
Solaris is a Unix-based operating system developed by Sun Microsystems, now owned by Oracle. Known for its robustness, security features, and scalability, it’s widely used in enterprise environments. Solaris offers advanced technologies like ZFS for efficient storage management and DTrace for system analysis. Its networking capabilities and support for high availability through clustering make it a reliable choice for mission-critical systems. Solaris administrators manage user accounts, system configurations, updates, and ensure the system’s security and optimal performance.
1. What is Sun Solaris?
Ans:
Solaris is the Unix based operating system that was initially developed by the Sun Microsystems.. A proprietary software, Solaris is now under the Oracle after acquisition of Sun Microsystems. The Oracle Solaris is known for scalability on SPARC systems and has support for the x86-64 workstations.
2. Explain Admin Command.
Ans:
Local Kerberos services can be managed by an administering policies, key tabs and principles by managing admin command. Admin.local is used to master KDC and it does not need any authentication. On server login information is passed through the secured server. It checks the principle name by value of the user environment variable.
3. How does Solaris operating system boots?
Ans:
The boot procedure of operating system can be divided into the four categories namely:
- Post
- Obprom
- Init phases
- Kernel initialization.
4. Is it feasible to create a new hard disk swap without formatting?
Ans:
“ No “ without label drive, can’t do anything.
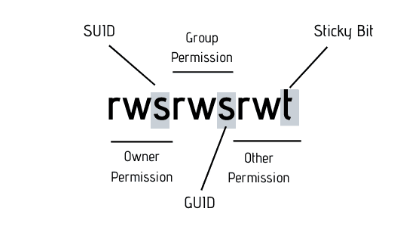
5. What is sticky bit in Solaris?
Ans:
Sticky Bit is the permission bit that protects the files with in Directory. If directory has sticky bit set, a file can be deleted by owner of the file, the owner of the directory or root. This Prevents the user from deleting the other users files from public directories . The sticky bit is displayed as a letter t in execute field for ‘others’.
6. Explain Command Prof_attr.
Ans:
This forms RBAC profile database. It displays the relationship between the among the profiles in the database. It also gives an authorizations between navigation for those files. One of the samples is be Solaris.admin.fsmgr.read.solaris.admin.serialmgr.read.
7. What does KERNEL INITIALIZATION?
Ans:
KERNEL INITIALIZATION: ufsboot load kernel (generic unix), kernel will load all the necessary devices modules to mount root partition to continue the booting process.
Init Phase : It will started by an executing of /etc/init program and start the other process reading the /etc/inittab files, as the directory in /etc/inittab files.
8. How does find RAM size in Solaris server ?
Ans:
In Solaris 10 can find RAM Size using the sdtwsinfo command. This command gives the complete Workstation Configuration Information in the pop up window.
9. Explain the types of installations in Solaris?
Ans:
Solaris Installation Program: This is the general way of Solaris installation through CD/DVD-ROM.
Solaris Installation Program over Network: Installing Solaris from a server that has access to the Solaris disc images.
10. What are NIS daemons?
Ans:
NIS services are provided by the five daemons and managed by a service management facility (SMF).
- – Ypserv – Server Process
- – Ypbind – Bind Process
- – Ypxfrd – High speed map transferring
- – Rpc.yppasswdd – NIS password update.
11. Describe FSCK.
Ans:
FSCK Utility is for checking and repairing files system inconsistencies,
Phase 1: Check the Blocks and Sizes – checks inodes for the inconsistencies.
Phase 2: Check a Path-Names – checks directory <-> inode consistencies.
Phase 3: Check Connectivity – checks that all the directories are connected to file system.
12. What is the difference between dsk and rdsk ?
Ans:
dsk: Block level devices, FS Which are formatted and mounted that device is called the block device.
rdsk: Raw level device or a character level device.
13. What does Port of Telnet, ssh, ftp, http, nfs, ntp?
Ans:
- ftp port is 21
- ssh port is 22
- Telnet port is 23
- ntp port is 123
- smtp port is 25.
14. What are the main differences between solaris 10 and 9?
Ans:
The main difference in the solaris 9 & solaris 10 is “SMF(Solaris Management Facility)”. In solaris 9, if any service goes down then should restart all the services this is the disadvantage. But in solaris 10,if any service goes down then that particular service can select and enable it instead of restarting all the services.
