
SAP RAR (Revenue Accounting and Reporting) is a comprehensive solution designed to streamline revenue recognition processes for businesses. It provides functionalities for recognizing revenue according to accounting standards, automating revenue-related tasks, and generating accurate financial reports. With SAP RAR, organizations can ensure compliance with regulations, improve transparency, and make informed business decisions based on reliable revenue data.
1. What is SAP RAR, and why is it important?
Ans:
SAP RAR is a module designed to help businesses misbehave with profit recognition norms similar as IFRS 15 and ASC 606. It’s pivotal because it ensures that profit from contracts with guests is honored in a manner that reflects the delivery of goods and services and not simply grounded on when the payment is entered. SAP RAR handles complex billing and profit recognition scripts, automates profit bulletins, and provides detailed reporting capabilities, enabling companies to maintain compliance with account norms and ameliorate fiscal delicacy.
2. Explain the integration of SAP RAR with other SAP modules.
Ans:
SAP RAR integrates considerably with other modules, primarily SAP SD( Deals and Distribution) and SAP FI( Financial Accounting). From SD, RAR receives data about deals orders, billing documents, and contract adaptations, which are essential for profit recognition processes. Integration with FI ensures that honored profit impacts fiscal statements directly.
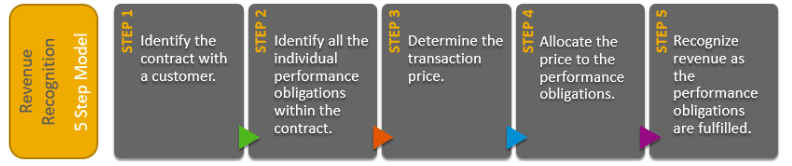
3. How does SAP RAR handle the five- step model of profit recognition?
Ans:
- The five- step model under ASC 606 and IFRS 15 is completely supported by SAP RAR.
- The way include relating the contract with a client, relating the performance scores, determining the sale price, allocating the sale price to the performance scores, and feting profit when/ as performance obligation is satisfied.
- SAP RAR automates these way by allowing configuration rules for each step, managing the data and processes through its integration with other modules, and ensuring accurate profit computations and reporting.
4. What are Performance scores and how does SAP RAR manage them?
Ans:
- Performance scores( POBs) are pledges in a contract to transfer goods or services to a client. SAP RAR allows to define and manage these scores by setting up specific rules that align with the company’s profit recognition programs.
- It can automatically fete profit as POBs are satisfied, grounded on either time- grounded or event- grounded criteria, ensuring compliance with account norms.
- This functionality is critical for companies that deal with complex contracts similar as those involving multiple deliverables over different ages.
5. What is the role of Contract Balances in SAP RAR?
Ans:
Contract Balances in SAP RAR include Contract means, Contract arrears, and Unbilled Receivables. They represent the fiscal positions performing from timing differences between profit recognition and invoicing. SAP RAR tracks these balances automatically, streamlining them as checks are issued and payments are entered. This point provides translucency in fiscal reporting and helps in accurate statement medication, which is essential for inspection trails and compliance.
6. What are some challenges in enforcing SAP RAR?
Ans:
Enforcing SAP RAR can be challenging due to the need for detailed understanding of the new profit recognition norms, the complexity of being contractual arrangements, and the integration needed with other systems. Successful perpetration requires thorough process mapping, customization to meet specific business requirements, and significant change operation to train users on the new processes and systems.
7. What is the significance of the profit Account Rule in SAP RAR?
Ans:
- The profit Account Rule in SAP RAR is abecedarian to the configuration and robotization of the profit recognition process.
- This rule defines how and when profit should be honored in different scripts and is linked to specific performance scores.
- By setting up these rules, businesses can automate profit computations grounded on the timing of satisfying performance scores, the allocation of sale prices, and compliance with various account norms.
- This reduces homemade crimes and ensures thickness in how profit is honored across the association, aligning fiscal reports with global norms.
8. What is the difference between Contract revision and Contract Extension in RAR?
Ans:
| Aspect | Contract Revision | Contract Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Involves modifying the terms and conditions of an existing contract. | Entails prolonging the duration or validity period of an existing contract. |
| Purpose | Allows for alterations or amendments to pricing, quantities, delivery schedules, etc. within the scope of the original contract. | Extends the timeframe during which the terms and conditions of the original contract remain in effect. |
| Impact on Duration | Does not extend the duration of the contract itself. | Extends the duration or validity period of the contract beyond its original end date. |
| Typical Scenario | Changes to existing contracts due to evolving business needs, renegotiations, or adjustments. | Prolonging the duration of contracts to continue service provision, ongoing projects, or renegotiations. |
9. Describe the process of remitted profit in SAP RAR?
Ans:
Prolonged profit in SAP RAR refers to plutocrat entered from guests for goods or services that haven’t yet been delivered or completely earned under the terms of a contract. SAP RAR tracks these quantities as contract arrears until the associated performance scores are satisfied. As services are rendered or goods delivered, RAR recognizes the profit proportionally, reducing the remitted balance.
