
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management) is a software solution developed by SAP SE to manage various aspects of human resources within an organization. It encompasses a range of modules that streamline HR processes, enhance workforce management, and optimize talent management strategies.
1. What’s SAP HCM?
Ans:
SAP Human Capital Management( SAP HCM) is an important module in SAP that provides tools and processes to manage an association’s pool effectively. This includes everything from Payroll to benefits, as well as hand engagement and performance operation. SAP HCM helps streamline and automate HR processes, ensures compliance with nonsupervisory requirements, and enhances hand engagement and productivity by furnishing integrated tools for managing all aspects of HR tasks.
2. How does the Organizational Management( OM) submodule help in SAP HCM?
Ans:
- The Organizational Management submodule in SAP HCM is pivotal for structuring an association in terms of its organizational units, positions, jobs, and reporting connections.
- This structure serves as the backbone for workflows and defines the scale and reporting channels, which are vital for process flows, reporting, and authorization operations.
- OM is integrated with other HCM submodules to use the organizational data for processing tasks like Payroll, career planning, and race planning.
3. What is the significance of Payroll in SAP HCM?
Ans:
Payroll in SAP HCM is a critical element that ensures accurate and timely payment to workers while complying with legal and nonsupervisory conditions. This module automates the computation of stipends, deductions, and levies, significantly reducing homemade work and implicit crimes. It also integrates with other modules like Time Management and Benefits, furnishing a comprehensive approach to hand fiscal compensation and record-keeping.
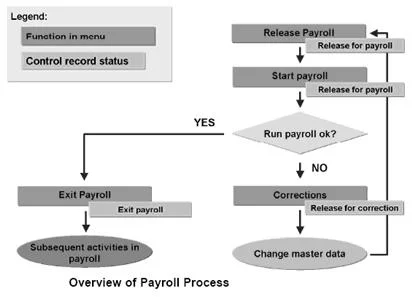
4. What’s Time Management in SAP HCM, and how does it serve?
Ans:
- Time Management in SAP HCM allows associations to track hand attendance and absences, manage time wastes, and apply hand scheduling.
- It’s essential for calculating outstanding hours, managing overtime, and ensuring compliance with working time regulations.
- This module supports different time recording practices and provides detailed analytics that help in optimizing pool operation and planning.
5. What is Personnel Administration (PA) in SAP HCM, and what functions does it serve?
Ans:
Personnel Administration (PA) in SAP HCM manages core HR tasks related to an organization’s employees. This includes managing personal data, employment history, organizational assignments, and other essential HR services. PA is crucial for maintaining comprehensive records throughout the employee lifecycle, from hiring to retirement. Additionally, it helps ensure compliance with labor regulations and company policies.
6. What is the functioning of the Performance Management system in SAP HCM?
Ans:
- Performance Management in SAP HCM facilitates the evaluation and operation of hand performance.
- This subsystem helps set performance pretensions, conducts reviews, and provides feedback mechanisms.
- It’s designed to align individual objects with organizational pretensions, promoting transparency and nonstop enhancement.
- Performance Management in SAP HCM is pivotal for gift development, race planning, and motivating workers, thereby driving overall organizational effectiveness.
7. What part does the Personnel Cost Planning submodule play in SAP HCM?
Ans:
Labour force Cost Planning in SAP HCM is a necessary submodule that aids in the effective budgeting and planning of labour force costs. This point enables associations to read future charges related to stipends, benefits, and other compensation-related costs. It integrates with other modules like Payroll and Benefits to pull literal data and prognosticate unborn costs grounded on various scripts and hypotheticals. This planning tool is vital for fiscal soothsaying and helps HR and finance departments make informed opinions regarding staffing, compensation strategies, and overall fiscal operation.
8. what is the different between Payroll and Employee Self-Service.
Ans:
| Aspect | Payroll | Employee Self-Service |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Processes employee salaries, wages, and benefits based on regulations and policies. | Allows employees to manage personal details, submit requests, and access pay information. |
| Focus | Primarily deals with payroll processing and compliance. | Centers on empowering employees to handle HR tasks independently. |
| Administrative Control | Managed by HR administrators for accurate payroll processing. | Enables employees to update personal information, reducing HR workload. |
| Data Entry | Involves inputting employee time, deductions, and benefits for payroll calculation. | Involves employees updating personal details and submitting requests directly. |
9. Discuss the Benefits submodule in SAP HCM.
Ans:
The Benefits submodule in SAP HCM offers functionalities to manage hand benefits, similar to insurance plans, withdrawal plans, and other company-handed benefits. It allows HR directors to define and administer different benefits packages acclimatized to different hand groups, automate registration and eligibility checks, and manage costs and benefactions from both employer and hand sides. This module is pivotal for ensuring that benefit programs are competitive, biddable with regulations, and aligned with organizational programs and hand requirements.
10. How does the literacy result submodule function within SAP HCM?
Ans:
- The Learning Solution submodule in SAP HCM is designed to manage all aspects of hand training and development.
- It supports the creation, booking, and shadowing of training enterprises, ranging from in-house shops to online courses.