15. What is LOM and how does access it?
Ans:
Lights out management is abbrevation and some of Sun severs a use this fecility to emotly operate a Sun sever by conneting a rollover cable from LOM port to a laptop. There is no need to turn on a server , but if the server is just powered , can connect the laptop to LOM port and operate the conected Server.
16. How does Formatting a disk in Solaris?
Ans:
Add the disk , run devfsadm command then format command > select disk , enter a required details for formatting. create the new partition table using a format command.
17. How does Solaris operating system boot?
Ans:
The boot procedure of operating system can be divided into the four categories namely:
- Post
- Obprom
- Init phases
- Kernel initialization.
18. Explain each of the phases involved in a booting the operating system?
Ans:
Post – As switch on power, it will identify the hardware and certain other information like system ID, memory division, serial number, architecture type, and IP address. In addition, it also loads the program that is known as a bootblk.
19. What does use ‘top’ command on Solaris operating system?
Ans:
An alternative to ‘top’ command is to use it while working on operating system. The top command in Solaris, as well as in many other Unix-based operating systems, provides the real-time, dynamic view of the processes running on system. It displays the detailed information about system’s performance, including CPU usage, memory usage, and the other statistics.
20. How many types of installation of OS are available and explain each of them?
Ans:
There are the seven types of installation of the Solaris operating system and they are follows:
- Solaris installation program is a general way in which can install the OS with the help of DVD or CD ROM.
Installation procedure over the network: Installing an operating system using a server that has easy access to the Solaris disc images.
Flash installation: With the help of this process, installation can be carried out by a master system.
21. How many types of installation of OS are available and explain each of them?
Ans:
RAID stands for a Redundant Array of Inexpensive or Independent Disks. It has a six levels as RAID Level 0 – RAID Level 6.
22. What are the run levels in Solaris operating system?
Ans:
- 0 – it is used during a power downstate
- 1 – the administrative state
- 2 – Multi-user state
- 3 –multi-use with NFS state
- 4 – alternative multi-user.
23. How does end any process in this operating system?
Ans:
Whether are a superuser or root user, should know how to terminate a process of another user on the operating system. In addition, to terminate the any process, also need to obtain the PID of the process.
24. Explain difference between dsk and rdsk?
Ans:
dsk Devices:
- dsk stands for “disk.”
- dsk devices represent a whole disk including partitions.
- They are used for the block-level I/O operations, where data is read or written in the blocks.
rdsk Devices:
- rdsk stands for “raw disk.”
- rdsk devices bypass operating system’s buffer cache and directly access raw disk partitions.
25. What does NFS daemons?
Ans:
In order to support the NFS activities, the NFS daemons are available in the various types and they are as follows:
Automount: It helps in mounting and unmounting the requests with the help of autofs service.
Mounted: It takes care of the mount requests and gives information regarding mounting nfs activities.
26. What does pkgadd command?
Ans:
This command helps to install the signed or unsigned software. In addition, it also helps to remove the any existing packing that is present with the same file name as that of the one that are trying to add.
27. How does the Solaris cluster work?
Ans:
The cluster configuration of operating system consists of both the hardware and software components
Hardware components:
- Servers with the local storage
- Cluster interconnections
Software components:
- Data services function
- Operating system cluster software and help in communicating with the customer.
28. How does login to the Solaris operating system and what does login shell used for the same?
Ans:
Solaris can be considered a secured platform and users need login credentials to get access to a same. Before starting operating system, the ‘hostname console login: Rohit’ message would pop up on screen.
Following this, as soon as user presses on the ‘return’ option, he or she is asked to use password for the account. To keep the password safe, it does not come up on screen, and instead, it is displayed in a form of dots.
29. What does Command ‘Ls’?
Ans:
With the help of this command, can have access to the main directory. In addition, it also permits to access the files present in an operating system. It shows and prints the different ownerships file accessibility, the file name including all its in other details.
30. What’s the contrast between using octal and symbolic codes to set file permissions in an operating system?
Ans:
The primary point of the difference between the two is that the former one is a relative whereas the latter one is present in the numeric codes. The settings remain unchanged with the help of a symbolic codes in the operating system.