10. Explain how SAP RAR supports inspection compliance.
Ans:
SAP RAR supports inspection compliance by providing detailed and traceable records of all profit deals and adjustments. It includes robust reporting tools that offer insights into every stage of the profit recognition process, from initial contract capture to final profit completion. These features ensure transparency and help auditors verify that recognized earnings comply with international standards like ASC 606 and IFRS.
11. What are the crucial reports generated by SAP RAR, and what’s their significance?
Ans:
- SAP RAR generates several crucial reports that are vital for fiscal analysis and decision- timber.
- These include profit recognition summaries, remitted profit reports, contract asset and liability reports, and detailed breakdowns of performance scores.
- Similar reports give fiscal directors and stakeholders with critical perceptivity into the profit aqueducts and fiscal health of the association.
- They’re pivotal for strategic planning, performance assessment, and ensuring compliance with fiscal reporting norms, making them necessary tools for businesses operating in different and dynamic request surroundings.
12. What typical challenges are faced during the data migration phase to SAP RAR?
Ans:
- During the data migration phase to SAP RAR, associations frequently face challenges similar as data volume operation, ensuring data quality, and mapping heritage data directly to the new system’s structure.
- It’s pivotal to establish clear data governance to maintain integrity and delicacy.
- Also, businesses must develop detailed migration strategies that include thorough testing phases to identify any data inconsistencies or issues before going live.
13. What is the approach to handling multiple element arrangements in SAP RAR?
Ans:
In SAP RAR, multiple element arrangements, or contracts with multiple performance scores, are managed by relating and separating the distinct goods or services involved. Each performance obligation is estimated and honored singly grounded on its own specific criteria for profit recognition. SAP RAR facilitates the allocation of the sale price to each performance obligation proportionally, grounded on their standalone selling prices.
14. What methodologies does SAP RAR give for profit soothsaying?
Ans:
SAP RAR offers sophisticated methodologies for profit soothsaying, which are pivotal for planning and decision- making processes. These include prophetic analytics and modeling tools that dissect literal data and current contract information to cast future profit scripts. By integrating with SAP’s advanced analytics capabilities, RAR can help finance brigades prognosticate when profit from specific contracts will be honored, grounded on being performance scores and their satisfaction criteria.
15. Explain the part of the Contract Management function in SAP RAR?
Ans:
- The Contract Management function in SAP RAR is central to tracking and managing the lifecycle of a client contract from inauguration through revision to completion.
- This function supports the creation, revision, and withdrawal of contracts and ensures that all changes are reflected directly in profit recognition and fiscal reporting.
- It automates the updating of performance scores and sale prices, which is essential when contracts are renewed or amended.
16. Describe the process of profit redistribution in SAP RAR.
Ans:
- Profit redistribution in SAP RAR occurs when there’s a change in the sale price or in the anticipated fulfillment of performance scores.
- SAP RAR handles these adaptations by recalculating the quantities allocated to each performance obligation according to their relative standalone selling prices.
- This process is vital when abatements are given after the original contract agreement or when fresh deliverables are added to an being contract.
17. What’s the significance of Standalone Selling Price( SSP) in SAP RAR, and how is it determined?
Ans:
The Standalone Selling Price( SSP) is a critical element in SAP RAR used to allocate the sale price to multiple performance scores in a contract. SSP is the price at which a good or service would be vended independently under analogous circumstances. Determining SSP can involve several styles, including observable prices, cost- plus periphery, or residual approach, depending on the vacuity of observable data and the nature of the goods or services.
18. How does SAP RAR deal with the challenges of retrospective contract variations?
Ans:
Retrospective contract variations, similar as changes in contract terms or cancellation of services, pose significant challenges in profit recognition. SAP RAR addresses these by allowing for full retrospective adaptation of the profit formerly honored if the contract revision affects once performance scores. The system recalculates the profit recognition entries and makes necessary adaptations to reflect the modified contract terms.
19. How does SAP RAR address the issue of variable consideration?
Ans:
- SAP RAR effectively manages variable consideration, which refers to profit quantities that can vary due to abatements, rebates, or performance lagniappes.
- The module allows users to estimate the quantum of variable consideration to be included in the sale price using either the anticipated value system or the most likely quantum system, depending on which better predicts the quantum of consideration to which the company will be entitled.
- These estimates are also streamlined at each reporting period as new information becomes available.
20. What capabilities does SAP RAR offer for handling time-based profit recognition?
Ans:
- SAP RAR offers robust support for time- grounded profit recognition, which is critical for services rendered over a period, similar as subscriptions or conservation services.
- It allows for profit to be honored moreover on a straight- line base over the service period or grounded on factual operation if operation patterns give a further faithful representation of the transfer of service to the client.
- Configurable schedules in SAP RAR automate the computation and advertisement of profit periodically, ensuring compliance with applicable account norms and reducing the eventuality for homemade crimes in long- term contracts.
21. What tools within SAP RAR can help in profit data analysis and decision- making?
Ans:
- SAP RAR is equipped with a suite of logical tools designed to give deep perceptivity into profit data and trends, abetting in strategic decision- timber.
- These tools include dashboards for real- time monitoring of profit aqueducts, detailed breakdowns of profit by product line, region, or client, and prophetic analytics capabilities that read unborn profit scripts grounded on current data.
