
What is Biometrics?
Biometrics is a technology used to identify, analyze, and measure an individual’s physical and behavioral characteristics.Each human being is unique in terms of characteristics, which make him or her different from all others. The physical attributes such as fingerprints, color of iris, color of hair, hand geometry, and behavioral characteristics such as tone and accent of speech, signature, or the way of typing keys of computer keyboard etc., make a person stand separate from the rest.
This uniqueness of a person is then used by the biometric systems to −
- Identify and verify a person.
- Authenticate a person to give appropriate rights of system operations.
- Keep the system safe from unethical handling.
What is a Biometric System?
A biometric system is a technology which takes an individual’s physiological, behavioral, or both traits as input, analyzes it, and identifies the individual as a genuine or malicious user.
Evolution of Biometrics
The idea of biometrics was present a few years from now. In the 14th century, China practiced taking fingerprints of merchants and their children to separate them from all others. Fingerprinting is still used today.
- In the 19th century, an Anthropologist named Alphonse Bertillion developed a method (named Bertillonage) of taking body measurements of persons to identify them. He had realized that even if some features of the human body are changed, such as length of hair, weight, etc., some physical traits of the body remain unchanged, such as length of fingers. This method diminished quickly as it was found that the persons with same body measurements alone can be falsely taken as one. Subsequently, Richard Edward Henry from Scotland Yard developed a method for fingerprinting.
- The idea of retinal identification was conceived by Dr. Carleton Simon and Dr. Isadore Goldstein in 1935. In 1976, a research and development effort was put in at EyeDentify Inc. The first commercial retina scanning system was made available in 1981.
- Iris recognition was invented by John Daugman in 1993 at Cambridge University.
- In 2001, Biometrics Automated Toolset (BAT) was introduced in Kosovo, which provided a concrete identification means.
Today, biometric has come up as an independent field of study with precise technologies of establishing personal identities.
Why is Biometrics Required?
With increasing use of Information Technology in the field of banking, science, medication, etc., there is an immense need to protect the systems and data from unauthorized users.
Biometrics is used for authenticating and authorizing a person. Though these terms are often coupled; they mean different things.
Authentication (Identification)
This process tries to find out the answer to the question, “Are you the same who you are claiming to be?”, or, “Do I know you?” This is one-to-many matching and comparison of a person’s biometrics with the whole database.
Verification
This is the one-to-one process of matching where a live sample entered by the candidate is compared with a previously stored template in the database. If both are matching with more than 70% agreeable similarity, then the verification is successful.
Authorization
It is the process of assigning access rights to the authenticated or verified users. It tries to find out the answer for the question, “Are you eligible to have certain rights to access this resource?”
Shortcomings of Conventional Security Aids
The conventional methods of information system security used ID cards, passwords, Personal Identification Numbers (PINs), etc. They come with the following disadvantages −
- They all mean recognizing some code associated with the person rather than recognizing the person who actually produced it.
- They can be forgotten, lost, or stolen.
- They can be bypassed or easily compromised.
- They are not precise.
In such cases, the security of the system is threatened. When the systems need high levels of reliable protection, biometrics comes to help by binding the identity more oriented to the individual.Basic Components of a Biometric System
In general, a biometric system can be divided into four basic components. Let us see them briefly −
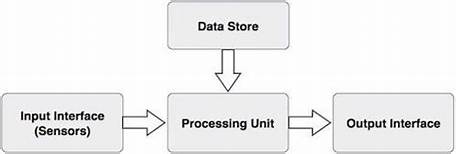
Input Interface (Sensors)
It is the sensing component of a biometrics system that converts human biological data into digital form.
For example,
- A Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) imager or a Charge Coupled Device (CCD) in the case of face recognition, handprint recognition, or iris/retinal recognition systems.
- An optical sensor in case of fingerprint systems.
- A microphone in case of voice recognition systems.
Processing Unit
The processing component is a microprocessor, Digital Signal Processor (DSP), or computer that processes the data captured from the sensors.
The processing of the biometric sample involves −
- Sample image enhancement
- Sample image normalization
- Feature extraction
- Comparison of the biometric sample with all stored samples in the database.