31. Does working on the Solaris operating system, how does user help check any process?
Ans:
The system creates the independent process after reading command, and the process comes with the PID relating to the process. In order to maintain track of each process, PID has been created. For finding any process, the PS command is enough to help users.
32. What is the procedure for displaying and changing the default boot device?
Ans:
The command ‘eeprom boot-device’ is used to display the default boot device. And ‘Devfsadm’ is used to reconfigure devices after a reboot.
33. Why does the Solaris operating system slow down?
Ans:
The system can start to the function slowly when there are faults in kernel memory leak. It takes place when process consumes a certain part of the memory which is unable to release back to operating system. Following this, in case of any object-oriented program, object that lies within memory, cannot be accessed.
34. What is the zone in Solaris?
Ans:
Zones in Solaris are used to the isolate software applications and services using the flexible software-defined boundaries. Previously known as Solaris containers, Can build the Oracle Solaris Zones using the technologies such as Solaris Resource Manager, and Solaris Zones Partitioning technology.
35. Mention some L RAID levels in Solaris?
Ans:
Solaris supports the six RAID levels from 0 to 6. Only the few storage environments support RAID levels 2, 3, and 4.
- The other three RAID levels are the most supported by storage environments.
- RAID level 0 – Here, data are spread across the relatively small, equally-sized fragments which are allocated evenly across the multiple physical disks.
36. What is Piping in Solaris?
Ans:
- A pipe is the pair of files between two process that is created in parent process. A pipe is used to connect only the two processes and a single pipe also connects multiple child processes to each other and related parent.
- A process can create the pipe with a call to pipe(). This call returns a two file descriptors in the array. Both processes read from p[0] and write to p[1].
37. How to check the Solaris Volume Manager Version?
Ans:
Can use the command “pkginfo | grep -i volume” and “pkginfo -l SUNWvolr” to check version of the Solaris Volume Manager in the Solaris 9 and 10.
38. What does LDOMS in Solaris?
Ans:
The LDoms (Logical Domains) are the virtualization and partitioning technology that allows administrators to allocate the various resources in the system such as memory, CPUs, and devices into the logical groups. This group, then creates multiple, discrete systems, with each having its own operating system resources that are identified within single computer system.
39. What is OBP in Solaris?
Ans:
The OBP (OpenBoot PROM) provides the list of useful OBP commands. It helps in booting, configuring, and performing diagnostics on Sun SPARC hardware and clones.
Some of OBP commands are,
Power-off: it will halt box and turn off the power.
Reset: it will perform the soft reset. Boot – it boots the system.
Show-devs: it provides the list of devices available to the system.
40. What is the maximum no. of slice that can be created in single disk?
Ans:
In Solaris operating systems, maximum number of slices that can be created on single disk is 8. These slices are identified as s0 through the s7. Each slice can be used to create separate file system or partition on disk. The limitation of 8 slices per disk is convention in Solaris systems.
41. How does find network card speed in Solaris?
Ans:
The kstat -p | grep link_ | grep bge command is used to display network interface variables. And can use the ndd command with it to set network interface configurable to check current network speed.
42. What does NFS daemons in Solaris?
Ans:
NFS daemons are used to handle and support NFS activities in the Oracle Solaris. Several NFS daemons for handling NFS activities. They are,
Automountd Daemon: It handles mounting and unmounting request from autofs service.
Lockd Daemon: It is used to support record-locking operations on NFS files.
43. What does use of df-k command in Solaris?
Ans:
The df -k command is used to display the amount of space is currently in use on each disk mounted on the system. It specifically displays a amount of space available and the percentage of space in use for every disk that is mounted on the system.
44. Explain Command Prof_attr?
Ans:
This paperwork the RBAC profile database. It shows relationship between the various profiles inside a database. It additionally gives an authorizations between navigation for ones files. One of the samples is Solaris.Admin.Fsmgr.Study.Solaris.Admin.Serialmgr.Read.
45. What does Best Solution To Avoid Large Number Of Groups?
Ans:
The best is for not developing a big range of corporations lies with system administrator. It is excellent to apply structural organization membership which reflects the organizational divisions. To manage document get entry to gadget admin can use the access control lists.
