
Drools is a powerful open-source rules engine that enables developers to implement and manage complex business rules and logic in Java applications. It provides a flexible and scalable framework for defining, executing, and maintaining rules using DRL or DMN. Drools supports rule-based decision-making, allowing applications to evaluate conditions, make decisions, and execute actions based on rules defined by domain experts.
1. What is Drools, and what problem does it solve?
Ans:
A business rule management system (BRMS) is called Drools, and it is an open-source rules engine written in Java. It offers a scalable and adaptable remedy for implementing and managing business rules and logic. Drools enables the separation of business rules from application code, allowing business analysts and domain experts to define and modify rules without requiring programming expertise. It enhances agility, reduces time-to-market for rule changes, and improves the maintainability of business logic in applications.
2. Explain the key components of Drools.
Ans:
- Rule Engine: Executes business rules against data known as facts.
- Facts: Data objects against which rules are evaluated.
- Working Memory: Runtime storage for facts and inferred data.
- Knowledge Base: Repository of rules and associated resources.
- Knowledge Session: Environment where rules are processed and evaluated.
3. Describe the difference between rules and facts in Drools.
Ans:
| Aspect | Rules | Facts |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rules define the conditions and actions for decision-making in Drools. | Facts represent the data or information that the rules evaluate and act upon. |
| Function | Execute logic based on patterns and conditions specified. | Serve as input data to be evaluated by the rules. |
| Format | Typically written using the Drools Rule Language (DRL) or via a rule engine interface. | Represented as Java objects inserted into the Working Memory. |
| Example | “If temperature is above 30°C, then activate cooling system.” | A Java object: Temperature temp = new Temperature(35); |
4. What is the Working Memory in Drools?
Ans:
- Working Memory: Runtime container within Drools where facts (data) are stored and manipulated during rule evaluation.
- Purpose: Allows rules to dynamically interact with data, assert new facts, modify existing facts, and retract facts as conditions change.
- Management: Facilitates efficient rule execution by maintaining a snapshot of application state relevant to rule evaluation.
5. How does Drools represent knowledge?
Ans:
Drools represent knowledge through rules and facts. Encapsulate business logic and conditions for decision-making. Represent data or application state that rules operate upon. Together, rules and facts form a knowledge base that defines the behavior and decision-making processes of an application.
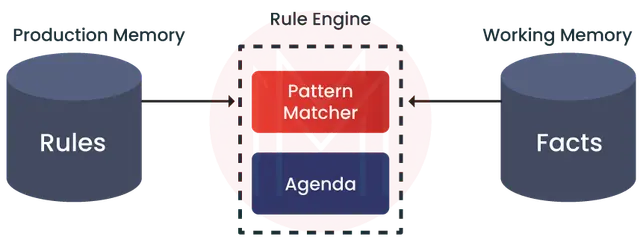
6. What is a knowledge session in Drools?
Ans:
- Runtime environment where rules are executed and evaluated against facts.
- Maintains state across multiple rule firings, allowing rules to react to changes in facts over time.
- It does not maintain a state between rule invocations, making it suitable for one-time rule execution with input data.
7. Explain the difference between stateful and stateless sessions in Drools.
Ans:
- Stateful Session: Maintains the state of facts (data) across multiple rule firings. It allows rules to react to changes in facts over time and retains the working memory between rule invocations.
- Stateless Session: It processes input data (facts) once and produces output without remembering previous interactions. It is more lightweight and suitable for stateless or transactional rule execution.
8. Define rules in Drools?
Ans:
- Rules in Drools are defined using the Drools Rule Language (DRL).Each rule consists of two main parts.
- LHS defines conditions or patterns that must be matched against facts in the working memory.
- RHS specifies actions or consequences to be executed when the conditions defined in the LHS are satisfied.
9. What is the syntax of the Drools Rule Language (DRL)?
Ans:
Rule Declaration: Begins with `rule` followed by a rule name. Conditions (LHS) – Defines patterns to match against facts using `when.` Actions (RHS)-Specifies operations to be performed when conditions are satisfied using `then.`
- “`
- rule “Example Rule”
- when
- $fact: FactType(condition)
- then
- // Actions to be executed when the condition is met
- modify($fact) {
- // Modify properties of $fact
- }
- end
- “`
10. Describe the purpose of the Left Hand Side (LHS) and Right Hand Side (RHS) in Drools rules.
Ans:
- Left Hand Side (LHS): Defines conditions or patterns that must be satisfied for the rule to activate. It specifies which facts (data) the rule is interested in and under what conditions the rule should fire.
- Right Hand Side (RHS): Specifies actions or consequences to be executed when the conditions defined in the LHS are satisfied. Actions can include modifying facts, executing application-specific logic based on the rule’s logic.
11. What is the role of the agenda in Drools?
Ans:
- The agenda in Drools manages and prioritizes rules for execution based on their activation status and rule salience.
- It holds a list of rules that are eligible to be executed based on matching conditions (LHS) against facts in the working memory.
- Rules are ordered in the agenda based on rule salience, activation order, and agenda group configurations.