Database Store
The database stores the enrolled sample, which is recalled to perform a match at the time of authentication. For identification, there can be any memory from Random Access Memory (RAM), flash EPROM, or a data server. For verification, a removable storage element like a contact or contactless smart card is used.
Output Interface
The output interface communicates the decision of the biometric system to enable the access to the user. This can be a simple serial communication protocol RS232, or the higher bandwidth USB protocol. It could also be TCP/IP protocol, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Bluetooth, or one of the many cellular protocols.
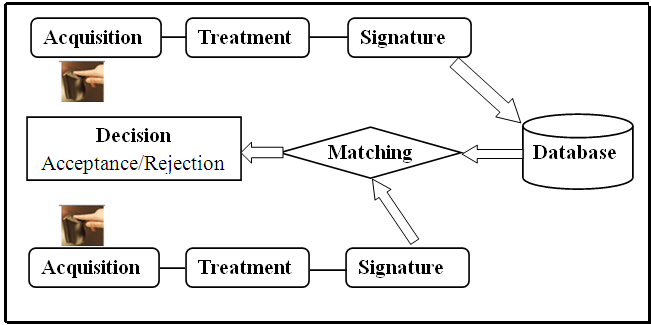
General Working of a Biometric System
There are four general steps a biometric system takes to perform identification and verification −
- Acquire a live sample from the candidate. (using sensors)
- Extract prominent features from samples. (using processing unit)
- Compare live samples with samples stored in the database. (using algorithms)
- Present the decision. (Accept or reject the candidate.)
The biometric sample is acquired from the candidate user. The prominent features are extracted from the sample and it is then compared with all the samples stored in the database. When the input sample matches with one of the samples in the database, the biometric system allows the person to access the resources; otherwise prohibits.
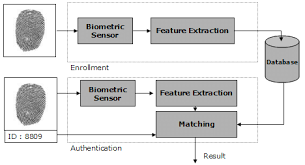
Biometrics Terminology
Biometric Template − It is a digital reference of the distinct characteristics that are extracted from a biometric sample.
Candidate/Subject − A person who enters his biometric sample.
Closed-Set Identification − The person is known to be existing in the database.
Enrollment − It is when a candidate uses a biometric system for the first time, it records the basic information such as name, address, etc. and then records the candidate’s biometric trait.
False Acceptance Rate (FAR) − It is the measure of possibility that a biometric system will incorrectly identify an unauthorized user as a valid user.
FAR =
Number of False Acceptances
Number of Identification Attempts
A biometric system providing low FAR ensures high security.
False Reject Rate (FRR) − It is the measure of possibility that the biometric system will incorrectly reject an authorized user as an invalid user.
FRR =
Number of False Rejections
Number of Identification Attempts
Open-Set Identification − The person is not guaranteed to be existing in the database.
Task − It is when the biometric system searches the database for matching sample.
Application Areas of Biometrics
There are a number of applications where biometric systems are useful. Few of them are given below −
- Controlling workplace access.
- Identity establishment of people for authentic citizenship and immigration systems.
- Applying access control to sensitive information and systems.
- Identifying criminals by forensics.
- Executing online e-commerce transactions.
- Fraud and theft reduction.
- Law enforcement.
Biometrics – Modalities
A biometric modality is nothing but a category of a biometric system depending upon the type of human trait it takes as input.Biometrics is largely statistical. The more data available from samples, the more the system is likely to be unique and reliable. It can work on various modalities pertaining to measurements of an individual’s body and features, and behavioral patterns. The modalities are classified based on the person’s biological traits.
Types of Biometric Modalities
There are various traits present in humans, which can be used as biometrics modalities. The biometric modalities fall under three types −
- Physiological
- Behavioral
- Combination of physiological and behavioral modality
Physiological Modalities
- As depicted earlier, the physiological modalities are based on the direct measurement of parts of the human body such as iris, fingerprint, shape, and position of fingers, etc.
- There are some physical traits which remain unaltered throughout a person’s life. They can be an excellent resource for identification of an individual.
Fingerprint Recognition System
- It is the most known and used biometrics solution to authenticate people on biometric systems. The reasons for it being so popular are there are ten available sources of biometric and ease of acquisition.