46. What does Umask?
Ans:
Wide set permissions can be set by the means of using umask that may set write, read and execute permissions on a new files created by the person. These settings may be crafted from command line to reflect huge settings. It also can be set from global gadget settings report. Umask command presentations all settings made with that command.
47. How does Determine Whether A File Is Setuid?
Ans:
The easiest way to decide whether a record is setuid or not by way of checking for a files which can be owned by basis and after checking for files which might be owned through root can test for s flag documents assigned to user permissions. In the permission desk first s refers to setuid root.
48. Explain Sticky Bit Permissions?
Ans:
This command allows network administrator to loosen up a piece. This command will now not permit deletion of the common documents present within not unusual location. This command enables the users by no longer allowing them to rewrite on the different files.
49. Explain the Limitations Present In Sudo?
Ans:
- It isn’t viable to assign the consumer to paintings on a specific file or profile.
- It is likewise now not viable to assign the user to paintings on particular command.
- By the use of shell instructions and certain features it’s miles feasible to have the few regulations on a consumer however it’d devour time for bigger setup.
50. What does Three Different System Management Roles?
Ans:
- There are three distinct roles specific by using the Solaris are:
- Primary administrator who’s responsible for a protection.
- System administrator is responsible for the day after day roles.
- Operator is responsible for the records back up and upkeep.
51. What does Solaris Roles?
Ans:
RBAC implementation relies upon position detailed inside the administrator profiles. Roles are carried out the consistent with the profile. Also get admission to sure documents and configuration may be assigned through user profile. It additionally permits the RBAC to distinguish high technical know-how roles from low ones.
52. What does Rbac?
Ans:
RBAC is brought into the Solaris for managing precise responsibilities. These specific tasks are primarily based and described inside administrator profile. It is based on standard advanced with aid of NIST. RBAC is the vital device for performing the multiple responsibilities.
53. What does Paging & Server Average Time?
Ans:
If disk shows consistently high reads/writes along with , percentage busy (%b) of the disks is greater than 5 percent, and average service time (svc_t) is greater than 30 milliseconds.
54. What does Difference Between Incremental Backup And Differential Backup?
Ans:
Incremental: Only those files will be included which have been changed since a last backup.
Differential: Only those files will be included which have been changed since a last Full backup.
55. What does Difference Between Ufs And Tar Command?
Ans:
ufsdump:
- Used for a complete file system backup.
- It copies the every thing from regular files in file system to special character and block device files.
Tar:
- Used for a single or multiple files backup.
- Can’t backup special character & block device files.
56. What does Physical Device To Check The 2 Nodes Connect In Cluster?
Ans:
In the Solaris Cluster environment, the physical device used to check connectivity between two nodes in the cluster is often referred to as “Private Interconnect” or “Cluster Interconnect.” This is the dedicated network connection between the cluster nodes used for communication and synchronization purposes.
57. What does Difference Between Hard And Soft Mount?
Ans:
Hardmount: Normal file system mount used mainly for a mounting local file systems. Once a file system is a hard mounted, can use the normal filesystem untill its umount.
Soft mount: It allows the automatic unmounting if filesystem is idle for a specified timeout period. It is mainly used for a network filesystems like NFS It can be configured using the Autofs and the network filesystem can be soft mounted.
58. What does Performance Tool Used?
Ans:
- Iostat ,
- vmstat ,
- prstat ,
- sar ,
- netstat,
- top.
59. What does Different Ways to Execute Profiles?
Ans:
Profiles can be executed in the many different ways some of them are
- Pfexec executes athe single command in profile.
- With the some restrictions pfsh and pfcsh can be executed.
- By directly logging into an account using su.
60. What does list of hot Keys For Bash Shell?
Ans:
Ctrl+l . Clears aScreen. Ctrl+r . Does search in previously given commands in the shell. Ctrl+l – Clears typing before the hotkey. Ctrl+a . Places cursor at the beginning of command at shell. Ctrl+e . Places cursor at the end of command at shell. Ctrl+d . Kills the shell. Ctrl+z . Places currently running process into the background.