- Also , SAP RAR can be integrated with SAP Business Warehouse( BW) and SAP Analytics pall to enhance data visualization and grease more complex analyses, helping directors and directors make informed opinions grounded on comprehensive profit intelligence.
22. What is the method for managing exposures related to profit recognition in SAP RAR?
Ans:
SAP RAR helps associations manage and automate the exposures needed under profit recognition norms similar as IFRS 15 and ASC 606. The module supports the generation of detailed reports that expose the nature, quantum, timing, and query of profit and cash overflows arising from contracts with guests. These reports can be customized to meet specific statutory conditions and insure translucency in fiscal dispatches.
23. Explain how SAP RAR handles the account for contract costs.
Ans:
SAP RAR includes functionality to manage costs associated with carrying and fulfilling a contract, as specified under IFRS 15 and ASC 606. The module allows for the capitalization of incremental costs of carrying a contract and costs to fulfill a contract if they’re anticipated to be recovered. SAP RAR tracks these costs, matches them with the affiliated profit, and amortizes them in line with the pattern of transfer of the goods or services to which the costs relate.
24. What are the challenges in configuring SAP RAR for a global enterprise, and how can they be addressed?
Ans:
- Configuring SAP RAR for a global enterprise presents several challenges, including handling multiple currencies, complying with different nonsupervisory conditions, and integrating with various heritage systems.
- To address these challenges, companies must design a flexible yet standardized system armature that can be acclimated to original requirements without compromising global policy compliance.
- Exercising SAP’s advanced tools like the SAP Central Finance function can grease the integration of distant systems and data adjustment.
25. What’s the part of Fair Value Pricing in SAP RAR?
Ans:
Fair Value Pricing is a critical concept in SAP RAR used primarily for allocating the sale price to various performance obligations in a contract when standalone selling prices aren’t directly observable. SAP RAR allows for the determination of fair value through various approaches, including market assessment, anticipated cost plus a margin, or the residual approach. This flexibility ensures that companies can accurately recognize revenue based on the economic realities of their contracts.
26. Explain the process for revising profit recognition schedules in SAP RAR.
Ans:
- In SAP RAR, revising profit recognition schedules is necessary when there are changes in the contract terms, performance scores, or anticipated timing of satisfaction of those scores.
- The system allows for flexible adaptations to the recognition schedules either manually or automatically, depending on the nature of the change.
- For illustration, if a client agreement is modified to extend a service period, SAP RAR will recalibrate the being schedule to spread the honored profit over the new period.
27. How does SAP RAR manage foreign currency transactions?
Ans:
- Handling foreign currency deals in SAP RAR involves recording profit in both the sale currency and the functional currency of the reporting reality.
- The module supports automatic conversion grounded on real- time exchange rates, ensuring that profit is directly reported in the fiscal statements according to the rearmost currency values.
- Also, SAP RAR can manage oscillations in exchange rates and their impact on profit recognition, by recalculating the sale price and associated profit when significant currency changes do.
28. How does SAP RAR support compliance with different geographic nonsupervisory conditions?
Ans:
SAP RAR is designed to support global compliance, enabling businesses to cleave to various geographic-specific nonsupervisory conditions for profit recognition, similar as ASC 606 in the U.S. and IFRS 15 internationally. The module can be configured to apply different rules grounded on the position of the sale and the applicable legal and counting fabrics.
29. What are the stylish practices for testing and validating SAP RAR executions?
Ans:
Testing and validating an SAP RAR perpetration involves several stylish practices to insure the system functions rightly and meets business conditions. These include comprehensive unit testing, integration testing with other SAP modules, and users acceptance testing to confirm that the system meets the end users’ requirements. Automated testing tools can also be employed to pretend various scripts and insure that all possible contract configurations are managed rightly by the system.
30. Explain the significance of linking SAP RAR with SAP CRM.
Ans:
- Linking SAP RAR with SAP CRM is pivotal for using complete client relationship operation capabilities alongside profit recognition.
- This integration allows businesses to maintain a cohesive inflow of data from client relations and agreements captured in SAP CRM to profit recognition processes in SAP RAR.
- It helps in tracking all contractual commitments and changes, ensuring that profit recognition is aligned with client agreements and variations.
31. What challenges arise in moving to SAP RAR from a legacy system, and how can they be addressed?
Ans:
- Transitioning to SAP RAR from a heritage system frequently presents challenges similar as data migration complications, users relinquishment, and system integration issues.
- To alleviate these challenges, companies should invest in comprehensive training programs to insure that users are comfortable with the new system.
- Data migration should be precisely planned and executed in stages to minimize dislocations to ongoing business operations.
32. What is the role of machine learning in enhancing SAP RAR functionalities?
Ans:
Machine learning can significantly enhance SAP RAR functionalities by automating complex processes and providing predictive insights into profit recognition scenarios. For example, machine learning algorithms can analyze historical contract data to anticipate variable consideration issues and optimize the allocation of sale prices to performance obligations. Additionally, these algorithms can identify patterns and trends that human analysts might overlook, allowing for more accurate forecasting and decision-making.
