product or supplier in SAP SRM, users can utilize the search functionality within the system. They can enter specific keywords, part numbers, or supplier names in the search bar, enabling them to quickly locate the desired product or supplier information.
43. What kinds of update requests are there?
Ans:
Types of update requests in SAP SRM include synchronous and asynchronous requests. Synchronous requests are processed immediately, while asynchronous requests are queued for background processing, allowing for more flexibility in handling large volumes of data.
44. Describe SAP Gui Manages the user’s output screen.
Ans:
SAP GUI (Graphical User Interface) handles the output screen for users by presenting a visual interface for interacting with the SAP system. It displays data, transaction results, and allows users to input information through various screens, enhancing the user experience and interaction with the application.
45. What is a Contract?
Ans:
In SAP SRM, a contract is a legal agreement between a buyer and a supplier outlining the terms and conditions for the provision of products or services. It outlines price, delivery timetables, and other pertinent data to ensure that all parties are on the same page.
46. What part of SAP SRM is catalog management?
Ans:
- Catalog Management in SAP SRM involves the creation, maintenance, and optimization of product catalogs.
- It enables users to browse and search for items, streamlining the procurement process by providing a centralized repository of standardized product information.
47. What part of SAP SRM is contract management?
Ans:
Contract Management in SAP SRM is a component focused on creating, managing, and monitoring contracts with suppliers. It includes features for defining contract terms, tracking compliance, and ensuring that procurement activities adhere to established contractual agreements.
48. How is contact and cooperation with suppliers handled by SAP SRM?
Ans:
SAP SRM handles supplier collaboration and communication through features like Supplier Self-Services (SUS) and collaborative procurement. SUS allows suppliers to access portal, update their information, and participate in bidding, while collaborative procurement ensures the seamless communication and information exchange.
49. What does SAP SRM’s sourcing component entail?
Ans:
The Sourcing component in SAP SRM involves the strategic sourcing process, including the creation of RFX (Request for Quotation), negotiation, and supplier selection. It encourages organizations in optimizing procurement by identifying the best suppliers and negotiating favourable terms.
50. How is purchase order management handled by SAP SRM?
Ans:
SAP SRM manages purchase order (PO) management by providing functionalities for creating, tracking, and managing purchase orders. It ensures that procurement transactions adhere to organizational policies, supplier agreements, and regulatory requirements, promoting efficiency in the procurement lifecycle.
51. In strategic sourcing, what is SAP SRM?
Ans:
- SAP SRM plays a crucial role in strategic sourcing by providing tools and functionalities for organizations to optimize their procurement processes.
- It facilitates strategic supplier identification, negotiation, and selection, ensuring companies can achieve cost savings, enhance supplier relationships, and make informed sourcing decisions.
52. How are other SAP modules integrated with SAP SRM?
Ans:
- SAP SRM integrates with other SAP modules through middleware and connectors.
- Integration points include SAP ERP for seamless procurement processes, SAP BW for reporting and analytics, and SAP CRM for customer relationship management.
- This interoperability ensures data consistency and streamlined business processes.
53. In SAP SRM, what is Supplier Evaluation?
Ans:
Supplier evaluation in SAP SRM entails reviewing and measuring supplier performance based on set criteria. It assists organisations in identifying dependable suppliers, improving communication, and making data-driven decisions to improve the overall efficiency of the procurement department.
54. How is procurement process automation handled by SAP SRM?
Ans:
SAP SRM handles procurement process automation by automating routine tasks such as purchase requisition creation, approval workflows, and purchase order processing. This automation reduces manual intervention, enhances efficiency, and ensures compliance with procurement policies.
55. In SAP SRM, what is the Supplier Collaboration Workspace?
Ans:
The Supplier Collaboration Workspace in SAP SRM is a collaborative platform that allows buyers and suppliers to interact efficiently. It provides a shared space for communication, document exchange, and collaboration on various procurement-related activities, fostering better supplier relationships.
56. How is contract lifecycle management handled by SAP SRM?
Ans:
- SAP SRM manages contract lifecycle management by providing tools for creating, storing, and managing contracts.
- It includes features for contract creation, monitoring compliance, and ensuring that contractual terms are adhered to throughout the lifecycle of the agreement.
57. In SAP SRM, what does Supplier Registration mean?
Ans:
Supplier Registration in SAP SRM involves the process of onboarding new suppliers.It allows suppliers to register their information, submit necessary documents, and undergo qualification processes. This ensures that the organization maintains an up-to-date and compliant supplier database.
58. What analytics and reporting on procurement does SAP SRM handle?
Ans:
- SAP SRM handles procurement analytics and reporting by providing robust reporting tools and dashboards.