- Allows control over which rules are fired and in what order, providing flexibility in the rule execution flow.
12. Explain the concept of rule salience in Drools.
Ans:
- Rule Salience: Rule salience is a mechanism in Drools to prioritize rules for execution within the agenda.
- Priority Management: Assigns a numeric value to rules, where higher values indicate higher priority.
- Execution Order: Rules with higher salience values are placed higher in the agenda and executed before rules with lower salience values.
- Override Default Activation: Allows overriding default activation order based on LHS matching.
13. How do Drools handle rule conflicts?
Ans:
Drools handles rule conflicts using a conflict resolution strategy based on the “Salience” attribute, which assigns a priority level to each rule. When multiple rules are activated, Drools evaluates their salience values to determine which rule to execute first. The “Agenda Group” feature allows rules to be organized into groups, enabling selective execution based on specific conditions. If salience is the same, Drools employs the “rule activation order,” executing rules based on their order in the knowledge base.
14. What is a Drools knowledge base (KieBase)?
Ans:
A Drools Knowledge Base, or KieBase, is a central repository that holds all the rules, processes, and associated metadata for a Drools application. It consists of various components, including rule definitions, workflows, and configuration settings. The KieBase enables the engine to evaluate and execute rules based on the data provided. It is designed to be immutable once created, ensuring consistency and reliability during rule execution.
15. Describe the role of the Drools rule engine.
Ans:
- Rule Engine: The core component of Drools is responsible for executing business rules against data (facts) stored in the working memory.
- Pattern Matching: Matches conditions specified in the LHS of rules against facts in the working memory.
- Activation: Manages the activation and prioritization of rules based on rule salience, agenda groups, and conflict resolution strategies.
- Execution: Executes actions specified in the RHS of rules when conditions LHS are satisfied, modifying facts, triggering application-specific logic.
16. What is the purpose of logical assertions in Drools?
Ans:
The purpose of logical assertions in Drools is to define conditions and rules that can evaluate the state of facts in the knowledge base. These assertions allow developers to express complex business logic by specifying relationships and dependencies between different facts. Logical assertions help in activating rules based on the presence or absence of specific conditions, enabling dynamic decision-making. They also facilitate reasoning over the data, allowing the Drools engine to derive conclusions and take actions based on the evaluated rules.
17. How to use global variables in Drool’s rules?
Ans:
- Declaration: Defined using the `global` keyword in DRL files or programmatically within the application.
- Scope: Global variables are initialized once per knowledge session and remain accessible throughout the session’s lifecycle.
- Data Sharing: Pass application-specific data or services (e.g., database connections, utility classes) to rules for decision-making.
18. Explain the concept of agenda groups in Drools.
Ans:
- Agenda Groups: In Drools, agenda groups are used to partition rules into separate groups within a knowledge session.
- Execution Control: Allows rules to be grouped logically, enabling selective activation and execution of rules based on application requirements.
- Priority Management: Each agenda group can have its own priority, influencing the order in which rules within that group are executed.
- Activation Control: Rules within agenda groups are activated independently, providing flexibility in managing rule execution flow.
19. What is the purpose of the “no-loop” attribute in Drool’s rules?
Ans:
A rule attribute in Drools that prevents a rule from being re-evaluated (firing) in the same rule execution cycle in which it has already fired. Ensures that a rule does not continuously trigger itself or other rules within the same cycle, preventing unintended recursion. Improves rule engine efficiency by avoiding unnecessary re-evaluation of rules that have already been fired. Used to control the flow and behavior of rules, particularly in complex rule sets where rule interactions need careful management.
20. How does Drools manage rule execution order?
Ans:
- Rule Execution Order: Drools manages rule execution order using several mechanisms:
- Rule Salience: Assigns numeric priorities to rules to influence their execution order.
- Agenda Groups: Rules are grouped into agenda groups, each with its own priority, controlling the order of rule activation and firing.
- Activation Order: Rules are activated based on their matching conditions (LHS) against facts in the working memory.
21. How to integrate Drools with Java applications?
Ans:
- Drools can be integrated into Java applications through the following steps:
- Include Drools libraries (JAR files) in the project’s build path using tools like Maven or Gradle.
- Define rules (DRL files) and create a knowledge base (KieBase) programmatically or via configuration files.
- Instantiate a knowledge session from the knowledge base to execute rules against application data.
22. Explain the role of Drools Fusion in complex event processing.
Ans:
- An extension of Drools that supports complex event processing (CEP) for real-time event-driven applications.
- Manages streams of events and processes them based on defined rules and patterns.
- Supports temporal constraints and windowing operations to analyze events over time.
- Detects complex event patterns and triggers actions or alerts based on detected patterns.
- Integrates with Drools rule engine to combine event processing with traditional rule-based decision-making.
23. What are accumulators, and how are they used in Drools?
Ans:
Drools accumulators are used to perform aggregations and calculations over groups of facts during rule evaluation. Calculate sums, averages, counts, minimums, maximums, and other aggregate functions over sets of matching facts. Define custom accumulators to perform specialized aggregations or calculations not supported by standard built-in functions. Used in conjunction with standard rule conditions (LHS) and actions (RHS) to derive conclusions or trigger further actions based on aggregated results.
