
The purpose of these carefully created Oracle SOA Admin Interview Questions is to familiarize you with the various types of questions that might be asked during your interview. Highly skilled interviewers, in my experience, typically start with basic ideas and work their way up depending on your answers. The top 100 Oracle SOA Admin Interview questions are included in this compilation, along with thorough responses. There are questions for beginners entering the sector, questions targeted toward testing experienced professionals, and questions based on scenarios. The nature of interviews may vary, so it’s important to be ready for a wide range of questions covering many aspects of Oracle SOA Administration.
1. What is a SOA [Service-Oriented Architecture]?
Ans:
- SOA is an IT architecture strategy for a business solution delivery based on the concept of service orientation.
- It is the set of components that can be invoked, and whose interface descriptions can be published and discovered.
- It aims at building systems that are extensible, flexible, and fit with the legacy systems.
2. Why do I need Oracle SOA Suite?
Ans:
- Service is an important concept. Services can be published, discovered, and used in the technology-neutral, standard form by a set of protocols of the web services.
- Other than being just architecture, SOA is policies, practices, and frameworks by which it ensures the right services are provided and consumed.
- It becomes critical to implement processes that ensure that there are at least two different and separate processes – one for provider and other for a consumer, using SOA.
- The Business Service Bus serves as a jumping-off point for developers, guiding them to a cohesive collection of services tailored to their domain.
3. What are Challenges faced in SOA adoption?
Ans:
- One of the challenges faced by SOA is managing the services metadata. The second biggest challenge is lack of testing in the SOA space. Another challenge is offering appropriate levels of security.
- Interoperability is another important aspect of SOA implementations. Vendor hype concerns SOA because it can create expectations that can not be fulfilled.
4. What is SOA governance?
Ans:
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) governance is a set of policies, processes, and controls put in place to ensure that the development, deployment, and management of services in a service-oriented architecture align with organizational goals and adhere to best practices.
It involves defining and enforcing standards, protocols, and guidelines to promote consistency, interoperability, and reusability of services across an enterprise.
5. What are Business Benefits of Service-Oriented Architecture?
Ans:
- The goals like increased interoperability, increased federation and increased business & technology domain alignment can be achieved by SOA due to its architectural and design discipline.
- SOA is an architectural approach for constructing difficult software-intensive systems from the services. SOA realizes its business and IT benefits through utilizing the analysis and design methodology when creating services.
The goal of separating users from the service implementations is promoted by a SOA.
6. What are the Benefits of Service-Oriented Architecture?
Ans:
- The ability to build composite applications is provided.
- Business services are offered across divisions.
- Provides truly real-time decision-making applications.
- Reliability is enhanced.
- It is not necessary that Services be on a specific system or network.
- The approach is completely loosely coupled.
- Hardware acquisition costs are reduced.
- Authentication and authorisation are supported at all levels.
- Existing development skills are being leveraged.
The benefits of SOA are :
7. Define Short and Long-Running Processes in SOA.
Ans:
- Tasks to extract, manipulate, or transform process the data.
- Scripts or inline the code snippets.
- Calls to systems and services, both synchronous and asynchronous.
- Events, including the timed events, callbacks, and unsolicited notifications from the systems.
8. Explain Web service?
Ans:
Web service is the type of a software system which is used to exchange data and use data from one machine to another machine through the network. Web services are based on the standards like TCP/IP, HTTP, Java, HTML, and XML.
9. What is SOA composite?
Ans:
- One or more services in entry points.
- One or more service components.
- Zero, One or more external references.
- The Bindings and properties.
SOA composite offers the coarsely-grained service for business application, Which processes messages in the xml format. The composite application explains an assembly model stored in the SCA descriptor file called the composite.xml that may contain :
10. Difference between Oracle SOA 10g and Oracle SOA 11g.
Ans:
- ORACLE SOA Suite 10g is based on Oracle AS 10g It used Oracle Application Server 10.1.x OC4J Sun JVM Repository tool irca to made SOA 10g repository Managed with Application Server Console Oracle SOA Suite 11g is based on Oracle FMW 11g It uses Oracle Weblogic server 10gR3 Sun or JRockit JVM Repository Creation Utility ( RCU ) to create or delete the SOA 11g repository Weblogic server console used for managing.