- It enables users to analyze procurement data, track key performance indicators, and generate insightful reports for informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
59. Is SAP SRM relevant to category management and strategic sourcing?
Ans:
In strategic sourcing and category management, SAP SRM helps organizations optimize their spending by strategically managing categories of goods and services. It involves analyzing supplier performance, negotiating favorable terms, and aligning procurement strategies with organizational goals.
60. How does SAP SRM manage interaction with external procurement systems?
Ans:
SAP SRM handles integration with external procurement systems through standard interfaces and protocols. It allows seamless communication and data exchange with third-party procurement systems, ensuring a smooth flow of information and transactions across the procurement ecosystem.
61. In SAP SRM, what is Purchase Order Collaboration?
Ans:
Purchase Order Collaboration in SAP SRM involves the efficient and transparent communication of purchase orders between buyers and suppliers. It enables real-time collaboration on order details, changes, and confirmations, fostering a streamlined procurement process and better supplier relationships.
62. How is procurement interaction with ERP systems managed by SAP SRM?
Ans:
SAP SRM integrates procurement with ERP systems through middleware and standard interfaces. This integration ensures seamless data flow between SRM and ERP, allowing for synchronized procurement processes, shared master data, and real-time visibility into procurement activities.
63. In SAP SRM, what is Supplier Performance Monitoring?
Ans:
Supplier Performance Monitoring is a tool in SAP SRM that allows organisations to evaluate and track supplier performance over time. It entails assessing key performance indicators (KPIs), finding areas for improvement, and making data-driven choices in order to optimise supplier relationships.
64. How is purchase requisition management handled by SAP SRM?
Ans:
- SAP SRM handles purchase requisition management by providing a user-friendly interface for creating, approving, and tracking requisitions.
- It streamlines the request process, ensures compliance with procurement policies, and facilitates a transparent and auditable workflow.
65. In terms of risk management and compliance, what is SAP SRM?
Ans:
In compliance and risk management, SAP SRM helps organizations enforce and monitor compliance with procurement policies, regulations, and contractual agreements. It includes features for risk assessment, audit trails, and ensuring that procurement activities adhere to legal and ethical standards.
66. How are supplier catalog integration and catalog management handled by SAP SRM?
Ans:
Catalog Management in SAP SRM involves the creation and maintenance of product catalogs. It enables organizations to manage and integrate supplier catalogs efficiently, ensuring that users have access to accurate and up-to-date product information during the procurement process.
67. What Does SAP SRM’s Sourcing Cockpit Entail?
Ans:
The Sourcing Cockpit in SAP SRM is a centralized workspace that supports strategic sourcing activities. It provides tools for creating RFx documents, managing negotiations, and evaluating supplier responses, streamlining the sourcing process and enhancing collaboration.
68. What is SAP SRM’s method for managing supplier certification and approval?
Ans:
SAP SRM handles supplier qualification and approval processes by establishing predefined criteria for evaluating and approving suppliers. It ensures that only qualified and reliable suppliers are onboarded, reducing risks and enhancing the overall quality of the supplier base.
69. In SAP SRM, what is the Central Supplier Database?
Ans:
The Central Supplier Database in SAP SRM is a centralized repository for supplier information. It consolidates data on suppliers, ensuring that information is consistent and up-to-date across the organization, promoting efficiency in supplier management.
70. How is EDI and supplier network integration handled by SAP SRM?
Ans:
- SAP SRM handles integration with supplier networks and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) by providing standard connectors and protocols.
- This allows seamless communication and data exchange with external supplier networks, improving collaboration and reducing manual data entry efforts.
71. What is SAP SRM in reporting on procurement and spend analysis?
Ans:
SAP SRM in spend analysis and procurement reporting enables organizations to analyze and report on procurement spending. It provides tools to track expenses, identify cost-saving opportunities, and generate comprehensive reports for strategic decision-making in procurement.
72. How are confirmations of service entry and purchase handled by SAP SRM?
Ans:
SAP SRM handles service procurement by supporting the end-to-end process of procuring services. It includes functionalities for creating service requests, managing service specifications, and handling service entry confirmations to ensure accurate and timely recording of services rendered.
73. What is SAP SRM’s Supplier Collaboration Portal?
Ans:
The Supplier Collaboration Portal in SAP SRM is a platform that allows suppliers to collaborate with buyers. It provides a centralized space for communication, document exchange, and collaboration on various procurement-related activities, fostering better supplier relationships.
74. How is inventory management and logistics integration handled by SAP SRM?
Ans:
SAP SRM integrates with logistics and inventory management by providing interfaces for seamless data exchange. This integration ensures coordination between procurement and inventory processes, optimizing stock levels and improving overall supply chain efficiency.
75. In SAP SRM, what does Contract Authoring mean?
Ans:
Contract Authoring in SAP SRM involves creating, editing, and managing contract documents. It includes features for defining contract terms, generating legally binding agreements, and ensuring that contracts adhere to organizational standards and compliance requirements.