24. Describe the concept of rule templates in Drools.
Ans:
- Rule Templates: Also known as rule templates or decision tables, rule templates in Drools provide a tabular representation for defining business rules.
- Business Rule Management: Allows non-technical users (business analysts) to define and maintain rules using a familiar spreadsheet-like format.
- Template Structure: Defines conditions (LHS) and actions (RHS) using placeholders or columns in the template, where actual values or variables can be filled in based on specific scenarios.
25. How do Drools support decision tables?
Ans:
Drools supports decision tables as a tabular format for defining rules in a structured manner. Decision tables in Drools allow business users to specify conditions and corresponding actions in a spreadsheet-like format, which Drools then translates into executable rules. This approach simplifies rule maintenance, facilitates collaboration between business and technical teams, and improves the readability and manageability of complex rule sets.
26. What is the purpose of domain-specific languages (DSL) in Drools?
Ans:
Domain-specific languages (DSL) in Drools provide a specialized syntax and vocabulary tailored to specific problem domains or business rules. DSLs allow business analysts and domain experts to express rules and constraints using familiar terminology and concepts, making rule definitions more intuitive and accessible. This abstraction layer enhances rule readability, reduces complexity, and accelerates rule development and maintenance in Drools.
27. Explain the role of the KIE (Knowledge Is Everything) API in Drools.
Ans:
The Knowledge Is Everything API in Drools provides a unified interface for managing and interacting with knowledge-based systems, including rules, processes, and decision tables. It facilitates programmatic access to Drools artifacts such as rule definitions, facts, and sessions, enabling dynamic rule execution, querying, and modification. The KIE API supports integration with external applications, orchestration of rule-based workflows, and provides runtime environments for executing rule-based decisions.
28. How to implement rule validation in Drools?
Ans:
- Rule validation in Drools involves ensuring that rules adhere to syntax, semantic correctness, and logical consistency.
- This includes checking rule conditions, verifying data types, evaluating rule conflicts, and detecting potential rule conflicts or ambiguities.
- Rule validation ensures the reliability and accuracy of rule execution, minimizing errors and ensuring consistent behavior in rule-based systems.
29. Describe the difference between declarative and imperative constraints in Drools.
Ans:
- Declarative Constraints: Declarative constraints in Drools specify conditions or rules in a descriptive, logic-based format without explicitly defining procedural steps. They focus on stating what needs to be achieved or checked, leaving the execution details to Drools’ inference engine. Examples include defining conditions based on facts or attributes.
- Imperative Constraints: Imperative constraints involve specifying rules or conditions using procedural or imperative programming constructs. This approach includes defining rule actions or behaviors explicitly, detailing step-by-step instructions for achieving desired outcomes. Imperative constraints may involve invoking methods, performing calculations, or executing business logic within rules.
30. What is the role of backward chaining in Drools?
Ans:
Backward chaining in Drools refers to a rule execution strategy where the system starts with the desired outcome (conclusion) and works backward to determine the conditions (premises or facts) required to satisfy that conclusion. It is commonly used in rule-based systems to infer or derive conclusions based on known facts and rules. Backward chaining allows Drools to dynamically reason and deduce conclusions based on changing data or conditions, supporting adaptive decision-making and complex rule interactions.
31. How do users handle dynamic rule creation and modification in Drools?
Ans:
- Rule Templates: Using rule templates or decision tables to define rules in a parameterized format that allows for easy modification of rule conditions and actions.
- Fact Insertion and Retraction: Dynamically inserting or retracting facts or data objects during runtime to trigger rule evaluation and adaptation.
- Rule Engine APIs: Leveraging Drools APIs to programmatically create, update, or remove rules based on changing business requirements or external inputs.
32. Explain the concept of truth maintenance in Drools.
Ans:
- Dependency Tracking: Tracks dependencies between rules and facts, ensuring that changes to input facts automatically trigger re-evaluation of dependent rules.
- Conflict Resolution: Manages rule firing order and resolution of conflicts to maintain accurate and up-to-date conclusions.
- Dynamic Updates: Allows dynamic updates to the knowledge base by inserting, modifying, or retracting facts, which automatically propagates changes to dependent rules.
- Traceability: Provides traceability and transparency into how conclusions are derived from input facts, aiding in debugging and auditing.
33. How to implement auditing and logging in Drools?
Ans:
- Integrate Drools with logging frameworks like Log4j, SLF4J, or JUL to capture rule execution details, debug information, and trace logs.
- Implement custom event listeners within Drools to capture rule execution events, such as rule activation, firing, and modifications to facts.
- Maintain an audit trail of rule executions, decisions, and changes to facts by logging relevant information to persistent storage.
- Implement exception handling within rules to capture and log errors or exceptional conditions encountered during rule evaluation.
