- Introduction
- Cause and Effect Diagram
- Cause and Effect Analysis
- Make Cause and Effect Diagrams with SmartDraw
- Cause and Effect Examples
- Utilization of Cause and Effect outlines
- Conclusion
- There are various usefulness and the board devices utilized in business associations.Cause and Effect Diagram, all in all, Ishikawa or Fishbone outline, is one such administration instrument.
- Because of the prominence of this apparatus, larger part of administrators utilize this device no matter what the size of the association.
- Issues are intended to exist in associations. That is the reason there should be a solid interaction and supporting apparatuses for distinguishing the reasons for the issues before the issues harm the association.
- A Cause and Effect graph analyzes why something occurred or may occur by getting sorted out possible causes into more modest classifications.
- It can likewise be helpful for showing connections between contributing elements. One of the Seven Basic Tools of Quality, it is regularly alluded to as a fishbone chart or Ishikawa graph.
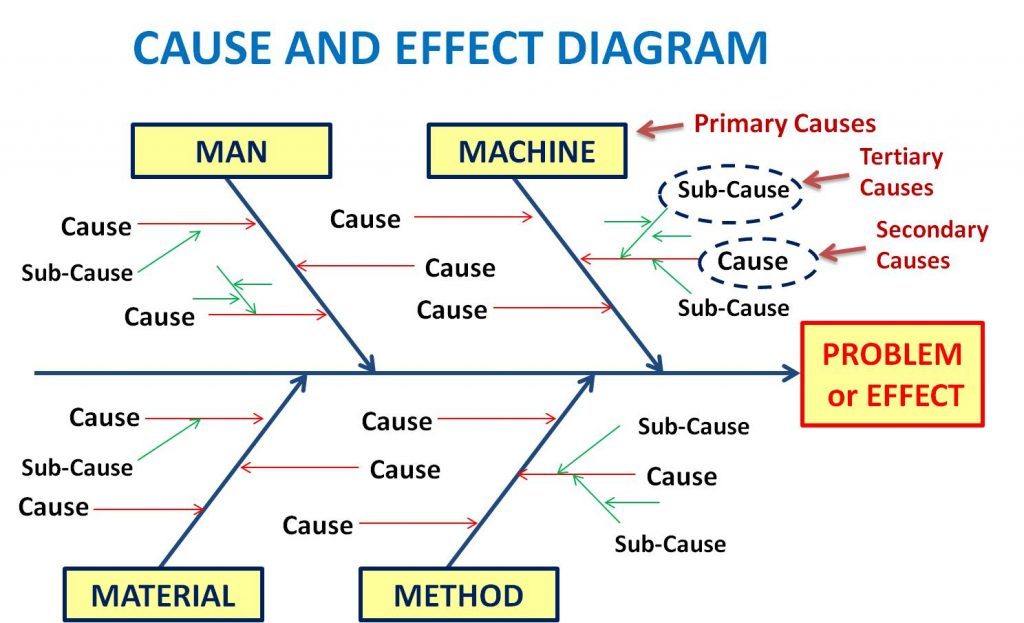
- One reason cause and impact graphs are likewise called fishbone charts is on the grounds that the finished outline winds up appearing as though a fish’s skeleton with the fish head to the right of the graph and the bones diverging behind it to the left.
- To start making a Cause and Effect chart, compose the principle issue or issue to be dissected in a crate that is normally on the right edge of the page, mostly down the drawing region or page.
- A line called the “spine” or “spine” ought to stretch out to the left beginning from the edge of the fundamental box (assuming that you’re utilizing a SmartDraw format, this will as of now show up for you).
- Then, point branches off of the spine, each addressing a reason or impact of the primary issue. Every one of these branches can contain extra branches.Most Cause and Effect outlines look at a comparable arrangement of potential reasons for any issue examined.