- Oracle SOA 11g all SOA Components of the Project deployed into Single Server whereas 10g each component is deployed into the specific server.
- In SOA 10g having the ESB Console, BPEL Console, Application Server Control these are all individual and not well integrated.
- In SOA 11g offers the service monitoring across all the SOA Components like ESB, BPEL, Human Workflow SOA suite 11g has Enterprise Management Console.
11. What are the principles of SOA?
Ans:
- Loose coupling
- Reusability
- Interoperability
- Flexible
12. What is the SOA suite used for?
Ans:
Oracle SOA Suite is the comprehensive, hot-pluggable software suite that enables the build, deploy, and manage integrations using the service-oriented architecture (SOA). Oracle SOA Suite offers capabilities: Consistent tooling. single deployment and management model.
13. Is Oracle SOA same as Oracle Fusion Middleware?
Ans:
No, because SOA is one of the parts in the Fusion middleware . SOA behaves like the user interface whereas Fusion is a big platform.
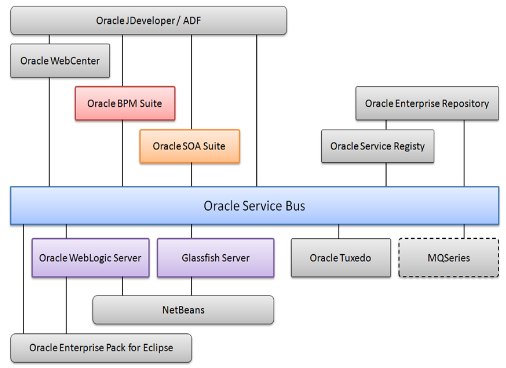
14. What is SCA?
Ans:
Service Component Architecture (SCA) provides the programming model for building applications and systems based on Service Oriented Architecture. SCA is a model that aims to encompass a wide range of technologies for service components and for access to the methods which are used to connect them.
15. What are the components of SOA Suite 11g?
Ans:
- Oracle Adapters
- Oracle Mediator
- Business Events and Events Delivery Network
- Oracle Business Rules
- Human Workflow
- Oracle Business Activity Monitoring
- Oracle Enterprise Manager
16. What is Choreography? How does it differ from Orchestration?
Ans:
In choreography there is no business process to control an integration between systems; every system will directly integrate with one another in sequence whereas in the Orchestration there is a business process which controls all the services (source/Target) which is part of integration.
17. What are the different design patterns In SOA?
Ans:
- Synchronous
- Asynchronous Fire and Forget
- Asynchronous Delayed Response
18. How many ways can a process be deployed?
Ans:
- Using Jdeveloper
- Through the Enterprise Manager Console
- Through the Weblogic Scripts
19. What are Dspmaxthread and Recieverthread properties?
Ans:
Receiver Threads property specifies the maximum number of MDBs that process the Async across all domains. The dspMaxThread is a high number of MDBs that process the Async and threads can operate across the domain. Need to ensure that dspMaxThread value is not greater than Receiver Threads.
20. How does Async Request run in backend?
Ans:
- The client posts the message to the delivery service.
- The initial state of the message is 0 (undelivered).
- The delivery service schedules the dispatcher message to process the invocation message asynchronously.
- The dispatcher message is delivered to the dispatcher through the afterCompletion() call. Therefore, messages are not delivered if the JTA transaction fails.
- MDB fetches an invocation message from the dispatcher.
The sequences of events involved in the delivery of invoke messages is as follows :
21. How to increase transaction timeouts in SOA?
Ans:
- JTA
- Engine Bean
- Delivery Bean
For transaction timeout to be increased, all settings are the timeout value required to be changed to an expected Timeout value.