- This module helps associations plan their training needs grounded on chops gaps and compliance conditions, offering tools for managing course registers, scheduling, enrollments, and educator assignments.
11. What is the role of Employee Self-Service (ESS) in SAP HCM?
Ans:
Hand tone- Service( ESS) in SAP HCM empowers workers by furnishing them direct access to view and manage their particular HR-related information. ESS allows workers to modernize their particular details, view pay remainders, submit time-off requests, and enrol in benefits. This functionality reduces executive burdens on HR departments and improves data delicacy and hand satisfaction by giving workers control over their information.
12. What’s the significance of Succession Planning in SAP HCM?
Ans:
- Succession Planning in SAP HCM is critical for ensuring long-term stability and leadership durability within an association.
- This module helps identify and develop internal gifts for critical places to ensure smooth transitions and minimize the impact of hand development on strategic positions.
- It integrates with Performance Management and Learning results to assess hand eventuality and knitter development programs that prepare high-implicit workers for unborn places.
13. What’s the significance of the Infotype conception in SAP HCM?
Ans:
Infotypes in SAP HCM are structures that store affiliated sets of hand data similar to particular data, payroll information, work schedules, and so on. They play a pivotal part by furnishing a structured way to handle all types of HR data, which ensures thickness and availability. Each Infotype is assigned a specific number and can be penetrated or modified through various deals. This conception not only facilitates effective data operation and reclamation but also supports compliance by ensuring that all applicable data is maintained directly and securely.
14. How does the Reporting point in SAP HCM help HR operations?
Ans:
- Reporting in SAP HCM is an important feature that enables associations to produce comprehensive reports on various aspects of mortal coffers, including pool analytics, Payroll, time operation, and benefits.
- These reports help HR directors and business leaders make informed opinions by providing insight into trends, performance criteria, and compliance issues.
- SAP HCM’s flexible reporting tools allow for custom reports to be erected according to specific requirements, easing strategic planning and functional advancements.
15. What is the integration of SAP HCM with other SAP modules?
Ans:
SAP HCM integrates seamlessly with other SAP modules to enhance functionality and give a comprehensive enterprise result. For illustration, integration with SAP Financials supports the processing of payroll results into fiscal accounts, ensuring accurate fiscal reporting and compliance with account norms. Also, its integration with SAP SuccessFactors extends capabilities in gift operation, combining traditional on-premise HCM functions with pall-grounded inventions for a holistic approach to HR operation.
16. What is the role of authorization checks in SAP HCM?
Ans:
- Authorization checks in SAP HCM are pivotal for securing sensitive hand data and ensuring that users have applicable access rights grounded on their places within the association.
- This point controls access to Infotypes, deals, and reports, precluding unauthorized data viewing or manipulation.
- Effective use of authorization checks is vital for maintaining data integrity, guarding sequestration, and complying with regulations similar to GDPR.
17. What’s the purpose of the point function in SAP HCM?
Ans:
The point function in SAP HCM is a decision tree that defines how specific labour force administration opinions are made, grounded on various criteria like country, hand group, or pay scale area. Features simplify the customization of SAP operations without demanding that the standard law be altered. They’re used to control dereliction values and switch functionalities, enhancing inflexibility and effectiveness in HR processes, similar to determining the payroll area or generating dynamic conduct during HR events.
18. What is the impact of configuration in SAP HCM?
Ans:
- Configuration in SAP HCM is essential for conforming the system to meet the specific requirements of an association.
- Through configuration, businesses can set up and modify payroll schemas, set rules for benefits administration, knit the organizational structure, manage time recording, and customize the user interfaces of various services like ESS and MSS.
- Effective configuration is crucial to optimizing HR operations, ensuring nonsupervisory compliance, and enhancing user behaviour, eventually leading to better HR operations and organizational success.
19. What is the approach of SAP HCM in managing global employment programs?
Ans:
SAP HCM is complete at handling global employment programs by allowing transnational companies to manage and integrate hand data across different countries within a single system. This global capability supports various original compliance conditions, currency transformations, multilingual requirements, and transnational payroll processes. It ensures that the association adheres to original labour laws and reporting conditions while maintaining a unified HR strategy and practices across all locales.
20. What are Dynamic conduct and how are they employed in SAP HCM?
Ans:
- Dynamic conduct in SAP HCM is a functionality that sparks fresh conduct automatically when certain conditions are met during data entry.
- For illustration, if a new hand is entered into the system, a dynamic action can automatically prompt the creation of user credentials in the system, registration in benefits plans, or assignment of a tutor.
- Dynamic conduct is largely customizable, allowing associations to define and apply workflows that match their specific functional conditions.
21. What is the significance of the Payroll Control Center in SAP HCM?
Ans:
The Payroll Control Center in SAP HCM revolutionizes how associations execute and cover their payroll processes. This tool enhances transparency, effectiveness, and compliance by polarizing payroll operations in a user-friendly interface that provides real-time monitoring and confirmation tools. It allows payroll professionals to reuse Payroll, identify issues before they become problems, and ensure that the Payroll is accurate and biddable with applicable laws and regulations.