61. How does Date And Time For . When Script Is Executed ?
Ans:
Add the following script line in the shell script. Eval echo “Script is executed at `date`” >> time info.inf Here, .timeinfo.inf. Contains a date & time details ie. When script is executed and history related to the execution.
62. How does LAN cards can have in server?
Ans:
Just Type in following command at prompt#ifconfig -a.That shall give LAN Cards as well as total Physical and Logical IP Addresses dmesg – It displays all the configured items on the systems.
63. Which command display diagnostics in ok boot prompt?
Ans:
Diagnostic Test Commands
- watch-net % To check the network connections.
- test net % To test a network conection.
- probe-scsi % To find devices attached to SCSI BUS.
64. What does difference between /dev/dsk and /dev/rdsk ?
Ans:
- /dev/dsk Devices:
- dsk stands for “disk.”
- /dev/dsk devices represent a whole disk including partitions.
- They are used for a block-level I/O operations, where data is read or written in the blocks.
- For example, /dev/dsk/c0t0d0s0 represents entire disk (c0t0d0) and slice 0 (s0).
65. What does use of Growfs utility in solaris?
Ans:
The growfs utility in Solaris is used to expand UFS (Unix File System) file system to fill all the available space on a disk partition. When create a file system, it is initially sized based on specified parameters. Over time, might need to increase the size of file system to accommodate more data.
66. What does difference between container and zones?
Ans:
Zones: A zone is the virtual operating system abstraction that provides the secured environment where applications run.The applications are protected from each other to provide a software fault isolation.
Container: zone + resource management The ability to control resource usage for the processes,task and zones.Resources can be CPU level,RAM,virtual memory,Kernel level tables etc.
67. What does file controls system wide password aging?
Ans:
In Solaris operating systems, the system-wide password aging the policies are controlled by the /etc/default/passwd file. This file contains the various configuration parameters related to the user passwords, including the password aging settings. Specifically, the parameters that control password aging include:
MAXWEEKS: Specifies maximum number of weeks password is valid.
MINWEEKS: Specifies a minimum number of weeks a password must be kept before it can be changed.
68. What does fmthard do?
Ans:
fmthard command in Solaris is used to format the fixed-size hard disk with a VTOC (Volume Table of Contents) label. VTOC is the structure on a Solaris disk that defines a layout of partitions and describes how partitions are used.
69. What does ndd?
Ans:
ndd is the command-line utility in Solaris and the other Unix-based operating systems that is used to view and configure kernel parameters at runtime. The name “ndd” stands for a Network Data Distributor and while it originally had a focus on the network-related parameters, it has evolved to cover the wide range of a kernel parameters beyond networking.
70. What does /etc/system?
Ans:
- Alternative for /etc/sysctl.conf ( linux)
- The /etc/system file provides the static mechanism for adjusting the values of the kernel variables. Values specified in this file are read at a boot time and are applied. Any changes made to the file are not applied to operating system until the system is rebooted.
71. What does jumpstart ?
Ans:
Jumpstart is used to manage the operating system installation in many Information technology environments (corporate and otherwise) where the Solaris operating system computers are be widely used.
72. what does various steps used in jumpstart?
Ans:
Preparing for jumpstart server (making export dir)
- Setting up Install server
- Setting up boot server
- Setting up configuration files
- Making Rules
- Verifying rules
73. What does roles and responsibilities of Solaris administrator?
Ans:
The Solaris Administrator are supervising and guiding staff, coordinating maintenance, troubleshooting a technical problems, ensuring a network security, and collaborating with the various departments in company.
74. What does difference between Solaris 10 and 11?
Ans:
| Aspect | Solaris 10() | Solaris 11() | |
| System Requirements |
Primarily SPARC and x86 architectures. |
Expanded support for modern hardware architectures, optimized for Oracle systems. | |
| Installation | SVR4 packaging system. | Image Packaging System (IPS) for network-based package management. |
75. What does Solaris operating system?
Ans:
Solaris is the Unix-based operating system developed by a Sun Microsystems, now owned by Oracle Corporation. It is known for scalability, reliability, and also security features.