22. Difference between Concrete and Abstract Wsdl.
Ans:
| Aspect | Concrete WSDL | Abstract WSDL | |
| Definition |
Contains specific implementation details |
Defines only the abstract interface | |
| Instance Details | Includes data types, message formats, etc. | Lacks implementation-specific information | |
| Usage | Suitable for service consumers and providers | Primarily for service contract definition | |
| Example |
Specifies operations, inputs, outputs, etc. |
Defines operations and their signatures |
23. What are SOA governance functions?
Ans:
- Managing portfolio of services: planning development of new services and updating current services.
- Managing a service lifecycle: This is meant to ensure updates of services do not disturb current services to consumers.
- Using policies to restrict behavior: Consistency of services ensured by having the rules applied to created services.
- Monitoring performance of services: The consequences of a service downtime or underperformance can severe because of service composition.
24. What is endpoint virtualization?
Ans:
The service bus is used for endpoint virtualization and in 11g stack; Oracle Service Bus is the primary service bus. In exposed proxy’s message flow, it can route requests to any of the environment’s actual service on the basis of whatever logic. Mediator can also be used to expose the service and in mediator routing rule, it can be routed to the actual service.
25. What are Dvm’s and how they are helpful in SOA?
Ans:
DVMs (Domain Value Maps) are like organizers in Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA). They help different services communicate by managing and standardizing data values.
Think of them as peacekeepers ensuring everyone speaks the same language, making the system more flexible and easy to update.
26. What is the difference between XREF and DVM?
Ans:
- XREF : Dynamic values to XREF can be populated dynamically and stored in the XREF_DATA table in SOA Dehydration store.
- DVM : Domain Value Map is the static mappings between the source and target system which can be used in transformations.
27. What is a dehydration store?
Ans:
Dehydration store is a database where the instances get saved when it gets to be dehydrated by process on occurrence of the non-idempotent activities and stores information on a long running processes.
28. What is a decision service?
Ans:
Oracle SOA Suite offers the support for decision components that support Oracle business rules. A decision component is a mechanism for publishing the rules and rule sets as reusable service can be invoked from multiple business processes. These rules can be changed without redeploying the code.
29. Why use Bpel and Osb?
Ans:
OSB is the light-weight service bus wherever there is not much business logic involved and there is a need to just get a message routed between systems OSB is used whereas when there is more business logic involved in the process, then BPEL will be used.
30. What is MDS?
Ans:
- JAR (Deployment unit) size will be reduced.
- Duplication of artifacts can be avoided between services.
MDS –Metadata Store : Wsdl and Schemas to be used in the process can published to MDS and get it used in code by a referring artifacts from the MDS
31. What is XA Data Source? How does it differ from Non-XA Data Sources?
Ans:
An XA transaction involved coordinating a transaction manager, with the one or more databases all involved in a single global transaction. Non-XA transactions have no transaction coordinator, and a single resource is doing all of the transaction work itself (this is sometimes called a local transaction).
32. How to deploy Xsl file without deployment of Bpel process?
Ans:
- Using an ANT script by a file replacement in the TMP folder.
- By creating the folder in BPEL PM Installation folder and specifying its location in BPEL code with http call and replacing the xslt to that location.
33. What is HA File And FTP Adapters?
Ans:
The term “H.A. file” is a bit unclear without more information. However, FTP adapters are essentially helpful assistants for computer systems. They use a protocol called FTP to simplify and secure the sharing of files between different applications.
These adapters play the role of dependable couriers, making it easier for businesses to automate and organize tasks related to files. They come with user-friendly features like scheduling and security measures to ensure everything runs smoothly.
34. What is Singleton Property in SOA?
Ans:
In Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA), a “singleton” typically refers to a design pattern ensuring that a specific service has only one instance in the entire system. This means there’s a single shared instance of that service handling requests from different parts of the system.
Using the Singleton pattern in SOA can be beneficial for maintaining a centralized state or resource. However, it’s essential to carefully consider the implications for scalability and flexibility in the overall system design.
35. What is Pick Activity?
Ans:
A “Pick Activity” in the context of business process modeling refers to a step where the system waits for one out of multiple events to occur. It’s like waiting for different things to happen, and once one of them occurs, the process moves forward based on that specific event.
