
- Introduction
- Parts of Decision Making
- Choice Theories
- Ways to deal with Decision Making
- Steps of Decision Making Process
- Sane Decision Making Model
- Limited Rationality or Behavioral Model
- Bartering Model
- Participative Decision Making Model
- Trash bin Model
- Mintzberg’s Model
- Examination of Models
- Conclusion
- Navigation is an every day movement for any individual. There is no special case regarding that. With regards to business associations, direction is a propensity and an interaction also.
- Powerful and effective choices create gain to the organization and ineffective ones make misfortunes. Hence, corporate dynamic interaction is the most basic cycle in any association.In the dynamic cycle, we pick one strategy from a couple of potential other options. During the time spent navigation, we might utilize many instruments, procedures and insights.
- Likewise, we might settle on our own private choices or may lean toward an aggregate choice.For the most part, navigation is hard. Larger part of corporate choices include some degree of disappointment or struggle with another party.
- Causal choice hypothesis: This is an old hypothesis that is as yet being used till date. This hypothesis embraces the rule of levelheaded decision which infers that your preferred result is an outcome of your choice.
- Evidential choice hypothesis: Evidential choice hypothesis in opposition to causal choice hypothesis assumes the most ideal choice contingent on having picked it is the one with the best result. This is accepted to be an unreasonable reasoning.
- Game hypothesis: Is a numerical investigation of vital independent direction. It is viewed as an intuitive choice hypothesis as it thinks about the contention and collaboration between shrewd levelheaded chiefs.
- Bayesian hypothesis: Bayesian hypothesis is a likelihood hypothesis utilized in independent direction. Bayesian is respected to be an expansion of rationale that empowers dissuading relational words with either a valid or misleading state.
- What precisely is the issue
- Why the issue ought to be addressed ●
- Who are the impacted gatherings of the issue
- Does the issue have a cutoff time or a particular course of events
- An issue of an association will have numerous partners. What’s more, there can be many elements included and impacted by the issue.
- During the time spent tackling the issue, you should assemble however much data connected with the elements and partners engaged with the issue. For the course of data gathering, instruments, for example, ‘Check Sheets’ can be really utilized.
- In this progression, the gauge models for passing judgment on the choices ought to be set up. With regards to characterizing the standards, authoritative objectives as well as the corporate culture ought to be thought about.
- For instance, benefit is one of the principle worries in each dynamic interaction. Organizations for the most part don’t settle on choices that diminish benefits, except if it is an extraordinary case. In like manner, standard standards ought to be distinguished connected with the issue close by.
- For this progression, conceptualizing to list down every one of the thoughts is the most ideal choice. Before the thought age step, it is crucial to comprehend the reasons for the issue and prioritization of causes.
- For this, you can utilize Cause-and-Effect graphs and Pareto Chart device. Circumstances and logical results outline assists you with recognizing all potential reasons for the issue and Pareto diagram assists you with focusing on and distinguish the causes with most noteworthy impact.
- Then, at that point, you can continue on creating every single imaginable arrangement (choices) for the issue close by.
- Utilize your judgment standards and dynamic rules to assess every other option. In this progression, experience and viability of the judgment standards become possibly the most important factor.
- You want to look at every option for their up-sides and negatives.
- When you go through from Step 1 to Step 5, this progression is simple.
- Also, the determination of the best option is an educated choice since you have as of now followed an approach to infer and choose the best other option.
- Convert your choice into an arrangement or a grouping of exercises.
- Execute your arrangement without anyone else or with the assistance of subordinates.
- Assess the result of your choice. See whether there is anything you ought to advance and afterward right in future independent direction. This is probably the best practice that will further develop your dynamic abilities.
- There are a few distinct methodologies on comprehension and introducing dynamic cycle. The interaction situated view contends that direction ought to be viewed as a cycle. As indicated by Forman and Selly independent direction is a course of picking an option from a bunch of options to accomplish characterized targets and objectives.
- Characterizing objectives
- Perceiving choices
- Inspecting the results of every other option
- Settling on choice in light of the particular models
- Checking execution
- Altering the underlying choice in view of the input
- People can’t settle on completely sane choices principally on the grounds that they can process and think about a little measure of information right now.
- Skill, data, and time in every circumstance are restricted; in this manner the thorough examination is exceptionally hard and beyond difficult generally speaking.
- People can not consider and perceive every conceivable impediment and limitations of an issue, hence not each of the potential choices are broke down in the objective dynamic cycle.