33. How does SAP RAR handle the recognition of profit in a subscription- grounded business model?
Ans:
In a subscription-based business model, SAP RAR manages profit recognition by allocating the subscription profit over the period during which services are rendered. The module supports the establishment of a profit recognition plan that aligns with service delivery, ensuring that profit is recognized as performance obligations are fulfilled. This approach allows for accurate financial reporting and enhances visibility into revenue streams.
34. How does SAP RAR ensure compliance with reporting standards like ASC 606 and IFRS 15?
Ans:
- SAP RAR is specifically designed to handle complex profit recognition scripts under different account norms, similar as ASC 606 and IFRS 15.
- The module allows the setup of binary reporting, where deals can be recorded and reported according to both sets of rules contemporaneously.
- It achieves this by enabling configurations that define how profit should be honored under each standard and can maintain separate checks for reporting purposes.
35. What challenges arise when enforcing SAP RAR in a company with multiple business units?
Ans:
- Enforcing SAP RAR in a company with different business units presents several challenges, including varying business processes, distinct nonsupervisory conditions, and differing situations of IT structure across units.
- To effectively overcome these challenges, a formalized yet flexible perpetration strategy is pivotal.
- This involves establishing a core model that defines common processes and configurations while allowing acclimations to meet original business conditions.
- Expansive stakeholder engagement and training are essential to insure a smooth transition and wide users relinquishment.
36. How does SAP RAR handle changes in contract terms that affect being profit recognition schedules?
Ans:
SAP RAR is complete at managing adaptations arising from changes in contract terms, similar as emendations in performance scores or sale prices. When contract terms are modified, SAP RAR recalculates the profit allocation across the modified performance scores and adjusts the profit recognition schedule consequently. This is done either prospectively or cumulatively, depending on the nature of the change and applicable account guidelines.
37. Where can SAP RAR significantly improve effectiveness in profit operation processes through scripting?
Ans:
In diligence like software or media, where companies frequently rush multiple products and services, SAP RAR significantly improves effectiveness by automating the allocation and recognition of profit across complexmulti-element arrangements. For illustration, a software company might vend a pack that includes a software license, updates for a time, and client support.
38. What role does user training play in the deployment of SAP RAR, and how should it be conducted?
Ans:
Users training is critical to the successful deployment of SAP RAR, ensuring that all applicable labor force understand how to use the system effectively to meet the company’s fiscal reporting and compliance conditions. Effective training should be part-specific, fastening on the specific functions and liabilities of each users group within the system. It should include hands- on sessions where users can exercise entering data, making adaptations, and generating reports in a controlled terrain.
39. What’s the description of profit?
Ans:
- Profit is the total quantum of plutocrat generated by a company for the trade of goods, services, or other means, within a specific period, related to its main operations.
- Profit is honored when it’s earned and doable, meaning that the goods or services have been delivered or rendered, and payment is assured.
- This measure is critical as it reflects the business’s capability to attract guests and induce deals, serving as the primary source of income that funds the operations, growth, and sustainability of the company.
40. When should profit be honored?
Ans:
- Profit should be honored when it meets specific criteria that confirm the earnings process is complete.
- According to utmost fiscal norms, including IFRS 15 and ASC 606, profit is honored when control of the goods or services is transferred to the client, and the company has a right to payment.
- The criteria involve relating the contract with the client, relating the performance scores, determining the sale price, allocating the sale price to the performance scores, and feting profit when( or as) the performance scores are fulfilled.
41. What’s the periodic approach and how is it used for profit recognition?
Ans:
The periodic approach in account refers to feting profit and charges in the specific period they’re incurred, anyhow of when factual cash deals do. This approach is used in scripts where earnings and related charges are honored within set account ages, similar as yearly, daily, or annually. For profit recognition, this system ensures that profit generation aligns with the associated costs in the same period to give a more accurate picture of a company’s fiscal performance, therefore abetting in better operation opinions and fiscal reporting.
42. What’s the addendum- grounded account approach?
Ans:
Addendum- grounded account is a system where profit and charges are recorded when they’re earned or incurred, anyhow of when the cash deals do. This approach gives a more accurate picture of a company’s fiscal health because it matches earnings to the charges incurred to induce those earnings within the same reporting period. addendum account is essential for complex businesses where deals gauge multiple ages, helping stakeholders understand the true fiscal status by considering receivables, payables, and other accrued arrears.
43. What happens to the remitted profit at the end of the contract?
Ans:
At the end of a contract, remitted profit, which is plutocrat entered from a client for goods or services not yet delivered or rendered, is completely honored as profit on the income statement. Throughout the contract duration, the remitted profit balance is gradationally reduced as the company recognizes profit corresponding to the portion of the service or product delivered.
44. What’s the dereliction term of the contract and how is the quantum divided into multiple ages?
Ans:
- The dereliction term of a contract refers to the standard or generally agreed duration over which the contractual services or goods are to be handed, frequently specified in the terms of the contract itself.
- The quantum honored in each period is divided grounded on the performance scores linked within the contract and when they’re satisfied, either over time or at a point in time.
- For case, in amulti-year service contract, profit may be honored on a straight- line base if the service is handed unevenly throughout the period, or according to mileposts if the contract specifies certain tasks to be completed at different stages.
