
- Introduction to Leads, Lags, and Float
- What are the best number of free floats and complete floats in a timetable?
- What is a Negative Float?
- What are float and Lag?
- What are Lag and lead?
- What is the purpose for a Lag float?
- How to Apply Leads and Lags in Project Management?
- Lead vs Lag
- Difference between Lag and Float
- Comprehend the distinction between Lead-Lag, Float/Lag, and Buffer Managemen
- The 8 sorts of requirements
- Four limits the board methodologies
- Start precisely dealing with your ability today
- Restrictions
- Conclusion
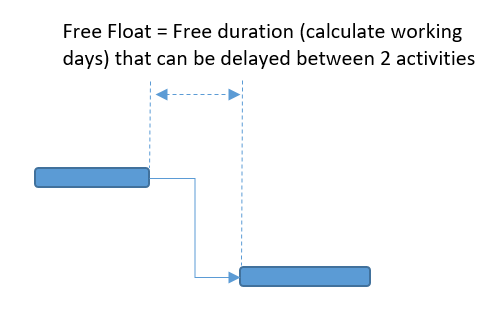
- Free Float is the hour of an action that can be delayed right away ambitious beginning or an early completion date of replacement action (contingent upon relationship FS, SS, FF, SF).
- Free Float is determined from the Early Start or Early Finish of action to the Early Start or Early Finish of replacement exercises (contingent upon the relationship FS, SS, FF, SF).
- Absolute Float is how much time an action can be postponed without deferring the general task length and is additionally called “float” or “Lag”.
- The Total Float is estimated as the distinction between the ambitious beginning and poor start dates (LS – ES) or late completion and early completion dates (LF – EF).
- The Total Float is appropriated as a free Float in a progression of exercises (the most basic way of a movement) consecutively (determined from the finish point of action to the culmination of the venture).
- An undertaking with a negative Total Float can be said the venture is delayed.
- At the point when the venture has a limitation, for instance, the task should be finished on a specific timetable, and if the undertaking plan ends up being postponed, this can make the absolute Float negative.
- The negative worth in Total Float addresses the length expected to make up for the lost time to wrap up according to schedule.
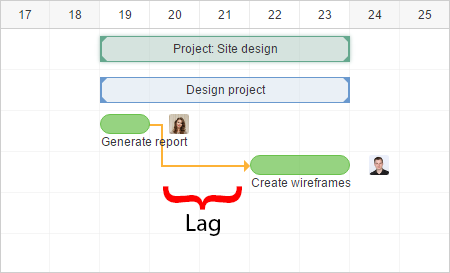
- Lag is how much standby time between two errands. Or then again at the end of the day, Lag is how much time by which a replacement movement will be postponed.
- Lag can be utilized in every one of the four legitimate connections in planning, for example, Finish-to-begin (FS), begin-to-begin (SS), finish-to-get done (FS), and beginning to end (SF).
- It is a movement relationship where replacement action is progressed to be directed corresponding to ancestor action.
- That implies the ancestor action is as yet running and replacement action starts.
- Leads, Lags, and float are ideas utilized in the plan advancement process. The course of timetable improvement incorporates recognizable proof, everything being equal, sequencing movements of every kind in light of reliance, assessing the span of every action, and concluding the timetable.
- Leads, Lags, and float are utilized as a feature of the movement sequencing process. Movements of every sort once sequenced will frame a timetable organization chart. Allow us first to check out the meaning of this large number of three ascribes.
- While making a plan for getting work done or an organization outline, experts regularly utilize numerous phrasings, for example, lead delay time, absolute float, free float, and so forth These booking devices are involved alongside movement connections to demonstrate the genuine idea of work to be performed.
- The principle motivation behind making a plan for getting work done is to show the truth and connections, lead time, Lag time, floats are supporting this powerful model. This article talks about lead versus Lag time in project booking with the assistance of models for understanding the idea without any problem.
- Lead and Lag time are generally utilized in planning terms. Project chiefs and arranging engineers generally make examinations between the plan for getting work done and the genuine work performed nearby. Some of the time it could be hard for them to comprehend the contrast between lead time and Lag time while performing plan examination.
- Numerous PMP competitors experience issues comprehending the ideas lead time, Lag time, lead versus Lag time since they sound very comparative. Accordingly, this article will be helpful for PMP competitors and up-and-comers who need to develop a vocation in project booking.
- Reactive results measure execution that follows occasions and permit the executives to follow how well real execution matches what was normal. A model could be the number of surprising mistakes announced after a specific programming discharge.
- Proactive factors measure progress towards occasions and permit the executives to follow whether it is on course to accomplish the normal presentation. A model would be the steady disappointment of a provider to meet quality necessities from the get-go in the task.
