
VSAM, known as Virtual Storage Access Method, is a pivotal data management system predominantly employed on IBM mainframe platforms. It offers robust file management capabilities and efficient access methods for organizing and retrieving data. VSAM organizes data into clusters and supports various access types including sequential, indexed, and key-sequenced. This system is integral for handling large datasets with high performance and ensuring data integrity within mainframe applications.
1. What’s VSAM?
Ans:
VSAM, or Virtual Storage Access Method, is an IBM fragment storehouse access system that allows programs to store, recoup, and update records in a fragment train. It provides adequate data access by organizing data into logical records and managing them in various train structures, similar to crucial-sequenced, entry-sequenced, or relative records.
2. Differentiate between ESDS, KSDS, and RRDS in VSAM.
Ans:
ESDS( Entry Sequenced Data Set) stores records successively in the order they’re added, making it suitable for operations with tack-only data. KSDS( Key Sequenced Data Set) organizes records grounded on a primary key, easing fast reclamation and adequate access to individual records. RRDS( Relative Record Data Set) enables direct access to documents using relative record figures, offering balanced performance for both reclamation and update operations.
3. What are the main advantages of utilizing VSAM?
Ans:
- VSAM offers several advantages, including high-performing data access, practical storehouse application, support for large datasets, and robust data integrity mechanisms.
- It also provides inflexibility in penetrating data through various train associations and supports sale processing with features like record-position locking.
4. Explain the conception of record-position sharing in VSAM.
Ans:
- Record-position sharing allows multiple programs or users to coincidentally pierce and modernize individual records within a VSAM dataset.
- This point enhances concurrency and improves operation performance by minimizing contention for dataset access.
- VSAM achieves record-position sharing through mechanisms like record-position locking and conflict resolution algorithms.
5. What are alternate indicators in VSAM, and why are they used?
Ans:
Alternate indicators in VSAM are fresh indicators created on non-primary crucial fields of a dataset to give indispensable access paths to the data. They enable effective reclamation of records grounded on different hunt criteria, enhancing operation performance and inflexibility. Alternate indicators can ameliorate query performance and support different access patterns without modifying the primary dataset structure.
6. Discuss the significance of IDCAMS mileage in VSAM.
Ans:
- IDCAMS( Access Method Services) is a mileage program used for defining, manipulating, and managing VSAM datasets.
- It performs various tasks, such as defining datasets, loading data into datasets, deleting datasets, and reorganizing datasets for optimal performance.
- IDCAMS plays a pivotal part in VSAM dataset administration and conservation, ensuring adequate data operation and availability.
7. What’s the difference between VSAM and QSAM?
Ans:
| Feature | VSAM (Virtual Storage Access Method) | QSAM (Queued Sequential Access Method) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Data management system providing efficient access methods on IBM mainframes. | Sequential file processing method on IBM mainframes. |
| Access Methods | Sequential (ESDS), indexed (KSDS and RRDS), relative record (RRDS). | Sequential access only. |
| Features | Supports advanced data organization and retrieval capabilities. | Primarily supports sequential access with basic file processing capabilities. |
| Usage | Used for handling large volumes of data with flexibility and high performance. | Suitable for simple batch processing jobs where data is processed sequentially. |
8. Explain the conception of AIX( Alternate indicator) in VSAM.
Ans:
AIX( Alternate indicator) in VSAM is a fresh indicator created on non-primary crucial fields of a dataset to offer indispensable access paths. It enables effective reclamation of records grounded on different hunt criteria, enhancing operation inflexibility and performance. AIX helps in optimizing query performance by allowing access through various crucial fields, reducing the need for total dataset reviews.
9. What’s the part of the VSAM IDCAMS mileage?
Ans:
The VSAM IDCAMS( Access Method Services) mileage is used for defining, managing, and manipulating VSAM datasets. It performs tasks similar to defining datasets, loading data, deleting datasets, and reorganizing datasets for optimal performance. IDCAMS is essential for VSAM dataset administration and conservation, ensuring adequate data operation and availability.
10. How does VSAM ensure data integrity and thickness?
Ans:
- VSAM ensures data integrity and thickness through mechanisms like record-position locking, which prevents concurrent updates to the same record by multiple users.
- VSAM also provides sales operation features, ensuring that updates are completely completed or rolled back in case of failures.
- These mechanisms maintain data integrity and thickness in multi-user surroundings.
11. Discuss the significance of the CI( Control Interval) and CA( Control Area) in VSAM.
Ans:
In VSAM, a Control Interval( CI) is the lowest unit of data that can be transferred between fragment and central storehouse during I/ O operations. A Control Area( CA) is a group of successive control intervals stored contiguously on fragments. Proper sizing and operation of CIs and CAs are pivotal for optimizing I/ O performance and minimizing fragment space destruction in VSAM datasets.
12. Explain the part of the VSAM roster in dataset operation.
Ans:
The VSAM roster is a centralized depository that contains metadata information about VSAM datasets, similar to dataset names, attributes, and positions on fragments. It helps with dataset identification, allocation, and access control. The roster provides means for operations to detect and pierce VSAM datasets efficiently, easing dataset operation and administration tasks.
