
- Overview of MySQL
- History and Evolution
- Core Features
- MySQL Architecture
- Installation and Configuration
- Data Types and Storage Engines
- SQL Commands in MySQL
- Security Features
- Performance Optimization
- MySQL Use Cases
- MySQL vs Other RDBMS
- Summary
Overview of MySQL
MySQL is a powerful, open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) that has been widely adopted across industries due to its speed, reliability, scalability, and ease of use. It serves as the backbone for many web applications and enterprise-level solutions. MySQL database foreign key utilizes Structured Query Language (SQL) for accessing, managing, and manipulating data, and supports a variety of storage engines and data types to accommodate different Performance Optimization and functionality needs. With extensive community support and continual development by Oracle Corporation, Database Training is crucial for professionals to keep their skills current and leverage new features effectively., MySQL has become a leading choice for developers building applications on platforms like LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP/Python/Perl). From powering blogs and small applications to serving as the relational database behind massive e-commerce platforms and data warehouses, MySQL offers unmatched versatility.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
History and Evolution
MySQL was first developed by Michael Widenius, Allan Larsson, and David Axmark in 1995 under the company MySQL AB. The initial goal was to provide a reliable and fast solution with an emphasis on open-source distribution. It quickly gained traction among developers due to its simplicity and Performance Optimization
. Key milestones in MySQL’s evolution include:- 1996: MySQL version 1.0 was released.
- 2000: MySQL became fully open source under the GNU General Public License (GPL).
- 2008: Acquired by Sun Microsystems.
- 2010: Sun Microsystems (and by extension, MySQL database ) was acquired by Oracle Corporation.
Under Oracle, MySQL foreign keys continued to thrive, receiving significant updates and support. Variants like MariaDB were also created to preserve the open-source spirit. Ultimate Solution for Database Management ensuring that developers have multiple options based on their specific requirements.
Core Features
MySQL offers a rich set of features that make it an ideal choice for a broad range of applications:
- ACID Compliance: Ensures reliability through atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability.
- Multi-User Support: Enables concurrent access by multiple users without data conflict.
- Replication: Supports master-slave and master-master replication for scalability and fault tolerance.
- Partitioning: Enhances performance by dividing tables into manageable pieces.
- Stored Procedures and Triggers: Facilitates complex business logic directly within the database.
MySQL Architecture
MySQL follows a layered architecture, which promotes flexibility and modularity. The core components of MySQL architecture include:
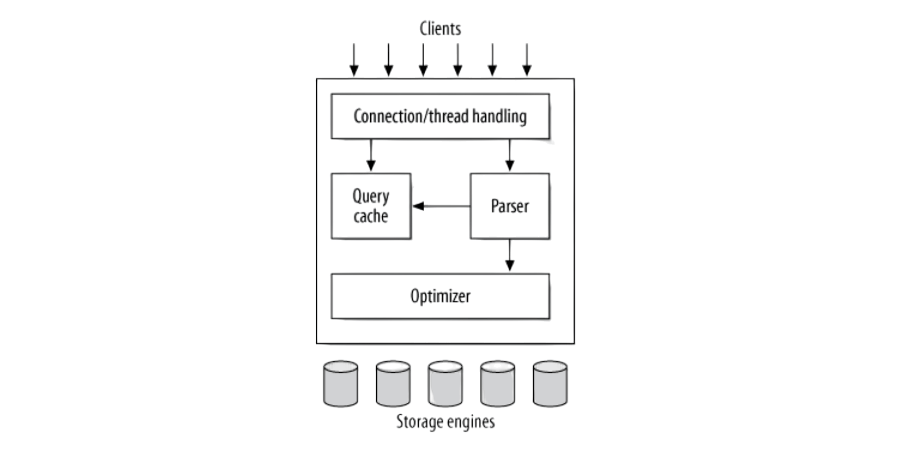
- Client Layer: Handles connections from various applications using MySQL APIs, connectors, or command-line tools.
- SQL Layer: Parses, preprocesses, and optimizes SQL queries.
- Storage Engine Layer: Provides an interface to various storage engines like InnoDB, MyISAM, Memory, and others Buzzword in Database Management
- File System Layer: Interacts with the underlying operating system for data storage and retrieval.
- Download and run the MySQL Installer.
- Choose a setup type (Developer Default, Server Only, etc.).
- Configure the server (port number, root password, user accounts).
- Start the MySQL server and test using the MySQL Command Line Client or Workbench.