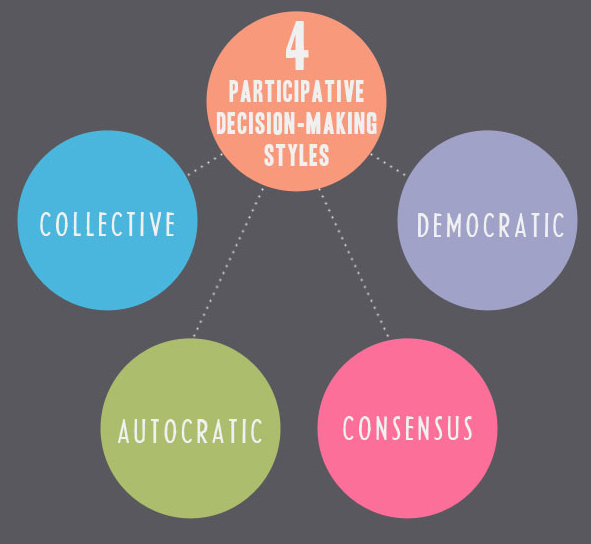
- The haggling dynamic model is extended and shaped the participative dynamic model. The participative dynamic model attempts to bring every one individuals who straightforwardly affected by the choice into dynamic cycle. This model is known as the most just dynamic cycle. Be that as it may, the interest of individuals during the time spent independent direction in this model plays simply the “meeting” job and not “choosing” job. As such, this model gives individuals the amazing chances to offer thoughts and data of real value however they don’t have genuine dynamic power.
- Any partner bunch inside the association might have its own plan and interests to seek after; thusly in this model, the partners are urged to introduce their critical worries before choices are made. It is worth focusing on that partner bunches are now and then sufficiently able to thwart the course of navigation on the off chance that they are excluded from the course of direction. Participative dynamic model should be visible in NATO, United Nations, and other worldwide bodies.
- The significant inconveniences of participative dynamic model are its cost and gradualness. Data in this dynamic model go about as blade that cuts both ways, while the data according to alternate points of view can explain different parts of the issue, the colossal measure of unstructured data is some way or another an issue for supervisors. For having effective participative choice model, members should attempt to subordinate their own advantages in quest for normal destinations.
- Enterprising mode : Definition of methodology is finished by a solitary individual in this mode. The emphasis is on open doors. Technique is directed by the author’s vision and is described by intense choices. In the Indian set-up, we can refer to the instance of Wipro InfoTech to act as an illustration of this method of technique detailing.
- Versatile mode : This method of choices making is alluded to as “wading through”. It is portrayed by responsive arrangements rather than a proactive quest for new open doors. We can again refer to the case of Wipro InfoTech presenting the offer of modified Personal Computers in light of Dell Computers entering the Indian market.
- Arranging mode : This method of independent direction includes efficient data gathering for situational investigation, producing substitute procedures and determination of the fitting methodology. As could be deduced, this mode incorporates both the proactive mode and the responsive answers for current issues. For instance, passage of MNCs into the car markets in India has made the lead player Maruti Suzuki to emerge with new models and dispose of/dial back creation of stationary and old models.
- The most utilized dynamic model is BOGSAT, an abbreviation for Bunch Of Old Guys Sitting And Talking. The term might be a piece discourteous, however holds a touch of truth in it. Generally speaking, the dynamic models and cycles are not adequately figured, essentially in associations with less assets to distribute into processes other than the center business capacities. Despite the fact that a few devices supporting navigation can have been utilized and “old folks” may have insight and vision, mental constraints can ruin the result. Hence navigation and the dynamic interaction can be improved by adjusting tried devices and practices.
- Forman and Selly propose that Herbert Simon’s three Stepd dynamic interaction model is the most broadly acknowledged. Be that as it may, Kansola goes through various ways of thinking in both characterizing independent direction and contrasts in depicting the interaction, including Simon’s model. Kansola states that Mintzbergs key dynamic interaction is one of the most notable portrayals and the most far reaching, as figure shows.
- Mintzberg, Raisinghani, and Theoret contend that simultaneously, essential choice cycles are very complicated and dynamic, yet at the same time they can be defended into structures, which the Mintzberg model is one illustration of. The model was made by noticing and dissecting 25 unique choice cycles in various association types going from institutional associations to administrative, producing organizations and administration organizations. The choices went from buying new hardware and the advancement of new items to HRM choices.