It’s a way to model processes that involve making a decision based on whichever event happens first among several possibilities.
36. What is Flow Activity?
Ans:
Flow activity is used, when the parallel execution of a flow is needed and to use this property “non blocking invoke should be set as a true “at the partner link level and no. of execution of the parallel flow is explained and static. Where in Flown the number of execution of parallel flow is not static and it is determined during the run time.
37. What is Non-idempotent Activity?
Ans:
A “Non-idempotent Activity” is a task or operation that, when performed multiple times, doesn’t produce the same result. In simpler terms, doing the activity more than once may have different or cumulative effects each time, making the outcome dependent on the number of repetitions.
38. How does Pick Activity differ From Receiving Activity?
Ans:
- Pick activity can act as the multiple receive activity in some business scenarios.
- If you have two inbound operations and both can trigger the bpel process then will go with pick activity as can’t have a two receive activity with create the Instance box checked.
39. How can make Partner Link Dynamic?
Ans:
If you have to send the request to the various services which have the same wsdl then dynamic partner link will be used and using addressing schema can set the endpoint dynamic to send request to desired service.
40. What is Non Blocking All Property?
Ans:
Non-blocking invocation is used when the Parallel flow needs to be executed where a new thread will be created for every invoke an activity and which will execute simultaneously.
41. How do you handle transactions in Bpel?
Ans:
Property needs to be explained to start a new transaction or to continue with the same transactions.
Property Name : Transaction and if this has value as needed then BPEL process will be continued in the same transaction where as if value is explained as requiring a new then it will start a new transaction.
42. What are Transient and Durable Bpel processes?
Ans:
- Durable: It is the long running process initiated through the one-way invocation and incur one or more dehydration points in the database during execution.
Example : Asynchronous
- Transient: It is the short-lived process, request-response style processes and do not incur the dehydration during their process execution.
Example : Synchronous
43. When will I go for Sync Process?
Ans:
Whenever the service returns a response in a few seconds, it is going for the synchronous BPEL process, if not the BPEL process should be Asynchronous the reason is calling application cannot proceed further in case of synchronous process.
44. What is sync file read operation?
Ans:
When a file has to be read in the middle of the BPEL process, then it will use the syncFileRead Operation, which means some process should initiate the file read process and it is an outbound operation and the process can’t begin with Sync File read.
45. How do resubmit faulted process?
Ans:
- Scenario A : BPEL code uses the fault-policy and a fault is handled using “ora human-intervention” activity, then fault is marked as a Recoverable and the instance state is set to “Running”.
- Scenario B : The BPEL code used fault-policy and a fault is caught and re-thrown using “ora-rethrow-fault” action, then a fault is marked as the Recoverable and an instance state is set to “Faulted”; provided fault is recoverable one (like URL was not available).
46. What are predefined errors in Bpel?
Ans:
- Custom errors
- Timed out errors
- BPM errors
- Validation Errors
47. What is a Web Service?
Ans:
A web service is a standardized technology that allows different software applications to communicate over the internet. It promotes interoperability between systems by using protocols like HTTP or SOAP.
Web services facilitate data exchange, integration of diverse systems, and remote procedure calls, enabling applications to work together seamlessly. They are a key element in Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA), with common types including RESTful and SOAP web services.
48. Difference between URI and URL.
Ans:
- A URI is an identifier for a resource, but a URL gives the specific information as to obtain that resource.
- A URI is a URL and as one commenter pointed out, it is now considered incorrect to use URL when describing the applications. Generally, if the URL describes both location and name of the resource, the term to use is URI. Since this is a common case most of us encounter every day, URI is a correct term.
49. What is a Mediator?
Ans:
- The Mediator is in charge of interconnecting, within an SOA composite application, components that expose the various interfaces. In addition, the Mediator can perform duties like filtering and making routing decisions.
- The composite editor in the Jdeveloper gives the flexibility to define the interface now, to choose an existing interface, or to explain the interface later as wire components to a Mediator.
- Transforming data from one representation to another is, along with routing, one of the key functions of the Mediator.