- Movement Sequencing is one of the center assignments in project action the board. Among the various boundaries used in the venture timetable, lead and Lag are the fundamental thoughts that are likewise being used.
- Amid each set of exercises in the undertaking network outline (PND) are the connections that portray how and when a replacement and combined exercises can begin. Priority Diagram helps you in deciding the undertaking movement stream. Through the task action stream, you can perceive the basic way and cycle the float of each development. The timetable is made by using the Precedence Diagram and understanding the association between exercises.
- You can use Lags and leads when joined with every one of the connections. A Lag is generally holding up time, while a lead is hustling along with time. On occasion, project chiefs need to move things alongside the undertaking. This is the spot lead time that turns out to be perhaps the most critical element. It empowers you to attract exercises nearer to the beginning date of the task by deducting time from each planned auction start time.
- Complete float is otherwise called “float.”
- Absolute float is how long an action can be deferred without putting off the venture fulfillment date.
- In a basic way, the complete float is zero. All-out float is frequently known as leeway.
- You can ascertain it by deducting the Early Start date of movement from its Late Start Date.
- Absolute Float = Late Start date – Early Start date
- Or on the other hand
- You can get it by taking away the movement’s Early Finish date from its Late Finish date.
- All out Float = Late Finish date – Early Finish date
- Free float is the way long an action can be postponed without deferring the Early Start of its replacement.
- You can ascertain the free float by deducting the Early Finish Date of the action from the Early Start Date of the following movement.
- Free Float = ES of next Activity – EF of current Activity
- Kindly note that assuming two exercises are uniting into a solitary action, just one of these two exercises might have a free float.
- Here, Task B is an ancestor to Task C and it additionally required holding up delay before the replacement undertaking can begin. Presently the Lag will be chosen by the undertaking chief in light of master judgment and other helpful strategies for this situation. Henceforth, Lead and Lag are forced all of the time by the undertaking administrators on a basic or non-basic way founded on task intelligent relationship.
- Float or Lag is again an action length unit where an errand can be postponed without affecting the promising beginning date of replacement task (free float) or undertaking span (Total Float) or client imperatives date (Project float) however the distinction here, it isn’t forced by project administrator physically rather they exist in network graph in light of the sequencing of the assignments.
- Cushion or Reserve Or Padding are utilized in the project of the executives as a dangerous reaction technique. They are again physically chosen by project administrators in light of master judgment or other help procedures with the group and different partners.
- In the Project network graph on the basic way, when we put cradle (Project Buffer) toward the finish of the organization, it is to moderate the obscure danger and henceforth to shield the task plan for delay from unidentified danger.
- For the point when we set Buffer on a non-basic way (Feeding Buffer), it is again for the hazard of postponement to task on the non-basic way which affects the undertaking on the basic way due to their relationship/limitations.
- To sum up, Float, Lead/Lag, and Buffer are not similar. Float for the assignment can’t be chosen by the project chief while Lead/Lag and Buffer can be chosen by him with others’ assistance.
- Lead/Lag can exist in both basic or non-basic ways equivalent to Buffer however the thing that matters is Buffer can likewise exist toward the finish of the basic way as go against Lead/Lag.
- Float or Lag can exist in a non-basic way.
- Recipe: Float = LS-ES or LF – EF
- Regardless of whether you’re dealing with your business’ first task or its 500th, precisely overseeing the limit is intense. There’s group accessibility, ranges of abilities, spending plans, and asset portion to contemplate.
- Be that as it may, overseeing limit successfully shouldn’t be a cerebral pain. It tends to be just about as straightforward as utilizing a brought together to limit the executive’s apparatus and survey your group’s accessibility, assets, and ranges of abilities in a single spot.
- With Float, you can rapidly see who’s accessible and who’s not, as well as track down the most ideal fit to make it happen. It’s additionally simple to add occasions and individual work hours, and timetable downtime for a reasonable image of your group’s actual limit. Like that, when another venture comes in, you can certainly perceive how and when you will get it across the end goal.
- While involving Lag and lead for sequencing exercises it is essential to take note, that it’s anything but a strategy that can be utilized as an independent. Lag and lead should be utilized in a mix with different apparatuses, as the Lag and lead times in a Project Schedule Network Diagram are insignificant without deciding the legitimate connections between the exercises. As such, there would be no utilization for them.
- Lag and lead times do exclude the term of exercises in the undertaking organization. It is a timetable measure to decide if a given movement can be deferred or progressed. They are fundamental and significant, but they don’t give further knowledge to the sequencing of exercises other than the time plan without anyone else.