- The model is figured out by noticing various cycles and tracking down likenesses and varieties between the cycles.In the Mintzberg model the course of navigation is partitioned into three phases. The primary Step is distinguishing proof that incorporates perceiving the requirement for a choice and a determination.
- The acknowledgment of the requirement for a choice rises out of seeing a distinction in present and wanted circumstance. Anyway it requires exertion for the chief to perceive the need(s) from all the data that goes through him/her. The diagnostics is tied in with going through present data sources and potentially assembling a few new ones.
- The following Step is fostering the other options, an interaction that comprises of two various types of schedules: Searching and arranging. Looking, is a cycle like the name demonstrates, looking for the other options. Looking can be separated into four sections: surveying authoritative as well as work force information, inactive “pausing”, utilizing “specialists” for search, lastly dynamic looking. Arranging is tied in with building an answer.
- The last Step is the determination. The options assembled in the last advance are screened and the leftover options assessed lastly the picked elective is approved by getting approval from the administration. Assessment has three unique strategies: Judgment assessment, examination assessment and bartering assessment.
- Judgment implies the interior decision making between individuals, dealing implies numerous people utilizing judgment and afterward settling their decision between them, where investigation choice cycle depends on legitimate realities, making it the “cool rationale” technique. Mintzberg’s model for process independent direction is exceptionally far reaching so this is just a synopsis.
Introduction
How about we examine the dynamic interaction exhaustively.
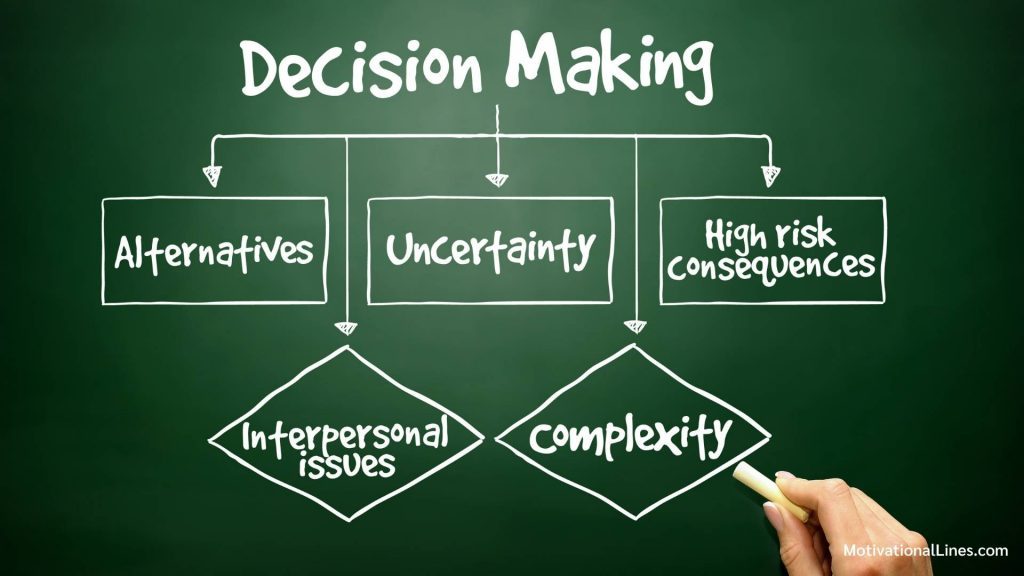
Navigation could be characterized as the investigation of recognizing and browsing options, the most ideal choice that suits a reason. It is normally viewed as a mental report as it includes mental and legitimate thinking. In direction, there are different choices that value to be thought about however the interest isn’t on the quantity of various choices rather to distinguish every one of the other options and pick the one with the most elevated likelihood of accomplishment or that best fits explicit objective or objective.
Independent direction is a cycle that diminishes vulnerability to a significant level. In many choices, vulnerability is diminished rather than being killed. Just in couple of cases choices are made unhesitatingly. This infers that most choice imply a specific measure of hazard. In the event that there is no vulnerability, there is no choice; as you are simply to act and anticipate a decent outcome.
Generally speaking, choices are made by moving forward and back between the models or put forth objectives and the recognizable proof of practical other options. The accessible choices impact the standards we apply to them and furthermore the put forth objectives can impact the options that will be accessible.
Parts of Decision Making
There are different sorts of choice. They have been assembled into three:
1. Choices on Whether: This is a choice that includes a yes/no. A case is the situation of an undertaking chief mulling over in whether or not to get more colleagues. The venture director can either go on to select more colleagues or not, there is no center reason to such choice and you want to conclude that before different options may come up. On the off chance that indeed, options of the number of do you want, of what specialization and some other option may come up.