22. What is the role of the pool process operation in SAP HCM?
Ans:
- Pool Process operation within SAP HCM encompasses a suite of tools and functionalities designed to optimize the day-to-day operation of HR tasks such as leave requests, shift planning, and benefits administration.
- This element enhances workflow robotization, increases HR process effectiveness, and improves data delicacy.
- It empowers HR brigades to concentrate more on strategic tasks rather than executive duties by streamlining operations and easing better hand tone-service capabilities, therefore perfecting overall hand satisfaction and functional effectiveness.
23. What is the integration process of talent management within SAP HCM?
Ans:
Talent Management in SAP HCM is deeply integrated with other modules to give a holistic view of hand performance, eventuality, and career development requirements. This integration allows for flawless operation of reclamation, onboarding, performance evaluations, learning and development, and race planning. By having these connected systems, associations can align their gift strategy with their business objects, identify and cultivate high-implicit workers, and ensure that gift operation processes are visionary and strategic rather than reactive.
24. What functionalities does SAPE-Recruiting give?
Ans:
- SAPE-Recruiting enhances traditional reclamation processes by automating job bulletins, aspirant shadowing, seeker selection, and hand onboarding.
- This module provides a comprehensive reclamation result that enables effective gift accession strategies by easing better seeker sourcing, engagement, and selection.
- With features like seeker relationship operation and analytics, associations can make gift pools, ameliorate hiring quality, and reduce time-to-hire.
25. What’s the difference between SAP HCM and SAP SuccessFactors?
Ans:
SAP HCM and SAP SuccessFactors differ primarily in deployment and focus. SAP HCM is traditionally an on-premise result that offers comprehensive HR functionalities, including Payroll, time operation, and particular administration, geared toward managing core HR operations. SAP SuccessFactors, on the other hand, is a pall-grounded suite that focuses on advanced HR strategies like gift operation, hand engagement, and performance analytics, offering scalability and regular updates.
26. What is the role of SAP HCM in facilitating employee performance management?
Ans:
- SAP HCM facilitates employee performance management through its intertwined modules that help set pretensions, assess performance, and furnish feedback.
- It allows for the creation of detailed hand appraisals and performance reviews that align with organizational objectives.
- The module integrates with Talent Management to ensure that performance assessments contribute to career development plans.
27. What are labour force Areas and labour force Subareas in SAP HCM, and why are they important?
Ans:
- Personnel Areas and Labour Force Subareas in SAP HCM are organizational units within a company law that represent distinct areas and subareas, similar to office locales or departments.
- Personnel Areas are used to apply different Payroll and legal considerations, whereas personnel subareas handle more specific conditions like work schedules and vacation timetables.
- These distinctions are essential for configuring the system to manage different HR programs and practices that vary by position or department, ensuring compliance and acclimatizing operations across the association.
28. How does SAP HCM handle legal reporting conditions?
Ans:
- SAP HCM handles legal reporting conditions through its robust data operation and reporting capabilities that ensure associations can meet original and transnational compliance norms.
- The system includes features to induce obligatory reports similar to duty affirmations, social security benefactions, and employment equity reports.
- These tools are regularly streamlined to reflect changes in legal norms, helping companies avoid penalties for non-compliance and ensuring they meet all statutory conditions efficiently and directly.
29. What strategies are used to manage payroll in a transnational environment with SAP HCM?
Ans:
Managing Payroll in transnational surroundings using SAP HCM involves using the system’s global capabilities to handle various currencies, duty regulations, and legal compliance needs across different countries. SAP HCM’s payroll functionality can be localized to meet the specific conditions of each country while maintaining a coherent overall operation system at the headquarters.
30. What is the role of SAP HCM in facilitating Employee Self-Service (ESS) and Manager Self-Service (MSS)?
Ans:
- Hand tone- Service( ESS) and director tone- Service( MSS) are critical factors of SAP HCM that empower workers and directors to perform certain HR functions singly through a user-friendly portal interface.
- ESS allows workers to pierce their particular data, payroll information, and benefit options and perform tasks similar to streamlining particular details and submitting time-off requests.
- These tools significantly reduce executive workload for HR departments, increase data delicacy, and ameliorate hand engagement by furnishing immediate access to HR-related tasks.
31. What is the function of Organizational Visualization in SAP HCM?
Ans:
Organizational Visualization in SAP HCM employs graphical tools to depict an organization’s structure, offering clear insights into the relationships between various units, positions, and roles. This feature aids HR professionals and managers in planning and decision-making, especially in large organizations with complex structures. It also facilitates effective change management by allowing users to visualize potential organizational changes before implementation.
32. What role does SAP HCM play in managing employee development and retention?
Ans:
- SAP HCM plays a pivotal part in managing hand development and retention by furnishing tools that dissect pool data to identify trends and reasons behind hand departure.
- Through its analytics and reporting capabilities, HR professionals can concoct further effective retention strategies grounded on data-driven perceptivity.