- Every person has a unique fingerprint which is composed of ridges, grooves, and direction of the lines. There are three basic patterns of ridges namely, arch, loop, and whorl. The uniqueness of fingerprint is determined by these features as well as minutiae features such as bifurcation and spots (ridge endings).
- Fingerprint is one of oldest and most popular recognition techniques. Fingerprint matching techniques are of three types −
- Minutiae Based Techniques − In these minutiae points are found and then mapped to their relative position on finger. There are some difficulties such as if the image is of low quality, then it is difficult to find minutiae points correctly. Another difficulty is, it considers the local position of ridges and furrows; not global.
- Correlation Based Method − It uses richer gray scale information. It overcomes problems of minutiae-based methods, by being able to work with bad quality data. But it has some of its own problems like localization of points.
- Pattern Based (Image Based) Matching − Pattern based algorithms compare the basic fingerprint patterns (arch, whorl, and loop) between a stored template and a candidate fingerprint.
Merits of Finger Recognition System
- It is the most contemporary method.
- It is the most economical method.
- It is highly reliable and secure.
- It works on a small template size, which speeds up the verifying process.
- It consumes less memory space.
Demerits of Finger Recognition System
- Scars, cuts or absence of fingers can hinder the recognition process.
- The systems can be fooled by using artificial fingers made of wax.
- It involves physical contact with the system.
- They leave the pattern of finger behind at the time of entering the sample.
Applications of Finger Recognition System
- Verification of driver-license authenticity.
- Checking validity of driving license.
- Border Control/Visa Issuance.
- Access control in organizations.
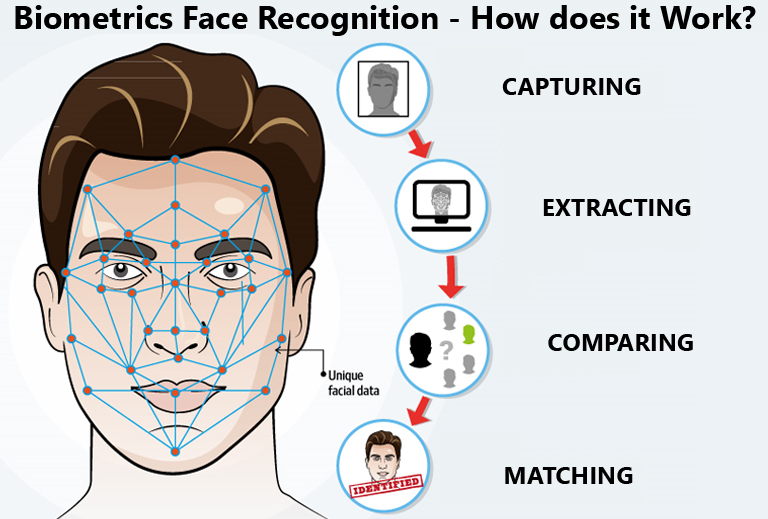
Facial Recognition System
Facial recognition is based on determining shape and size of jaw, chin, shape and location of the eyes, eyebrows, nose, lips, and cheekbones. 2D facial scanners start reading face geometry and recording it on the grid. The facial geometry is transferred to the database in terms of points. The comparison algorithms perform face matching and come up with the results. Facial recognition is performed in the following ways −
- Facial Metrics − In this type, the distances between pupils or from nose to lip or chin are measured.
- Eigen faces − It is the process of analyzing the overall face image as a weighted combination of a number of faces.
- Skin Texture Analysis − The unique lines, patterns, and spots apparent in a person’s skin are located.
Merits of Facial Recognition System
- It offers easy storage of templates in the database.
- It reduces the statistical complexities to recognize face images.
- It involves no physical contact with the system.
Demerits of Facial Recognition System
- Facial traits change over time.
- Uniqueness is not guaranteed, for example, in case of identical twins.
- If a candidate face shows different expressions such as a light smile, then it can affect the result.
- It requires adequate lighting to get correct input.
Applications of Facial Recognition System
- General Identity Verification.
- Verification for access control.
- Human-Computer Interaction.
- Criminal Identification.