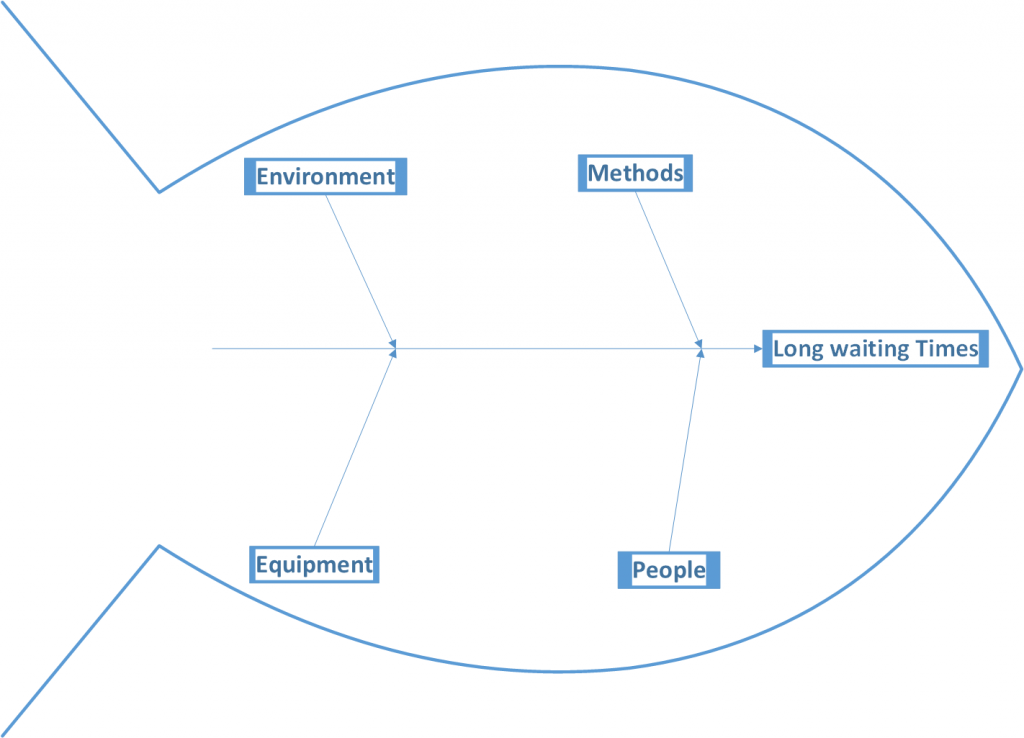
- Environmental elements. Does your foundation project the right picture? Is it desolate? Is it generic? Is it agreeable?
- Providers. Are there any issues conveying your administration? Do you dislike inferior quality food conveyances? Are there too many dropped calls? Would your server be able to deal with traffic spikes? Is it safe to say that you are helping sufficient traffic through promoting channels you’re paying for?
- Frameworks. Do you have strategies and methodology set up for all situations? Do you have present day sales enrolls that assist your servers with setting orders and convey checks effectively?
- Expertise. Are your representatives appropriately prepared? Do they have the right insight?
- Recognize the issue. Characterize the cycle or issue to be analyzed.
- Conceptualize. Talk about every conceivable reason and gathering them into classifications.
- Draw the spine. When the subject is recognized, draw a straight, level line (this is known as the spine or spine) on the page, and on the right side, draw a square shape toward the end. Compose a concise depiction of the issue in the square shape.
- Add circumstances and end results. Causes are added with lines expanding from the fundamental spine at a point. Compose the portrayal of the reason toward the finish of the branch.
- Dissect. When the outline has been finished, dissect the data as it has been coordinated to come to an answer and make things to do.
- Begin articulating the specific issue you are confronting. Now and then, recognizable proof of the issue may not be clear. In such cases, record every one of the impacts and perceptions exhaustively. A short meeting to generate new ideas might have the option to bring up t the real issue.
- With regards to appropriately recognizing the issue, there are four properties to consider; who are involved, what the issue is, the point at which it happens, and where it happens. Record the issue in a case, which is situated at the left hand corner (allude the model Cause and Effect chart).
- From the container, define a boundary on a level plane to the right hand side. The course of action will currently resemble the head and the spine of a fish.
- In this progression, the principle elements of the issue are recognized. For each component, draw off a line from the fish’s spine and appropriately name it.
- These variables can be different things like individuals, material, apparatus or outside impacts. Think more and add as numerous as variables into the Cause and Effect outline.
- Conceptualizing turns out to be very valuable in this Step, as individuals can check out the issue in various points and distinguish different contributing elements.
- Take each variable in turn while recognizing potential causes. Conceptualize and attempt to distinguish all causes that apply to each factor. Add these causes on a level plane off from the fish bones and name them.
- n the event that the reason is enormous in size or complex in nature, you can assist breakdown and add them as sub causes to the primary driver. These sub causes should fall off from the pertinent reason lines.
- Invest more energy in this progression; the assortment of causes should be far reaching.
- Whenever this progression begins, you have a chart that demonstrates the issue, the contributing elements, and all potential foundations for the issue.
