
System, Applications, and Products in Data Processing, or SAP, is a well-known enterprise software provider best recognized for its array of business solutions. SAP helps with tasks like finance, HR, supply chain management, and customer relationship management. It offers a broad range of modules designed for different sectors. SAP helps businesses increase productivity, streamline operations, and stimulate strategic decision-making with its powerful capabilities in data management, analytics, and process automation.
1. What’s SAP, and why is it used in associations?
Ans:
SAP, or Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing, is an enterprise resource planning( ERP) software used by associations to manage business operations and client relations. It integrates all angles of an enterprise into one comprehensive information system that can be penetrated by individualities across an association, easing data processing and information inflow across departments. This integration helps associations streamline processes, reduce redundancy, and achieve effectiveness and cost- savings.
2. What is the organizational structure in SAP MM, and how does it work?
Ans:
In SAP MM( Accoutrements operation), the organizational structure includes several situations: customer, company law, factory, storehouse position, and purchase association. The customer represents the top-position unit with multiple company canons, which are independent legal realities. Shops are functional units within a company law where accouterments are produced or services handed. Storage locales are set up within shops to manage stocks of accouterments.
3. How does SAP benefit from real-time data processing?
Ans:
- SAP’s capability to reuse data in real- time significantly enhances decision- timber and functional effectiveness.
- With real- time data, companies can cover their operations continuously and respond instantly to request changes or internal demands.
- This capability is pivotal for functions like force operation, where real- time analytics can help in maintaining optimal stock situations, therefore reducing carrying costs and avoiding stockouts.
4. What is the relationship between a work center’ and’ routing’ in SAP?
Ans:
In SAP, a work center is a physical or logical position where product operations are performed(e.g., assembly workstation, oil area). It contains specific data related to scheduling, capacity, and going necessary for product planning. Routing, on the other hand, defines the sequence of operations to be performed at different work centers to manufacture a specific product. It acts as a template for product processes and is essential for planning, executing, and monitoring product operations effectively.
5. What’s IDoc and its use in SAP systems?
Ans:
- IDoc, or Intermediate Document, is a standard SAP format for transferring data between SAP systems or between an SAP system and an external reality.
- It serves as a vehicle for data transfer in business processes involving, for illustration, transferring purchase orders to suppliers or integrating with external CRM systems.
- Using IDocs, associations can ensure that data transmissions are dependable, secure, and traceable, which is particularly important in scripts that comply with data integrity and auditability norms.
6. What steps can be taken to handle error operations in SAP?
Ans:
Error operation in SAP is generally handled through a combination of SAP’s standard error reporting tools and custom routines. They are monitoring sale canons like SM37 for job monitoring and ST22 for dump analysis to help in relating and diagnosing issues. For visionary error running, SAP provides fabrics like ALERT or CCMS( Computing Center Management System) for system cautions and performance issues.
7. What is SAP Fiori and its significance in the SAP ecosystem?
Ans:
SAP Fiori is a user experience( UX) design approach intended to give a responsive, harmonious, and holistic experience across various biases and operations. It’s grounded on ultramodern design principles and simplifies the user interface to facilitate usability and productivity. Fiori is significant in the SAP ecosystem because it transforms complex transactional systems into simple, part-grounded interfaces that enhance user satisfaction and effectiveness.
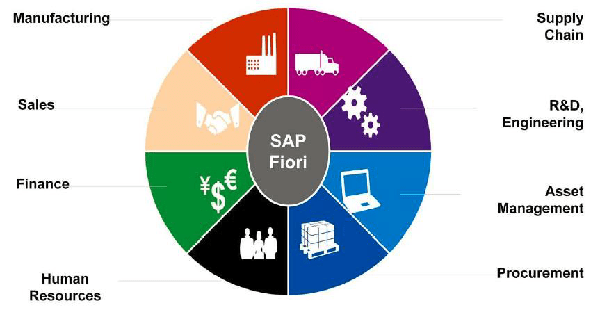
8. What is the difference between SAP ECC and SAP S/ 4HANA?
Ans:
| Aspect | SAP ECC | SAP S/4HANA |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Traditional client-server architecture | In-memory computing architecture |
| Database | Typically runs on traditional databases like Oracle, MS SQL Server, etc. | Runs primarily on SAP HANA database |
| User Interface | Classic SAP GUI | Fiori-based user interface |
| Data Processing Speed | Limited by disk-based processing | Accelerated by in-memory processing |
| Data Model | Complex, with numerous tables and redundant data | Simplified data model, eliminating redundancies |
9. What’s a BAPI, and how is it used in SAP integrations?
Ans:
BAPI) is a standardized programming interface that allows external operations to interact with the SAP modules. BAPIs are critical for integrating SAP with other operations because they give a stable and standardized system for penetrating business processes and data in SAP systems. This ensures data integrity and security while enabling flawless integration, which is essential for businesses that calculate on different software ecosystems to operate efficiently.