- Surveillance.
Iris Recognition System
- Iris recognition works on the basis of the iris pattern in the human eye. The iris is the pigmented elastic tissue that has adjustable circular opening in the center. It controls the diameter of the pupil. In adult humans, the texture of iris is stable throughout their lives. The iris patterns of left and right eyes are different. The iris patterns and colors change from person to person.
- It involves taking the picture of iris with a capable camera, storing it, and comparing the same with the candidate eyes using mathematical algorithms.
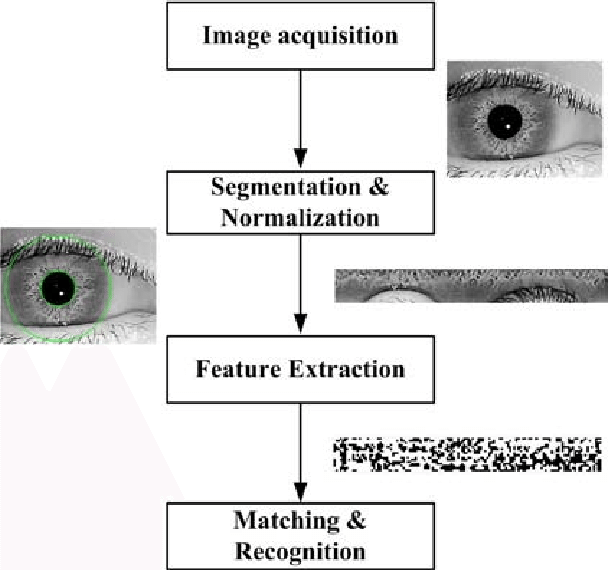
Merits of Iris Recognition System
- It is highly accurate as the chance of matching two irises is 1 in 10 billion people.
- It is highly scalable as the iris pattern remains the same throughout a person’s lifetime.
- The candidate need not remove glasses or contact lenses; they do not hamper the accuracy of the system.
- It involves no physical contact with the system.
- It provides instant verification (2 to 5 seconds) because of its small template size.
Demerits of Iris Recognition System
- Iris scanners are expensive.
- High quality images can fool the scanner.
- A person is required to keep his/her head very still for accurate scanning.
Applications of Iris Recognition System
- National security and Identity cards such as Adhaar cards in India.
- Google uses iris recognition for accessing their data centers.
Hand Geometry Recognition System
It includes measuring length and width of palm, surface area, length and position of fingers, and overall bone structure of the hand. A person’s hand is unique and can be used to identify a person from others. There are two Hand Geometry systems −
- Contact Based − a hand is placed on a scanner’s surface. This placement is positioned by five pins, which guide the candidate hand to position correctly for the camera.
- Contact Less − In this approach neither pins nor platform are required for hand image acquisition.

Merits of Hand Geometry Recognition System
- It is sturdy and user friendly.
- The changes in skin moisture or texture do not affect the result.
Demerits of Hand Geometry Recognition System
- Since the hand geometry is not unique, it is not very reliable.
- It is effective in the case of adults and not for the growing children.
- If the candidate’s hand is with jewelry, plaster, or arthritis, it is likely to introduce a problem.
Applications of Hand Geometry Recognition System
- Nuclear power plants and the military use Hand Geometry Recognition for access control.
Retinal Scanning System:
- Retina is the lining layer at the back of the eyeball that covers 65% of the eyeball’s inner surface. It contains photosensitive cells. Each person’s retina is unique due to the complex network of blood vessels that supply blood.
- It is a reliable biometric as the retina pattern remains unchanged throughout the person’s life, barring the patterns of persons having diabetes, glaucoma, or some degenerative disorders.
- In the retinal scanning process, a person is asked to remove lenses or eyeglasses. A low-intensity infrared light beam is casted into a person’s eye for 10 to 15 seconds. This infrared light is absorbed by the blood vessels forming a pattern of blood vessels during the scan. This pattern is then digitized and stored in the database.

Merits of Retinal Scanning System
- It cannot be forged.
- It is highly reliable as the error rate is 1 out of a crore samples (which is almost 0%).
Demerits of Retinal Scanning System
- It is not very user friendly as the user needs to maintain steadiness that can cause discomfort.