- Contingent upon the conceptualizing thoughts and nature of the issue, you can now focus on the causes and search for the most probable reason.
- This examination might prompt further exercises like examinations, meetings and overviews.
- There should be an issue proclamation that portrays the issue precisely. Everybody in the meeting to generate new ideas ought to settle on the issue proclamation.
- Should be concise all the while.
- For every hub, think every one of the potential causes and add them into the tree.
- Associate every loss line back to its main driver.
- Associate moderately void branches to other people.
- In the event that a branch is excessively cumbersome, think about parting it in two.
- Cause and Effect outlines can be utilized to determine authoritative issues proficiently.
- There are no impediments or limitations on applying the graphs to various issues or spaces. The level and power of conceptualizing characterizes the achievement pace of Cause and Effect charts.
- Along these lines, all significant gatherings ought to be available in the meeting to generate new ideas to distinguish every single imaginable reason.When probably causes are distinguished, further examination is expected to uncover further subtleties.
Introduction :-
Cause and Effect Diagram :-
Cause and Effect Analysis :-
In the assembling business, these are alluded to as the 6Ms:
Techniques. Are there elegantly composed and suitable preparation rules set up? Are sure arrangements or guidelines causing log jams or making superfluous advances?
Machines. Are there any support issues with the devices utilized or the quantity of apparatuses accessible?
Materials. Are there any issues getting unrefined components from providers? Any issues with transportation (timing) or with the nature of the provisions?
Estimations. Might there be mistakes in estimation or tainting that caused misleading readings? Would the manner in which you be able to gauge be conflicting somehow or another? Is your hardware routinely aligned and kept up with?
Earth/Environment. Is there an excessive amount of dampness in the climate? Are temperatures excessively hot or excessively cold? Is there unreasonable residue or other tainting?
Labor/People. Do you have excessively little of your labor force dedicated to a cycle? Are new individuals satisfactorily prepared? Is the preparation steady? Are the perfect individuals with the right experience being employed or advanced? Is there a particular position making a bottleneck or committing incessant errors?
Once in a while, an assembling investigation will likewise incorporate two different classifications: Management and Maintenance. In the help business, these are depicted as the 4S:
Every so often, a fifth classification will be incorporated called “Security”. In the promoting business, Cause and Effect charts will frequently comprise of 7Ps:
1.Item. Think about all parts of what you’re selling including its quality, its apparent picture, accessibility, guarantees, backing and client care.
2.Individuals. Whenever individuals purchase your item or administration they might communicate with many individuals: salesmen, client assistance individuals, conveyance individuals, etc. Are there any likely issues with your organization culture?
3.Process/Procedure. How would you deal with issues when they emerge? Could it be said that they are heightened appropriately? Is your staff prepared fittingly and do they follow their preparation?
4.Advancement. Think about promoting, deals, PR, marking, direct showcasing, associations, and web-based media.
5.Cost. How does the cost of your item or administration contrast with contenders? What limits and installment techniques are accessible?
6.Actual proof/Packaging. How is your item or administration consumed? Is how or where you present your item harming your capacity to change over? Are your offices perfect and clean? Is the bundling modest or costly?
7.Place/Plant. Is your dispersion productive and financially savvy? Is your item sold in the right stores or neighborhoods? Are your stores advantageous for your objective clients?
Make Cause and Effect Diagrams with SmartDraw :-
SmartDraw makes making Cause and Effect graphs simple with worked in shrewd layouts that let you add new causes in a solitary snap and arrangement your outline naturally.
Best Practices in Cause and Effect Analysis :
These are awesome and most normal practices while making Cause and Effect outlines.
Cause and Effect Examples :-
The most ideal way to get Cause and Effect outlines is to check out certain instances of Cause and Effect graphs. Click on any of these Cause and Effect charts remembered for SmartDraw and alter them:
Peruse SmartDraw’s whole assortment of Cause and Effect models and formats
Ventures for Using the Tool :
Following are the means that can be followed to effectively draw a Cause and Effect chart:
Step 1 – Properly distinguish the issue close by
Step 2 – Add the main considerations that add to the issue
Step 3 – Identify the causes
Step 4 – Diagram investigation
Utilization of Cause and Effect outlines :-
With regards to the utilization of Cause and Effect outlines, conceptualizing is a basic advance. Without legitimate conceptualizing, a productive Cause and Effect graph can’t be determined. Hence, following contemplations ought to be tended to during the time spent inferring a Cause and Effect outline: