
Blue Prism is a pioneer in Robotic Process Automation (RPA) platform designed to automate business processes within organizations. RPA is a software robot-based technology, or “bots” to perform repetitive, rule-based tasks previously done by humans. Blue Prism specifically focuses on providing a platform for creating and managing these software robots. Blue Prism development involves the creation and management of automation solutions using the Blue Prism RPA platform. In this context, development refers to the process of designing, configuring, and implementing software robots (bots) to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks within an organization.
1. What is Blue Prism and its primary purpose in the field of RPA?
Ans:
Blue Prism is a leading RPA platform focused on automating routine tasks.
In the field of RPA, Blue Prism serves as a catalyst for digital transformation, enabling businesses to achieve greater productivity and agility while liberating human resources to be more innovative and strategic.
2. What are the main components of the Blue Prism RPA platform?
Ans:
- Process Studio
- Object Studio
- Control Room
- Process Repository
- Object Repository
- Runtime Resource
3. Describe the Blue Prism architecture and its components.
Ans:
Blue Prism’s architecture is composed of several key components. At its core is the Control Room, which serves as the central hub for managing and monitoring automation processes. The Runtime Environment houses software robots that execute these processes. The Development Studio comprises tools like Object Studio and Process Studio, enabling the creation, testing, and maintenance of automation workflows.
4. How do you create a process in Blue Prism?
Ans:
To create a process in Blue Prism, you use the Process Studio, a visual design interface. Within Process Studio, you drag and drop actions, objects, and stages onto a canvas, configure their properties, and create a sequence of steps that define the automated process.
5. What are the benefits of utilizing Blue Prism over other RPA tools?
Ans:
Advantages of Blue Prism over other RPA tools:
- Ease of Use: User-friendly, visual interface for process design.
- Scalability: Suitable for small- to large-scale automation.
- Security: Strong emphasis on data security and compliance.
- Control Room: Centralized process management and monitoring.
- Application Compatibility: Supports various application types.
6. What is a Bot in Blue Prism, and how can you manage and deploy bots?
Ans:
A “Bot” in Blue Prism refers to a software robot or automation agent that performs tasks in a robotic process automation (RPA) solution. These bots execute the automation processes designed in Blue Prism.
You can manage and deploy bots through the Blue Prism Control Room, which provides centralized management of bot licenses, scheduling, allocation of tasks (work items), and monitoring of bot activities.
7. What is a Business Object in Blue Prism?
Ans:
A Business Object in Blue Prism is a modular and reusable automation component designed to interact with specific applications or systems. Business objects encapsulate the logic and actions required to manipulate and extract data from these applications.
8. How does Blue Prism handle exception handling in automation processes?
Ans:
Blue Prism handles exceptions in automation processes through:
Exception Blocks: Segments of logic to manage errors.
Exception Stages: Specialized stages to catch and handle exceptions.
Logging: Recording exception details for troubleshooting.
Retries: Automatic retries of actions upon exceptions.
Notification: Alerts and notifications for stakeholders.
Exception Queues: Dedicated queues for efficient resolution and tracking.
9. What is a Work Queue in Blue Prism, and why is it important?
Ans:
A Work Queue in Blue Prism is a repository that stores tasks for automation, facilitating their allocation to robots for execution. It’s vital for efficient task management, prioritization, and monitoring, enhancing RPA scalability and control.
10. What are the different types of data items in Blue Prism and their usage?
Ans:
In Blue Prism, there are three main data types:
- Text: Used for storing alphanumeric characters.
- Number: Used for numeric values.
- Flag: Used for Boolean (true or false) values.
11. What is Credential Manager, and why is it used in Blue Prism?
Ans:
Credential Manager in Blue Prism is a secure repository used for managing and storing sensitive data, such as usernames and passwords, required for authentication in automation processes. It’s important for security and compliance reasons because it helps protect sensitive information from exposure and ensures that only authorized robots can access and use these credentials.
12. How does Blue Prism ensure the security of sensitive data during automation?
Ans:
Blue Prism ensures the security of sensitive data during automation through several measures:
- Credential Encryption: Sensitive credentials are encrypted when stored in Credential Manager.
- Role-Based Access Control: Access to sensitive data is restricted based on user roles, ensuring only authorized users can access it.
- Audit Trails: Comprehensive audit logs track who accessed sensitive data and when, aiding in monitoring and detecting unauthorized access.