- It tends to reveal some poor health conditions such as hypertension or diabetes, which causes privacy issues.
- Accuracy of the results is prone to diseases such as cataracts, glaucoma, diabetes, etc.
Applications of Retinal Scanning System
- It is practiced by some government bodies such as CID, FBI, etc.
- Apart from security applications, it is also used for ophthalmological diagnostics.
DNA Recognition System
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) is the genetic material found in humans. Every human barring identical twins, is uniquely identifiable by the traits found in their DNA, which is located in the nucleus of the cell. There are a number of sources from which DNA patterns can be collected such as blood, saliva, nails, hair, etc.
- Within cells, DNA is organized in a long double helix structure called chromosomes. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Out of the 46 total chromosomes, the offspring inherits 23 chromosomes from each biological parent. 99.7% of an offspring’s DNA is shared with their parents. The remaining 0.3% DNA contains repetitive coding unique to an individual.
The fundamental steps of DNA profiling are −
- Separating the DNA from samples acquired from either of blood, saliva, hair, semen, or tissue.
- Separating the DNA sample into shorter segments.
- Organizing the DNA segments according to size.
- Comparing the DNA segments from various samples.
The more detailed the sample is, the more precise the comparison and in turn the identification of the individual is.

DNA Biometrics differs from all others in the following ways −
- It needs a tangible physical sample instead of image.
- DNA matching is done on physical samples. There is no feature extraction or template saving.
Merit of DNA Recognition System
It provides the highest accuracy.
Demerits of DNA Recognition System
- Length of procedure from sample acquisition to result is large.
- Being more informative, it brings privacy issues.
- It needs more storage space.
- Sampling contamination or degradation of samples may affect the result.
Applications of DNA Recognition System
- It is mainly used to prove guilt or innocence.
- It is used in physical and network security.
Gait Recognition
- Gait is the manner of a person’s walking. People show different traits while walking such as body posture, distance between two feet while walking, swaying, etc., which help to recognize them uniquely.
- A gait recognition based on analyzing the video images of the candidate’s walk. The sample of the candidate’s walk cycle is recorded by Video. The sample is then analyzed for the position of joints such as knees and ankles, and the angles made between them while walking.
- A respective mathematical model is created for every candidate person and stored in the database. At the time of verification, this model is compared with the live sample of the candidate walk to determine its identity.
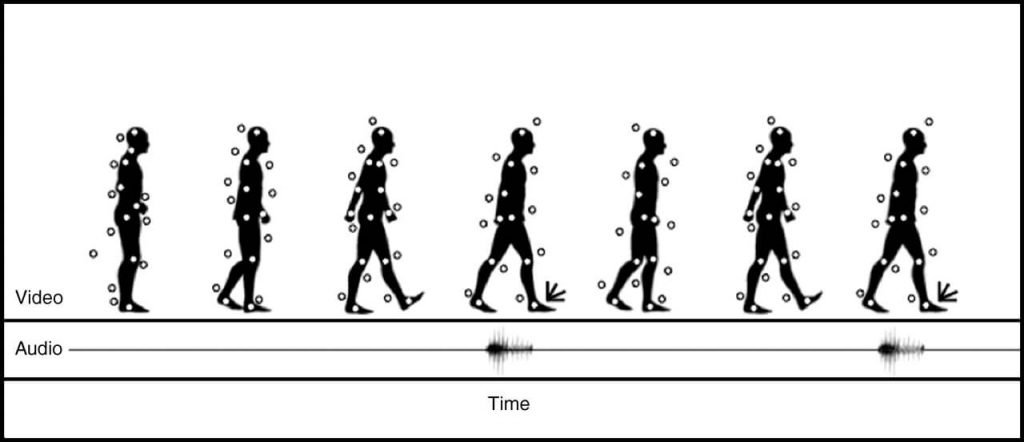
Merits of Gait Recognition System
- It is non-invasive.
- It does not need the candidate’s cooperation as it can be used from a distance.
- It can be used for determining medical disorders by spotting changes in the walking pattern of a person in case of Parkinson’s disease.