13. What are the crucial considerations for performance tuning in VSAM?
Ans:
- Performance tuning in VSAM involves optimizing dataset association, buffer pool sizing, CI/ CA sizing, and access patterns.
- Proper indexing, effective use of alternate indicators, and tuning parameters like buffer pool thresholds can significantly enhance performance.
- Also, optimizing I/ O operations and minimizing contention for dataset access through proper locking strategies are essential for maximizing VSAM performance.
14. What’s the difference between VSAM and ISAM?
Ans:
- VSAM( Virtual Storage Access Method) and ISAM( listed Sequential Access Method) are both access styles used for organizing and penetrating data on IBM mainframe systems.
- still, VSAM offers more advanced features similar to direct access through indexing, support for multiple access styles, and erected- data integrity mechanisms.
- ISAM, on the other hand, primarily provides successional access with limited indexing capabilities, making VSAM more adaptable and effective for various data access patterns.
15. Explain the significance of the VSAM buffer pool.
Ans:
The VSAM buffer pool is a portion of the central storehouse used to cache constantly penetrated VSAM dataset runners, perfecting I/ O performance by reducing fragment access quiescence. It stores both control information and data records recaptured from VSAM datasets during read operations. Proper sizing and operation of the buffer pool are essential for optimizing VSAM performance, as they directly impact the frequency of fragment I/ O operations and overall system outturn.
16. What are VSAM train status canons, and how are they used?
Ans:
VSAM train status canons are numeric values returned by VSAM access routines to indicate the outgrowth of train operations. These canons give information about the success, failure, or specific conditions encountered during dataset access. Programmers can use train status canons to handle crimes, diagnose problems, and apply error recovery mechanisms in their operations. Understanding and meetly handling these canons are essential for robust and dependable VSAM operation development.
17. Discuss the part of VSAM RLS( Record- Level participating) in multi-user surroundings.
Ans:
- VSAM RLS( Record- position participating) enables concurrent access and update of individual records within VSAM datasets by multiple users or programs.
- It employs record-position locking mechanisms to ensure data integrity and thickness, precluding conflicts between concurrent deals.
- VSAM RLS enhances operation scalability and performance in multi-user surroundings by minimizing contention for dataset access and maximizing concurrency.
18. What are the different types of VSAM dataset associations, and when are they used?
Ans:
- VSAM supports various dataset associations, including key-sequenced ( KSDS), entry-sequenced ( ESDS), and relative-record ( RRDS) associations.
- KSDS is suitable for operations taking direct access grounded on a primary key, ESDS is ideal for successional data processing with minimum arbitrary access conditions, and RRDS offers balanced performance for both successional and direct access patterns.
- Choosing the applicable dataset association depends on the operation’s access patterns and performance conditions.
19. Explain the conception of VSAM dataset sharing situations.
Ans:
- VSAM dataset-sharing situations define the degree of concurrent access and update allowed for VSAM datasets by multiple users or programs.
- The sharing situations range from exclusive( no concurrent access allowed) to participated(read-only concurrent access) and update( both read and write concurrent access).
- Understanding and opting for the applicable sharing position is pivotal for ensuring data thickness, performance, and compatibility with operation conditions in multi-user surroundings.
20. What are VSAM extended attributes, and how are they used?
Ans:
VSAM extended attributes are fresh dataset attributes beyond the standard attributes defined during dataset creation. They include characteristics similar to extended addressability, data encryption, and inspection logging. Extended attributes enhance dataset functionality and security, allowing for features like ample dataset support, data protection, and compliance with nonsupervisory conditions. Proper configuration and operation of extended attributes are essential for meeting operation requirements and data governance norms.
21. What’s the purpose of VSAM clusters, and how are they defined?
Ans:
- VSAM clusters are logical groupings of VSAM datasets that partake in common attributes and characteristics.
- They serve as holders for organizing affiliated data and give a means for adequate access and operation.
- Clusters are defined using VSAM IDCAMS mileage commands, specifying attributes similar to dataset association, crucial structure, and access system options. Proper clustering is essential for optimizing data access and performance in VSAM surroundings.
22. Explain the part of VSAM AMS( Application Management Services) in VSAM dataset operation.
Ans:
VSAM AMS( Application Management Services) is a set of mileage programs and services handled by IBM for managing VSAM datasets and related coffers. It offers functions similar to dataset backup and recovery, space operation, integrity checking, and performance monitoring. VSAM AMS automates routine executive tasks and ensures the trustability, vacuity, and performance of VSAM datasets, thereby simplifying dataset operation and enhancing functional effectiveness.
23. What are the advantages of using VSAM relative to traditional flat train systems?
Ans:
VSAM offers several advantages over traditional flat train systems, including listed access for faster data reclamation, support for multiple access styles, effective space application through dataset contraction and clustering, and erected- -data integrity mechanisms similar to position locking. Also, VSAM provides scalability, trustability, and comity with sales processing surroundings, making it suitable for large-scale data processing operations.
24. Discuss the part of VSAM IDCAMS DEFINE CLUSTER command in dataset creation.
Ans:
- The VSAM IDCAMS DEFINE CLUSTER command is used to produce VSAM clusters.
- It specifies attributes similar to dataset association, crucial structure, allocation parameters, and access system options.
- It initializes the cluster and allocates necessary coffers on fragments, including control intervals, control areas, and indicator structures.