45. What are some crucial benefits of using SAP RAR for profit recognition?
Ans:
SAP Revenue Accounting and Reporting( RAR) offers several crucial benefits, primarily in abetting compliance with transnational profit recognition norms similar as ASC 606 and IFRS 15. SAP RAR provides a flexible result that automates and manages the entire profit recognition process in a comprehensive manner. It enables real- time profit data analysis and reporting, which enhances fiscal delicacy and visibility.
46. What is the accounting entry produced when generating a proforma invoice?
Ans:
- When producing a proforma invoice in SAP, it is important to note that this document is generally not associated with any accounting entry.
- Proforma checks are used primarily for instructional purposes, similar as furnishing a quotation or an estimate to a client before delivering goods or services.
- They’re considered a primary bill of trade and don’t represent a legal request for payment, hence no advertisement occurs in the fiscal accounts.
47. What is the accounting entry produced when generating a cash transaction?
Ans:
- In SAP, when a cash trade is created, it generally triggers immediate account entries to reflect the deals sale and damage of payment.
- The typical account entries for a cash trade would be a disbenefit to the cash or bank account and a credit to the deals profit account, indicating the flux of cash and the recognition of deals profit contemporaneously.
- Also, force accounts are acclimated( debited) to reflect the cost of goods vended( COGS) and credited to reduce the force.
48. What does the term “accounting document type” mean?
Ans:
In SAP, an account document type is used to classify counting documents and distinguish between the various business deals that do. It controls the types of deals that can be recorded and helps in organizing them into manageable groups. Each document type specifies which accounts can be posted to, whether the document number is internally or externally assigned, and the range of document figures allowed.
49. How do systems understand whether to pick KOFI or KOFK?
Ans:
- In SAP, the determination between using KOFI( cost of deals account) or KOFK( cost of deals counting for costs) generally depends on the configuration of the controlling area and the type of business sale.
- The system uses these settings to determine how costs and earnings are posted.
- KOFI is generally named for scripts where cost rudiments need to be reserved directly against fiscal accounts, similar as in deals order scripts. KOFK is used where there are specific conditions for posting costs directly to CO( Controlling) objects like orders or systems.
50. What is the accounting entry produced during Post Goods Issue (PGI)?
Ans:
Performing Post Goods Issue( PGI) in SAP signifies the reduction of force and the recording of an expenditure related to the cost of goods vended. When PGI is executed, the typical account entry includes a disbenefit to the Cost of Goods vended( COGS) account and a credit to the Inventory account. This entry reflects the movement of goods out of force and recognizes the associated cost as an expenditure, impacting both the balance distance and the income statement.
51. How does SAP RAR handle profit recognition for long- term construction systems?
Ans:
SAP RAR manages profit recognition for long- term construction systems by using the over-time recognition system, which aligns with criteria that fete profit as work is completed. This approach is essential for systems where performance occurs over a period, similar as in construction. In SAP RAR, this can be set up using specific rules that measure progress towards completion, which could be grounded on mileposts or the chance of costs incurred relative to the total estimated costs.
52. What’s the T law to manually post tab values into account?
Ans:
- In SAP systems, the sale law to manually post tab values into account is generally” FB70″ for client checks and” FB60″ for seller checks.
- These T canons allow users to enter checks directly into the fiscal account module, bypassing the deals and distribution or procurement processes that would typically automate this advertisement.
- This homemade entry is frequently used for corrections, adaptations, or in lower operations where robotization isn’t enforced. Users must insure delicacy in these entries as they directly affect fiscal reporting and compliance.
53. How do profit G/ L accounts set up in the standard system?
Ans:
- Profit General Ledger( G/ L) accounts in a standard SAP system are set up through the map of accounts linked to specific company canons.
- These accounts are distributed under the profit account type, and each profit account is generally associated with specific profit types, similar as product deals, service income, or licensing freights.
- During system configuration, these accounts are assigned to the applicable profit recognition rudiments in SAP RAR to insure that profit from contracts is rightly recorded against the right G/ L account grounded on the nature of the income.
54. What are the differences between Master Data, Metadata, and Sales Data?
Ans:
- Master data refers to the core data that’s essential to business operations in SAP systems, similar as data about guests, merchandisers, accoutrements , and workers.
- This data remains fairly stable over time and is constantly used by various modules within SAP.
- Metadata is data about data; it defines and describes other data within the system, similar as the structure of databases or the attributes of data fields, furnishing information on how data is reused and stored.
55. How can SAP RAR streamline an association’s profit account and reporting processes?
Ans:
SAP RAR streamlines profit account and reporting processes by automating the operation of profit recognition in line with transnational account norms like IFRS 15 and ASC 606. It integrates deals, billing, and profit data into a centralized platform, furnishing real- time visibility and control over profit deals. SAP RAR simplifies complex processes similar as allocation of sale prices, running of contract variations, and profit scheduling.
56. How does SAP RAR manage changes in sale prices or contract variations?
Ans:
- SAP RAR is complete at managing contract variations, which include changes in sale prices, adding or terminating performance scores, and other emendations.
- It automatically recalculates the sale price and reallocates it across the performance scores grounded on predefined rules.
- This point ensures that profit recognition remains accurate and biddable with norms like ASC 606 or IFRS 15, indeed as contract terms evolve over time.