Demerits of Gait Recognition System
- For this biometric technique, no model is developed with complete accuracy till now.
- It may not be as reliable as other established biometric techniques.
Application of Gait Recognition System
- It is well-suited for identifying criminals in the crime scenario.
Signature Recognition System
- In this case, more emphasis is given on the behavioral patterns in which the signature is signed than the way a signature looks in terms of graphics.
- The behavioral patterns include the changes in the timing of writing, pauses, pressure, direction of strokes, and speed during the course of signing. It could be easy to duplicate the graphical appearance of the signature but it is not easy to imitate the signature with the same behavior the person shows while signing.
- This technology consists of a pen and a specialized writing tablet, both connected to a computer for template comparison and verification. A high quality tablet can capture the behavioral traits such as speed, pressure, and timing while signing.
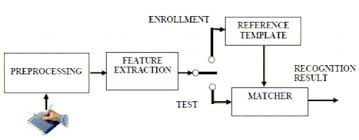
- During the enrollment phase, the candidate must sign on the writing tablet multiple times for data acquisition. The signature recognition algorithm then extracts the unique features such as timing, pressure, speed, direction of strokes, important points on the path of signature, and the size of signature. The algorithm assigns different values of weights to those points.
- At the time of identification, the candidate enters the live sample of the signature, which is compared with the signatures in the database.
Constraints of Signature Recognition System
- To acquire adequate amounts of data, the signature should be small enough to fit on a tablet and big enough to be able to deal with.
- The quality of the writing tablet decides the robustness of signature recognition enrollment template.
- The candidate must perform the verification processes in the same type of environment and conditions as they were at the time of enrollment. If there is a change, then the enrollment template and live sample template may differ from each other.
Merits of Signature Recognition System
- Signature recognition process has a high resistance to imposters as it is very difficult to imitate the behavior patterns associated with the signature.
- It works very well in high amount business transactions. For example, Signature recognition could be used to positively verify the business representatives involved in the transaction before any classified documents are opened and signed.
- It is a non-invasive tool.
- We all use our signature in some sort of commerce, and thus there are virtually no privacy rights issues involved.
- Even if the system is hacked and the template is stolen, it is easy to restore the template.
Demerits of Signature Recognition System
- The live sample template is prone to change with respect to the changes in behavior while signing. For example, signing with a hand held in plaster.
- Users need to get accustomed to using a signing tablet. Error rate is high till it happens.
Applications of Signature Recognition System
- It is used in document verification and authorization.
- The Chase Manhattan Bank, Chicago is known as the first bank to adopt Signature Recognition technology.
Keystroke Recognition System
During World War II, a technique known as Fist of the Sender was used by military intelligence to determine if the Morse code was sent by enemy or ally based on the rhythm of typing. These days, keystroke dynamics is the easiest biometric solution to implement in terms of hardware.This biometric analyzes a candidate’s typing pattern, the rhythm, and the speed of typing on a keyboard. The dwell time and flight time measurements are used in keystroke recognition.
Dwell time − It is the duration of time for which a key is pressed.
Flight time − It is the time elapsed between releasing a key and pressing the following key.
The candidates differ in the way they type on the keyboard as the time they take to find the right key, the flight time, and the dwelling time. Their speed and rhythm of typing also varies according to their level of comfort with the keyboard. Keystroke recognition system monitors the keyboard inputs thousands of times per second in a single attempt to identify users based on their habits of typing.
There are two types of keystroke recognition −
- Static − It is one time recognition at the start of interaction.
- Continuous − It is throughout the course of interaction.
Application of Keystroke Dynamics
- Keystroke Recognition is used for identification/verification. It is used with user ID/password as a form of multifactor authentication.
- It is used for surveillance. Some software solutions track keystroke behavior for each user account without the end-user’s knowledge. This tracking is used to analyze if the account was being shared or used by anyone else than the genuine account owner. It is used to verify if some software license is being shared.
Conclusion : Fingerprint biometrics provide a very robust and mature choice for biometric technology. As such, there are many solutions on the market.This familiarity has allowed attackers to study and try different types of attacks on fingerprint readers.Hope you have found all the details that you were looking for, in this article.