50. Difference between ESB and Mediator.
Ans:
- In 10g for routing, separate routers need to be kept along with the ESB for routing and filter expressions.
- Whereas in 11g mediator contains the routing rules and filter expressions itself.
51. Is it possible to use Ms Sql server as a dehydration store with SOA suite ?
Ans:
Yes it is possible to automatically maintain long-running asynchronous processes and current state information in a database while they wait for asynchronous callbacks, use the database as a dehydration store. This feature increases BPEL process reliability and scalability. Used to support the clustering and failover.
52. What is Service Component Architecture (SCA) used for?
Ans:
Service Component Architecture assembly model abstracts an implementation and allows the assembly of components, with little implementation details. SCA enables the business logic as reusable service components that can be simply integrated into any SCA-compliant application.
The resulting application is known as the SOA composite application. The specification for SCA standard is maintained by the Organization for an Advancement of Structured Information Standards (OASIS).
53. What is Service Data Objects (SDO)?
Ans:
Service Data Objects (SDO) offers the data programming architecture. It offers a standardized view on data, and provides efficient transportation, as well as change capture, in the form of change summary. More specifically, it collects the data graph of related business objects, called DataObjects. This graph tracks a schema that describes a DataObjects.
54. What is Business Process Execution Language (BPEL)?
Ans:
BPEL offers enterprises with the industry standard for the business process orchestration and execution. Using the BPEL, design a business process that integrates a series of discrete services into the end-to-end process flow. This integration reduces the process cost and complexity.
55. What components comprise Oracle Soa Suite installation?
Ans:
- Service Infrastructure
- Oracle Mediator
- Oracle Adapters
- Business Events and Events Delivery Network
- Oracle Metadata Repository
- Oracle Business Rules
- Oracle WSM Policy Manager
- Oracle BPEL Process Manager
- Human Workflow
- Oracle Business Activity Monitoring
56. What is Oracle Mediator?
Ans:
- Route: Finds the service component to which to send the messages.
- Validate: Provides the support for validating incoming message payload by using schematron or an XSD file.
- Filter: If specified in rules, apply the filter expression that specifies the contents of a message be analyzed before any service is invoked.
- Transformation: If specified in the rules, transforms document data from a one XML schema to another, thus enabling data interchange among the applications using the various schemas.
Oracle mediator is used for the route, validate, filter and transform data from a service provider to an external partner.
57. What is an Oracle Service Bus?
Ans:
Oracle Service Bus provides the standalone service bus capabilities, enabling separation between the application developers and target systems or services. Oracle Service Bus receives the messages through the transport protocol like HTTP(S), JMS, File, and FTP, and sends messages through the same or a variety of transport protocols.
Service response messages follow an inverse path. Oracle Service Bus handles the deployment, management, mediation, messaging, security and governance of implementing SOA to enterprise applications.
58. What are Oracle Adapters?
Ans:
- BAM
- FTP
- Java Messaging Service (JMS)
- Advanced Queuing (AQ)
- Files
- Message Queuing (MQ) Series
- Legacy Adapters
- Application Adapters
Oracle Adapters use JCA technology to connect the external systems to be Oracle SOA Suite. Oracle SOA Suite provides following technology adapters to an integrate with transport protocols, data stores, and messaging middleware:
59. What is Business Events?
Ans:
Business events are the messages sent as a result of the occurrence or situation, such as new order or completion of order. In Oracle SOA Suite, a mediator service component subscribes .When an event is published, other applications can subscribe to it.
60.What is Oracle Metadata Repository?
Ans:
Oracle Metadata Repository MDS stores business events, rulesets for use by a Oracle Business Rules, XSLT files for Oracle Service Bus and Oracle Mediator, XSD XML schema files for an Oracle BPEL Process Manager, WSDL files, and metadata files for a difficult Event Processing.
61. What is Oracle Business rules used for?
Ans:
Oracle Business Rules, initiated by the BPEL process service component, enable dynamic decisions at a runtime. In addition, human task and mediator service components can make use of rules for dynamic routing.