10. Explain the purpose and functionality of SAP BW( Business Warehouse).?
Ans:
- SAP BW( Business Warehouse) is an integral part of the SAP structure, designed to consolidate data from different sources, transfigure it, and store it in a way that’s optimized for analysis and reporting.
- It supports better decision- making through features like data modeling, ETL( excerpt, transfigure, cargo) tools, and a query developer to manage data storehouse and induce perceptivity.
- SAP BW is pivotal for associations that need robust data warehousing capabilities to handle complex analytics, reporting, and data mining across various sources.
11. What measures can be implement to ensure data security in SAP?
Ans:
- Ensuring data security in SAP involves multiple layers of protection ranging from network security measures to operation-position controls.
- This involves setting up proper access controls, using encryption for data in transit and at rest, and conducting regular audits to monitor access and changes to sensitive data.
- Integrating SAP with identity operations ensures consistent access rights across the enterprise, vital for data integrity and compliance with global data protection regulations.
12. What is the concept of LSMW, and what role does it play in the SAP environment?
Ans:
LSMW( Legacy System Migration Workbench) is a tool in SAP that facilitates data migration fromnon-SAP systems into SAP systems. It’s beneficial during the original setup phases of SAP executions, where large volumes of data need to be transferred directly and efficiently. LSMW provides a variety of ways for data migration, including direct input, batch input, and BAPIs, allowing it to handle complex data scripts and significantly reduce the time and trouble needed for data migration systems.
13. What is understood by SAP NetWeaver?
Ans:
SAP NetWeaver is an intertwined technology platform that serves as the specialized foundation for all SAP operations across business intelligence, web operations, and enterprise portal technology. It enables the integration of information and processes from distant sources using web services and other means. This platform is beneficial as it allows the use of IT investments with unborn SAP technologies, reducing the total cost of power and ensuring that businesses can acclimatize to new conditions without expansive reconfiguration.
14. How does the SAP Business Suite acclimatize to the changing requirements of businesses?
Ans:
SAP Business Suite is a group of operations that provides intertwined end-to-end functional results covering all core business functions, such as logistics, finance, client relationship operations, mortal coffers, and products. It’s adaptable mainly due to its modular structure, allowing businesses to apply the functionalities they need and integrate fresh modules as their conditions evolve.
15. What SLT stands for in SAP and its purpose.?
Ans:
SLT stands for SAP Landscape Transformation Replication Garçon, a detector-grounded data replication technology used primarily to facilitate real-time and listed data replication between SAP and non-SAP systems. Its primary purpose is to support SAP HANA executions by furnishing an original cargo of data and also continuing real-time data replication services.
16. What are some common challenges when enforcing SAP in an association?
Ans:
- One of the common challenges in SAP perpetration is managing the change in organizational processes and culture, as SAP generally requires homogenizing and streamlining of business processes that may differ from being practices.
- There can also be specialized challenges related to data migration, system integration, and custom development.
- Also, ensuring that all users are adequately trained and buy into the new system is critical for successful perpetration.
17. What strategies are used to manage SAP upgrade systems and minimize downtime?
Ans:
- Managing SAP upgrades with minimum timeout is critical to business operations.
- Methods similar to using a shadow system, where the upgrade is performed while the original system is still in operation, can be effective.
- Employing SAP’s Near-Zero Downtime( NZDT) fashion helps significantly reduce the system attainability period.
18. What’s the part of the SAP result director in the SAP software lifecycle?
Ans:
SAP result director is an intertwined platform that supports the entire lifecycle of SAP software, from planning and perpetration to operation and nonstop enhancement. It’s essential for managing complex system surroundings efficiently, ensuring that all aspects of SAP operation conservation, system monitoring, and issue resolution are effectively addressed.
19. What approaches are taken to handle performance issues in an SAP system?
Ans:
To address performance issues in SAP, first, identify the root cause by assaying system logs, work processes, and sale performance. Use sale canons like ST04 for database performance, ST22 for ABAP dumps, and ST12 for trace analysis. Optimizing SQL queries and conforming buffer sizes can also significantly lessen performance. Regular system conservation tasks, similar to database reorganization and archiving old data, are critical.
20. What’s the purpose of ALE and IDocs in SAP?
Ans:
ALE( operation Link Enabling) and IDocs( Intermediate Documents) together grease data exchange between different systems. ALE provides a frame for distributing business documents and master data out of the SAP system without duplication. IDocs serve as the vessel for data that needs to be transferred. They’re extensively used for asynchronously integrating SAP systems internally and with external mates, ensuring accurate and secure data transfer without the need for nonstop connections between these systems.
21. What does the process of a typical SAP implementation design involve?
Ans:
- A typical SAP perpetration design follows the ASAP( Accelerated SAP) methodology, which includes five main phases: Project Preparation, Business Blueprint, consummation, Final Preparation, and Go Live & Support.