34. Describe the use of listeners and event handlers in Drools.
Ans:
Capture events such as rule activation, rule firing, rule match, and rule modification using event listeners. Monitor changes to facts in the working memory using working memory event listeners. Track knowledge session lifecycle events, such as session creation, destruction, and state changes, using session event listeners. Implement custom event handlers to execute specific actions or trigger external processes based on detected events within Drools.
35. What is the purpose of the KIE Scanner in Drools?
Ans:
The KIE Scanner in Drools serves as a monitoring and automatic update tool for knowledge bases. It periodically checks Maven repositories for new versions of KIE project artifacts, such as rules, processes, and models, and updates the knowledge base accordingly without requiring a system restart. This feature is particularly useful in dynamic environments where business rules are frequently modified.
36. How does Drools support rule versioning and deployment?
Ans:
- Manage versions of rules using version identifiers or tags within the Drools repository (KIE Workbench or Git repository).
- Deploy rules to runtime environments using deployment descriptors, Maven dependencies, or through integration with containerized environments like Docker.
- Support dynamic updates and hot deployment of rules using tools like KIE Scanner to detect and apply changes to rules without disrupting running applications.
37. Explain how to use Drools with Spring Framework.
Ans:
- Spring Boot Starter: Utilize Spring Boot Starter for Drools to automatically configure Drools dependencies, session factories, and rule management within Spring Boot applications.
- Dependency Injection: Inject Drools components, such as KieContainer, KieSession, and KieBase, into Spring-managed beans using Spring’s DI capabilities.
- Configuration: Configure Drools beans and resources (DRL files, decision tables) as Spring beans using annotations or XML-based configuration files.
38. What are the best practices for writing efficient Drools rules?
Ans:
- Rule Design: Keep rules simple, focused, and logically organized to enhance readability and maintainability.
- Rule Salience: Use rule salience judiciously to prioritize important rules and manage rule execution order effectively.
- Fact Modeling: Optimize fact models to represent domain entities and relationships clearly, minimizing redundancy and improving rule-matching efficiency.
39. How to handle exceptions in Drool rules?
Ans:
It implement try-catch blocks within rule actions (RHS) to handle specific exceptions or error conditions encountered during rule execution. Capture and log exceptions using event listeners or custom error handling mechanisms to maintain visibility and traceability of error events. Define fallback strategies or alternative paths in rules to handle exceptional scenarios gracefully, ensuring consistent application behavior. Integrate Drools with logging frameworks to capture detailed error messages, contextual information for debugging and troubleshooting.
40. Describe the role of decision modeling and notation (DMN) in Drools.
Ans:
Decision Modeling and Notation (DMN) plays a pivotal role in Drools by providing a standardized framework for modeling and executing business decisions. DMN allows business analysts and developers to collaborate more effectively by using a common, easy-to-understand notation that bridges the gap between business requirements and technical implementation. In Drools, DMN models are used to define decision logic in a visual and declarative manner, enabling the encapsulation of complex business rules, decision tables, and decision requirements diagrams.
41. What are the performance considerations when using Drools?
Ans:
- Rule Complexity: The complexity of rules and their interdependencies can impact execution time.
- Rule Set Size: Larger rule sets may require more processing time.
- Fact Model: Efficiency depends on the structure and size of the fact model.
- Inference Engine: Utilization of efficient algorithms and optimization techniques.
- Caching: Leveraging caching mechanisms to store intermediate results.
- Indexing: Optimizing rule matching through efficient indexing of facts and conditions.
42. Explain the Rete algorithm and its significance in Drools.
Ans:
The Rete algorithm in Drools is a pattern-matching algorithm used for efficient rule evaluation. It maintains an internal network (Rete network) of nodes representing conditions and actions of rules. Matches incoming facts against conditions in rules. Supports incremental updates without re-evaluating all rules. Reduces computational overhead by storing and reusing intermediate results. Scales well with increasing rule complexity and fact volume.
43. How do users optimize rule execution in Drools?
Ans:
- Reviewing and simplifying complex rules to reduce execution time.
- Efficiently indexing facts and conditions for faster rule matching.
- Prioritizing rule execution based on criticality and dependencies.
- Grouping similar rules for batch execution to minimize overhead.
- Utilizing multi-threading or parallel processing for concurrent rule evaluation.
- Monitoring performance metrics to identify bottlenecks and optimize rule execution.
44. Describe the use of complex event processing (CEP) patterns in Drools.
Ans:
- Event Patterns: Defining complex patterns of events or conditions using Drools’ event-driven architecture.
- Temporal Logic: Handling temporal relationships and sequences of events.
- Event Correlation: Detecting correlations between multiple events in real-time.
- Rule Triggering: Triggering rules based on predefined event patterns or sequences.
- Scalability: Handling large volumes of events and real-time processing for decision-making.
45. What is the role of decision optimization in Drools?
Ans:
- Constraint-Based Optimization: Defining constraints and objectives to optimize decisions.
- Optimization Algorithms: Using algorithms like linear programming or genetic algorithms.
- Resource Allocation: Optimizing resource allocation, scheduling, or configuration decisions.
- Real-Time Decision Making: Making optimal decisions based on changing data and constraints.
- Integration: Integrating optimization models with rule-based systems for dynamic decision-making.