- Secure Execution Environment: Robots operate in secure runtime environments, isolating sensitive data from the automation workflow.
- Tokenization and SSO: Tokenization and Single Sign-On (SSO) mechanisms reduce the need to store and transmit actual credentials.
13. What is the role of Object Studio and Process Studio in Blue Prism?
Ans:
Object Studio is where you build reusable automation components, called business objects, tailored for specific applications or systems. These objects encapsulate interactions, making it efficient to use them across various automation processes.
Process Studio, on the other hand, is where you create complete automation workflows by orchestrating these business objects. It allows you to design the sequence of actions, decision logic, and error handling required to execute end-to-end business processes.
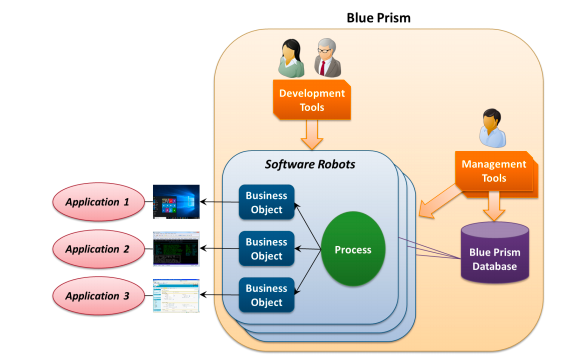
14. Explain the concept of Blue Prism “stages” in a process flow.
Ans:
In Blue Prism, “Stages” are fundamental building blocks within the Process Studio where you design automation workflows. Stages represent specific actions or decisions, and you arrange them to create a sequence of steps that define the process flow. Stages include actions like data manipulation, interactions with applications, decision-making, and error handling.
15. How can you integrate Blue Prism with other software applications or systems?
Ans:
Blue Prism can be integrated with other software applications or systems using a range of methods. These include UI automation for mimicking human actions, consumption of web services (RESTful or SOAP), direct interaction with APIs, database connectivity, file operations, and message queues for asynchronous communication. .
16. Explain the fundamental variations between Automation Anywhere and Blue Prism.
Ans:
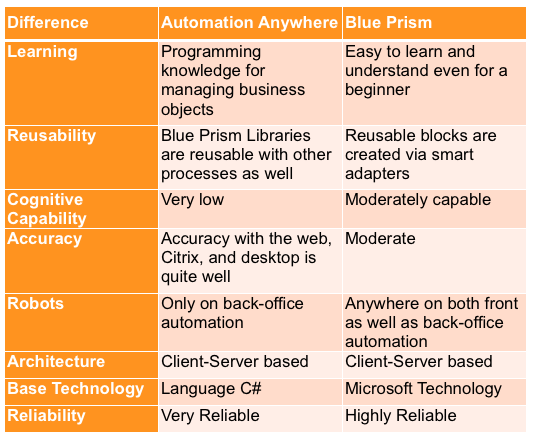
Automation Anywhere and Blue Prism, both leading RPA platforms, differ in their architecture and pricing.
Automation Anywhere has a user-centric, decentralized design, making it user-friendly but potentially complex to manage at scale. It offers flexible pay-as-you-go pricing.
In contrast, Blue Prism follows a centralized, IT-centric approach with an emphasis on reusability. It historically used a per-bot licensing model, but it has also introduced more flexible pricing options.
17. What is the Blue Prism Control Room’s function?
Ans:
The Blue Prism Control Room serves as the centralized hub for managing, monitoring, and controlling robotic process automation (RPA) activities.
Its core functions include task scheduling, workload allocation to software robots, maintenance of bot configurations and licenses, real-time process monitoring, and reporting and analytics for automation performance.
18. Describe the process of error handling and recovery in Blue Prism.
Ans:
Error handling and recovery in Blue Prism involves:
Error Detection: Identifying errors or exceptions during process execution.
Exception Blocks: Defining blocks with actions and logic to manage specific errors.
Exception Stages: Placing exception stages in the process flow to handle errors.
Retry Mechanisms: Configuring automatic retries for actions or stages.
Logging: Capturing error details for troubleshooting and auditing.
Exception Queues: Managing exceptions in dedicated queues for resolution, including manual or automated handling.
19. Which factors are most important for creating scalable and effective Blue Prism processes?
Ans:
Creating scalable and effective Blue Prism processes requires consideration of several critical factors:
- Modularity: Design processes with modular components (business objects) for reuse and easier maintenance.
- Error Handling: Implement robust error handling to ensure processes can recover from unexpected issues.