2. Choice on Which: This sort of choice include settling on a decision from at least two other options, estimating the one with most noteworthy likelihood of accomplishment or that best fits the conditions. An illustration of such choice incorporates a financial backer settling on what brand or item to put resources into from different choices. Various techniques are utilized to settle on such choice as it includes the idea of the chief and furthermore the idea of the actual choice.
3. Restrictive or Contingent choice: These are as of now settled on choice in view of specific conditions being met. This settles on it more straightforward for the chief to make a move once those conditions are met. A decent occurrence is a group chief who said “I have chosen to enroll more colleagues assuming we are granted the venture”.
Choice Theories
Choice hypothesis is the investigation of standards and calculations use for settling on choice. This is accomplished by recognizing values, vulnerabilities and different things that may impact the choice. Choice speculations can essentially be assembled into two: Normative and graphic choice hypothesis. While regulating hypothesis clarifies how choice should be made, clear hypothesis clarifies how choices are made.
Choice speculations could be under sureness (every elective lead to an objective or outcome), hazard (every option has at least one result and the likelihood of each are known) and vulnerability (every elective lead to at least one result with an obscure likelihood). There are various kinds of choice speculations that have been carried out. These include:
Ways to deal with Decision Making
In an association or a group, there are essentially two ways to deal with direction, which are
Dictator: The director or group pioneer settles on a choice in light of his own insight or encounter and impart his choice to the gathering and anticipate their acknowledgment.
Bunch: The assemble will in general settle on the choice by examining the various choices that accommodates their target. A few investigations thought of the examination that in an Authoritarian methodology, the pioneer burns through five minutes to settle on a choice, thirty minutes to impart his choice and another 30minutes for the gathering to acknowledge while a gathering approach burns through 30 minutes to break down and settle on the most ideal choice. Along these lines, the gathering approach is more supported as gathering individuals will quite often like thoughts they consider and have more energy in accomplishing objectives set by their own drive than when choice are being taken for their sake.
Mechanizing System: This is a PC framework that computerizes critical parts (or all) of a managerial dynamic cycle. The essential component of this framework is its capacity to fabricate and computerize managerial choice involving some rationale in a PC framework. Computerized frameworks might go from traditional data innovation frameworks (which might ascertain a pace of installment as per an equation set out) through to more complicated frameworks, for example, ‘master’, ‘business rules motors’, ‘rules-based’ and ‘choice help’ instruments. The mechanized framework is a creating way to deal with decision making as directors find it more straightforward to settle on fair choice once the right standards has been entered.
Steps of Decision Making Process
Following are the significant Steps of the dynamic interaction. Each progression might be upheld by various instruments and strategies.
Step 1: Identification of the motivation behind the choice
In this progression, the issue is entirely examined. There are a few inquiries one should pose to with regards to recognizing the motivation behind the choice.
Step 2: Information gathering
Step 3: Principles for passing judgment on the other options
Step 4: Brainstorm and investigate the various decisions
Step 5: Evaluation of choices
Step 6: Select the best other option
Step 7: Execute the choice
Step 8: Evaluate the outcomes
Sane Decision Making Model
This model, otherwise called “the sane far reaching” model, depends on the renowned monetary methodology where a definitive objective of any activity or change is boosting the productivity of explicit measures by picking the most ideal choice. This model is typically separated into 6 explicit advances:
This model is generally utilized by specialists for the most part in light of its engaging quality and effortlessness. This model offers an organized way to deal with address issue or opportunity and assist directors with arriving at the choice. This model neglects any vulnerability and it is the most ideal for very much organized and basic issues in unsurprising enterprises. In view of its component, the fundamental utilization of this model is in specialized climate where objectives are precisely characterized and there is a settlement on the rules and estimation of objectives.
For example, NASA utilizes the normal model since designing variables, methods, and objectives are generally clear and less questionable. This model is hard to use in the associations which work in powerful and world of politics. The issues and open doors in the powerful climate are mind boggling, accordingly the unmanageable number of potential choices ought to be considered prior to settling on choices in this methodology.
Limited Rationality or Behavioral Model :-
Herbert Simon, Nobel Laureate, scrutinized the levelheaded dynamic methodology and presented the idea of “limited sanity” (5-4). As per this idea:
In genuine world, considering the judicious constraints the administrators ordinarily work on the issue and limit themselves to only a few principle choices. Chiefs as a rule recognize a couple of quantities of rules and normally survey the choices that have worked for their association or other comparable organizations previously.