- Also, SAP HCM’s Talent Management and Employee Engagement modules help ameliorate job satisfaction and fidelity by ensuring workers’ career bournes align with organizational pretensions and by feting and awarding high performance.
33. What is ERP?
Ans:
Associations employ enterprise resource planning, or ERP, software to manage and integrate essential business operations. ERP systems combine all angles of an operation, including product planning, development, manufacturing, deals, and marketing, into a single, unified system. By easing the inflow of data between various business functions, ERP systems exclude data silos, increase process effectiveness, and foster data delicacy.
34. What’s the benefit of enforcing an Enterprise Resource Planning( ERP) system in a business?
Ans:
- Enforcing an ERP system in a business offers multitudinous benefits, including bettered functional effectiveness, better data delicacy, and enhanced productivity.
- By polarizing information, ERP systems reduce duplication, streamline processes, and ensure that all business functions are aligned, which saves time and reduces functional costs.
- Overall, an ERP improves a company’s capability to respond more snappily to request changes and client requirements, thereby adding to its competitiveness
35. What’s the significance of integrating all business functions into a software system?
Ans:
Integrating all business functions into a single software system significantly enhances functional consonance and effectiveness across the association. This integration allows for flawless communication and data inflow between departments, reducing process detainments and the threat of crimes associated with homemade data entry and duplication. It supports a holistic view of business operations, enabling directors to make informed opinions grounded on real-time data.
36. What’s SAP HR?
Ans:
- SAP HR( Human coffers), also known as SAP HCM( Human Capital Management), is a comprehensive software module developed by SAP that supports all the processes of mortal resource operation in the enterprise.
- SAP HR helps automate these processes, making them more effective and furnishing centralized access to hand information.
- The system ensures compliance with global and original regulations and provides logical capabilities to manage and alleviate the association’s pool effectively.
37. What’s the part of HR in maintaining a healthy and productive work terrain?
Ans:
The part of HR in maintaining a healthy and productive work terrain is vital. HR is responsible for enforcing programs that promote a culture of respect, equity, and positivity. This includes designing comprehensive heartiness programs that support physical and internal health, ensuring plant safety, and easing conflict resolution. HR also plays a pivotal part in hand development and engagement strategies, which are essential for provocation and retention.
38. What’s the end- to- end process of paying workers?
Ans:
- The end-to-end process of paying workers, generally known as payroll processing, involves several ways.
- Originally, the hours worked by hand were collected and vindicated.
- Deductions similar to levies, social security, and benefits are decreased to determine the net pay.
- The Payroll must misbehave with all legal conditions.
39. What are business intelligence advisers in SAP HR?
Ans:
Business intelligence advisers in SAP HR specialize in assaying complex data related to mortal coffers and transubstantiating it into practicable perceptivity. These advisers use SAP’s important logical tools to assess pool effectiveness, compensation, benefits, reclamation effectiveness, and other critical HR functions. They help associations understand trends, predict unborn HR requirements, and make data-driven opinions to ameliorate HR strategies and operations.
40. What are specialized, functional advisers in SAP HR?
Ans:
- In SAP HR, specialized advisers concentrate on the system’s software aspects, including programming, customization, and troubleshooting.
- They ensure that the SAP terrain is optimally configured, perform updates, and maintain system health.
- Functional advisers, on the other hand, specialize in HR processes and conditions.
- They configure SAP HR modules according to organizational requirements, ensuring the software aligns with business processes.
41. What’s the end of the original phase of working with SAP HR?
Ans:
The initial stage of utilizing SAP HR, also referred to as the design phase or design medication, seeks to establish a strong basis for a successful implementation. During this phase, design brigades define design pretensions, compass, and timelines and gather detailed conditions from various stakeholders. This is also when the business processes are counterplotted and anatomized, ensuring that the system setup will adequately support all HR functions.
42. What’s the thing about SAP HR’s improvement systems?
Ans:
- The goal of SAP HR’s improvement systems is to lessen or extend the functionality of an SAP HR system to meet organizational requirements.
- Improvement systems are generally accepted to acclimate to changes in business practices and compliance conditions or to influence new SAP technologies that can give competitive advantages.
- Eventually, these systems aim to increase effectiveness, user satisfaction, and the overall effectiveness of the HR department.
43. What’s the last phase of working with SAP HR?
Ans:
The last phase of working with SAP HR is the Go-Live and Support phase. This phase involves making the system functional and transferring it from a design terrain to a live product. During Go-Live, final data migrations are completed, and the system is completely tested under real conditions. Once the system is live, the focus shifts to ongoing support and conservation, addressing any user issues and making necessary adaptations.
44. What are the three main structures in SAP HR?
Ans:
- The Organizational Structure maps the hierarchical arrangements of various departments, jobs, and positions within the company, reflecting reporting connections and functional areas.
- The Personnel Structure classifies workers as being grounded in hand groups and groups similar to salaried, hourly workers and directors, helping in executive and payroll processing.
- The Enterprise Structure defines the crucial organizational units, including company law, labour force areas, and labour force subareas, pivotal for legal and reporting purposes.