- Data Management: Efficiently use data items and employ best practices for data manipulation.
- Exception Management: Define clear exception handling processes to minimize process disruptions.
- Security: Apply security best practices to protect sensitive data and adhere to compliance requirements.
20. What is Prism’s license model, and what editions are available?
Ans:
Licensing Model:
Blue Prism primarily used a per-bot licensing model, where organizations paid for licenses based on the number of software robots (bots) deployed. The cost depended on the number of bots in use.
Blue Prism offered several editions tailored to different business needs:
- Blue Prism Enterprise
- Blue Prism Cloud
- Blue Prism Community Edition
- Blue Prism Intelligent Automation Edition
- Blue Prism Interact
- Blue Prism Decipher
21. How do you manage version control and change management in Blue Prism?
Ans:
Blue Prism provides version control through process versions, change logs, and designated environments for development, testing, and production.
Change logs record details of modifications, including the user, nature of change, and timestamps. Additionally, Blue Prism offers distinct environments to isolate development and testing from production, ensuring thorough testing of changes before deployment. Role-based access control restricts who can make changes, enhancing security and compliance.
22. Can you explain how Blue Prism handles credential management and security?
Ans:
Blue Prism handles credential management and security through its Credential Manager, where sensitive data like usernames and passwords are securely stored and encrypted. Access to Credential Manager is controlled through role-based access control (RBAC), which makes certain that only authorized users can access and use credentials. Additionally, Blue Prism encrypts sensitive data at rest and in transit, and audit logs track user activities for security and compliance.
23. What distinguishes attended from unattended automation in Blue Prism?
Ans:
Attended Automation: Bots in attended automation work collaboratively with human users. They assist users with tasks in real-time, often on the user’s machine, and are triggered by users when needed.
Unattended Automation: Unattended bots operate independently without human intervention. They execute predefined tasks or processes on remote servers or virtual machines, typically following schedules or event triggers.
24. How do you schedule and monitor Blue Prism processes for unattended automation?
Ans:
For unattended automation, Blue Prism provides the Control Room, where you can schedule and monitor processes. You can schedule processes to run at specific times or in response to events. The Control Room also offers real-time monitoring of bot activities, including task execution, logging, and performance tracking. It provides alerts and notifications for processing status changes.
25. Can you offer any successful strategies for Blue Prism implementations?
Ans:
Best Practices for Successful Blue Prism Implementations:
- Begin with a well-defined automation strategy aligned with your business goals.
- Prioritize processes based on complexity, volume, and potential ROI.
- Design automation processes with modularity and reusability in mind.
- Implement robust error handling and exception management.
- Enforce security best practices for sensitive data.
- Establish clear governance and compliance policies.
26. What does the Process Studio in Blue Prism do?
Ans:
The Process Studio in Blue Prism is where you design, build, and configure the steps and logic for automation processes. It provides a graphical interface for generating and managing workflows, allowing you to define how software robots perform tasks and interact with applications.
27. How does Blue Prism handle long-running processes and timeouts?
Ans:
Blue Prism handles long-running processes by allowing you to configure timeouts for specific actions or stages within a process. If an action takes longer than the defined timeout, Blue Prism can trigger error handling or other predefined actions to manage the delay and prevent process disruptions. This ensures that processes remain responsive and adaptable to varying execution times.
28. Can you explain the concept of “Collections” in Blue Prism?
Ans:
In Blue Prism, “Collections” are data structures used to store and manipulate multiple pieces of data of the same or different types. They offer flexibility for handling lists, tables, or arrays, allowing you to perform operations like adding, retrieving, or modifying data efficiently within automation processes.
29. How do you troubleshoot and debug Blue Prism processes effectively?
Ans:
To troubleshoot and debug Blue Prism processes effectively, utilize Blue Prism’s debugging tools, such as “Debug Mode” and “Data Item Debugging,” to step through processes, inspect data, and identify issues. Additionally, use detailed logging and error handling to capture and analyze errors for root cause identification and resolution.
30. Is programming required for Blue Prism?
Ans:
Programming skills are not typically required for Blue Prism, as it offers a no-code or low-code approach to automation. Users design processes using a visual interface, defining actions and logic through drag-and-drop elements. However, a basic understanding of programming concepts can be beneficial for complex scenarios or custom code actions.
31. Can you describe the “Environment Locking” idea from Blue Prism?
Ans:
“Environment Locking” in Blue Prism restricts user access to designated environments, enhancing security and ensuring that changes made in one environment do not affect others in the RPA system.