57. What is the configuration process in SAP RAR to recognize revenue either at a point in time or over time?
Ans:
In SAP RAR, profit recognition at a point in time or over time is configured grounded on the nature of the performance scores outlined in a contract. For recognition at a point in time, generally used for goods or services transferred incontinently, the system is set to fete profit when control of the asset is transferred to the client, which can be determined by payload or delivery terms.
58. What’s a record- to- report process in SAP?
Ans:
- The record- to- report( R2R) process in SAP is a comprehensive fiscal operation process involving data collection, data entry, data processing, and generating reports to give strategic, fiscal, and functional feedback.
- It encompasses everything from recording deals in the tally to fiscal connections and closing books, eventually climaxing in fiscal reporting.
- SAP systems grease this process by ensuring data delicacy and integrity, automating workflows, and integrating various fiscal functions to produce timely and accurate fiscal statements that help in decision- timber and compliance reporting.
59. What’s the full form of RAR in billing?
Ans:
- In the environment of billing and profit recognition, RAR generally stands for” profit Account and Reporting”.
- It’s a software result designed by SAP to help companies misbehave with transnational fiscal reporting norms similar as IFRS 15 and ASC 606.
- SAP RAR facilitates the operation of profit recognition processes by automating the computations, managing multiple element arrangements, and furnishing detailed reporting capabilities that help businesses directly and efficiently report their fiscal results in agreement with the rearmost regulations.
60. What steps should be taken if the accounting document is not generated as expected?
Ans:
Still , as a adviser , the first step is to check for any error dispatches or logs that could indicate why the document wasn’t created, If an account document isn’t generated in SAP. Common issues might include deficient obligatory fields, incorrect configuration settings, or data inconsistencies. Review the affiliated sale data and configurations, similar as account determination, document type, and posting rules.
61. What information is required for the system to generate counting documents?
Ans:
An account document in SAP may not be generated if critical information is missing or incorrect. This generally includes deficient master data, similar as client or seller information, incorrect or missing account assignment details( GL accounts, cost centers,etc.), or lack of authorization for sale posting. Also, configuration settings that don’t align with sale data for illustration, duty canons, payment terms, or currency settings — can also help document creation.
62. What is the integration process with a CO consultant?
Ans:
- Collaboration with a Controlling( CO) adviser in SAP surroundings generally involves aligning the operation account aspects of SAP FI( Financial Accounting) with SAP CO for accurate cost shadowing and profitability analysis.
- This integration includes configuring cost centers, internal orders, profit centers, and matching FI bulletins to CO rudiments to insure data thickness and detailed fiscal control.
- The setup of activity types, overhead cost management, and product costing runs is frequently conducted to ensure that financial data flows accurately between the FI and CO modules for comprehensive reporting and analysis.
63. Why should the counting document number not match the billing document number?
Ans:
When a customer requires that counting document figures differ from billing document figures, it involves configuring SAP to handle document numbering independently for each process. In SAP, this can be managed by setting up different number ranges for accounting and billing documents within their separate modules (FI and SD). This allows for greater flexibility in document management and ensures that each document type is tracked accurately.
64. What activities does the system perform when an invoice is generated?
Ans:
- When producing an invoice in SAP, the system performs several crucial checks. It first verifies the details against the sales order and delivery data to ensure that all information is accurate and complete.
- It calculates pricing, levies, and any applicable abatements grounded on predefined pricing conditions.
- The system also generates an account document that captures the fiscal deals, streamlining accounts delinquent and profit accounts.
- Also , it updates force situations if the goods are packed . Eventually, the tab document is prepared for distribution to the client, either through print or electronic means.
65. What is the procedure to cancel the tab in SAP RAR?
Ans:
In SAP, the sale law to cancel an tab depends on the specific SAP module in use. For illustration, in SAP ERP, a billing document can be canceled using the transaction code VF11, which is used for canceling billing documents in Sales and Distribution. This action will reverse any account documents and restore any force movements associated with the original tab, ensuring that all fiscal and force records are accurate and reflect the cancellation.66. What fields can be changed after and before the account document is generated?
Ans:
- Before an account document is generated, change a wide range of fields in the tab document, similar as client details, pricing conditions, payment terms, and amounts.
- Once the account document is generated, changes are significantly confined to maintain fiscal integrity.
- Fields like the payment terms or due dates can occasionally be acclimated, but changes to quantities or particulars generally bear reversing the original document and creating a new bone , to insure that all fiscal records are kept harmonious and accurate.
67. How systems understand whether to pick KOFI or KOFK?
Ans:
- In SAP, the decision between using KOFI( cost object for cost centers) and KOFK( cost object for internal orders) is determined grounded on the configuration settings in the Controlling( CO) module.
- These settings mandate how cost flows should be captured depending on the nature of the expenditure.
- KOFI is generally named for charges that should be allocated to a specific cost center, whereas KOFK is used for charges that relate to a specific design or task managed as an internal order.