45. What’s the end of the commercial law in organizations?
Ans:
Commercial law in organizations, especially within SAP systems, acts as the fundamental legal framework for financial reporting. It is a vital component of the Enterprise Structure in SAP, defining a company or entity recognized under specific legal standards. The primary aim of establishing commercial law is to consolidate and manage financial transactions, ensure compliance with regulations, and facilitate accurate financial reporting.
46.. What are the functions of hand groups and sub-groups in organizations?
Ans:
- Hand groups and sub-groups in SAP HCM classify workers into various orders, which can be used to apply different HR programs and payroll processing rules.
- Hand groups might distinguish between workers similar to salaried workers, hourly workers, and contractors, while subgroups give farther brackets, like full-time or part-time status within those groups.
- This categorization helps in presiding organizational rules, benefits eligibility, Payroll, and legal reporting more efficiently and ensures that HR programs are applied slightly across analogous types of workers.
47. What’s the purpose of the payroll area in organizations?
Ans:
The payroll area in SAP HCM is a critical organizational unit that defines the frequency of payroll processing(e.g., yearly, bi-weekly) for hand groups. It ensures that Payroll is reused contemporaneously for a specific group of workers and helps manage the control and monitoring of payroll runs. This configuration is pivotal for aligning payroll processes with company programs and legal conditions, ensuring timely and accurate payment payments, and maintaining effective payroll operation across different hand groups.
48. What are the different modules of SAP HCM?
Ans:
- SAP HCM encompasses several intertwined modules that support various HR functions.
- Personnel Administration manages core hand data;
- Organizational Management handles organizational structure and reporting connections;
- Payroll processes hand compensation;
- Time Management tracks hand time entries and attendance;
- Benefits Administration manages hand benefits;
49. What do you mean by Evaluation Path in SAP HCM?
Ans:
An evaluation path in SAP HCM is a set of rules that defines the connections between objects in the Organizational Management module. It helps in navigating the structure of an association by defining a sequence to follow, similar to which department a position belongs to or which workers report to a particular director. This tool is essential for reporting, planning, and executing various HR processes, furnishing a clear pathway to recoup connected data across the organizational scale.
50. What’s the part of TCode in SAP HCM?
Ans:
- Sale Canons( TCode) in SAP HCM are lanes or canons that snappily pierce various functions within the SAP system.
- They’re essential for navigating the vast array of features in SAP, allowing users to pierce different defences or execute specific tasks efficiently.
- For HR professionals, using TCodes can significantly streamline daily operations by reducing the time spent navigating through menus to reach constantly used functions, enhancing productivity in managing HR tasks.
51. What is the T-code used for creating remuneration statements in SAP?
Ans:
The “T-law” for creating remuneration statements typically refers to regulations and guidelines set forth by tax authorities and labor laws within a given jurisdiction. These laws mandate that remuneration statements, or pay slips, include specific details such as the employee’s gross earnings, deductions (taxes, social security, health insurance, etc.), net pay, and any additional benefits or bonuses.
52. What do you understand about shift planning?
Ans:
- Shift planning in SAP HCM refers to the process of scheduling handwork shifts to meet functional conditions.
- This element of Time Management allows directors to allocate shifts grounded on hand vacuity, chops, and organizational requirements, ensuring optimal staffing situations.
- Shift planning is pivotal in diligence that operates around the timepiece or has variable staffing requirements, similar to healthcare, retail, and manufacturing.
53. What are the benefits of using SAP Human Capital Management?
Ans:
SAP Human Capital Management( HCM) offers comprehensive tools for streamlining pool processes, enhancing gift operation, and perfecting functional edge. It provides modules for Payroll, time operation, labour force administration, and organizational operation, among others, easing integrated and consolidated control of all HR tasks. SAP HCM improves decision-making through robust analytics and reporting features, increases HR process effectiveness, and enhances hand satisfaction through tone-service doors.
54. What distinguishes SAP HCM from SAP HRMS?
Ans:
- SAP HCM( Human Capital Management) and SAP HRMS( Human Resource Management System) are basically the same, with SAP HCM being the further ultramodern term that reflects its broader capabilities beyond traditional HR tasks.
- Originally, the term HRMS was generally used, fastening primarily to executive and payroll functions.
- SAP rebranded the software as HCM to reflect its evolution into a comprehensive approach for managing human capital, including talent management, workforce planning, and analytics.
55. What is the distinction between CAP and PCR in SAP HCM?
Ans:
In SAP HCM, CAP (Configuration Access Protocol) and PCR (Payroll Calculation Rule) play crucial roles in payroll processing but serve distinct purposes. While CAP is not a standard term within SAP HCM and may refer to general configuration protocols or access operations, PCR specifically defines the rules governing the calculation and application of payroll elements. PCRs are customizable, allowing for complex computations and conditions based on company policies or legal requirements, thereby enabling flexible payroll processing.
56. What are the various methods that SAP HCM provides for hiring a new employee?
Ans:
- In SAP HCM, hiring a new hand can be done in various ways. The most common is using the Personnel Administration module, where you can directly produce a hand master record through sale canons like PA40 or PA30.