32. How does Blue Prism handle dependencies between tasks or processes?
Ans:
Blue Prism handles task and process dependencies through scheduling, triggers, and explicit dependency management within the Control Room. This enables you to define the order of execution, initiate processes based on events, and monitor progress, ensuring efficient automation workflows.
33. What is the role of “Process Groups” in Blue Prism, and how are they useful?
“Process Groups” in Blue Prism serve as containers for organizing related processes, making it easier to manage and maintain automation assets. They help streamline process management, access control, and versioning by grouping related processes together, enhancing organization and efficiency in large-scale RPA implementations.
34. What distinguishes the “Process Validation” and “Interactive Validation” features of Blue Prism?
Ans:
The “Process Validation” feature in Blue Prism is designed for automated, hands-free validation of processes by comparing output data to expected results, ensuring process accuracy.
On the other hand, “Interactive Validation” involves human validation or supervision during the execution of a process. It allows users to manually review and validate specific steps or data before proceeding, making it suitable for tasks requiring human judgment or intervention in the automation workflow.
35. How does Blue Prism support integration with cloud services and platforms?
Ans:
Blue Prism supports cloud integration through connectors and web services for platforms like AWS and Azure, enabling data exchange and automation. It offers cloud-specific features such as message queues for asynchronous communication and custom code actions for advanced cloud integrations, making it adaptable to diverse cloud environments. This versatility allows businesses to seamlessly connect and automate processes in cloud-based services and platforms.
36. What are some typical use cases for attended automation in Blue Prism?
Ans:
Typical use cases for attended automation in Blue Prism include:
- Customer Support: Assist agents with customer data, order tracking, and inquiries.
- Data Entry: Automate form filling and data validation.
- Invoice Processing: Streamline accounts payable and approval workflows.
- Email Management: Categorize, route, and respond to emails efficiently.
- On-Demand Reports: Generate customized reports instantly.
- HR Tasks: Simplify onboarding, payroll, and leave management.
- Finance Operations: Help with expense tracking and reconciliation.
- IT Helpdesk: Troubleshoot issues and manage user requests.
- Inventory Control: Monitor and optimize stock levels.
- Compliance Checks: Ensure adherence to regulations and policies.
37. What is the role of Blue Prism’s “Release Manager” in deployment processes?
Ans:
Blue Prism’s “Release Manager” is a key component that facilitates the deployment of automation processes. It plays a central role in managing the release and distribution of new or updated automation assets, ensuring proper version control, and orchestrating the transition of processes from development and testing environments to production.
38. How do you configure Blue Prism to handle dynamic web elements?
Ans:
To handle dynamic web elements in Blue Prism:
- Use “Wait for Element” stages to wait for element availability.
- Employ dynamic selectors that adapt to changing attributes.
- Implement error handling and retries for reliability.
39. Can you describe the role of Blue Prism’s “Scheduler” in managing automation processes?
Ans:
Blue Prism’s “Scheduler” automates the execution of predefined automation processes at scheduled times or intervals. It plays a pivotal role in managing repetitive, time-sensitive tasks by ensuring that processes are initiated on time without manual intervention. The Scheduler enhances operational efficiency and accuracy, allowing organizations to optimize resource allocation and focus on higher-value activities.
40. How does Blue Prism handle multi-environment deployments?
Ans:
Blue Prism handles multi-environment deployments through environment separation and role-based access control. It ensures the controlled promotion of processes from development to production while maintaining security and configuration settings specific to each environment. This structured approach minimizes risks and ensures efficient, secure, and reliable automation implementations.
41. What function do “Resource pools” play in Blue Prism’s workload management?
Ans:
“Resource pools” in Blue Prism’s workload management serve as a means to allocate and manage the execution of automation processes efficiently. They allow organizations to group and categorize their digital workforce (software robots) based on skills, priorities, or specific tasks. Each resource pool represents a subset of robots with similar capabilities or functions.
42. What does the Blue Prism “Thin Client” mode serve?
Ans:
The purpose of Blue Prism’s “Thin Client” mode is to enable automation in environments where traditional desktop automation is challenging or restricted. It allows the digital workforce to interact with applications and systems through a lightweight interface, reducing the impact on the host system’s resources and facilitating automation in scenarios with limited graphical user interface (GUI) access.