68. What options exist to block the automatic advertisement of tab values into the account?
Ans:
In SAP, it is possible to block the automatic posting of tab values into accounts. This is generally managed through the configuration of the posting block settings in the accounts receivable module. By setting a posting block, the tab can be reviewed for accuracy and completeness before impacting financial accounts. This is particularly useful in complex transactions or where additional approvals are needed before financial recognition.
69. What is the integration process with the FI consultant in revenue account determination?
Ans:
Integration with an FI adviser during profit account determination involves cooperative sweats to insure that the profit account processes align with both the company’s fiscal programs and nonsupervisory conditions. The FI adviser and generally review the map of accounts, determine the correct profit accounts for various types of deals, and configure the SAP system to automatically post earnings to these accounts grounded on the deals data.
70. What is the accounting entry produced when generating a credit memo?
Ans:
- When a credit memo is created, the typical account entry involves debiting the profit account and crediting the accounts delinquent or client account.
- This entry effectively reduces the profit that was preliminarily honored because a credit memo is generally issued in response to a client return, dissatisfaction, or as a deals reduction.
- This reversal acknowledges that the original trade was either incompletely or wholly unwarranted, therefore correcting the fiscal records to reflect the true nature of the sale and maintaining delicacy in the company’s earnings reports.
71. What is the accounting entry produced when generating a debit memo?
Ans:
The creation of a disbenefit memo results in an counting entry that debits the accounts delinquent or client account and credits the profit account. This entry is made when fresh charges need to be billed to the client, conceivably due to price adaptations, fresh services rendered, or correction of under- billed particulars. By issuing a disbenefit memo, the company increases its profit and receivables, indicating an improvement or correction to the original sale value, reflecting a more accurate profit collection process for services or goods handed.
72. What is the accounting entry produced when generating a return invoice?
Ans:
The counting entry for a return tab generally involves debiting the deals returns and allowances regard and crediting the accounts delinquent account. This entry is made when goods preliminarily vended are returned by the client, indicating a reversal of the trade. This action reduces both the profit earned and the receivables, directly reflecting that the original sale has been negated.
73. What combination does the system use to determine profit G/L accounts in standard operations?
Ans:
In a standard account system, profit G/ L( General Ledger) accounts are determined by a combination of factors similar as the map of accounts, standard rules set within the ERP system, and specific configurations grounded on the business’s reporting conditions. generally, the type of product or service, business division, and geographical position play pivotal places in determining the applicable profit accounts.
74. What is the accounting entry produced when generating a proforma invoice?
Ans:
- When creating a proforma tab, no account entry is generally recorded in the fiscal checks.
- A proforma tab is considered an instructional document, rather than a true tab, used primarily for customs purposes in transnational trade or to give a buyer apre-sale quotation.
- It outlines the volume and quality of goods or services offered, but since it doesn’t represent a perfected trade, it doesn’t impact the fiscal statements directly until it’s followed by an factual tab, which also triggers the fiscal recognition of the sale.
75. Why RAR is veritably necessary for SAP BRIM?
Ans:
- RAR( profit Account and Reporting) is pivotal for SAP BRIM( Billing and profit Innovation Management) because it enhances the capability to manage and fete profit directly as per transnational fiscal reporting norms, similar as IFRS 15. SAP BRIM deals with complex billing scripts and subscription- grounded business models, where profit recognition rules can be complex.
- RAR provides a frame to totally fete profit by aligning the profit recognition with the delivery of goods and services, ensuring compliance, reducing fiscal threat, and perfecting translucency.
76. How are the functions to be taken over?
Ans:
In SAP RAR, the preemption of functions involves migrating and integrating being profit recognition processes into the SAP RAR terrain. This generally starts with a thorough assessment of current profit operation practices to align them with the capabilities of SAP RAR, ensuring adherence to new account norms like ASC 606 and IFRS 15. The functions are transferred through a combination of system configuration, customization, and occasionally development of fresh functionalities to fill any gaps.
77. What are the crucial considerations when configuring SAP RAR for a new perpetration?
Ans:
When configuring SAP RAR for a new perpetration, crucial considerations include understanding the specific profit recognition requirements of the business, aligning them with the capabilities of SAP RAR, and ensuring compliance with fiscal norms like ASC 606 and IFRS 15. It’s pivotal to collude out the business’s profit aqueducts and contract types to knitter the configuration directly.
78. How does SAP RAR help in the fiscal reporting and analysis of profit data?
Ans:
- SAP RAR significantly enhances fiscal reporting and analysis by furnishing detailed perceptivity into profit processes and criteria .
- It generates comprehensive reports that can break down profit by various confines similar as product lines, geographical regions, and contract types.
- These reports aid in understanding the sources of profit and relating trends and anomalies. also, SAP RAR integrates with SAP’s business intelligence tools, enabling deeper logical capabilities, prophetic analytics, and script planning.
79. Explain the binary reporting point in SAP RAR and its benefits.
Ans:
Binary reporting in SAP RAR allows companies to manage and report their fiscal results under multiple account norms contemporaneously. For case, a company can report its profit according to both IFRS and US GAAP. This is particularly salutary for transnational pots or companies listed in different countries. The binary reporting point ensures that all profit deals are reused and recorded in compliance with both norms coincidently, reducing the need for separate systems or homemade conciliation processes.