- Another system is via Recruitment Management, which integrates with external career spots and allows for the flawless transition of seeker data into hand records upon hiring.
- Also, associations can use Mass Hiring deals to reuse multiple hires contemporaneously, which is effective for large-scale reclamation drives or seasonal hiring.
57. What options are available for canceling an advertisement run in SAP HCM?
Ans:
In SAP HCM, formerly, a payroll run is completed and posted, but it could be more prudent and standard practice to cancel the posting run. Still, corrections can be made by reversing the payroll results if crimes are set up. This reversal is done before the finalization and exit of the payroll period. This ensures the integrity of fiscal reporting and compliance with inspection conditions. Deleting payroll results should be handled with caution and generally involves adaptations in posterior payroll runs to correct any disagreement.
58. What are the steps to configure a single payroll to pay individuals in multiple currencies?
Ans:
- Yes, in SAP HCM, it’s possible to configure a single payroll system to handle payments in multiple currencies.
- SAP HCM’s payroll system can be configured to reuse payments in the original currency of each hand grounded on the legal and company-specific rules governing each country.
- Exchange rates can be maintained and streamlined regularly in the system to ensure accurate currency conversion during payroll processing.
59. What are Global Employment roles in SAP HCM?
Ans:
Global employment roles in SAP HCM pertain to managing employees working in multiple countries during their tenure. This feature supports international assignments and dual responsibilities across locations. SAP HCM ensures compliance with local labor laws, handles currency conversion for payroll, and manages various benefit schemes, providing a seamless HR experience for both employees and the organization, regardless of their location.
60. What do you understand about Matchcode W?
Ans:
- Matchcode W in SAP is a specific type of hunt help used to detect hand records by labour force number.
- Matchcode W facilitates the easy reclamation of hand data without requiring users to navigate through expansive lists manually.
- Users simply enter a part of the labour force number, and the system provides a list of all records matching that input, making the process of finding and opting for hand records much more brisk and more effective.
61. What does it mean to evaluate pay envelope types across different categories?
Ans:
Yes, in SAP HCM, it’s possible to estimate pay envelope types laterally. Circular evaluation is used to automate the computation of pay envelope quantities grounded on certain rules or factors, similar to organizational assignments, hand groups, or pay scales. For illustration, benefits or introductory pay can be determined using circular valuation, ensuring that pay envelope types acclimate automatically grounded on predefined parameters, which reduces homemade input crimes and ensures thickness across the association.
62. What Is the Customer in The SAP System?
Ans:
- In SAP systems, a customer represents a tone-contained specialized and marketable organizational unit with its data terrain.
- Each customer maintains its own set of master data, user rights, and customization settings, making it possible for multiple legal realities or departments within an association to operate singly within the same SAP terrain.
- This separation is pivotal for businesses that operate in different geographical locales or have various business units, as it allows for acclimatized configurations without affecting another corridor of the system.
63. What’s the difference between Indian and US Payroll?
Ans:
The primary difference between Indian and US payroll in SAP HCM lies in the specific legal and nonsupervisory conditions each must cleave to. Indian Payroll must manage unique factors similar to the Provident Fund( PF), Employee State Insurance( ESI), Professional Tax( PT), and Labour Welfare Fund( LWF), which have specific computation rules. In discrepancy, the US payroll involves different duty computations, similar to civil, state, and original levies, and complies with regulations like FICA( Social Security and Medicare).
64. What ways are there to perform pay scale reassignment?
Ans:
- Pay scale reassignment in SAP HCM can be performed through several styles depending on the script. Common styles include organizational reassignment, where a hand’s pay scale group and position are changed due to a transfer or creation.
- Homemade adaptations can also be made directly in the Basic Pay Infotype( 0008).
- These flexible styles ensure that changes in employment conditions are directly reflected in the pay structure, maintaining equity and compliance with employment agreements.
65. How can you define dereliction pay envelope types for the Basic Pay Infotype?
Ans:
Dereliction pay envelope types for the Basic Pay Infotype( 0008) in SAP HCM can be defined using point TARIF. This point allows you to set up dereliction pay envelope types grounded on various criteria, such as hand group, hand group, pay scale type, and area. Configuring this point ensures that whenever a new introductory pay record is created, the system automatically proposes the applicable pay envelope types, simplifying data entry and reducing the eventuality of crimes.
66. What is the difference between PCR and CAP?
Ans:
PCR(labour force computation Rule) and CAP( Cumulation Adjustment Period) are terms associated with Payroll in SAP HR. PCR is used within the payroll function to define specific rules for calculating payroll rudiments, such as stipends, lagniappes, and deductions grounded on conditions set within the system. On the other hand, CAP refers to the ages over which payroll results are acclimated or cumulated, generally used for managing and assessing overtime payments, perk computations, and other cumulative payroll factors.
67. What does the “copy plan interpretation” feature in Organizational Management (OM) involve?
Ans:
- In SAP HR’s Organizational Management( OM), the’ Copy Plan Version’ function is used to duplicate organizational structures from one plan interpretation to another.