46. How does Drools handle distributed rule execution?
Ans:
Drools handles distributed rule execution through its integration with various clustering and distributed computing technologies. By leveraging frameworks such as Apache Ignite, JBoss Data Grid, or other distributed in-memory data grids, Drools can distribute the rule execution across multiple nodes in a cluster. This allows for scalable and fault-tolerant rule processing, ensuring high availability and improved performance.
47. Explain the integration of Drools with cloud-based environments.
Ans:
Deploying Drools-based applications on cloud platforms. Leveraging cloud scalability features for handling variable workloads. Utilizing cloud-native services for data storage, messaging, and analytics. Using cloud-managed services for infrastructure needs. Implementing robust security measures and access controls ensures that the application remains secure in a cloud environment. Monitoring and logging services can also be integrated to track performance and troubleshoot issues effectively.
48. Describe the role of artificial intelligence and machine learning in Drools.
Ans:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) enhance Drools by improving decision-making and automating rule generation.
- AI analyzes large datasets to identify patterns that inform more effective business rules, while ML algorithms adaptively refine these rules based on real-time data.
- This integration enables dynamic responses to changing conditions and optimizes rule execution by prioritizing which rules to fire, resulting in more intelligent systems capable of complex reasoning and continuous learning for better insights and decision-making.
49. How does Drools support integration with other rule engines?
Ans:
- Standard Formats: Using standard rule interchange formats (e.g., Decision Model and Notation, DMN).
- API Integration: Exposing APIs for interoperability with other rule engines or systems.
- Rule Interchange: Importing/exporting rules in compatible formats for cross-platform compatibility.
- Service Orchestration: Orchestrating rule-based decisions across heterogeneous rule engines.
50. Explain the concept of rule-based governance in Drools.
Ans:
Rule-based governance in Drools refers to the systematic management and oversight of business rules throughout their lifecycle to ensure they align with organizational policies, compliance requirements, and strategic objectives. This concept encompasses the creation, validation, deployment, and monitoring of rules within the Drools ecosystem. By implementing rule-based governance, organizations can maintain control over rule changes, ensure consistency in rule application, and facilitate collaboration between business and IT stakeholders.
51. How to implement rule-based security policies in Drools?
Ans:
- Define rules that match user roles, actions, and resource permissions to grant or deny access.
- Use Drools to dynamically adjust security policies based on changing conditions or contextual information.
- Implement rules that enforce specific access levels, exceptions based on business requirements.
- Integrate Drools with authentication mechanisms, access control frameworks to enforce rule-based security policies across applications.
52. Describe the role of rule-based routing and workflow management in Drools.
Ans:
- Define workflows as sequences of rule-based decisions and actions to manage process flows, approvals, and task assignments.
- Adjust workflows in real-time based on changing conditions, inputs, or external events using Drools event-driven capabilities.
- Integrate with BPMN tools, workflow engines, or microservices architectures to orchestrate complex workflows and process automation.
53. What is the purpose of fuzzy logic and uncertainty handling in Drools?
Ans:
- Drools supports fuzzy logic to handle Imprecise or uncertain data and reasoning:
- Define rules with fuzzy logic operators to model degrees of truth or uncertainty in rule conditions.
- Apply fuzzy logic to interpret qualitative data, subjective assessments in decision-making processes.
- Use probabilistic models and uncertainty factors to evaluate alternative outcomes, predictive analytics in complex scenarios.
54. Explain the concept of rule-based anomaly detection using Drools.
Ans:
Rule-based anomaly detection using Drools involves defining and applying business rules to identify patterns and behaviors that deviate from the norm within a dataset. In this approach, Drools leverages its powerful rule engine to evaluate incoming data against predefined rules that characterize normal and abnormal conditions. When data points or events match the criteria set for anomalies, the rule engine triggers alerts or actions, enabling real-time detection and response.
55. How to handle temporal reasoning and event sequencing in Drools?
Ans:
Utilize Drools’ built-in temporal operators like after, before, during, and after or equal to define rules that consider the timing of events. Implement Complex Event Processing using the Drools Fusion module, which allows for the detection and handling of patterns across multiple events over time. Organize rules into agenda groups to control the order of rule execution based on specific time conditions or event sequences. Use fact expiration and time-to-live settings to manage the lifecycle of facts, ensuring that outdated events do not affect decision-making.
56. Describe the integration of Drools with microservices architectures.
Ans:
- Design microservices that encapsulate specific business functionalities, including rule evaluation, decision automation, or workflow orchestration.
- Expose Drools functionalities as RESTful APIs or service endpoints to enable seamless communication and integration with other microservices.
- Deploy Drools components within containerized environments to ensure scalability, portability, and isolation of rule execution contexts.
57. What are the considerations for using Drools in real-time decision-making systems?
Ans:
- Optimize rule execution and inference speed to meet real-time response requirements, minimizing latency in decision processing.
- Design scalable architectures using stateful or stateless Drools sessions to handle concurrent requests, high-throughput data streams, or distributed processing.
- Implement event-driven architectures and streaming data processing to support continuous event monitoring, pattern detection, and timely decision updates.