- Proper operation of the DEFINE CLUSTER command ensures the correct setup and configuration of VSAM datasets, easing adequate data access and operation.
25. How does VSAM handle data concurrency and locking in multi-user surroundings?
Ans:
- VSAM employs various locking mechanisms, such as record-position locking and enqueue/ dequeue mechanisms, to manage data concurrency and ensure data integrity in multi-user surroundings.
- Record-position locking prevents multiple users from contemporaneously streamlining the same record, while enqueueing/ dequeue mechanisms manage access to participating coffers similar to a dataset control block.
- These locking mechanisms enable VSAM to support concurrent access and update of the datasets by multiple users while maintaining data thickness.
26. Explain the part of VSAM path status canons in dataset access.
Ans:
VSAM path status canons are numeric values returned by VSAM access routines to indicate the status of the access path used to recoup data from a dataset. These canons give information about success, failure, or specific conditions encountered during access path initialization and conservation. Programmers can use path status canons to diagnose access path-related issues, optimize dataset access performance, and apply error recovery strategies in their operations.
27. What are VSAM dataset participating modes, and how do they impact data access?
Ans:
VSAM dataset-sharing modes define the position of concurrent access allowed for VSAM datasets by multiple users or programs. The sharing modes range from exclusive( no concurrent access allowed) to read-only and update( concurrent read and write access). The choice of participating mode affects data access concurrency, performance, and data thickness in multi-user surroundings. Opting for the applicable sharing mode is essential for balancing operation conditions with concurrency and data integrity considerations.
28. What’s the role of VSAM AMS( Application Management Services) in VSAM dataset operation?
Ans:
- VSAM AMS provides a suite of mileage programs and services for managing VSAM datasets and related coffers.
- It facilitates tasks such as dataset backup and recovery, space operation, integrity checking, and performance monitoring.
- VSAM AMS automates routine executive functions, ensuring the trustability, vacuity, and performance of VSAM datasets.
- Simplifying dataset operation tasks enhances functional effectiveness and reduces executive outflow.
29. Discuss the significance of VSAM AMS IDCAMS mileage in VSAM dataset administration.
Ans:
The VSAM AMS IDCAMS mileage is the crucial element of VSAM dataset administration, offering commands for defining, manipulating, and managing VSAM datasets. It enables tasks similar to dataset creation, omission, reorganization, and trait revision. IDCAMS also provides installations for dataset backup, recovery, and integrity checking. By furnishing a comprehensive set of executive functions, IDCAMS simplifies the VSAM dataset operation and ensures data integrity and vacuity.
30. What are VSAM access system options, and how are they used?
Ans:
- VSAM access system options are parameters that specify various characteristics and actions of VSAM datasets, similar to softening, locking, and caching options.
- These options are set during dataset creation or revision using VSAM IDCAMS mileage commands.
- Access system options allow customization of dataset access geste to suit operation conditions, optimizing performance, concurrency, and data integrity.
31. Explain the conception of VSAM data space operation.
Ans:
VSAM data space operation involves the allocation and association of physical storehouse space for VSAM datasets on fragments. It includes tasks similar to space allocation, extent operation, and space application monitoring. Proper data space operation ensures effective use of fragment coffers, minimizes fragmentation, and optimizes dataset performance. Ways similar to dynamic space allocation and space recovery help maintain optimal storehouse application and performance in VSAM surroundings.
32. What are VSAM dataset roster entries, and how are they used?
Ans:
VSAM dataset roster entries are:
- Metadata records are stored in the VSAM roster.
- It contains information about VSAM datasets that are similar to dataset names.
- Attributes.
- Position on fragments.
Roster entries are used by system software and operations to detect, access, and manage VSAM datasets. They give a centralized depository for dataset identification, allocation, and administration, easing dataset operation tasks and ensuring data availability and integrity.
33. Discuss the part of VSAM IDCAMS REPRO command in dataset copying and migration.
Ans:
The VSAM IDCAMS REPRO command is used to copy or resettle data between VSAM datasets or between VSAM and non-VSAM datasets. It duplicates dataset contents while conserving dataset attributes, association, and integrity. REPRO supports various data transfer operations, including dataset backup, data migration, and dataset connection. By furnishing a dependable and effective means of data replication and migration, REPRO simplifies dataset operation tasks and ensures data vacuity and thickness.
34. What are VSAM dataset encryption options, and why are they used?
Ans:
- VSAM dataset encryption options allow data stored in VSAM datasets to be translated for enhanced security and confidentiality.
- Encryption options include encryption algorithms, crucial operation mechanisms, and encryption crucial lengths.
- Encrypted datasets cover sensitive information from unauthorized access and data breaches, ensuring compliance with nonsupervisory conditions and data protection norms.
- By enforcing encryption, associations can guard their data means and alleviate the threat of data loss or theft.
35. Discuss the part of VSAM buffer pools in optimizing I/ O performance.
Ans:
VSAM buffer pools are allocated portions of a significant storehouse used to cache constantly penetrated VSAM dataset runners, reducing fragment I/ O quiescence and perfecting overall performance. Buffer pools store both control information and data records recaptured from VSAM datasets during read operations. Proper buffer pool sizing and operation are pivotal for optimizing VSAM performance by minimizing fragment I/ O operations and enhancing system outturn.