76. How does monitor system performance in Solaris?
Ans:
Solaris provides the tools like vmstat, iostat, and prstat for a monitoring system performance. These commands give information about the virtual memory statistics, CPU usage, disk I/O, and process statistics, respectively.
77. Explain SMF (Service Management Facility) plays in Solaris administration.
Ans:
SMF is the feature in Solaris that manages the system services. It ensures system services are started, stopped, and managed consistently. SMF replaces the traditional init system, providing the dependency management and automatic restart of failed services. And can manage services with the commands like svcadm and svccfg.
78. Explain ZFS (Zettabyte File System) in Solaris.
Ans:
ZFS is the modern file system in Solaris that offers an advanced features like data integrity, snapshots, and data compression. It is designed to handle the large amounts of data and provides a features for data management, data protection, and efficient storage utilization.
79. What does Solaris patch, and how does apply patches to the system?
Ans:
Solaris patches are the updates or fixes for operating system. And can apply patches using patchadd command.
For example: command installs specified patch to system, addressing known the issues and vulnerabilities.
80. Explain zoneadm command in Solaris.?
Ans:
The zoneadm command is used to be manage and administer Solaris Zones, which virtualization technology in the Solaris. And can use zoneadm to create, start, stop, and manage individual zones, providing the isolation and resource management on the Solaris system.
81. How does troubleshoot a system boot issue in Solaris?
Ans:
Troubleshooting the system boot issue in the Solaris typically involves:
- Using a boot -a option to interactively select a boot archive and diagnose boot issues.
- Examining output of svcs and svcs -x to identify the failed services.
- Running format command to check disk integrity.
82. The term “jeopardy” in VCS refers to the dangers associated with code changes.
Ans:
In software development and system administration, version control systems like a Git are used to track changes in a code and configuration files. When changes are made without a proper testing or validation, it can jeopardize the stability, security, or functionality of a software or system being developed or managed.
83. What does command interactive boot from ok prompt?
Ans:
- In the Solaris operating system, an interactive boot from ok prompt can be initiated using b command with the -i option.
- This command will initiate the interactive boot, allowing to interactively select various boot options and configurations during boot process.
84. What command will display VTOC for disk c0t0d0s0?
Ans:
In Solaris, can use the prtvtoc command to display VTOC (Volume Table of Contents) for specific disk and slice. This command provides the detailed output of the VTOC for a specified slice (s0 in this case) on disk c0t0d0. Remember to use an appropriate privileges or sudo if necessary to execute command.
85. What does use of ufsdump command in solaris?
Ans:
The ufsdump command in the Solaris is used to create a backups of UFS (Unix File System) file systems. It allows to back up entire file systems, individual directories, or specific files. The ufsdump command operates at file system level, making it suitable for creating the full backups and incremental backups.
86. What does fmthard do?
Ans:
The fmthard command in the Solaris is used to format fixed-size hard disk with a VTOC (Volume Table of Contents) label. VTOC is the structure on a Solaris disk that defines a layout of partitions and describes how partitions are used.
87. What does ndd?
Ans:
ndd is the Solaris command-line utility used to view and configure a kernel parameters at runtime. It stands for “network data distributor.” With the ndd command, can inspect and modify the various network-related settings and parameters, allowing to fine-tune the behavior of network interfaces and the kernel’s networking subsystem without requiring the system reboot.
88. How does Check The No Of User Logged Into The System?
Ans:
To check the number of users currently logged into the Unix-based system, including Solaris, can use the who command. Open a terminal or a shell session and type: This command will display the list of currently logged-in users, along with usernames, terminal or session information, login time, and originating IP addresses if applicable.
89. How does Check The Process For Particular User?
Ans:
- To check processes associated with the particular user on a Unix-based system, including Solaris, and can use the ps command with the -u option followed by the username.
- Syntax: Ps –u username.
90. How does Bring the Process to offline or online?
Ans:
Suspend (Offline) a Process:
To suspend the process and take it offline, can use the kill command with the STOP signal. need to know the process ID (PID) of the process and want to suspend. can find the PID using ps command. For example, if PID of the process is 12345:
Resume (Online) a Suspended Process:
To resume the suspended process and bring it back online, can use the kill command with CONT signal. Using a same PID as before (12345 in this example):