62. Can we buy an SOA or must build one?
Ans:
To move an organization toward the greater service orientation, we need to take a balanced approach to building versus buying. To create infrastructure for an SOA, need right commercial off-the-shelf software that complements (rather than replaces) existing IT infrastructure.
This is a “buy” statement. On a “build” side, may also choose to access know-how and hands-on involvement to use Software products effectively and get most out of them. This infrastructure and associated tools can help to create business services that run on the SOA.
63. What is the target namespaces function?
Ans:
The target namespace declares namespace for the other xml and xsd documents to refer to schema. The target prefix in this case refers to the same namespace and would use it within this schema definition to reference other elements, attributes, types, etc.
64. What is File ChunkedRead?
Ans:
This is the feature of Oracle File and FTP Adapters that invoke activity within a while loop to process the target file. This feature enables the process of arbitrarily large files.If invalid payload is provided, ChunkedRead scenarios do not throw the exception. When a translation exception is encountered, the return header is populated with the translation exception message including the details such as line and column where error occurred.
65. What are multiple directories supported in File & FTP adapter?
Ans:
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters are the support polling multiple directories within single activation. specify the multiple directories in a JDeveloper as opposed to a single directory. This is applicable to physical and logical directories.
66. What is a DB-Based MDS Repository?
Ans:
Database-based repositories are used in production environments where robustness is needed. These repositories are created using the Repository Creation Utility application from Oracle. This utility helps with creation of new database schema with its corresponding tables and objects. Repositories can later be registered or deregistered by the Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control console.
67. What is OWSM?
Ans:
OWSM stands for the Oracle Web Service Manager. Oracle Web Services Manager provides a comprehensive and easy-to-use solution for policy management and security of service infrastructure. It is a standalone platform for securing and managing the access to web services.
68. What is echo in Oracle Mediator?
Ans:
The purpose of echo option is to expose all Oracle Mediator functionality as callable service without having to route it to any other service. For example, you can call an Oracle Mediator to perform transformation, a validation, or an assignment, and then echo Oracle Mediator back to the application without routing it anywhere else.
69. Difference between Read & Sync-Read operation in File & FTP adapter.
Ans:
Read is used when Polling is required to be done while SyncRead is used when required to read a file in between the need to have the asynchronous communication.
70. What is File Debatching?
Ans:
When a file contains multiple messages, it can choose to publish messages in the particular number of batches. This is referred to as debating. During debatching, file reader, on restart, proceeds from where it left off in the previous run, avoiding the duplicate messages. File debatching is supported for files in XML and native formats.
71. What are the types of Rejection Message Handlers?
Ans:
- Web Service Handler
- Custom Java Handler
- JMS Queue
- File
72. What is an inline schema?
Ans:
Inline schemas are the XML schema definitions including the inside XML instance documents. Like an external schema document, inline schemas can be used to validate that instance matches the schema constraints.
73. What are 3 major roles of SOA?
Ans:
- service provider
- service broker
- service registry
- service repository
- service requester/consumer
There are the three roles in each of the Service-Oriented Architecture building blocks:
74.What are the 3 types of SOA templates?
Ans:
- Project Level Template
- Component Level Template
- Custom Activity Level Template
Templates in SOA 12c can be created at the three different levels:
75. Why use Decision service ?
Ans:
- For the business rules & policies
- For Decision Making & Policies
- Business Rules are also called the Decision Component
76. What is MDS ?
Ans:
MDS stands for the Oracle MetaData Service. It is a central repository inside Oracle Fusion Middleware
MDS’s purpose is to provide a centralized store where users can keep, manage & access metadata.
77. What is a DB-Based MDS Repository?
Ans:
Database-based repositories are used in production environments where robustness is needed. These repositories are created using the Repository Creation Utility (RCU) application from Oracle. This utility helps with the creation of a new database schema with corresponding tables and objects. Repositories can later be registered or deregistered by the Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control console.
78. What is Dynamic Routing in Mediator?
Ans:
The dynamic routing rule can externalize the routing logic to an Oracle Rules Dictionary, which in turn enables the dynamic modification of the routing logic in a routing rule.