- The Project Preparation phase involves defining objects and a compass. The Business design maps the company’s business processes to SAP functionalities.
- During consummation, the system is configured and customized. Final Preparation involves testing, user training, and system migration.
22. What are SAP Business Objects, and how are they used?
Ans:
SAP Business Objects is a suite of frontal-end operations that allow business users to view, sort, and dissect business intelligence data. The suite includes tools for reporting, querying, and assaying data, and it integrates seamlessly with both SAP and non-SAP data sources. It’s beneficial for creating complex reports and dashboards that help in decision-making processes.
23. What steps would be taken to secure a recently implemented SAP environment?
Ans:
- Securing a recently enforced SAP terrain involves multiple layers of security.
- At the operation position, configure strong authentication and authorization controls and regularly update and patch the system to cover against vulnerabilities.
- Encrypt sensitive data in transit and at rest. Apply logging and covering to describe and respond fleetly to implicit security pitfalls.
24. What is the significance of SAP HANA, and how does it impact businesses?
Ans:
SAP HANA is a revolutionary in-memory database and operation platform that allows businesses to reuse large volumes of data in real time. It transforms business processes by enabling brisk data processing, more flexible reporting, and better decision-making capabilities. SAP HANA’s advanced analytics capabilities, including prophetic analytics and machine literacy, offer businesses the tools to anticipate unborn trends and make visionary opinions.
25. What are SAP Smart Forms, and how do they differ from SAP Script?
Ans:
SAP Smart Forms allow the creation of forms for printing in SAP systems without the need for programming knowledge. They give a further intuitive visual interface compared to SAPscript, enabling more accessible adaptations and configurations. Brilliant Forms are preferred for their inflexibility in design, better integration with other operations, and capability to automatically convert forms into PDFs, shoot them via dispatch, or induce them in XML format.
26. What methods are used to manage version control in SAP ABAP development systems?
Ans:
- Managing interpretation control in SAP ABAP development systems involves using the SAP Transport Operation System( TMS) to handle development changes across different system geographies.
- ABAP inventors generally produce objects in a development terrain; these changes are also captured in transport requests that can be moved to testing and product surroundings.
- Using external version control systems like Git, especially with the SAP Cloud Platform, enhances collaboration, improves change tracking, and facilitates rollbacks in case of issues.
27. What’s SAP PI XI, and why is it essential for system integration?
Ans:
SAP PI( Process Integration) or XI( Exchange structure) is a middleware tool that allows flawless integration between SAP and external systems, ensuring adequate data inflow across different systems. It supports communication protocols and formats and allows the central monitoring of data exchanges. This is pivotal for businesses that calculate on a miscellaneous blend of operations, as it reduces the complexity and costs associated with system integration, ensures data thickness, and supports real-time data processing across the enterprise network.
28. What is the concept of Master Data Governance in SAP?
Ans:
Master Data Governance( MDG) in SAP is a state-of-the-art system for managing, validating, and distributing master data across enterprise systems. SAP MDG ensures that master data is harmonious and accurate across the entire business network, which is pivotal for functional excellence and dependable reporting. It offers workflows for data blessing processes, a central depository for master data, and features to apply data quality rules.
29. What role does SAP CRM play in enhancing customer relationships?
Ans:
- SAP CRM( client Relationship operation) is a comprehensive suite designed to support all aspects of commerce a company has with its client, whether it be deals, services, or marketing.
- SAP CRM helps businesses manage their client engagement effectively, furnishing tools for managing leads, deal openings, and client support issues.
- It facilitates better client data operation, integration with social media, and mobile functionalities, enabling companies to deliver substantiated results, enhance client satisfaction, and eventually drive deal growth.
30. What’s the significance of SAP S/ 4HANA for moment’s businesses?
Ans:
- SAP S/ 4HANA is an advanced ERP system explicitly designed to run on the SAP HANA database, which supports in-memory computing.
- It represents a significant shift from traditional ERP systems because of its capability to reuse and dissect large volumes of data in real time.
- This capability allows for informed decisions and faster responses. SAP S/4HANA’s simplified data model enhances performance and supports essential technologies like AI and IoT for digital transformation.
31. What is the difference between OLAP and OLTP in the context of SAP?
Ans:
- In SAP surroundings, OLAP( Online Analytical Processing) and OLTP( Online Transaction Processing) serve different business requirements.
- OLTP is used for managing day-to-day business operations and is characterized by a large number of short online deals similar to inserts, updates, and deletes.
- SAP HANA has revolutionized this model by combining OLAP and OLTP into a single in-memory database, allowing businesses to run analytics on live transactional data and furnishing real-time perceptivity.
32. What is the role of SAP ECC in enterprises?
Ans:
SAP ECC( Enterprise Core Component) is the core of the traditional SAP Business Suite. It’s an intertwined suite offering comprehensive functionalities for all processes within an enterprise, including logistics, product planning, marketing, deals, and finance. SAP ECC allows for customization and scaling, making it suitable for both large and small enterprises.
33. What methods are used to ensure data quality in SAP systems?
Ans:
Ensuring data quality in SAP systems involves enforcing robust data operation practices, including data confirmation, regular checkups, and sanctification routines. Tools like SAP Data Services can automate the process of data confirmation and sanctification, ensuring data delicacy and absoluteness. Establishing strict governance with apparent data power and responsibility is pivotal.
34. What are the benefits of using SAP BW/ 4HANA?
Ans:
- SAP BW/ 4HANA is an advanced data storehouse result that leverages the power of the HANA in-memory database.
- It simplifies data structures, data flows, and storehouse operation, furnishing real-time data processing and easier modeling of data.
- This platform supports a wide range of logical machines for real-time analytics, prophetic analytics, and machine literacy, enabling businesses to gain deeper perceptivity into their data.
35. What are SAP Modules, and which are the most important?
Ans:
SAP modules are specialized functional units in SAP ERP that are designed to handle specific business processes. Modules similar to SAP Financial Accounting( FI), Controlling( CO), Deals and Distribution( SD), Material Management( MM), and Human Capital Management( HCM) are considered core to SAP functionality. Each module can work singly but integrates seamlessly with others to ensure a comprehensive enterprise resource planning result.
36. What are the different types of work processes in SAP?
Ans:
- In SAP, several types of work processes handle different tasks within the SAP system terrain.
- Dialog or Online( DIA) processes handle users’ requests for task prosecution in real time, while Background( BTC) processes manage tasks that are listed to run at specific times without user commerce.
- Update( UPD) processes are devoted to performing database variations to ensure data integrity.
37. What are SAP Transport Requests?
Ans:
Transport Requests (TR) in SAP manage the movement of configurations and development objects between environments, typically from development to testing and production. They are crucial for change management, allowing for tracking, validation, and rollback of changes. TRs can include simple configurations or complex developments, categorized into Workbench requests for cross-client objects and Customizing requests for specific settings.
38. What are the benefits and challenges of implementing SAP S/4HANA compared to SAP ECC?
Ans:
SAP S/4HANA is a next-generation ERP suite built on the SAP HANA database, offering benefits like improved performance, a simplified data model, enhanced user experience with SAP Fiori, and advanced analytics. However, transitioning from SAP ECC to S/4HANA can be challenging due to structural changes, data migration issues, and the need for user training on the new interface. Organizations must carefully plan and execute the transition to maximize the advantages while minimizing disruptions.
39. How does SAP support IoT, and what functionalities does it give?
Ans:
- SAP’s approach to IoT( Internet of Effects) is integrated through SAP Leonardo, a digital invention system that incorporates IoT services along with machine literacy, Big Data, and analytics.
- SAP IoT provides tools to connect and manage IoT biases, collect data from them, and integrate this data into SAP systems for real-time perceptivity and decision-timber.
- It supports scripts across various diligence, including manufacturing, logistics, and retail, enhancing operations through automated monitoring, conservation schedules, and in- depth analytics.
40. What part does SAP play in data analytics?
Ans:
- SAP provides robust data analytics capabilities through tools similar to SAP BW/ 4HANA, SAP Analytics Cloud, and bedded analytics within SAP S/ 4HANA.
- SAP Analytics pall offers accurate-time analytics, planning, and prophetic capabilities on a single pall-grounded platform, easing access to perceptivity and promoting a data-driven culture within the association.
- SAP’s analytics tools integrate seamlessly with both SAP and non-SAP data sources, offering comprehensive visualization, reporting, and analytics capabilities that help businesses stay competitive in a data-centric world.
41. What is the significance of the SAP Solution Manager, and what functionalities does it offer?
Ans:
SAP result director is an intertwined end-to-end platform intended to support the lifecycle of SAP results, from the planning and making phase through deployment and operations. It facilitates both perpetration systems and ongoing support, offering tools for monitoring, managing, and optimizing SAP systems and operations. The resulting director is critical for effective operation Lifecycle Management( ALM), helping to ensure compliance and business durability.
42. Discuss the SAP authorization conception and its significance in security.?
Ans:
- The SAP authorization conception is a framework designed to ensure that users have applicable access rights grounded in their positions and liabilities within an association.
- It prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data and functions, guiding the integrity and confidentiality of data.
- In SAP, authorizations are structured around places that contain specified deals and conditions users are allowed to perform.
43. What is SAP Extended Warehouse Management( EWM), and how does it improve logistics?
Ans:
SAP Extended Warehouse Management( EWM) is an advanced interpretation of the traditional SAP Warehouse Management( WM) result, offering further robust and comprehensive features to manage crucial conditioning in a storehouse. EWM provides detailed visibility into force operation, storehouse conditions, and goods movement, optimizing the entire warehousing process. It facilitates complex warehousing setups, similar to managing multiple distribution centers and controlled storehouse areas.
44. What is the Difference between Partial Payment and Residual Payment?
Ans:
In SAP, a partial payment is a payment that’s lower than the total quantum owed for a tab, leaving a balance that remains as open. The original tab remains in the books, and the partial payment is recorded against it. A residual payment, on the other hand, clears the original tab and creates a new tab for the remaining balance. This allows the original tab to be closed out, and the residual quantum is treated as a new obligation, simplifying the operation of outstanding balances and perfecting clarity in fiscal reporting.
45. What exactly is NetWeaver?
Ans:
- SAP NetWeaver is a platform from SAP that integrates technology components, supports other SAP applications, and facilitates the integration of business processes and data across various systems.
- NetWeaver is both a development and runtime terrain that supports operations erected on various platforms with robust capabilities for customization and integration.
- It includes a comprehensive toolset for web services and supports the creation of doors, integration via exchange structure, business intelligence, and more.
46. What exactly are Metadata, master data, and sale data?
Ans:
Metadata, master data, and sale data are crucial types of data in any information system. Metadata is data about data, describing the structure or schema of data rudiments; it helps systems and users understand how data is organized and how to use it effectively. Master data refers to core realities of a business like guests, products, workers, accoutrements, and merchandisers that are harmonious and generally do not change constantly.
47. What do you mean by “datasets”?
Ans:
- In programming and data analysis, datasets are collections of data organized in tables, with rows representing unique cases and columns representing specific variables.
- Datasets can be sourced from various data stores or generated through data recycling operations and are used for analysis, machine literacy models, reporting, and decision-making processes.
- They’re abecedarian to data-driven perceptivity and are manipulated through software and tools designed for data analysis, statistical modeling, and machine literacy operations.
48. What are some of the downsides of SAP?
Ans:
While SAP is a critical enterprise resource planning tool, it does come with downsides. The complexity and compass of SAP’s results can lead to lengthy and expensive perpetration systems that occasionally exceed budget and time estimations. Its customization features, while expansive, can also result in increased complexity and advanced conservation costs. Also, SAP products generally bear significant training due to their sophisticated and occasionallynon-intuitive interfaces.
49. What is the distinction between OLAP and data mining?
Ans:
OLAP( Online Analytical Processing) and data mining serve different purposes in data analysis. OLAP is the order of software tools that offers an analysis of data stored in a database. OLAP allows users to perform multidimensional analysis of data from multiple perspectives, enabling quick, harmonious, interactive access to a wide variety of possible views of information converted from raw data to reflect real-time perceptivity.
50. What are the three ways involved in data mining?
Ans:
- Data mining involves three primary ways: data medication, data analysis, and affect interpretation.
- The data medication phase includes data cleaning, data integration, and data selection, where applicable data is chosen and sanctified for analysis.
- The data analysis phase involves applying various modeling and algorithmic ways to discover patterns or connections within the data.
51. What are the different categories of the R/3 system?
Ans:
The SAP R/ 3 system follows a three-league armature that includes the donation league, operation league, and database league. The donation league is where the user interface resides; it interacts directly with end-users through the SAP GUI or other interface operations. The operation league hosts the SAP operation garçon and all business-specific sense; it processes users’ requests, performs functional functions, and manages deals.
52. What is AWB?
Ans:
- AWB stands for Administrator Workbench in SAP. It’s a pivotal tool for managing, covering, and configuring processes related to data staging and data warehousing in SAP Business Information Warehouse( BW).
- AWB includes functionalities for data modeling, scheduling data loads, and covering the data cargo processes.
- It serves as the central hub for managing metadata and executing tasks related to data warehousing, such as data sourcing and ensuring quality in SAP BW systems.
53. What is BEx?
Ans:
BEx (Business Explorer) is a set of tools for reporting, query design, and analysis within the SAP Business Information Warehouse (BW). BEx tools allow users to access, format, and analyze data to aid decision-making. Key components include BEx Query Designer, BEx Analyzer for Excel, BEx Web Analyzer for web-based analysis, and BEx Report Designer for report formatting and distribution. Together, these tools enhance user experience and streamline the analytics process.
54. What is the significance of ODS in BIW?
Ans:
- ODS( functional Data Store) in Business Information Warehouse( BIW) is significant for its part in detailed data storehouse and reporting.
- ODS objects allow for the storing of grainy data at the sale position, furnishing a clean and consolidated dataset for detailed reporting and analysis.
- Unlike InfoCubes, which are optimized for multi-dimensional analysis, ODS objects are designed to support flat structures that are more suited for line-item reports and time-dependent data storehouses.
55. What is the distinction between a sphere and a data element?
Ans:
In SAP, a sphere defines the specialized characteristics of a table field similar to datatype, length, and possible value range. It’s a global description, which means multiple fields across different tables can be used to ensure thickness. A data element, on the other hand, links the sphere to a particular business environment by adding a field description. Data rudiments are used to describe the contents of a field in business terms and can be reused in multiple tables.
56. What are the distinctions between Set and Get parameters?
Ans:
Set and Get parameters in SAP are used to pass data between deals.’ Set parameter’ is used to define a parameter value that can be penetrated using’ Get parameter’ in another sale. The value set using the’ Set parameter’ is stored in the memory until the session ends, allowing for the sharing of values across different programs and deals without database updates. Again, the’ Get parameter’ retrieves this value to use in a sale.
57. What are ALE, IDoc, EDI, and RFC?
Ans:
- ALE( operation Link Enabling), IDOC( Intermediate Document), EDI( Electronic Data Interchange), and RFC( Remote Function Call) are technologies used in SAP for integrating and transferring data.
- ALE is a frame for configuring and managing distributed operations using IDOCs as the data format.
- IDOCs are standard data structures for an electronic data cloverleaf between the systems.
58. Explain what LUW( Logical Unit of Work) is.?
Ans:
- A Logical Unit of Work( LUW) is a concept in SAP that refers to a sequence of database operations that are executed together as a single work unit.
- This ensures that either all operations within this unit are completed successfully or none of them are, maintaining data integrity and thickness.
- In SAP, an LUW is used to group multiple operations so that if one operation fails, the entire group can be rolled back to maintain the database’s stable state.
59. What is the description of one-time vendors?
Ans:
One-time merchandisers in SAP are used for processing deals with merchandisers with whom business is conducted rarely or for a single occasion. Instead of creating an endless seller master record for each sale, a general master record is used for all one-time merchandisers, which simplifies the operation of seller data and reduces the master data volume. Specific sale details like address and payment information are entered at the time of sale processing.
60. What are the typical phases of the SAP payment run?
Ans:
The SAP payment run process, used to settle seller and other payments, generally consists of several phases: selection, offer, and payment. During the selection phase, open checks that match the given criteria are named. In the offer phase, the system lists all checks due for payment; users can review and acclimate this list as necessary before the final blessing. Eventually, in the payment phase, the system processes payments to merchandisers grounded on the approved list, generating payment documents and streamlining the fiscal accounts consequently.
61. What does the SAP law pushdown number?
Ans:
- SAP law pushdown is a conception in the HANA armature where data- ferocious sense is moved from the operation subcaste directly into the database.
- This approach leverages the high-performance capabilities of the SAP HANA database, allowing complex computations, aggregations, and data metamorphoses to be executed directly at the database position.
- By doing so, it significantly reduces data transfer volumes, improves operation performance, and minimizes processing times.
62. What is the SAP gateway?
Ans:
- The SAP Portal( SAP Enterprise Portal) offers a single point of access to SAP and non-SAP information, operations, and services across organizational places and web cybersurfers.
- It consolidates essential information and operations to give part-grounded users operation, which enhances productivity and inflexibility.
- Users can pierce a substantiated, secure interface that integrates both structured and unshaped content into a coherent work terrain.
63. What is the SAP Launchpad?
Ans:
SAP Helipad is a web-grounded or mobile entry point that delivers configured operations and perceptivity to users across a company on any device. It’s frequently seen as the frontal door to SAP Fiori apps, designed to give a part-grounded, intuitive, and substantiated user experience. The helipad displays apps as penstocks, which update in real time and can display live status pointers, similar to the number of open tasks or critical emails.
64. What exactly is a posting key?
Ans:
- A posting key in SAP is a two-number numerical law that controls the entry of document line particulars in a sale and determines the account type, the type of advertisement, and the layout of entry defenses.
- It specifies whether the line item is a disbenefit or credit, as well as the possible field status in the entry sale.
- This key ensures data integrity in fiscal records by guiding transaction recording and distinguishing between payments, checks, and adjustments.
65. What exactly is an Information model?
Ans:
In SAP HANA, an information model is a structured representation of databases that enables efficient data management and analysis. These models support real-time reporting and analytics, allowing users to create graphical views (attribute views), combine views with logical computations (logical views), or perform complex calculations (calculation views), transforming raw data into actionable insights.
66. What’s the description of a transactional RFC?
Ans:
Transactional RFC( tRFC, or Transactional Remote Function Call) in SAP is a variant of the standard RFC and is used to ensure guaranteed dispatch delivery between SAP systems. Unlike standard RFC, which executes a function module just formerly, tRFC ensures that the function module is executed exactly formerly in the target system, indeed, if the call is repeated due to a communication error.
67. What benefits can SQL script give?
Ans:
- SQL Script extends SQL to enhance querying and allows developers to perform data-intensive operations, like complex computations, directly in the SAP HANA database.
- It enables executing operations in the database subcaste, which minimizes data movement and maximizes the performance of operations by using the high-speed processing capabilities of SAP HANA.