43. Describe the Blue Prism concept “Session management.”
Ans:
“Session management” in Blue Prism refers to the process of controlling and maintaining interactions between the automation software and various applications or systems. It involves managing sessions to ensure that the software can efficiently and securely communicate with target applications, carry out tasks, and maintain data integrity throughout the automation process.
44. Describe the role of the “Application Modeller” in Blue Prism’s interaction with software applications.
Ans:
The Application Modeller is a key component in Blue Prism used to interact with software applications. It allows Blue Prism to understand and manipulate the user interface of target applications by defining elements, actions, and data inputs/outputs. The Application Modeller plays a pivotal role in enabling the automation of tasks within applications that do not offer APIs for direct integration.
45. What is “Credential rotation,” and why is it important in Blue Prism?
Ans:
Credential rotation is the practice of regularly changing authentication credentials, such as usernames and passwords, used by Blue Prism to access various systems and applications. This security measure is essential in Blue Prism to decrease the possibility of unwanted data access or data breaches. By periodically rotating credentials, organizations enhance their security posture and comply with security best practices and policies.
46. How does Blue Prism support integrations with legacy systems that lack APIs?
Ans:
Blue Prism can integrate with legacy systems lacking APIs by employing techniques like screen scraping and terminal emulation. It interacts with the legacy system’s user interface just like a human user, mimicking keystrokes and mouse clicks to input and retrieve data. This enables organizations to automate processes within older systems that do not provide modern APIs for direct integration.
47. What are “Environment variables,” and how can you use them in Blue Prism processes?
Ans:
Environment variables in Blue Prism are dynamic values that can be used to store and manage data or settings across different environments or stages of automation. They are especially useful for storing configuration settings, credentials, or any data that may change across environments. Environment variables can be accessed and updated within Blue Prism processes, allowing for flexibility and customization without modifying the process logic.
48. Explain the Blue Prism concept of “Data item exposure”.
Ans:
Data item exposure in Blue Prism allows specific data elements to be accessed and shared among different automation processes. It promotes data consistency, reusability, and efficient integration by providing a standardized way to manage shared data, such as configuration settings, reference data, and credentials, across various tasks and processes. This enhances data governance and reduces redundancy.
49. How can the performance of Blue Prism processes be optimized for optimal efficiency?
Ans:
To optimize Blue Prism processes for efficiency:
- Reduce delays and wait times.
- Minimize UI interactions.
- Optimize database queries.
- Efficiently manage resources.
- Implement effective error handling.
- Use parallel processing when possible.
50. Describe the procedure for transferring Blue Prism processes between environments.
Ans:
Transferring Blue Prism processes between environments involves exporting the desired processes, including dependencies and configurations, from the source environment. Then, the exported package is transferred to the target environment, where the processes are imported. During this process, it’s crucial to ensure that environment-specific settings are adjusted to match the target environment’s requirements.
51. What is the function of Blue Prism’s “Work Queue Management” feature?
Ans:
The functions of Blue Prism’s “Work Queue Management” feature:
- Efficient Task Distribution: Assigns tasks to appropriate robots based on criteria like priority and availability.
- Prioritization: Allows prioritization of tasks to meet critical deadlines and SLAs.
- Real-time Monitoring: Provides visibility into task status for better workload management.
- Exception Handling: Addresses errors during task execution promptly.
- Load Balancing: Distributes tasks evenly to prevent overloading of specific robots.
- Reporting and Analytics: Offers insights into task completion times and overall process efficiency.
52. How does Blue Prism handle unattended automation on virtual machines or cloud platforms?
Blue Prism can execute unattended automation on virtual machines or cloud platforms by deploying its digital workforce to these environments. It provides the flexibility to run automation processes on virtual machines hosted in cloud infrastructure, allowing organizations to scale their automation efforts and leverage cloud resources as needed.
53. What is the role of “Run-time resource allocation” in Blue Prism?
Ans:
Run-time resource allocation in Blue Prism involves dynamically assigning robots to tasks or processes based on their availability and capabilities. This ensures efficient utilization of the digital workforce by allocating the right robot for the right job at the right time, optimizing resource usage, and improving overall automation performance.
54. How can you ensure that Blue Prism processes compliance with privacy regulations like the GDPR?
Ans:
To ensure Blue Prism processes comply with data privacy regulations, organizations can implement practices like data encryption, access controls, and audit trails. They can also pseudonymize or anonymize sensitive data and establish strict data handling protocols. Compliance with regulations such as GDPR requires a combination of technical measures, process design, and policy adherence.