- Lag and lead times are likewise not outright and can be a subject to shift all through the direction of the undertaking, and can be exceptionally difficult to decide at the start of the task. Consequently, the project network typically should be refreshed as the task advances. It is of most extreme significance for an undertaking supervisor to remember this, as the ramifications for the booking can be serious assuming incorrectly Lag and lead times are utilized.
Introduction to Leads, Lags, and Float:
With regards to project movement the executives, action sequencing is one of the primary errands. Among numerous different boundaries, a float is one of the key ideas utilized in project booking. Float can be utilized to work with the opportunity for a specific errand. We should examine the float exhaustively.
Float:
Float (otherwise called Lag) is how much time by which the beginning of a movement can be postponed without deferring the undertaking finishing time. Each assignment will have the following arrangement of start and finish times.
Earliest beginning time (ES) – The earliest time, an action can begin once the past ward exercises are finished.
Earliest completion time (EF) – This would be ES + movement span.
Most recent completion time (LF) – The most recent time a movement can be complete without deferring the undertaking.
Most recent beginning time (LS) – This would be LF – action span.
The float season of action can be determined by taking the contrast between Late Start (LS) and Early Start (ES) OR between Late Finish (LF) and Early Finish (EF).
Float = LS-ES OR =LF-EF
A positive float time shows the adaptability we will have in deferring the particular action without postponing the venture fruition time. Normally, while doing planning, the basic way errands will have zero float and the non-basic way assignments will have a positive float. That implies non-basic way errands can be postponed to a specific degree without thinking twice about the venture consummation time. Float time data of assignments is extremely helpful to the venture group for taking booking choices when there will be asset requirements.
Free Float:
What are the best number of free floats and complete floats in a timetable?
As indicated by DoD controls, the greatest number of floats should be something like 44 workdays.
Absolute Float:
What is a Negative Float?
Lag:
Lead:
What are float and Lag?
Lag is a deferral in the replacement movement. Absolute Float is how much time by which you can postpone a movement from its ambitious beginning date without deferring the undertaking finish date
What are Lag and lead?
What are Leads and Lags in a Project? Lag alludes to how much time by which a replacement action is expected to delay in regards to an ancestor movement. Lead alludes to the total time by which a replacement action can continue concerning an ancestor action.
What is the purpose for a Lag float?
Float data is helpful in asset assignment when there are asset limitations. Lead is utilized for speeding up the beginning of assignments (optimizing) for lessening project timetables. Lag is utilized for guaranteeing that expected inactive or stand-by time after an undertaking is fittingly provisioned.
Lead, Lags, and Float:
Lead versus Lag (Lead Time Lag Time) in Scheduling:
Lead versus Lag Time:
Application:
From the English norm for the project the executives “Sovereign 2”, the meaning of leadership and Lag pointers is:
How to Apply Leads and Lags in Project Management?
Lead vs. Lag
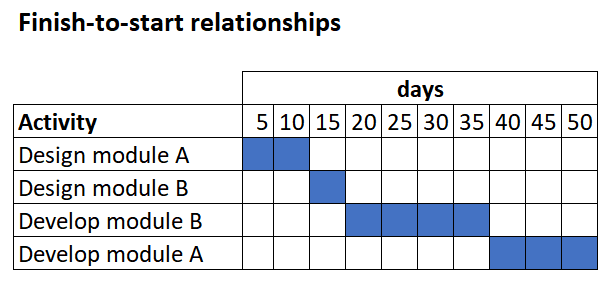
1. Lead and lag are both used in the development of the project schedule.
2. Lead is an acceleration of the successor activity and can be used only on finish-to-start activity relationships.
3. Lag is a delay in the successor activity and can be found on all activity relationship types.
4. Lead is only found in activities with finish-to-start relationships: A must finish before B can start.
5. Lag may be found in activities with all relationship types: finish-to-start, start-to-start, finish-to-finish, and start-to-finish.
Total Float:
Free Float:
Difference between Lag and Float:
Float is how much time an errand can be postponed without deferring the following assignment (Free-Float) or without deferring the Project Finish (Total Float). Float is numerically determined in light of the legitimate grouping of works, including Lag, characterized in the timetable, though Lag is remembered for reason and structures some portion of work arrangement. Float is a side-effect, got ‘because’ of planning. Lag itself isn’t reliant upon Float however can influence it. Float for a similar assignment can change all through the undertaking term however Lag stays fixed.
Lag (a time frame) is ‘brought’ into the timetable. This component is a piece of the timetable rationale. Lag is input given involvement or legally binding prerequisites. for example, structure work evacuation after a specific time-frame of restoring: There will be a pre-decided non-working span between concrete pouring and structure work expulsion. Some of the time individuals present one more action of relieving here, subsequently addressing the actual Lag as an action. As is self-evident and at the danger of sounding tedious, Lag is an inborn part of timetable rationale, not a subsidiary, in contrast to Float. In the structure work model, the arrangement of “cementing relieving structure work expulsion” itself may have float accessible.