36. Explain Freespace.
Ans:
Freespace in VSAM refers to the unused space within a VSAM dataset that’s available for unborn data allocation. It allows for dynamic growth of datasets by furnishing room for fresh records or data extents without the need for immediate dataset expansion. Freespace operation optimizes dataset application, reduces fragmentation, and improves performance by minimizing frequent dataset resizing operations.
37. State difference between VSAM and andNon-VSAM Files.
Ans:
- The primary difference between VSAM( Virtual Storage Access Method) and non-VSAM lines lies in their access styles and associations.
- VSAM lines offer listed or direct access styles, allowing for effective reclamation of records grounded on keys.
- They also support various dataset associations like crucial—sequenced, entry—sequenced, and relative—record, furnishing inflexibility in data access.
- In discrepancy,non-VSAM lines generally follow successional access styles, where data is read or written successively from beginning to end without indexing capabilities.
38. When to choose a VSAM train over a regular successor train?
Ans:
VSAM lines are preferred over regular successional lines when operations bear fast and adequate access to data grounded on specific keys or indicators. VSAM provides direct access to records through indexing, enabling brisk data reclamation compared to successional lines, which bear surveying through the entire train. Also, VSAM offers features like record-position locking, data integrity mechanisms, and support for large datasets, making it suitable for sale processing and data- ferocious operations.
39. What are share options?
Ans:
- Share Opts, short for” share options,” is a parameter used in the VSAM dataset description to specify the level of concurrency allowed for dataset sharing among multiple users or programs.
- It defines whether the dataset can be penetrated coincidently for read-only, update, or exclusive access.
- Share Opts settings ensure data integrity and thickness in multi-user surroundings by controlling access to participating coffers and precluding conflicts between concurrent deals.
40. Can an empty VSAM train be used as input to a Cobol program?
Ans:
Yes, an empty VSAM train can be used as input to a COBOL program. COBOL programs generally handle train processing using input/ affair( I/ O) operations defined in the program’s code. However, if the VSAM train is empty, the program will assume that there are no records to reuse and do so. Still, proper error running and confirmation should be enforced to handle cases where the train may be suddenly empty or unapproachable during program prosecution.
41. What’s the procedure for converting a flat train to a VSAM train?
Ans:
Converting a flat train to a VSAM( Virtual Storage Access Method) train involves several ways. First, need to define a VSAM dataset using the IDCAMS mileage. Also, need to produce a COBOL program or another suitable program to read the flat train and write the data into the recently created VSAM dataset. This program should handle the conversion process, ensuring that the data is duly formatted and written into the VSAM train according to the defined record layout.
42. Explain CI Split and CA Split?
Ans:
- CI Split and CA Split are ways used in VSAM to manage space allocation and perfect performance.
- CI( Control Interval) Split occurs when a control interval becomes full, and there’s no space to accommodate fresh records.
- In this case, VSAM splits the full CI into two separate CIs to accommodate new records.
- CA( Control Area) Split occurs when a control area becomes full, and there’s no space to accommodate fresh CIs. VSAM splits the full CA into two separate CAs to accommodate new CIs.
43. On what base to choose the optimum values for CI and free space?
Ans:
- The optimum values for CI( Control Interval) and free space in a VSAM dataset are chosen based on factors similar to the anticipated record size, access patterns, and performance conditions.
- Generally, lower CI sizes are preferred for datasets with lower records or frequent arbitrary access, as they reduce the quantum of data read into memory.
- Larger CI sizes are more suitable for datasets with more extensive records or successional access patterns, as they reduce the number of CI splits and facilitate performance.
44. Which IDCAMS commands are available for VSAM?
Ans:
Some of the IDCAMS commands available for VSAM include DEFINE, DELETE, LISTCAT, PRINT, REPRO, EXPORT, IMPORT, ALTER, and corroborate. These commands are used for various tasks, such as defining VSAM datasets, deleting datasets, listing roster information, publishing dataset contents, copying datasets, exporting and importing datasets between systems, altering dataset attributes, and vindicating dataset integrity.
45. How to define a KSDS? What’s GDG in VSAM?
Ans:
A KSDS( Key Sequenced Data Set) is a type of VSAM dataset that organizes records grounded on a unique crucial field. Records in a KSDS are physically stored in the order of their essential values, allowing for adequate arbitrary and successional access grounded on the key. GDG( Generation Data Group) in VSAM is a system of organizing and managing affiliated datasets as a group. It allows for the creation of multiple performances of a dataset, with each interpretation linked by a relative number or qualifier.
46. How are the GDG performances named?
Ans:
- GDG performances are named using a picking convention that includes a base name followed by a generation number or qualifier.
- The base name represents the root name of the GDG group, while the generation number or qualifier identifies the specific interpretation within the group.
- For illustration, a GDG interpretation might be named GDG.BASE.G0001V00, whereGDG.BASE is a base name, and G0001V00 is the generation number or qualifier.
- As new performances are created, the generation number is incremented, creating a sequence of affiliated datasets within the GDG group.
47. What does’ 02′ train status law indicate?
Ans:
In COBOL programming, a’ 02′ train status law generally indicates that the train is open for business and the operation has been successful. This status signifies that the train is available to write data. When a train is opened with the intention to write data into it, a’ 02′ train status law confirms that the train is ready to accept data without any crimes.