55. Describe Attach.
Ans:
In Blue Prism, the “Attach” stage is essential for connecting RPA bots to specific applications or systems. It identifies target applications using attributes and properties, enabling precise interaction. The bot operates within a defined scope, ensuring actions are limited to the attached application. It can perform various tasks like keystrokes, clicks, and data input. Attach stages also include error handling for robust automation.
56. Which stage must be completed in order to capture exceptions?
Ans:
In Blue Prism, the stage that is typically completed in order to capture exceptions is the “Exception Handling” stage. Exception handling is an essential part of any RPA process, as it allows you to anticipate and handle unexpected errors or issues that may arise during the automation.
57. What is the function of utilizing blocks?
Ans:
Utilizing blocks in programming or automation simplifies code organization, enhances readability, aids debugging, encapsulates data, and encourages code reuse.
58. Describe the RPA lifecycle.
Ans:
The RPA (Robotic Process Automation) lifecycle involves discovery, planning, design, development of bots, integration with systems, testing, deployment, monitoring, and continuous improvement. It streamlines and automates business processes to enhance efficiency.
59. What is the significance of keeping the checkbox in the blue prism?
Ans:
Checking the checkbox in Blue Prism signifies enabling specific features or functionality, impacting bot behavior and customization.
60. What is an Environment Variable?
Ans:
The term “Environment Variable” in Blue Prism refers to a configurable value that can be set at different levels within the Blue Prism platform. These variables are used to store and manage data or configuration settings that can be accessed by processes or objects within your automation.
61. Describe Statistic data item.
Ans:
A statistic data item is a variable used in Blue Prism to capture and store quantitative data for analysis and reporting within an automation process.
62. Is it possible to Initialize page in BP?
Ans:
In Blue Prism, you can’t directly initialize a page like a web application, but you can design your automation process to start with specific actions or data configurations to simulate initialization.
63. What does SDD stand for and what does SDD serve?
Ans:
SDD stands for “Software Design Document,” and it serves as a detailed reference outlining the architecture, functionalities, and technical specifications of a software project, aiding developers and stakeholders in its implementation and understanding.
64. What does a Queue manager in Blue Prism do?
Ans:
In Blue Prism, a queue manager oversees the management and distribution of work items or tasks in a queue, ensuring they are processed efficiently by RPA bots while providing tracking and reporting capabilities.
65. Explain Mark Exception and System Unavailable Exception in Blue Prism.
Ans:
“Mark Exception” in Blue Prism allows explicit marking of an exception during a process without immediate termination. “System Unavailable Exception” addresses temporary unavailability of the automated system, enabling retries and alternative actions for reliable automation in intermittent outages.
66. What are the advantages of creating Visual Business Objects (VBO)?
Ans:
- VBOs promote the reuse of automation logic across processes, reducing duplication and development time.
- They enable the organization of complex processes into manageable, independent components for easier maintenance.
- VBOs abstract technical complexity, making automation accessible to non-technical stakeholders for collaborative development.
67. List the steps to create a Web service in Blue Prism.
Ans:
Step 1: Prepare your existing Blue Prism process for web service integration.
Step 2: Identify the data or functionality to be exposed through the web service.
Step 3: Design the web service, defining input and output parameters and operations.
Step 4: Use Blue Prism’s web service generation feature to create web service code.
Step 5: Configure web service settings, including authentication, endpoints, and protocols.
Step 6: Implement authentication mechanisms for secure access.
Step 7: Define a Web Services Description Language (WSDL) file for the web service interface.
Step 8: Generate service artefacts (client and server components) from the WSDL.
Step 9: Implement server-side logic to process incoming requests and invoke the Blue Prism process.
Step 10: Deploy the web service in a suitable hosting environment.
Step11: Test the web service using tools like SoapUI or Postman.
Step12: Install safety precautions like SSL certificates and firewalls.
68. What does OID mean? Give it a definition.
Ans:
OID stands for “Object Identifier.” It is a unique alphanumeric string or numerical value used in various computing and network protocols to uniquely identify objects, attributes, or entities within a specific naming or hierarchical structure.
OIDs are commonly used in technologies like SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) and X.500 directory services to ensure the precise identification of objects in a standardized manner.
69. What is the PDI in Blue Prism?
Ans:
In Blue Prism, “PDI” typically stands for “Process Design Instruction.” PDI is a document or set of instructions that provides detailed guidance on how to design and build an automation process within the Blue Prism platform.