- This point is critical when testing changes in anon-production terrain or setting up new organizational structures grounded on being bones without affecting the current live system.
68. How would you record time in your SAP HR system?
Ans:
Time in the SAP HR system is recorded using the Time Management module, where employees enter their hours and absences through the Employee Self-Service (ESS) portal. Administrators can review and approve this data directly in the system. Additionally, SAP HR integrates with electronic time recording devices to automatically capture data, reducing manual entries and errors for accurate payroll processing and operational planning.
69. What do you mean by the term rewards operation?
Ans:
- Prices operation in SAP HR refers to the comprehensive running of hand compensation, benefits, recognition, and prices.
- This includes payment, lagniappes, impulses, non-monetary gratuities, and benefits like health insurance and withdrawal plans.
- An effective price operation aims to attract, motivate, and retain workers by aligning prices with business pretensions and hand performance.
70. What is the reliability of SAP HR in handling boundaries?
Ans:
SAP HR provides various tools and features that can help associations help and address differentiation in the plant. It makes it possible to generate comprehensive data and analytics that may analyze recruiting procedures, pay, promotions, and terminations in order to guarantee equity and adherence to equal employment opportunity regulations. Still, the effectiveness of SAP HR in combating demarcation also heavily depends on how it’s enforced and used by the association, taking robust programs and training to ensure it supports a fair and inclusive plant culture.
71. Define BEX?
Ans:
- BEX( Business Discoverer) is an element of SAP NetWeaver that provides important tools for reporting, analysis, and design of business intelligence.
- It enables users to pierce data from SAP BI databases and present it in a scrutable format through reports, queries, and dashboards.
- BEX tools, such as BEX Analyzer and BEX Query Developer, provide insights from large data sets to support decision-making. They help businesses understand their operational and financial landscapes, driving data-driven strategies.
72. What is SAP NetWeaver?
Ans:
SAP NetWeaver is a unified technology platform that supports SAP applications and ensures interoperability with non-SAP systems. It underpins ERP and enterprise operations, incorporating components for business integration, application platforms, and business intelligence, facilitating seamless integration of processes and data across the organization.
73. How does SAP HCM handle global employment programs across different countries?
Ans:
- SAP HCM handles global employment programs by allowing associations to configure and manage HR operations according to the original regulations of each country in which they operate.
- This includes managing different payroll practices, statutory reporting conditions, and compliance with original labour laws.
- SAP HCM’s global settings can be acclimated to various currencies, languages, and legal conditions, ensuring that transnational companies can maintain standardized HR practices while also meeting original requirements.
74. What tools does SAP HCM provide to support diversity and inclusion within an organization?
Ans:
SAP HCM provides tools for tracking diversity metrics such as age, gender, race, and disability status. It enables the creation of reports and analytics to guide HR decisions on diversity programs. Additionally, SAP HCM facilitates tailored hiring and development practices, fostering an inclusive culture and helping organizations meet their social responsibility goals.
75. What are the challenges of enforcing SAP HCM, and how can they be eased?
Ans:
- Enforcing SAP HCM can present challenges similar to significant outspoken costs, complexity in configuration, and the need for technical training.
- It’s pivotal to engage educated SAP advisers who understand the specific requirements of the business and can consequently conform to the system.
- Also, gaining strong buy-in from all stakeholders by demonstrating the system’s benefits can create a smoother perpetration and relinquishment process.
76. How does SAP HCM integrate with other digital HR results, similar to pool analytics tools?
Ans:
SAP HCM integrates with other digital HR results, including pool analytics tools, through its open armature and expansive APIs that allow for flawless data exchange between systems. This integration enables associations to enhance their HR functionalities by combining SAP HCM’s core data operation capabilities with advanced analytics, machine literacy, and AI-driven perceptivity from external platforms.
77. What is the Employee Interaction Center in SAP HCM?
Ans:
- The Hand Interaction Center( EIC) in SAP HCM acts as a helpdesk, furnishing workers with a single point of contact for all HR-related queries and issues.
- This point uses a marking system where workers can raise tickets, which HR professionals also handle.
- The EIC is equipped with a knowledge base to grease brisk resolution of common inquiries and integrates with other HCM modules to give comprehensive support.
78. How does Succession Planning work in SAP HCM?
Ans:
Succession Planning in SAP HCM enables organizations to identify and develop potential leaders from within their workforce, aligning them with key positions based on skills, performance, and career aspirations. The module provides tools to create succession plans that ensure critical roles are consistently filled while offering growth opportunities for high-potential employees. This strategic approach reduces risks from unplanned vacancies and fosters a strong leadership pipeline for long-term organizational resilience.
79. What are the benefits of integrating SAP HCM with SAP Business Intelligence( BI)?
Ans:
- Integrating SAP HCM with SAP Business Intelligence( BI) significantly enhances HR decision-making capabilities by providing advanced analytics on HR data.
- This integration allows associations to prize, dissect, and report on data across various HR modules, such as Payroll, time operation, and gift operation.
- With SAP BI, HR data becomes a strategic asset that can inform broader business opinions, helping align HR objects with commercial pretensions and facilitate organizational performance.
80. What are the liabilities of the mortal resource department of the association?
Ans:
- Recruiting and staffing.
- Conducting training and development.
- Managing performance systems.
- Ensuring compliance with employment and labour laws.
HR also oversees hand benefits, compensation, hand relations, and organizational development. By aligning the HR strategy with the association’s pretensions, the HR department supports the overall functional effectiveness, contributes to hand satisfaction and retention, and drives the association’s success.
81. What’s a PCL 2 cluster, and how can users pierce the same in SAP HR?
Ans:
In SAP HR, the PCL 2 cluster(labour force computation Cluster) stores payroll results that are reused during each payroll run. This cluster contains data such as gross pay, deductions, and net pay. Users can pierce this data through the payroll reports or by using sale canons such as PC_PAYRESULT, which allows browsing of payroll results. Due to the keenness of the data it contains, access to the PCL 2 cluster is generally confined to the authorized labour force, ensuring compliance with data sequestration and protection guidelines.
82. How can we define a processing class?
Ans:
- In SAP HR, a processing class is used to classify pay envelope types during payroll processing, specifying how each pay envelope type should be treated or reused under different conditions.
- Directors define processing classes in the payroll schema, where each class is associated with specific attributes that determine its running during the payroll run.
- These attributes include whether the pay envelope type is taxable, whether it should be included in pension computations, or how it should be portioned.
- Defining processing classes rightly is critical for accurate payroll computations and compliance with legal conditions.
83. Why is it important to restrict data entry in the Payroll area?
Ans:
Restricting data entry in the Payroll area of SAP HR is crucial for maintaining data integrity and ensuring payroll accuracy. It involves controlling access to sensitive information, allowing only authorized personnel to modify payroll-related data. These restrictions help prevent errors and fraud, protecting both the organization and its employees, and are typically implemented through authorization checks and validation rules within the SAP system.
84. What does the term “Authorizations” mean in the SAP HR tool?
Ans:
- In SAP HR,’ Authorizations’ relate to the warrants or access rights assigned to users to perform specific tasks or access particular data within the system.
- This is part of the broader SAP security frame, which ensures that workers can only pierce information applicable to their part, thereby securing sensitive hand data.
- Authorizations are pivotal for administering data security, maintaining data integrity, and ensuring compliance with various legal and commercial programs regarding information access.
85. What do you mean by the term TMSTA?
Ans:
In SAP HR, TMSTA stands for Time Management Status. This term defines a hand’s time recording conditions. TMSTA is a crucial element in configuring the Time Management module as it determines whether workers need to timepiece in and out, whether their absences bear blessings, or whether they’re pure from time evaluation. Setting the correct TMSTA for each hand helps ensure accurate data collection for attendance and payroll processing and is pivotal for compliance with working time regulations.
86. What does the term “Go Live” mean?
Ans:
Go Live” refers to the moment when a system, such as SAP HR, officially becomes operational and is used in a live environment. It signifies the completion of the implementation project and the beginning of daily operations. Successful Go Live requires careful planning, training, and testing to ensure smooth functionality and minimal disruption to business processes, directly impacting the system’s effectiveness in supporting organizational goals.
87. What methods can be used to group employees in Payroll?
Ans:
In SAP Payroll, workers can be grouped using various criteria, such as payroll area, hand group, and labour force subarea. Payroll areas define the payroll period and frequency for processing payments, allowing associations to manage different payroll cycles efficiently. Hand groups classify workers based on their employment status or job type, which can affect payroll processing rules. Labour force subareas help distinguish workers by their geographical position or organizational unit, impacting legal and nonsupervisory reporting.
88. What’s SAP Version 3?
Ans:
- Developed by SAP SE, SAP R/3 is an enterprise resource planning (ERP) program that assists large associations in managing corporate activities in HR, manufacturing, finance, and other modules.
- It stands for” Real- Time 3 Tier,” pertaining to its armature the donation subcaste, operation subcaste, and database subcaste.
- SAP R/ 3 was one of the first ERP systems that allowed companies to integrate all their business processes into a unified system, thereby perfecting effectiveness and data thickness across departments.
89. How can associations work SAP HR on pall?
Ans:
Organizations can leverage SAP HR in the cloud, specifically through SAP SuccessFactors, to improve flexibility, scalability, and innovation in HR management. Cloud-based solutions allow access from anywhere, facilitating remote work and real-time updates while reducing IT maintenance costs, as SAP handles upgrades and security compliance. This transition can result in cost savings, enhanced user experiences, and quicker adoption of new HR technologies.
90. What are the uses of a simple conservation interface?
Ans:
- The simple conservation interface in SAP HR is used primarily for managing organizational structures, labour force structures, and reporting connections.
- This interface allows HR directors to fantasize and edit the organizational plan with a user-friendly graphical interface, making it easier to maintain delicacy and thickness in data entries.
- It supports essential tasks similar to creating and modifying organizational units, positions, and jobs and assigning workers to these structures.