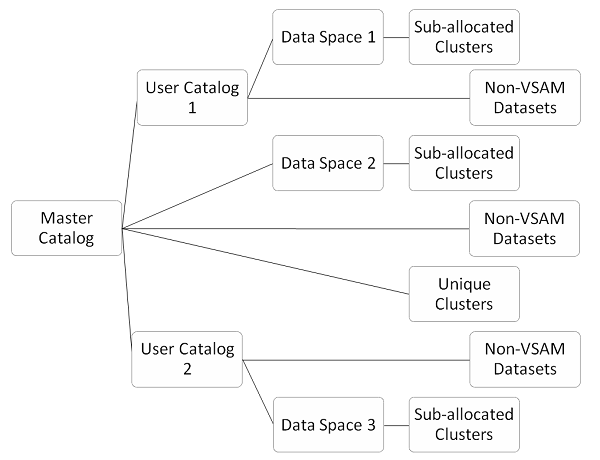
48. What is a Unique Cluster?
Ans:
Unique Cluster in VSAM refers to a clustering system where each crucial value within the dataset is unique. Basically, it ensures that no two records in the dataset share the same critical value. This oneness simplifies a data reclamation process and aids in effective data operation, as each crucial serves as a distinct identifier for a particular record. This uniqueness also enhances data integrity, making it easier to enforce business rules and maintain consistency across applications that interact with the dataset.
49. What are Sub-allocated Clusters?
Ans:
- Sub-allocated Clusters in VSAM involve the allocation of storehouse space in lower units known as control intervals( CIs) or control areas( CAs).
- Unlike traditional allocation styles where ample conterminous space is allocated outspoken,sub-allocated clusters stoutly allocate space as demanded.
- This approach enhances inflexibility and optimizes storehouse application by allocating space in lower, more manageable units as needed.
50. What’s a control interval?
Ans:
A control interval( CI) in VSAM is an abelian unit of a storehouse within a dataset. It consists of a fixed number of successive records stored together on a fragment block. The size of a control interval is determined during dataset creation and is generally small to facilitate effective data access and manipulation. Control intervals play a pivotal part in VSAM’s internal association and storehouse operation.
51. What’s a path?
Ans:
- In the environment of VSAM, a path refers to an access system or route used to recoup data from a VSAM dataset.
- Paths give different ways to pierce data within a dataset, similar to successional, keyed, or alternate listed access.
- Each path corresponds to a specific indicator structure defined during dataset creation, allowing for effective data reclamation grounded on different access criteria.
52. What’s the Association for a KSDS in the COBOL SELECT statement?
Ans:
In COBOL’s SELECT statement, the ORGANIZATION clause specifies the association of the train being penetrated. For a crucial Sequenced Data Set( KSDS), the ORGANIZATION clause is specified as Association IS INDEXED. This indicates that the train is organized in such a way that records are stored grounded on a unique crucial field, allowing for adequate arbitrary and successional access. By specifying the association as INDEXED, COBOL programs can use VSAM’s indexing capabilities to pierce and manipulate data within the KSDS efficiently.
53. What are the Upgrade and No Upgrade options in the Alternate indicator?
Ans:
In the Alternate indicator( AIX) in VSAM, the Upgrade and Noupgrade options specify how VSAM handles indicator crucial updates when a record in the base cluster is streamlined. When the Upgrade option is selected, VSAM automatically updates the alternate indicator key whenever the corresponding key in the base cluster is streamlined. Again, with the No upgrade option, VSAM doesn’t modernize the alternate indicator crucial automatically when the base cluster essential changes.
54. What are the access modes available for the KSDS dataset?
Ans:
- KSDS( Key Sequenced Data Set) datasets in VSAM support various access modes to recoup and manipulate data efficiently. The primary access modes available for KSDS datasets include
- Successional access Reading records in the order they’re physically stored on fragments.
- Random access Directly penetrates records grounded on their crucial values, allowing for quick reclamation of specific records.
- Dynamic access Combining both successional and arbitrary access styles furnishes inflexibility in penetrating records grounded on different criteria.
55. What’s the purpose of the train STATUS clause in the SELECT statement?
Ans:
- The train STATUS clause in the SELECT statement of COBOL programs is used to capture the status of train operations performed on external lines, similar to opening, reading, memo, and closing lines.
- It allows the program to handle train-related crimes and exceptions effectively by furnishing information about the success or failure of train operations.
- The train STATUS clause defines a two-character alphanumeric field where the train status law is stored after each train operation.
- This enables the program to take applicable conduct grounded on the status returned by the operating system.
56. What’s the mileage program nearly associated with VSAM?
Ans:
The mileage program that is nearly associated with VSAM is IDCAMS( Interactive Data Control Access Method Services). IDCAMS provides a set of commands and functions for defining, managing, and manipulating VSAM datasets and registers. IDCAMS is an essential tool for VSAM dataset administration and conservation in mainframe surroundings. It supports operations such as data backup, recovery, and reporting, ensuring the efficient handling of VSAM datasets throughout their lifecycle.