PDI documents help ensure that the automation development process follows best practices and aligns with the organization’s objectives.
70. What are the functions of Global Mouse Click and Global Send Keys?
Ans:
Global Mouse Click in Blue Prism allows the automation to perform mouse clicks, simulating user interactions with UI elements. On the other hand, Global Send Keys enables the bot to emulate keyboard inputs for tasks like data entry or navigation within applications, enhancing automation capabilities.
71. How do you safeguard a repository?
Safeguarding a Blue Prism repository involves strict access controls, version tracking, data encryption, and regular backups. Access control ensures authorized users can access and modify the repository. Version tracking helps identify changes and allows rollbacks when needed. Data encryption protects sensitive information, and regular backups ensure data recovery in case of incidents.
72. What does the Active Accessibility Interface in Blue Prism mean?
Ans:
In Blue Prism, the “Active Accessibility” interface refers to a technology that enables RPA bots to interact with software applications, including those that may not have native automation support.
Blue Prism uses the Active Accessibility interface to bridge the gap between its automation capabilities and applications that may not have built-in automation hooks or APIs, allowing for broader compatibility in the automation of various software systems.
73. What do Sub-Pages in process mean?
Ans:
In Blue Prism, “Sub-Pages” within a process represent a way to modularize and organize automation logic. They allow you to break down a complex process into smaller, more manageable sections, each with its own set of actions and responsibilities.
This modular approach simplifies troubleshooting and facilitates collaboration among team members working on different aspects of the automation project.
74. How many endpoints ought to be on a page?
Ans:
There is no fixed number of endpoints for a page in Blue Prism; it depends on the complexity and requirements of the automation task.
75. How do you add data items to an expression?
Ans:
You can add data items to an expression in Blue Prism by referencing them using the “@” symbol followed by the data item’s name or by using the “Data Item” option in the expression editor.
76. How may the collection field be incorporated into an expression?
Ans:
In Blue Prism, you can include a collection field in an expression by referencing the collection’s name with an index using “@” symbol, like ‘@CollectionName[1]’.
77. How do Global data items work?
Ans:
Global data items in Blue Prism are variables that can be accessed and modified across multiple processes or objects. They provide a centralized and consistent way to store and share data, making it accessible to various parts of your automation solution.
78. What do Start-up parameters mean?
Ans:
Start-up parameters in Blue Prism are configuration settings or values provided at the initiation of a process or bot. These parameters serve as input data and instructions that can influence the behavior and execution of the automation. Start-up parameters can include values like file paths, user credentials, or other inputs specific to the process’s current run.
79. What do the Blue Prism resources and sessions entail?
Ans:
Blue Prism resources are the software elements, such as processes, objects, and data that bots interact with during automation. Sessions, on the other hand, represent the instances of a bot’s interaction with these resources, including the execution of specific tasks and processes, allowing multiple bots to work concurrently in separate sessions.
80. How frequently can a session run?
Ans:
A Blue Prism session can run as frequently as required, depending on the automation schedule and resource availability.
81. What does “Exclusive process” mean?
Ans:
- An “Exclusive process” in the context of Blue Prism refers to a type of automation process that operates without interruption or interference from other processes.
- Exclusive processes are typically allocated dedicated resources and are isolated from regular queue-based processing to guarantee their performance and efficiency.
82. What is an Application Modeller uses?
Ans:
The Blue Prism Application Modeller is used to:
- Capture and highlight UI elements for automation.
- Identify elements by attributes like labels and positions.
- Define specific regions within an application for interaction.
- Interact with web applications using HTML mode.
- Extract and work with text-based UI elements.
83. What does Always Wait for Screen Change mean?
Ans:
“Always Wait for Screen Change” is a setting in Blue Prism used to ensure that the automation process waits for a visual change on the screen before proceeding with the next action. When this setting is enabled, the bot will pause and monitor the screen for any visual updates or changes, such as the appearance of a specific element or the alteration of screen content, before continuing its execution.
84. Describe Business Object Definition.
Ans:
A Business Object Definition (BOD) in Blue Prism serves as a blueprint for creating reusable automation components. It defines attributes, methods, and data flow, promoting consistency and efficiency in the development of automation processes. BODs enhance standardization, reusability, and maintainability, ensuring effective automation design.