Simon declared that since all the data isn’t accessible for a decider, the administrators who utilize the limited soundness model, in contrast to objective model, look for “fulfillment” for their concerns and not “expansion”. (Simon) as such, this model shows a decider the “adequate” choices to meet least chosen standards at the dynamic time. In this model, the “rules weighting” assumes a significant part in settling on extreme choice.
Bartering Model
The fundamental utilization of this model is in the circumstances where at least two gatherings taking part in the choice might have irreconcilable situation. The delegates of the associations ought to learn and know the standards of exchange. Ranking directors select this methodology in the essential choices which include tradeoff between various associations or between various gatherings inside the association. In this model, the chiefs or moderators look for the shared advantages or normal interests to boost the possibility coming to the suitable choice. The subsequent choice ought to be OK by every one of the elaborate sides.
The bartering model is profoundly utilized in governmental issues fundamentally on the grounds that in this setting numerous dynamic gatherings are taken care of from similar monetary and non-monetary assets and these assets are restricted. In any case, some contend that involving bartering model in governmental issues can prompt circulate power similarly that therefore decline the impact of force which is now and then fundamental in the general public, association, and different networks. The haggling model is valuable for getting various perspectives prior to settling on choice; and it can assist chiefs with settling on the more supportable choice.
The haggling model gives each party including in the choice a situation for mirroring their inclinations. Bartering model pays a lot of thoughtfulness regarding the contenders and their activities in dynamic cycle. One of the disadvantageous of this model is its tedious component sometimes since parties attempt to determine conflicts. Albeit the interests of all gatherings are generally viewed as in the dealings, the desires of the most impressive sides are bound to be addressed than necessities and wishes of the most un-strong gatherings. By and by, a few directors reject a few gatherings from haggling model for getting arrangements all the more rapidly and saving time, however this approach undermines the achievement of the came about choice since certain gatherings may not help the activities relating to the choice. To summarize it, the bigger pool of members in dealing dynamic model prompts even better additional tedious choices.
Participative Decision Making Model
Trash bin Model
As indicated by Cohen, March, and Olsen, numerous choices are made in light of sloppy collaborations of specialists and potential open doors, possibility, and the current accessible human abilities and different assets inside the association. (25) This model suggests that associations and administrators have dynamic, badly characterized, and conflicting inclinations, and associations are run on a premise of experimentation. Partners to some extent comprehend the cycles in the association, and the deciders act haphazardly and hastily. In light of the showed structure, Cohen et al. contended that administrators inside the associations consider numerous arrangements when they have not dealt with issues yet. They keep these arrangements and use them when the issues happen inside the association. They affirmed that: “choices are unloaded in a holding can – the trash bin for sometime later.”
Administrators use trash bin model in exceptionally equivocal conditions which called organized disorders. Cohen et al. contended that deciders are as prone to recognize their objectives through activities as they are to find them preceding choice. Also, they contended that because of existing coordinated insurgencies inside the association a few advancements utilized in the associations are muddled. Additionally, they contended that directors have free comprehension of objectives and means toward the start. Cohen et al. contend that authoritative members learn through experimentation activities without understanding the causes. They likewise contended that generally speaking the dynamic members go back and forth into the cycle continually and their contribution differ due to their advantage, energy, and time (Cohen et al., 1972).
Accordingly, it’s extremely challenging to perceive who will really take an interest in a choice (Cohen et al., 1972). The trash bin model presents four surges of irregularity: 1) arbitrariness in amazing open doors 2) arrangements 3) members 4) issues. Hence, the dynamic cycle is brimming with irregularity and the came about choice can be chosen arbitrarily. Immediately, Cohen and his partners contended that choices are not the result of normal examination or alliance of abilities but instead arbitrary occasions. Then again, a few researchers contend that trash bin model doesn’t offer a hypothetical structure and this is its principle disadvantageous and can’t be broadly utilized in genuine world.
Mintzberg’s Model
As per Mintzberg, the methods of vital choices making are:
Examination of Models
Conclusion :-
With regards to simply deciding, one ought to continuously gauge the positive and negative business results and should incline toward the positive results. This dodges the potential misfortunes to the association and stays with the running with a supported development. Now and again, staying away from independent direction appears to be simpler; particularly, when you get into a great deal of a showdown subsequent to settling on the difficult choice. However, settling on the choices and tolerating its ramifications is the best way to remain in charge of your corporate life and time.