57. Define the share option in VSAM?
Ans:
In VSAM, the share option specifies how a dataset can be penetrated coincidentally by multiple programs or users. It determines the position of data participating and locking to ensure data integrity and thickness in multi-user surroundings. Different share options are available in VSAM. SHARE OPTIONS ( 2) Allows multiple programs to read the dataset coincidently but prohibits any updates or variations while the dataset is open for reading.
58. When is it preferable to use a VSAM train versus a standard successional train?
Ans:
- Choosing between a VSAM train and a standard successional train depends on various factors, such as access patterns, performance conditions, and data association needs.
- VSAM lines are preferable when there’s a need for adequate arbitrary access grounded on crucial values, as they offer listed access and can handle large datasets with optimized performance.
- Also, VSAM lines are suitable for operations taking frequent updates or where data integrity and concurrency control are pivotal.
- On the other hand, standard successional lines are more appropriate for simple, successional data processing tasks where arbitrary access isn’t needed, and data volumes are relatively small or manageable.
59. How to resolve the issue when VSAM runs out of space?
Ans:
When a VSAM dataset runs out of space, several approaches can be used to resolve the issue. One result is to increase the space allocation for the dataset by either extending the space allocation or allocating fresh space using serviceability like IDCAMS. Another approach is to reorganize the dataset using serviceability like REPRO or REORG to reclaim unused space and optimize storehouse applications. Alternatively, data archiving or purging can free up space by removing obsolete or spare records from the dataset.
60. What’s the upgrade set?
Ans:
The upgrade set in VSAM refers to a group of affiliated datasets that partake in the same alternate indicator. When records in the base cluster of an upgrade set are streamlined, the corresponding entries in the alternate indicator are automatically streamlined to reflect the changes. This ensures synchronization between the base cluster and its associated alternate indicator, maintaining data integrity and thickness across the datasets within the upgrade set.
61. What’s the base cluster?
Ans:
- In VSAM, the base cluster refers to the primary dataset, which contains factual data records organized according to a specified key.
- It serves as the central data depository and is generally associated with one or further alternate indicators that give alternate access paths to the data.
- The base cluster defines the dataset’s physical storehouse structure and access styles, playing a central role in VSAM data operation and access operations.
62. What’s the meaning of dynamic processing?
Ans:
Dynamic processing in the VSAM environment refers to a system of penetrating and manipulating VSAM datasets where the access system and record selection criteria are determined stoutly at runtime based on program sense or user input. Unlike static processing, where access styles and criteria are predefined and fixed, dynamic processing allows for lesser inflexibility and rigidity in responding to changing data access conditions. It enhances performance and user experience by enabling more efficient data retrieval and manipulation tailored real-time needs.
63. Name some common VSAM error conditions and canons?
Ans:
Common VSAM error conditions and canons include:
- 00 Successful completion
- 02 Record not set up
- 04 inadequate space in the dataset
- 08 End of train reached
- 10 Duplicate crucial setup during insert or update
64. What’s a VSAM niche?
Ans:
In VSAM, a niche refers to a fixed-size area within a control interval( CI) or control area( CA) used to store control information or pointers to data records. Each niche corresponds to a specific record position within the CI or CA and is used to manage record access and storehouse. Places play a pivotal part in VSAM’s internal association, allowing for effective record reclamation, insertion, and omission operations within the dataset.
65. What’s the significance of the SHAREOPTIONS parameter?
Ans:
The SHAREOPTIONS parameter in VSAM specifies the position of data participating and locking geste for a dataset. This allows multiple programs or users to pierce the dataset coincidentally while ensuring data integrity and thickness. SHAREOPTIONS’s significance lies in its capability to control access to the dataset and manage record-position locking to help conflicts between concurrent access attempts. By specifying applicable share options, users can conform data participating geste according to operation conditions and concurrency requirements.
66. What’s the meaning of the DEFINE MODEL parameter?
Ans:
- The DEFINE MODEL parameter in VSAM is used to define a template or model for creating VSAM datasets with predefined attributes and characteristics.
- By specifying the DEFINE MODEL parameter, users can define a set of dereliction attributes, similar to record format, allocation size, and access system, which are applied when creating new VSAM datasets.
- This parameter simplifies dataset creation by furnishing a standardized template that ensures thickness and uniformity across multiple datasets within a terrain.
67. What’s the meaning of VSAM RETURN- law?
Ans:
- VSAM RETURN- law is a status law returned by VSAM mileage programs or operations to indicate the outgrowth of a VSAM operation.
- The return law provides information about the success, failure, or specific conditions encountered during the operation, allowing programs to handle crimes and exceptions.
- VSAM return canons are numeric values that help diagnose and troubleshoot issues related to dataset operations, similar to opening, reading, writing, closing, or managing VSAM datasets.
68. How to cancel a member using JCL?
Ans:
To cancel a member using Job Control Language( JCL), can use the IDCAMS mileage with the DELETE command. Then, there is an illustration of how to cancel a member named MEMBER1 from a VSAM cluster named mycluster. This JCL instructs IDCAMS to cancel the specified member( MEMBER1) from the VSAM cluster( MYCLUSTER), and the affair is directed to SYSOUT. This process effectively removes the member from the cluster, freeing up resources and ensuring that only the relevant data remains accessible for future operations.