85. What does the Navigate to New Proposal action mean?
Ans:
The “Navigate to New Proposal” action typically refers to a step in an automation process where the RPA bot is instructed to access or create a new proposal within a specific software application or system. This action involves navigating through the application’s user interface to reach the relevant section or form for initiating a new proposal.
86. What is the Main Page and what does it contain?
Ans:
The Main Page in Blue Prism is the starting point of a process and contains the primary automation logic and actions for that process.
87. Why do systems throw retry exceptions?
Ans:
Systems may throw retry exceptions in Blue Prism to signal temporary issues or errors that may resolve with a retry attempt, such as network timeouts or intermittent connection problems.
88. How can I determine whether an object is connected to the application?
Ans:
To determine whether an object is connected to the application in Blue Prism, you can use the “Element Exists” or “Wait for Element” action within a stage. These actions can check the existence of the object on the screen, indicating its connection to the application.
89. In Blue Prism, is it possible to set the priority for working with queue items?
Ans:
Yes, in Blue Prism, you can set the priority for working with queue items. The priority can be defined when adding items to the queue, allowing you to specify the order in which queue items are processed. Higher-priority items are typically processed before lower-priority items, enabling customization of processing order based on business needs.
90. How do you configure safe stops?
Ans:
To configure safe stops in Blue Prism, you define specific criteria or conditions that must be met before a process or bot can safely halt or exit. These conditions ensure that the automation stops gracefully without errors or unexpected interruptions, enhancing process reliability.
91. Describe the Functional Requirements Questionnaire (FRQ).
Ans:
The Functional Requirements Questionnaire (FRQ) is a tool used to gather detailed information about the functional aspects and specific requirements of a software or automation project, aiding in its planning and development.
92. How should a connector be chosen for a blue prism?
Ans:
Choosing a connector in Blue Prism involves evaluating compatibility with the target system or application and selecting one that offers pre-built functionalities and ease of integration.
- Identify Automation Needs: Understand the specific requirements and functionalities your automation project demands.
- Compatibility Check: Ensure that the connector is compatible with the target system or application you intend to automate.
- Available Choices: Consider the connectors available within Blue Prism’s ecosystem and assess their suitability for your project.
- Functionality: Evaluate the connectors based on the range of pre-built functionalities they offer for your automation tasks.
- Documentation: Check the availability and quality of documentation and resources for the chosen connector to aid in its implementation.
93. Which symbol is used to mark a Control Room pending or unworked item?
Ans:
In Blue Prism’s Control Room, pending or unworked items are indeed marked with three blue dots (⚫ ⚫ ⚫ ) to indicate their status.
94. Explain the role of the “Output” parameters in Blue Prism actions.
Ans:
In Blue Prism, “Output” parameters enable actions to share data and results with other parts of the automation process or subsequent actions, facilitating data passing and decision-making within the workflow.
95. Is Blue Prism an RPA application?
Ans:
Yes, Blue Prism is indeed an RPA (Robotic Process Automation) application. It is a popular RPA software platform used for a variety of business process automation.
96. What equipment do I need to run Blue Prism’s Robotic Automation Platform?
Ans:
To run Blue Prism’s Robotic Automation Platform, you will require appropriate hardware, such as a computer or server, equipped with adequate processing power, memory, and storage capacity. The chosen operating system should be compatible with Blue Prism’s requirements, typically Windows.
97. How do I begin communicating forms with Blue Prism?
Ans:
To start communicating with forms using Blue Prism, you need to utilize the Blue Prism Application Modeller. This tool allows you to interact with the user interface of applications by capturing and configuring UI elements on forms. You can spy, recognize, and manipulate these elements within your automation processes, enabling data input, extraction, and navigation through forms with ease.
98. How much does mechanical mechanization cost?
Ans:
The cost of implementing mechanical automation using Blue Prism can vary significantly depending on various factors, including the complexity of the automation, the number of processes to be automated, the licencing model chosen, and the specific needs of your organization.
99. Explain the concept of Blue Prism’s Digital Workforce.
Ans:
Blue Prism’s Digital Workforce is a concept that involves deploying software robots (bots) to mimic human tasks within an organization. These bots automate rule-based, repetitive processes by interacting with digital systems and applications. They execute actions, process data, make decisions, and communicate with other systems, leading to increased operational efficiency, accuracy, and scalability.
100. How does Blue Prism handle Data encryption?
Ans:
Blue Prism ensures Data encryption through mechanisms such as encryption at rest, encryption in transit, and secure credential management, safeguarding sensitive information within automation processes and complying with data security standards.