58. How does Drools support rule-based recommendation systems?
Ans:
Drools supports rule-based recommendation systems by providing a robust framework for defining and executing recommendation logic based on business rules. In such systems, rules are formulated to infer recommendations or suggestions based on the characteristics or behaviors of users, products, or other entities. Drools allows developers and domain experts to model complex decision-making processes using its rule engine, where rules can evaluate user preferences.
59. Explain the role of Drools in business process automation (BPM) and decision management.
Ans:
- Drools serves as a powerful tool for BPM and decision management by automating business processes and enforcing decision rules.
- Define business workflows, process rules, and decision flows using Drools BPMN capabilities to model and automate end-to-end processes.
- Embed decision logic, validation rules, and compliance checks within BPMN diagrams or business rules to enforce business policies and regulations.
60. Describe the implementation of a rule-based chatbot using Drools.
Ans:
- Define rules to identify user intents, keywords, or phrases from chatbot interactions using Drools’ pattern matching and rule conditions.
- Maintain conversational context and session state using Drools’ stateful session management to track user interactions, preferences, and ongoing dialogues.
- Define rules for generating chatbot responses based on user intents, contextual understanding, and conversation flow.
61. How to implement a pricing engine using Drools?
Ans:
Defining rules for pricing based on product attributes, customer segments, and market conditions. Drools will be used to evaluate and apply pricing rules dynamically. Integrating with data sources to retrieve real-time pricing information. Testing and validating pricing rules to ensure accuracy and compliance. Scaling the pricing engine to handle large volumes of transactions efficiently.
62. Explain the use of Drools for fraud detection in financial transactions.
Ans:
- Analyzing transactional data in real time to detect fraudulent activities.
- Integrating with external data sources for additional context and validation.
- Automating decision-making based on predefined fraud detection rules.
- Enhancing accuracy and reducing false positives through rule refinement and optimization.
63. Describe the implementation of dynamic rule-driven user interfaces with Drools.
Ans:
- Defining rules that govern UI behavior based on user input, system state, or business logic.
- Using Drools to evaluate rules and dynamically adjust UI components, validations, or workflows.
- Enhancing user experience by personalizing UI elements based on user roles or preferences.
- Testing and iterating UI rules to ensure responsiveness and usability.
- Integrating with front-end technologies to implement rule-driven interactions effectively.
64. How to use Drools for product configuration and customization?
Ans:
- Defining rules to configure product features, options, and pricing based on customer requirements.
- Implementing decision tables or DSLs in Drools to model complex product configurations.
- Automating product customization based on user inputs or predefined rules.
- Integrating with product lifecycle management systems for seamless updates and version control.
- Supporting agile product development and adaptation to market demands through rule-driven configuration.
65. Explain the role of Drools in insurance claims processing.
Ans:
Drools plays a crucial role in streamlining and enhancing insurance claims processing by automating decision-making and ensuring consistency and accuracy throughout the process. In insurance claims processing, Drools is used to define and enforce business rules that govern various aspects such as claim validation, eligibility criteria, policy coverage assessment, and settlement calculations.
66. How to integrate Drools with a content management system?
Ans:
- Defining rules to manage the content lifecycle, access permissions, and publishing workflows.
- Using Drools to enforce content governance policies, metadata tagging, and version control.
- Automating content classification, indexing, and retrieval based on predefined rules.
- Enhancing CMS functionality with rule-driven content personalization or recommendation systems.
- Supporting scalable content management solutions through Drools’ flexible rule execution capabilities.
67. Describe the implementation of rule-based recommendations in e-commerce platforms using Drools.
Ans:
- Defining rules to generate personalized product recommendations based on customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history.
- Integrating with product catalogs, customer databases, and analytics platforms for data-driven decision-making.
- Enhancing user engagement and conversion rates through targeted and context-aware recommendations. Monitoring recommendation effectiveness and refining rules to optimize sales performance.
68. How does Drools support regulatory compliance in healthcare systems?
Ans:
- Implementing rules to enforce healthcare regulations, privacy laws, and clinical guidelines.
- Automating compliance checks, audits, and reporting based on rule-driven decision-making.
- Integrating with electronic health records (EHR) and health information exchanges (HIE) for data governance.
- Ensuring patient data security, confidentiality, and consent management through rule-based policies.
- Facilitating interoperability and standardization in healthcare practices to meet regulatory requirements.
69. Explain the use of Drools for personalized marketing campaigns.
Ans:
Drools is instrumental in creating personalized marketing campaigns by leveraging its rule-based engine to tailor messages and offers based on customer behavior, preferences, and demographics. In this context, Drools allows marketers to define rules that segment customers into specific categories or profiles, such as high-value customers, frequent buyers, or first-time visitors. These rules can be created using Drools Rule Language, specifying conditions that trigger personalized actions or recommendations.
70. Describe the implementation of a rule-based supply chain optimization system using Drools.
Ans:
- Using Drools to dynamically adjust supply chain operations based on market trends, supplier availability, and cost factors.