- SQL script supports features like circles, tentative statements, and original variables, making it largely effective for enforcing sophisticated data models and business sense within the database.
68. How numerous SAP Sessions Can Run contemporaneously?
Ans:
In SAP, a user can open up to 6 sessions contemporaneously under the same login. These sessions allow the users to perform multiple tasks or deals at the same time without requiring them to log out and log back in, which enhances productivity and multitasking capabilities. This limit is generally sufficient for most users, but it’s essential to manage these sessions wisely to maintain system performance and avoid gratuitous resource consumption.
69. Where are T- law Name and Program Values Stored?
Ans:
In SAP, sale canons( T- T-Canons) and their associated program names are stored in the SAP table TSTC. Each sale law is counterplotted to a specific program that’s executed when the sale law is entered. Also, descriptive details about these sale canons can be set up in table TSTCT, which includes the sale law descriptions. These tables are pivotal for directors and inventors to navigate and understand the link between sale canons and the programs they spark.
70. What is the difference between a domain and a data element?
Ans:
- A sphere in SAP defines the specialized characteristics of a field, similar to its data type, length, and possible value range.
- It basically outlines the template from which multiple data rudiments can be created.
- A data element, on the other hand, builds on a sphere to include semantic information like field markers or attestation that are specific to business surroundings.
71. What’s the Baseline Date in SAP AR and AP?
Ans:
- The birth date in SAP Accounts Receivable( AR) and Accounts Payable( AP) is the reference date used to calculate payment due dates and discounts for checks and bills.
- Depending on company programs, it can be the document date, advertisement date, or specified date.
- This data is critical for determining when payments should be made to take advantage of early payment discounts or to avoid late payment penalties, therefore helping in effective cash inflow operations.
72. Which Protocol is Used by the SAP Gateway Process?
Ans:
The SAP Gateway process primarily uses the OData( Open Data Protocol) service, which is an open protocol for creating and consuming queryable and interoperable REST APIs in a simple and standard way. OData helps SAP Gateway enable connectivity between SAP operations and external systems or customer surroundings, easing data exchange and integration through a web-based interface. This ensures that SAP systems can be accessible and functional across different platforms and operations.
73. What programming language does SAP use?
Ans:
SAP primarily uses ABAP( Advanced Business Application Programming), a personal programming language. ABAP is explicitly designed for SAP operations to develop reports, module pool programming, or affiliate programming. Lately, SAP has also incorporated SAPUI5 for frontal-end development, which is grounded on HTML5 and JavaScript, to produce more responsive and user-friendly interfaces with Fiori. Java is also used, especially in SAP NetWeaver and SAP Pall Platform surroundings.
74. What are pooled tables in SAP?
Ans:
Pooled tables in SAP are logical tables that collude with physical tables in the database called pools. These tables are used to store control data and small datasets that don’t bear complex joins or frequent penetrating. Multiple pooled tables are stored together in a single database table, reducing the outflow of managing multitudinous small tables and optimizing the database storehouse. They’re handy for storing rarely penetrated data in a structured and compact manner.
75. What’s the Extended Star Schema?
Ans:
- The Extended Star Schema is a revision of the classic star schema used in SAP BW( Business Warehouse) data modeling.
- The extended star schema distinguishes itself by adding SID( Surrogate ID) tables that link the dimension tables to the fact table, enhancing performance and supporting language and interpretation operations.
- This schema allows more flexible and effective data reclamation and storehouse, particularly for complex queries over large data sets.
76. What are the differences between Salesforce and SAP?
Ans:
- Salesforce and SAP are both leading software companies but concentrate on different aspects of business operations.
- Salesforce is primarily known for its pall- grounded CRM( client Relationship operation) results, helping businesses manage and dissect client relations and data throughout the client lifecycle.
- SAP, on the other hand, offers a broader range of enterprise software results, including ERP( Enterprise Resource Planning), CRM, and data operation.
77. What’s SAP PI/ PO( Process Integration/ Process Orchestration)?
Ans:
SAP PI/ PO( Process Integration/ Process Orchestration) is a tool within the SAP ecosystem designed for integrating different operations across various tackle and software surroundings. SAP PI is the element that facilitates this integration by allowing different systems to communicate with each other using different protocols and norms. SAP PO, which builds on the capabilities of PI, includes fresh features for designing, modeling, and executing business processes that involve different operations.
78. What are the common transport crimes?
Ans:
Standard transport crimes in SAP involve issues related to the import and import processes of configuration settings or development work across SAP systems. Crimes can be due to inadequate authorizations, missing objects or dependencies, conflicts with objects, or incorrect transport routes. These issues can beget dislocations in the system geography and affect the stability of the surroundings. Effective operation of transport requests and thorough testing can alleviate these crimes.
79. What are. Sca lines?
Ans:
- SCA lines, or Software Component Libraries, are used in SAP systems to package and emplace software factors, particularly in SAP NetWeaver surroundings.