When choosing to create a dynamic routing rule then it creates the new business rule service component that is wired to the Oracle Mediator service component within SOA composite of an Oracle Mediator service component. The business rule service component includes the rule dictionary.
The rule dictionary is the metadata container for rule engine artifacts, like fact types, rulesets, rules, decision tables, and so on.
79. What are standard faults in BPEL?
Ans:
- BindingFault
- ConflictingReceive
- Conflicting request
- Correlation violation
- Forced termination
- Invalid reply
- Join failure
- MismatchedAssignmentFailure
- Remote fault
- RepeatedCompensation
- Selection failure
80. How many ways can we add OWSM policy to Web Service?
Ans:
- Through the policy annotations at design time
- By the Administration Console at runtime
- By Fusion Middleware Control or WLST
81. Why use Call-template inside XSL?
Ans:
Call-template works similarly to apply-template elements in XSLT. Both attach the template to specific XML data. This provides formatting instructions for the XML. The main difference between two processes is that a call function only works with a named template. And must establish a ‘name’ attribute for the template in order to call it up to a format document.
82. What is the use of a Trigger file?
Ans:
By default, polling by inbound Oracle File and FTP Adapters start as soon as the endpoint is activated. However, if you want more control over polling, then you can use a file-based trigger. Once an Oracle File or FTP Adapter finds a specified trigger file in a local or remote directory, it starts polling for files in the inbound directory.
83. Difference between XA & Non-XA transactions.
Ans:
Non-XA (Local Transaction): It involves only one resource. When using Non-XA transactions then you can’t involve the multiple resources (different databases, Queues, application servers, etc), can rollback or commit transactions for only one resource. There is no transaction manager for this transaction as we are dealing with only one resource at time.
XA (Global Transaction): It involves more than one resource (different databases, queues, application servers) all participate in a one transaction. It uses the two-phase commit to ensure that all resources either all commit or rollback any particular transaction. When you have a scenario like needing to connect to the two different databases, JMS Queue and application server, in this case, will use XA transaction that means all the resources participate in the one transaction only.
84. What are the types of Rejection Message Handlers?
Ans:
- Web Service Handler
- Custom Java Handler
- JMS Queue
- File
85. What are the types of Adapters?
Ans:
Transactional & Non- Transactional Adapter
Transactional: Database, JMS, AQ, MQ adapters
Non Transactional: File & FTP adapter
86. What is the scope of Policy Sets?
Ans:
Domain: All the policy subjects of the specified type in the domain
Application or Partition: All policy subjects of specified type in an application or SOA partition
Application module or SOA composite: All the policy subjects of the specified type in the application module or SOA composite
Service or reference: All policy subjects of a specified type in SOA service or reference
Port or component: All policy subjects of a specified type in the port or SOA component
87. What is SCA with respect to Oracle SOA platform?
Ans:
SCA is also known as Service Component Architecture. This type of architecture provides the underlying programming model in order to design the application in the Oracle environment.
It is also regarded as the model whose primary purpose is to encompass a broad range of service strategies and technologies.
In this context, it is also important to note that it facilitates necessary technical know-how to connect access methods.
88. Difference between components and services.
Ans:
Should be well aware of the fact that services are also known as the logical coupling of various parts so that functionality of developing the business application can be achieved.
On the other hand, the components are also referred to as the implementation approaches in order to create the service. And should also be aware of the fact that these components can be in the C++ and Java.
On the contrary, the services would be exposed in the general format that resembles the web services.
89. Define DVM and utility in SOA implementation process.
Ans:
DVM is also known as the Domain Value Map. It is defined as the static mapping between the trigger system and source. It can also be used in transformations. Moreover, this value can be changed with help of SOA Composer.
90. Shed light on dehydration store in SOA environment.
Ans:
A dehydration store is also known as the database where the instances are stored. The database gets dehydrated or devoid of the values when there is a constant occurrence of the various futile activities.
It also saves information when the application runs for the extended period of time.