- Integrating with ERP systems, warehouse management solutions, and transportation networks for end-to-end visibility.
- Automating procurement decisions, order fulfillment processes, and supply chain planning through rule-driven workflows.
71. How do users implement adaptive learning systems using Drools?
Ans:
- Adaptive Learning Systems: Drools supports adaptive learning by dynamically adjusting rules and decision logic based on learner interactions, performance data, and evolving educational objectives:
- Rule-Based Adaptation: Define rules that personalize learning paths, content recommendations, or assessment criteria based on learner profiles, progress, or learning styles.
- Feedback Loop: Incorporate feedback mechanisms to capture learner responses, preferences, and performance metrics to refine adaptive rules using Drools’ rule management capabilities.
- Scalable Decision Support: Implement scalable architectures that leverage Drools’ rule engine to process learner data in real-time, optimize learning interventions, and adapt instructional strategies dynamically.
72. Explain the use of Drools for real-time monitoring and alerting.
Ans:
- Drools enables real-time monitoring and alerting by evaluating streaming data, event patterns, or operational conditions against predefined rules:
- Capture and process real-time events, sensor data, or transaction streams using Drools’ event processing capabilities to detect patterns, anomalies, or critical events.
- Define rules that trigger notifications, alerts, or automated responses based on threshold breaches, business rules violations, or operational insights derived from real-time data.
- Analyze temporal sequences, event correlations, or aggregated metrics to generate actionable alerts and facilitate proactive decision-making in dynamic environments.
73. Describe the integration of Drools with IoT devices for rule-based automation.
Ans:
The integration of Drools with IoT devices for rule-based automation enables sophisticated decision-making and control in IoT environments. Drools’ rule engine can process real-time data streams from IoT sensors and devices, applying predefined rules to automate responses, trigger actions, or adjust device settings based on specific conditions or events. For example, rules can be set to adjust room temperature settings based on occupancy sensors, optimize energy usage in smart buildings.
74. How to use Drools for workload optimization in cloud environments?
Ans:
- Drools supports workload optimization by dynamically allocating resources, managing scalability, and optimizing performance based on business rules and operational conditions:
- Define rules that govern workload distribution, scaling policies, or resource provisioning decisions based on workload patterns, performance metrics, and cost considerations.
- Implement auto-scaling strategies that dynamically adjust cloud resources in response to fluctuating demand, traffic spikes, or workload variations using Drools’ adaptive rule execution.
- Optimize resource utilization, minimize idle capacity, and optimize cloud service costs by leveraging Drools’ predictive analytics, rule-based forecasting, and capacity planning capabilities.
75. Explain the role of Drools in adaptive resource allocation strategies.
Ans:
- Drools plays a pivotal role in adaptive resource allocation by dynamically adjusting resource allocation policies, workload prioritization, and operational decisions based on changing conditions:
- Define rules that prioritize resource allocation, task scheduling, or service delivery based on business rules, user priorities, and operational constraints using Drools’ decision management capabilities.
- Optimize resource allocation efficiency, minimize contention, and maximize throughput by applying Drools’ rule engine to evaluate workload characteristics, performance metrics, and workload dependencies.
- Implement adaptive scaling strategies that dynamically adjust resource allocation in response to workload demands, traffic patterns, or system performance using Drools’ rule-based orchestration.
76. Describe the implementation of a rule-based reservation and scheduling system using Drools.
Ans:
- Drools facilitates the implementation of rule-based reservation and scheduling systems to optimize resource allocation, manage bookings, and streamline operational workflows.
- Define rules that govern reservation policies, booking constraints, and resource availability based on scheduling rules, user preferences, and operational guidelines using Drools’ declarative rule language.
- Automate scheduling decisions, conflict resolution, and resource allocation adjustments in real-time using Drools’ event-driven processing, rule-based decision-making, and adaptive scheduling capabilities.
77. How to implement rule-based quality assurance and testing frameworks with Drools?
Ans:
Implementing rule-based quality assurance and testing frameworks with Drools involves leveraging its rule engine and flexible rule management capabilities to automate and validate business rules in software applications. Firstly, define test scenarios and quality criteria as rules using DRL or decision models like DMN. These rules should encompass conditions, expectations, and actions that validate the correctness and performance of the application under test.
78. Explain the use of Drools of dynamic pricing strategies in retail.
Ans:
Defining rules based on market conditions, competitor pricing, and customer behavior. Automating price adjustments in real-time using Drools’ rule engine. Integrating with sales data and analytics to optimize pricing strategies. Enhancing competitiveness and profitability through agile pricing responses. Enabling personalized pricing offers based on customer segmentation and loyalty programs.
79. Describe the implementation of rule-based risk assessment models using Drools.
Ans:
- Defining rules to evaluate risk factors, compliance requirements, and financial metrics.
- Using Drools to automate risk scoring, decision-making, and mitigation strategies.
- Integrating with data sources for comprehensive risk analysis.
- Facilitating regulatory compliance and auditability through rule-driven risk assessments.
- Improving risk management efficiency and accuracy through continuous rule refinement.