- These lines contain all necessary factors similar to Java classes, metadata, and coffers needed for deployment.
- They’re integral to the transport and operation of compound operations erected on the SAP platform, ensuring that all corridors of an operation are whisked and transported together efficiently.
80. Explain the terms InfoSet and MultiProvider
Ans:
- InfoSet and MultiProvider are generalities used in SAP BW for data reclamation and reporting purposes.
- An InfoSet is basically a join of two or more data sources ( like DataStore Objects, InfoObjects, or InfoProviders), enabling complex reports that gauge multiple tables or sources.
- A MultiProvider, on the other hand, is a virtual provider that doesn’t physically store data but combines data from different InfoProviders, similar to InfoCubes or DataStore Objects.
81. What’s the difference between the ALV Grid and the ALV List?
Ans:
ALV( ABAP List Viewer) Grid and ALV List are both used in SAP to display lists in a formatted manner, but they differ significantly in functionality and display. The ALV Grid control provides a rich set of features for displaying, sorting, and filtering data in a table format within a custom control area, suggesting Excel- suchlike functionality with the capability to bed plates and use different cell styles.
82. What is SAP R/3?
Ans:
SAP R/ 3 is a former interpretation of SAP’s enterprise resource planning( ERP) software that handed integrated results for managing business operations and client relations. It stands for Real-Time Data Processing, 3- 3-league armature the database subcaste, operation subcaste, and customer( donation) subcaste. SAP R/ 3 was erected on the ABAP programming language and could run on several databases like Oracle, SQL Garçon, and later on SAP’s own HANA.
83. What does Transaction mean in SAP language?
Ans:
- In SAP language, a sale refers to a sequence of logically connected operations that must all be completed successfully; otherwise, the entire operation is rolled back to the state before the sale begins.
- Deals in SAP are executed through sale canons, which are unique identifiers used to pierce specific tasks or programs.
- Each sales transaction links to an executable program that allows users to efficiently navigate SAP’s features without complex menu paths.
84. What are the three phases of data mining?
Ans:
- Data Preparation involves gutting and converting data into a suitable format for mining and removing anomalies and inconsistencies.
- Data Exploration, where various methods, similar to clustering and association analysis, are used to explore patterns and connections within the data.
- Pattern Evaluation and Knowledge donation, where linked patterns are estimated against business objects and presented in a format that decision-makers can use.
85. What’s the main difference between transparent tables and pool tables?
Ans:
- In SAP, transparent tables and pool tables are two types of database tables used to store data.
- Transparent tables correspond one-to-one with database tables for operational data needing frequent access, each having a single physical counterpart in the database.
- Pool tables, on the other hand, are logical tables that are grouped into a single physical table in the database to optimize space and performance for lower, less constantly penetrated tables.
86. What are the differences between SAP ABAP and SAP Basis?
Ans:
SAP ABAP( Advanced Business Application Programming) and SAP Base( Business Application Software Integrated Solution) are two abecedarian factors of the SAP ecosystem with distinct places. ABAP is a high-position programming language created by SAP for developing operations within the SAP terrain, including reports, interfaces, extensions, and forms. Inventors primarily use it to produce SAP operations.
87. What is an extractor?
Ans:
- An extractor in SAP primarily refers to an element that facilitates data birth from various source systems for use in SAP BW( Business Warehouse).
- Extractors can pull data from SAP ERP systems or other external sources, recapitulating the business sense demanded to recoup meaningful business data.
- These extractors define the data structure and the system for collecting data, which can be either total ( complete data set) or incremental( only changes since the last birth).
88. What are the two kinds of services that are used for handling communication?
Ans:
In SAP and networking, there are two main types of communication services: synchronous and asynchronous. Synchronous services, like Remote Function Calls (RFC), require the requesting program to wait for a response, ensuring real-time data processing. Asynchronous services, such as IDocs (Intermediate Documents), let the program continue without waiting for a response, improving efficiency but potentially causing temporary data sync issues.
89. What are pooled tables and cluster tables?
Ans:
Pooled and cluster tables are types of table structures used in SAP databases to manage space and facilitate the performance of the database efficiently. Pooled tables are used to store control data and small-sized, infrequently used data. They group multiple table entries into a single table pool in the database. Cluster tables, on the other hand, are used to store data that are logically connected and frequently penetrated together, allowing for several tables to be clustered in the database.
90. What are the main advantages of reporting with BW over R/ 3?
Ans:
Reporting with SAP BW( Business Warehouse) offers several advantages over traditional reporting directly from SAP R/ 3( now part of SAP ECC). Initially, BW allows for data connection from multiple sources, furnishing a holistic view of the information, which is pivotal for in-depth analysis. Unlike R/ 3, which frequently runs on functional data, BW is optimized for reporting and analytics, ensuring that complex queries don’t affect transactional processing.