69. What’s the Difference between LDS & ESDS?
Ans:
The main difference between Linear Data Set( LDS) and Entry Sequenced Data Set( ESDS) lies in their association and access styles within VSAM. LDS is organized successionally, allowing only successive access to records. Records are added at the end of the dataset, and reclamation is performed in the order they were added. On the other hand, ESDS allows for direct access grounded on relative byte positions within the dataset.
70. How many buffers are allocated to VSAM KSDS and ESDS?
Ans:
- In VSAM, the number of buffers allocated to KSDS and ESDS depends on various factors such as system configuration, performance conditions, and buffer pool settings.
- Still, users can configure buffer pools and specify the number of buffers allocated to VSAM datasets to optimize performance and resource application.
- Generally, a more significant number of buffers are allocated to constantly penetrated datasets or datasets with high I/ O exertion to minimize fragment access and ameliorate overall performance.
71. What does the KEYRANGES parameter in Define Cluster recommend?
Ans:
- The KEYRANGES parameter in the DEFINE CLUSTER command in IDCAMS specifies the range of crucial values to be used for pre-defining indicator entries in a VSAM cluster.
- By specifying KEY RANGES, users can optimize indicator space application and ameliorate access performance by pre-allocating indicator entries for a specified range of crucial values.
- This parameter allows for more effective indicator operation and can help reduce indicator expansion outflow during dataset operations.
72. What’s the difference between import and import in IDCAMS?
Ans:
In IDCAMS, the EXPORT command copies VSAM datasets from a mainframe to an external storehouse medium or another system in a format suitable for migration or backup purposes. On the other hand, the IMPORT command copies VSAM datasets from an external storehouse medium or another system back to the mainframe, converting them into VSAM datasets compatible with the mainframe terrain. During Import excerpts datasets from the mainframe, easing data transfer and interoperability between different platforms.
73. What are the parameters demanded to produce a cluster using the IDCAMS mileage?
Ans:
To produce a cluster using the IDCAMS mileage, several parameters are demanded to define the characteristics and attributes of the cluster. The essential parameters include:
- CLUSTER Specifies the name of the cluster being created.
- Listed Indicates that the cluster is a listed VSAM dataset.
- KEYS Specifies the crucial fields used for record association and access.
- RECORDSIZE Defines the size of each record in the dataset.
- ALLOCATE Specifies the original allocation size and posterior proliferation for the dataset.
74. Which data element is generated for an LDS cluster?
Ans:
For an LDS( Linear Data Set) cluster in VSAM, the data element generated is a direct dataset containing records stored successionally without any indexing or key-grounded association. The data element of an LDS cluster consists of data records arranged in the order they were added to the dataset, allowing only successional access to the records. Unlike listed VSAM datasets, LDS clusters don’t have associated indicator structures or crucial fields for arbitrary access, making them suitable for operations taking simple successional data processing.
75. What’s the difference between an RRDS( Relative- Record Data Set) cluster and an ESDS cluster?
Ans:
The main difference between an RRDS( Relative- Record Data Set) cluster and an ESDS( Entry Sequenced Data Set) cluster lies in their association and access styles within VSAM. RRDS clusters organize data into fixed-length records and each record is penetrated and grounded on its relative record number( RRN). In discrepancy, ESDS clusters organize data into variable-length records and allow records to be penetrated and grounded in their physical order within the dataset.
76. What are subscripts, indicators, and subscripts in Cobol?
Ans:
- In COBOL, subscripts, indicators, and subscripts are used to pierce and manipulate rudiments within arrays or tables.
- An indicator is a special register or variable used to control the replication or traversal of a variety during processing.
- Subscripts and indicators are generally used interchangeably in COBOL to relate to the position of array rudiments.
- By incrementing or decrementing subscripts or indicators, programs can navigate through arrays and perform operations on individual rudiments, easing data manipulation and processing.
77. What are subprograms in Cobol?
Ans:
- In COBOL, subprograms are applicable sections of the law that perform specific tasks or functions within a program.
- Subprograms are invoked by a CALL statement from the main program or other subprograms and can accept parameters to admit input data or return results.
- There are two types of subprograms in COBOL subroutines and functions. Subroutines execute a series of statements and don’t return a value, while functions return a single result value to the calling program.
- Subprograms enhance law modularity, readability, and maintainability by recapitulating sense into separate units, promoting law exercise, and simplifying program structure.
78. What’s the virtual storehouse access system( VISA) in Cobol?
Ans:
Virtual Storage Access Method( VSAM) in COBOL refers to a data access system generally used in mainframe surroundings to manage and pierce large datasets efficiently. VSAM provides listed and successful access to datasets, allowing programs written in COBOL and other languages to read, write, and manipulate data stored in fragments. VSAM organizes data into clusters, each containing records arranged according to a crucial field.
79. What are CACS?
Ans:
CACS stands for Common Access Control Services, a set of installations handled by IBM’s RACF for controlling access to coffers in a mainframe terrain. CACS includes features similar to authentication, authorization, and auditing, allowing directors to manage users’ access rights, warrants, and security programs for datasets, programs, and system coffers. By enforcing CACS, associations can apply for security programs, and ensure data integrity and confidentiality in COBOL operations and other mainframe systems.