80. How do Drools support personalized healthcare recommendations based on patient data?
Ans:
Defining rules to analyze patient health records, medical history, and diagnostic data. Using Drools to generate personalized treatment plans, preventive care strategies, and medication recommendations. Integrating with clinical decision support systems (CDSS) and EHR platforms for real-time insights. Enhancing patient outcomes through tailored healthcare interventions based on rule-driven algorithms. Ensuring compliance with medical protocols, privacy regulations, and ethical guidelines.
81. What are the advantages of using a rule engine like Drools over traditional programming approaches?
Ans:
- Agility: Rules can be modified and deployed independently without changing the core application code.
- Transparency: Rules are expressed in a human-readable format, promoting clarity and maintainability.
- Scalability: Drools’ rule engine efficiently handles large volumes of rules and data, scaling with business needs.
- Flexibility: Rules can be dynamically adjusted based on changing business requirements or external factors.
- Integration: Drools integrates seamlessly with existing systems and applications through standard APIs and protocols.
82. Explain the scalability challenges and solutions in rule-based systems using Drools.
Ans:
- Processing large rule sets and complex rule interactions.
- Memory usage and performance optimization for handling concurrent rule evaluations.
- Efficient data retrieval and processing to support real-time decision-making.
- Managing distributed rule execution across multiple nodes or cloud environments.
- Distributing rule processing across multiple nodes for parallel execution.
83. How does Drools support interoperability with legacy systems and third-party applications?
Ans:
Providing connectors and APIs for seamless data exchange with legacy systems and third-party applications. Supporting industry standards for data interoperability and integration. Implementing rules for reusable services that are accessible via web services or RESTful APIs. Leveraging middleware platforms for protocol mediation and message transformation. Facilitating gradual migration and coexistence with existing IT infrastructure through interoperable rule-based solutions.
84. Describe the role of Drools in maintaining business agility and responsiveness.
Ans:
Enabling rapid rule updates and deployment without impacting core systems. Supporting adaptive decision-making based on real-time data and changing business conditions. Facilitating quick adjustments to market demands, regulatory changes, or customer preferences. Promoting collaboration between business users and IT teams through rule authoring and management tools. Improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction through agile, rule-driven processes.
85. What are the limitations and challenges of using Drools in highly complex rule environments?
Ans:
- Managing large rule bases and complex rule interdependencies can impact performance and scalability.
- Complex rule environments may require extensive effort for rule creation, debugging, and maintenance.
- Resolving conflicts and ensuring consistency across rules in intricate rule sets can be challenging.
- Evaluating complex rules efficiently, especially in real-time or high-throughput systems.
86. Explain the role of declarative versus procedural knowledge representation in Drools.
Ans:
- Drools emphasizes declarative knowledge representation, where rules and facts define conditions and actions without specifying the procedural steps to achieve them.
- In contrast, procedural knowledge representation involves specifying step-by-step instructions or algorithms to achieve a task or decision-making process.
- Declarative representation in Drools promotes clarity, separation of concerns, and easier maintenance by focusing on what needs to be done rather than how.
87. How does Drools support adaptive and self-learning systems?
Ans:
Drools enables adaptive systems by allowing dynamic rule modification, activation, and deactivation based on changing conditions, user feedback, or learning outcomes. Integrates with machine learning models, predictive analytics, and data-driven insights to enhance rule-based decision-making, adaptability, and learning capabilities. Incorporates feedback mechanisms, performance metrics, and continuous evaluation to refine rules, optimize decision strategies, and improve system performance over time.
88. Describe the impact of explainable AI and transparency in rule-based decision-making with Drools.
Ans:
- Interpretability: Drools provides transparent rule evaluation, traceability of decision logic, and explanations for rule outcomes, enhancing trust and understanding of automated decision-making processes.
- Rule Explanation: Facilitates rule-based explanation of decisions, justifications, and rule activations to stakeholders, auditors, and end-users, promoting accountability and compliance.
- Compliance and Regulations: Supports compliance with regulatory requirements by ensuring transparency, fairness, and accountability in rule-based decision systems.
89. How does Drools handle rule consistency and conflict resolution in distributed environments?
Ans:
- Drools employs distributed rule engines, consistency protocols, and coordination mechanisms to ensure rule synchronization, conflict detection, and resolution across distributed nodes.
- Manages rule versioning, updates, and synchronization to maintain consistency, avoid rule conflicts, and ensure coherent decision-making in geographically dispersed environments.
- Utilizes conflict resolution strategies, distributed locks, or consensus algorithms to reconcile conflicting rules, prioritize rule executions, and enforce rule consistency across distributed deployments.
90. Explain the future trends and advancements expected in Drools and rule-based technologies.
Ans:
Enhanced integration with AI/ML technologies for cognitive reasoning, predictive analytics, and adaptive decision-making. Adoption of cloud-native architectures, serverless computing, and containerization for scalable, resilient rule execution. Focus on real-time event processing, streaming analytics, and complex event processing (CEP) for dynamic decision systems. Continued emphasis on explainable AI, transparency, and trustworthiness in automated decision-making systems.