76. How is interaction with financial accounting systems managed by SAP SRM?
Ans:
SAP SRM handles integration with financial accounting systems by providing standard interfaces and connectors. This integration ensures that procurement transactions are accurately recorded in financial systems, supporting financial reporting and compliance.
77. What does supplier performance improvement mean by SAP SRM?
Ans:
In supplier performance improvement, SAP SRM provides tools to assess and analyze supplier performance. It supports initiatives to collaborate with suppliers for continuous improvement, driving enhanced efficiency, quality, and reliability in the supply chain.
78. What is SAP SRM’s way to managing invoices and working with payment systems?
Ans:
SAP SRM handles integration with payment systems and invoice management by supporting electronic invoicing and connecting with financial systems. This ensures streamlined invoice processing, timely payments, and improved cash flow management.
79. What Does SAP SRM’s Bidding Engine Mean?
Ans:
The SAP SRM Bidding Engine is a technology that simplifies the design and administration of bidding events. It facilitates a variety of bidding procedures, such as auctions and discussions, enabling fair competition among providers and appropriate pricing for goods and services.
80. How are contract compliance and monitoring handled by SAP SRM?
Ans:
SAP SRM handles contract compliance and monitoring by providing tools to track and enforce compliance with contract terms. It includes features for monitoring contract performance, managing deviations, and ensuring that contractual obligations are met throughout the contract lifecycle.
81. What is SAP SRM for processing payments and verifying invoices?
Ans:
SAP SRM streamlines invoice verification by providing tools for matching purchase orders, goods receipts, and supplier invoices. It facilitates the integration of financial data with payment systems, ensuring accurate and timely payment processing. Invoice verification in SRM enhances accuracy, reduces manual errors, and supports compliance with financial policies.
82. How is supplier risk management system integration handled by SAP SRM?
Ans:
- SAP SRM integrates with supplier risk management systems to assess and mitigate risks associated with suppliers.
- It facilitates monitoring and evaluating supplier performance and compliance to minimize supply chain disruptions.
- Enables real-time collaboration between SRM and risk management systems for proactive risk mitigation.
83. What does SAP SRM’s Central Purchasing mean?
Ans:
- Central Purchasing in SRM consolidates procurement activities for better coordination and cost optimization.
- It involves centralizing purchasing functions to negotiate better terms, standardize processes, and leverage economies of scale.
- Enables organizations to achieve cost savings and streamline procurement processes by centralizing purchasing activities.
84. How are supplier networks and e-sourcing platforms linked with SAP SRM?
Ans:
- SAP SRM integrates with e-sourcing platforms and supplier networks to enhance collaboration and extend sourcing capabilities.
- It enables SRM and external procurement systems to communicate and share data in real time.
- Point-out supports connectivity with external platforms to broaden the pool of suppliers and sourcing options.
85. What does SAP SRM mean for auditing and contract lifecycle compliance?
Ans:
SAP SRM ensures contract lifecycle compliance by providing tools for monitoring and enforcing contract terms. It supports audit management by maintaining an audit trail of contract-related activities for transparency and accountability. Offers features to track deviations, compliance violations, and audit trails for comprehensive contract management.
86. In terms of travel procurement integration, how is SAP SRM handled?
Ans:
- SAP SRM integrates with travel management systems to streamline travel procurement processes.
- It provides tools for managing travel requests, approvals, and expenses, ensuring compliance with travel policies.
- Enables seamless integration with travel management systems for end-to-end travel procurement.
87. What is SAP SRM’s Supplier Scorecard?
Ans:
- The Supplier Scorecard in SRM assesses and measures supplier performance based on predefined key performance indicators (KPIs).
- It provides a visual representation of supplier performance to aid decision-making and strategic supplier management.
- Allows organizations to track and evaluate supplier performance for continuous improvement.
88. How does SAP SRM manage document storage and link with business communication systems?
Ans:
- SAP SRM integrates with enterprise content management systems for efficient document management.
- It ensures that relevant documents, such as contracts and agreements, are stored, organized, and easily accessible.
- Enables seamless access and management of procurement-related documents within SRM.
89. What does SAP SRM mean in performance tracking and contract compliance?
Ans:
- SAP SRM focuses on contract compliance by tracking adherence to contractual terms and conditions.
- It includes tools for monitoring and evaluating supplier performance against contractual obligations.
- Point-out supports real-time tracking and reporting on contract compliance and supplier performance.
90. How is demand forecasting and planning system integration in SAP SRM?
Ans:
- SAP SRM integrates with demand planning and forecasting systems to align procurement with anticipated demand.
- It facilitates collaboration between procurement and demand planning functions for accurate inventory management.
- Enables organizations to optimize procurement based on demand forecasts for efficient supply chain management.