- Numeric Types: INT, BIGINT, DECIMAL, FLOAT, DOUBLE
- Date and Time Types: DATE, TIME, DATETIME, TIMESTAMP
- String Types: CHAR, VARCHAR, TEXT, BLOB
- Spatial Types: GEOMETRY, POINT, LINESTRING
- InnoDB: Default engine, supports transactions, row-level locking, foreign keys.
- MyISAM: Legacy engine, fast for read-heavy operations but lacks transactions.
- Memory: Stores all data in RAM for ultra-fast access, Buffer data is volatile.
- CSV: Stores data in CSV format, useful for import/export.
- CREATE TABLE employees (id INT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(100));
- ALTER TABLE employees ADD COLUMN salary INT;
- DROP TABLE employees;
- INSERT INTO employees VALUES (1, ‘John Doe’, 50000);
- UPDATE employees SET salary = 55000 WHERE id = 1;
- DELETE FROM employees WHERE id = 1;
- SELECT * FROM employees;
- SELECT name FROM employees WHERE salary > 50000;
- GRANT SELECT ON employees TO ‘user’@’localhost’;
- REVOKE SELECT ON employees FROM ‘user’@’localhost’;
- Authentication: Ensures users have valid credentials before accessing the server.
- User Privileges: Granular control over what each user can read/write/execute Real-Time Big Data Convert
- SSL/TLS Encryption: Secures data transmitted over networks.
- Data-at-Rest Encryption: Encrypts physical files using keys.
- Firewall Plugin: Monitors and filters queries based on predefined rules.
- Audit Log: Tracks database activities for forensic and compliance purposes.
- Indexing: Use indexing on columns used in WHERE, JOIN, and ORDER BY clauses. Query Optimization: Avoid SELECT *, use LIMIT clauses, and analyze with EXPLAIN.
- Connection Management: Adjust max_connections, wait_timeout, etc.
- Buffer Configuration: Increase buffer pool size (innodb_buffer_pool_size) for InnoDB.
- Caching: Enable query cache (deprecated in recent versions), consider external caching tools like Memcached.
- Monitoring Tools: Use MySQL Enterprise Monitor, Performance Schema, or third-party tools to identify bottlenecks Database Training
- Web Development: Powers popular CMS platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal.
- E-Commerce: Used by platforms such as Magento and WooCommerce.
- Data Warehousing: Supports large-scale analytical workloads with partitioning and replication.
- Mobile Applications: Backends for mobile apps often use MySQL for data persistence.
- Education: Frequently used in academic environments for teaching database fundamentals.
- ERP and CRM Systems: Many business software suites rely on MySQL for data storage.
- PostgreSQL offers more advanced features (e.g., full ACID compliance, custom data types).
- MySQL is easier to set up and typically faster for read-heavy applications COALESCE in SQL Explained MySQL vs Oracle DB:
- Oracle DB supports more enterprise features and is preferred for large-scale commercial applications.
- MySQL is open-source and cost-effective, ideal for startups and mid-sized businesses. MySQL vs SQL Server:
- SQL Server is tightly integrated with Microsoft tools.
- MySQL is cross-platform and preferred for open-source stacks.
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
Installation and Configuration
Installing MySQL can be done through native packages or installers provided by Oracle. The process varies slightly depending on the operating system:
On Windows:Data Types and Storage Engines
MySQL supports a wide variety of data types, grouped into categories:
Storage engines determine how data is stored, indexed, and managed. Key storage engines include:
SQL Commands in MySQL
MySQL supports a full range of SQL commands in MySQL categorized into Data Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation Language (DML), Data Query Language (DQL), and Data Control Language (DCL).
DDL:To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Security Features
MySQL provides comprehensive security mechanisms to protect data from unauthorized access:
Performance Optimization
Optimizing MySQL Commands performance involves tuning queries, indexing, and server parameters. Key areas include:
MySQL Use Cases
MySQL Apache Cassandra is used across a wide range of industries and application types:
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
MySQL vs Other RDBMS
Comparing MySQL with other relational database management system highlights its strengths and limitations:
MySQL vs PostgreSQL:Summary
MySQL database remains one of the most popular and versatile relational database management system RDBMS solutions in the world. Its combination of Performance Optimization, scalability, open-source accessibility, and broad platform support make it suitable for a vast array of applications, from small websites to large-scale enterprise systems. With a rich feature set, active development, SQL commands in MySQL, along with robust community support, ensure that MySQL commands like foreign key management continue to evolve and adapt to modern data management needs highlighting the importance of ongoing Database Training .Whether you’re a developer looking for a fast and relational database management system or an organization needing a scalable and secure data solution, MySQL offers the Buffer tools and flexibility to meet your requirements effectively.