80. What strategies should companies borrow when enforcing SAP RAR to insure a smooth transition?
Ans:
- Enforcing SAP RAR effectively requires a strategic approach involving scrupulous planning, stakeholder engagement, and comprehensive testing.
- Companies should start by completely mapping their being profit recognition processes and relating specific compliance requirements.
- Engaging crucial stakeholders from finance, deals, and IT departments beforehand in the design helps insure that the system meets all business conditions. Comprehensive training programs are pivotal to insure users are comfortable with the new system.
81. What are operations of SAP RAR?
Ans:
SAP Revenue Accounting and Reporting (RAR) is designed to help businesses manage and recognize profit in compliance with international financial reporting standards such as IFRS 15 and ASC 606. Its operations include automating profit recognition processes, which were previously manual and error-prone, providing a clear audit trail for profit transactions. The system also enables real-time monitoring of revenue recognition, allowing organizations to make informed decisions.
82. What are the disadvantages of implementing SAP RAR for profit management?
Ans:
While SAP RAR brings numerous advantages to profit operation, there are several disadvantages. Its perpetration can be complex and expensive, taking significant time and coffers, which might not be doable for lower enterprises. The complexity of SAP RAR also necessitates substantial training for users, which can be a hedge in terms of both time and expenditure.
83. Describe the process of handling incremental borrowing rates in SAP RAR.
Ans:
- The incremental borrowing rate( IBR) is a critical factor in parcel account and can affect profit recognition, especially under the new parcel norms like IFRS 16.
- In SAP RAR, handling the IBR involves calculating the present value of parcel payments using the IBR as the reduction rate.
- This rate represents what the boarder would have to pay if borrowing over a analogous term, and under analogous conditions, to gain the finances necessary to buy the leased asset.
- SAP RAR integrates this computation to acclimate the parcel arrears and right- of- use means, ensuring that the fiscal statements reflect the true cost and benefit of the leasing arrangements under the current fiscal conditions.
84. How does SAP RAR manage profit participating agreements with mates or third parties?
Ans:
SAP RAR is able of managing complex profit participating agreements, which are common in diligence like media, entertainment, and telecommunications. The system allows for defining terms of profit sharing within profit contracts, ensuring that earnings collected from guests are duly allocated between mates according to agreed- upon terms. This allocation is generally grounded on predefined probabilities or quantities.
85. How can SAP RAR be configured to conflict with sector-specific regulations?
Ans:
- SAP RAR can be configured to meet the specific nonsupervisory conditions of various sectors by using its flexible rule- grounded frame to handle different profit recognition scripts.
- In the telecommunications sector, for illustration, SAP RAR can manage multiple rudiments similar as bias, services, and guaranties, each with different recognition criteria.
- For the healthcare sector, it can manage complex arrangements like whisked payments and outgrowth- grounded payments, which bear profit to be honored grounded on achieving certain medical efficacity.
86. Explain the significance of users training and support in the deployment of SAP RAR?
Ans:
- Users training and support are pivotal for the successful deployment of SAP RAR, as the system’s complexity and the critical nature of fiscal reporting demand complete users.
- Effective training programs help insure that users understand the functionality of SAP RAR and are able of exercising its features to the fullest.
- This includes understanding the setup of contracts, performance scores, and profit recognition rules, as well as the ongoing operation of these rudiments.
87. What emerging trends in profit recognition could impact SAP RAR operations?
Ans:
The future of profit recognition in SAP RAR is likely to be shaped by adding robotization, the integration of artificial intelligence( AI), and continued nonsupervisory changes. robotization will enhance effectiveness, reduce crimes, and streamline processes. AI could further revise SAP RAR by furnishing prophetic analytics for more accurate profit soothsaying, and by automating complex decision- making processes associated with profit recognition.
88. Explain the significance of the Contract means and Contract arrears in SAP RAR.
Ans:
In SAP RAR, Contract means and Contract arrears are critical factors for accurate fiscal reporting. Contract means represent the reality’s right to consideration for goods or services formerly transferred to a client when that right is tentative on commodity other than the passage of time. Again, Contract arrears relate to scores to transfer goods or services to a client for which the company has entered consideration( or an quantum of consideration is due) from the client.
89. What role does automation play in improving SAP RAR operations?
Ans:
- Robotization plays a critical part in enhancing the effectiveness and delicacy of SAP RAR operations. By automating routine tasks, similar as data entry, contract updates, and profit computations, companies can reduce homemade crimes and free up coffers for further strategic conditioning.
- Robotization also facilitates briskly recycling times, which is pivotal for timely fiscal reporting and decision- timber. Also , enforcing advanced analytics and machine literacy within SAP RAR can prognosticate trends and give perceptivity into profit patterns, helping companies make informed business opinions.
90. What script illustrates acclimating to the original setup of SAP RAR post-implementation?
Ans:
Conforming the original setup of SAP RAR post-implementation is frequently necessary as businesses evolve and their requirements change. For example, after the original deployment at a customer site, it was observed that profit allocation wasn’t reflecting the true profitability of the deals due to inadequately defined standalone selling prices. To address this, a thorough review of all performance scores was conducted, and the allocation rules were streamlined to more accurately reflect the fair value of each distinct good or service.