Comprehend the distinction between Lead-Lag, Float/Lag, and Buffer Management:
Over numerous long stretches of my preparation experience, I have observed that individuals are mistaken for the accompanying task the executive’s wordings. I have invested my best energy to explain these terms. Kindly offer your criticism and remarks for the advantages of the others. Lead and Lag are the span unit of assignments. Lead is depicted by negative (-) sign though Lag is by sure (+) sign. A lead is a how much time by which a replacement action can be progressed regarding an ancestor action while A Lag is how much time by which a replacement movement will be postponed concerning an ancestor action.
Lead and Lag are chosen by the Project director in light of the legitimate connection between two errands. For instance, Hang a photograph outline on the divider. For this situation, consider you have the accompanying assignment.
a. Task A – Construct a divider
b. Task B – Paint a Wall
c. Task C – Hang a photograph outline
The 8 sorts of requirements:
In a Gantt Chart, a “limitation” addresses a limitation that is applied to the beginning or end date of an assignment. They are useful because they offer different levels of adaptability while planning. Meanwhile, you need to comprehend that when utilized related to conditions, a few planning clashes may show up. How about we presently investigate each type and see how they treat when you should utilize them.
1. At the earliest opportunity – when you apply this limitation to an unlinked task, the beginning date of that undertaking will be equivalent to the beginning date of the venture. Whenever this is applied to a reliant errand, that undertaking will begin when the reliance of its ancestor permit.
2. As late as could be expected – this is an adaptable imperative that when applied to an unlinked task, will match its end date to the completion date of the whole venture. Assuming that this is applied to a reliant undertaking, the assignment will be booked to complete when its replacement task needs to begin.
The following 6 requirements keep similar guidelines, no matter what the sort of errand (unlinked or subordinate).
3. Start no sooner than – the undertaking can begin on or after the predefined date
4. Start no later than – the errands can begin at the very latest the predetermined date
5. Finish no sooner than – the undertaking needs to complete on or after the predefined date
6. Finish no later than – the undertaking needs to be complete at the latest a predefined date
7. Should begin on – the assignment needs to begin the predetermined date
8. Should complete on – the undertaking needs to complete on the predefined date
Requirements 1-2 are thought of as adaptable (they don’t attach an undertaking to a particular date), 3-6 are semi-adaptable (they incorporate either a beginning or finish date however are not restricted to these) and 7-8 are firm (since they have an explicit beginning or finish dates).
Four limits the board methodologies:
There are four significant limits to the board methodologies to browse. While concluding which is appropriate for you, ponder your business structure and the degree of hazard you’re happy with taking on.
1. Lag:
Following the Lag system, a group delays until their present limit is extended as far as possible before adding more. Utilizing this procedure, directors increment interest by further developing limits after the current technique runs at its maximum capacity. Chiefs keep away from the issue of having too many colleagues or assets yet could wind up losing expected clients to contending organizations that in all actuality do have a limit.
2. Lead:
The lead procedure is a more confrontational methodology. It requires a forthright interest in more limit than is presently required. The lead system deals with the anticipated expansion popular. In genuine terms, this may look like employing one more staff part before an expected occupied period during the year. Like that, when a convergence of new work comes in, your group isn’t left scrambling attempting to track down nonexistent accessibility for new undertakings. All things considered, they’re ready to match interest. However, this methodology isn’t without its dangers. If genuine interest doesn’t match forecasts, organizations are left with more colleagues, assets, or hardware that they might require.
3. Match:
The match methodology sits somewhere close to Lag and lead. This system utilizes slow changes to a group’s ability rather than expanding the limit ahead of time or supporting the limit after the current sum is consumed. This is finished by checking changes in the commercial center. Although it’s harder to get right, it is a more secure bet for most directors, as it’s a lower hazard than different techniques.
4. Change:
The change methodology includes adding or decreasing the limit given client interest or critical changes to your item or administration structure. Since this depends on current interest or real changes to your business offering, it’s substantially more exact for arranging limits and staying away from deficiencies or such a large number of assets. Be that as it may, getting things right utilizing the change technique relies upon solid limit the board apparatuses and precise recording strategies. Like that, you can make the right changes by your ability given constant information and experiences.
Start precisely dealing with your ability today:
Restrictions:
Restrictions of Lag and lead in Sequencing Activities
Conclusion:
Float, lead, and Lag are vital ideas and data for the booking group. Float data is valuable in asset distribution when there are asset imperatives. Lead is utilized for speeding up the beginning of undertakings (optimizing) for lessening project timetables.