80. How do visa and non-visiting data sets differ in Cobol?
Ans:
- In COBOL, Visa and Non-Visa datasets relate to datasets penetrated using the Virtual Storage Access Method( VSAM), and datasets penetrated using non-VSAM styles independently.
- Visa datasets are managed by VSAM and support listed or successional access styles, furnishing effective data reclamation and manipulation capabilities.
- Non-Visa datasets, on the other hand, include traditional flat lines or datasets penetrated using styles other than VSAM, similar to successional lines( PDS, PDSE) or relational databases.
- While Visa datasets offer enhanced performance and indexing capabilities, Non-Visa datasets may have simpler access styles and storehouse structures.
81. What are the differences between P.S. and D.S. lines?
Ans:
- Physical successional lines and DS lines are both types of successional lines in COBOL. Data access is performed successionally from the morning to the end of the train.
- Still, there are differences in their association and operation. P.S. Lines are traditional successional lines where records are stored in physical order on fragments.
- D.S lines, on the other hand, are VSAM datasets organized as successional lines, allowing for both successional and direct access to records grounded on crucial values.
82. What are the functions of REPRO, balcony, publish, and list cat in ID Camps?
Ans:
In IDCAMS, REPRO is used to copy datasets, either between VSAM datasets or between VSAM and non-VSAM datasets. ALTER is used to modify attributes of VSAM datasets, similar to space allocation, record format, or crucial delineations. PRINT is used to publish the contents of a VSAM dataset, while LISTCAT is used to list roster information about VSAM datasets, including attributes, space allocation, and indicator details.
83. What’s LISTCAT in VZM?
Ans:
- LISTCAT in VSAM( Virtual Storage Access Method) is a mileage command used to list roster information about VSAM datasets.
- It provides detailed metadata about VSAM datasets stored in the roster, including dataset name, association type, record format, crucial structure, allocation parameters, space application, and indicator details.
- LISTCAT allows users to recoup essential information about VSAM datasets without penetrating the dataset itself, easing dataset operation, analysis, and troubleshooting tasks in mainframe surroundings.
84. What’s a print command?
Ans:
The PRINT command in mainframe surroundings is used to publish the contents of datasets or reports on physical printers connected to the system. It allows users to induce hardcopy affairs from electronic data stored in datasets, easing document distribution, record keeping, and archival purposes. The PRINT command accepts parameters to specify the dataset to be published, publishing options such as runner range, number of clones, and printer destination details.
85. What’s the difference between print and dump in a print command?
Ans:
The main difference between PRINT and DUMP in a PRINT command lies in their affair formats and purposes. PRINT generates formatted mortal-readable affairs suitable for publishing on physical paper, while DUMP produces unformatted hexadecimal or double affairs ideal for analysis or debugging purposes. PRINT converts dataset contents into a printable format with line breaks, pagination, and character encoding, making it suitable for document generation.
86. What are the main advantages of a REPRO command?
Ans:
- The REPRO command in mainframe surroundings offers several advantages for data operation and manipulation tasks.
- Initially, it facilitates the efficient copying of datasets, allowing users to replicate datasets within the same system or transfer data between different systems.
- Secondly, REPRO preserves dataset attributes and integrity during the copy process, ensuring that metadata and data integrity are maintained.
- REPRO supports various options and parameters for customizing the copy operation, similar to specifying record selection criteria, and error running, enhancing inflexibility and control over the copy process.
87. What’s DITTO( Data Interfile Transfer, Testing, and Operations)?
Ans:
DITTO( Data Interfile Transfer, Testing, and Operations) is a mileage program used in mainframe environments for data transfer, testing, and operations operations tasks. DITTO provides an adaptable set of functions for copying, comparing, editing, and manipulating datasets, easing various data operations, and testing conditioning. It allows users to perform tasks similar to dataset copying, data conversion, record selection, and data confirmation, making it a valuable tool for data processing and conservation in mainframe surroundings.
88. What’s the identification division program?
Ans:
- The Identification Division is a section of a COBOL program that contains information about the program itself, similar to its name, author, and purpose.
- It serves as the title or introductory section of the COBOL program and provides essential metadata for program attestation and operation.
- The Identification Division generally includes statements similar to PROGRAM-ID, AUTHOR, DATE—WRITTEN, and INSTALLATION, which describe the program’s identity, authorship, creation date, and installation details.
89. Can AMS commands be run from the TSO advice?
Ans:
AMS commands can be run from the Time Participating Option advice in mainframe surroundings. TSO provides a command-line interface for interacting with the mainframe operating system, allowing users to execute various system commands and be serviceable, including AMS commands. Users can enter AMS commands directly at the TSO advice to perform tasks similar to dataset operation, roster manipulation, and access system operations, furnishing an accessible and effective means of interacting with mainframe coffers.
90. Which VSAM type is swift?
Ans:
The fastest type of VSAM dataset depends on the specific conditions and access patterns of an operation. Generally, Key Sequenced Data Sets( KSDS) are frequently considered the fastest type of VSAM dataset for operations taking adequate arbitrary access grounded on crucial values. KSDS utilizes indexing structures to grease quick record reclamation and manipulation, making it suitable for operations with frequent arbitrary access operations. KSDS are fastest for arbitrary access, while LDS excel in sequential processing.






