
An integrated suite of business tools called Oracle E-Business Suite makes a number of organisational tasks simpler and more automated. Providing a comprehensive solution for organisations, it includes modules for supply chain, human resources, financials, and other areas. With a robust architecture, Oracle EBS supports multi-organization structures, providing flexibility to adapt to diverse business needs. Its key features include scalability, customization capabilities, and a unified data model, fostering efficiency and collaboration across different functional areas. Oracle EBS continues to be a widely used enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution, helping businesses optimize operations and enhance decision-making.
1. What is Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS)?
Ans:
The integrated package of business applications known as Oracle E-Business package (EBS) is offered by Oracle Corporation. It encompasses various enterprise resource planning (ERP) modules to streamline various business processes, including financials, supply chain, human resources, projects, and more.
2. Explain the major modules in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
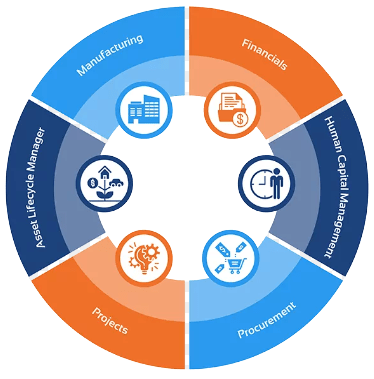
Oracle EBS consists of several major modules, including:- Financial Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Human Capital Management
- Projects
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Procurement
- Manufacturing
3. What are the key features of Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Key features of Oracle EBS include:
- Comprehensive Suite: Covers various business functions.
- Integrated: Modules seamlessly share information.
- Flexibility: Adaptable to industry-specific needs.
- Scalability: Scales with the growth of the organization.
- Global Support: Supports multi-currency and multi-language operations.
- Robust Reporting: Provides extensive reporting and analytics capabilities.
4. What distinguishes Oracle Fusion from Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Oracle EBS and Oracle Fusion are both ERP systems from Oracle, but there are differences:- Technology: EBS uses a more traditional architecture, while Fusion uses a more modern service-oriented architecture (SOA).
- Deployment: EBS is typically on-premises, while Fusion offers both on-premises and cloud deployment options.
- Integration: Fusion is designed with better integration capabilities, and it combines the best features from various Oracle applications.
5. What is a Concurrent Manager in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
A Concurrent Manager in Oracle EBS is a component responsible for managing concurrent requests. Concurrent requests are background processes that run simultaneously with the online operations, performing tasks such as running reports, data processing, and batch jobs.
6. Explain the key tables in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Oracle EBS has numerous tables, and some key ones include:- FND_USER: Stores user information.
- HR_ALL_ORGANIZATION_UNITS: Contains organizational unit details.
- AR_INVOICE_ALL: Stores information about invoices.
- AP_INVOICES_ALL: Contains details about accounts payable invoices.
- PO_HEADERS_ALL: Stores information about purchase order headers.
7. Describe the Multi-Org structure in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Multi-Org (Multi-Organization) in Oracle EBS enables the management of multiple legal entities within a single installation. It allows organizations to operate various entities independently while sharing common data and setup. Each organization has its own set of books, operating units, and other organizational elements.
8. What is Flexfield in Oracle EBS? Explain its types.
Ans:
A Flexfield in Oracle EBS is a customizable field that allows users to define additional data fields as needed. There are two main types:
- Key Flexfields (KFF): Used to capture key information unique to an organization’s business model.
- Descriptive Flexfields (DFF): Provide additional attributes or contextual information for transactional or master data.
9. What is AOL (Application Object Library) in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
AOL is a set of services and utilities in Oracle EBS that provides a framework for building applications. It includes features like concurrent processing, Flexfields, security, and profile options. AOL ensures consistency and standardization across Oracle EBS applications.
10. What is the significance of MOAC (Multi-Org Access Control) in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
MOAC allows users to access data across different organizations within Oracle EBS. It enables a user to operate in multiple organizations simultaneously while maintaining data security. MOAC ensures that users see only the data relevant to their responsibilities in each organization, providing a consolidated view across entities.
11. How does Oracle Workflow function in EBS?
Ans:
Oracle Workflow in EBS automates business processes by defining, managing, and tracking the flow of information within an organization. It allows users to design workflows that represent business processes and automate the routing of information and tasks among individuals or systems.
12. Explain the purpose and use of Oracle Alerts in EBS.
Ans:
Oracle Alerts in EBS are used for real-time monitoring of business events. They allow users to define conditions or events that, when met, trigger notifications, reports, or other actions. Oracle Alerts help organizations proactively manage exceptions and respond quickly to critical situations.
13. What is the Application Tier and Database Tier in Oracle EBS architecture?
Ans:
The Application Tier in Oracle EBS architecture includes components that handle user interfaces, business logic, and application processing. The Database Tier consists of the database server where data is stored and managed. These tiers work together to provide a complete ERP solution.
14. Describe the various types of responsibilities in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
In Oracle EBS, responsibilities define the user’s access and privileges. Types of responsibilities include:
- System Administrator Responsibility: Grants access to administrative functions.
- Data Entry Responsibility: Provides access to data entry and transactional tasks.
- Inquiry Responsibility: Allows users to view data but not perform transactions.
15. What are the concurrent programs in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Concurrent programs in Oracle EBS are background processes that run simultaneously with online operations. They perform tasks such as running reports, data processing, and batch jobs. Concurrent programs are submitted by users and executed by the Concurrent Manager.
16. What is the purpose of the ‘Request Set’ in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
A Request Set in Oracle EBS is a collection of related concurrent programs that are submitted and executed together as a unit. It allows users to group and run multiple programs in a specific sequence, streamlining complex business processes.
17. Explain the importance of Key and Descriptive Flexfields in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Key Flexfields capture unique identifiers for business entities, while Descriptive Flexfields provide additional information for customization. Both types of Flexfields offer a high degree of flexibility, allowing organizations to adapt Oracle EBS to their specific business needs.
18. What is the purpose of Application Object Library (AOL) in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Application Object Library (AOL) in Oracle EBS provides a set of common services and utilities used by Oracle applications. It includes features such as security, Flexfields, profile options, and concurrent processing, ensuring consistency and standardization across the application suite.
19. Explain the difference between Key and Descriptive Flexfields.
Ans:
| Aspect | Key Flexfields (KFF) | Descriptive Flexfields (DFF) | |
| Purpose |
Uniquely identifies records/entities. |
Captures additional information about records. | |
| Flexibility | Limited, predefined segments. | Highly customizable, user-defined segments. | |
| Usage | Common in critical areas like Chart of Accounts. | Custom attributes in entities like employees. | |
| Common Examples |
Chart of Accounts, Item Codes. |
Employee details, Customer profiles. |
20. What are the various types of patches in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Various types of patches in Oracle EBS include:
- Release Update Packs (RUPs): Cumulative patches providing bug fixes and updates.
- Family Packs: Collections of RUPs for specific functional areas.
- Critical Patch Updates (CPUs): Security patches addressing critical vulnerabilities.
- One-Off Patches: Individual patches for specific issues.
- Mini-Packs: Consolidated patches for specific modules or features.
21. How can you manage security in Oracle EBS?
Ans: The SQL Statements are:
Security in Oracle EBS is managed through various components, including:
- Responsibilities: Assigning specific responsibilities to users based on their roles.
- User Management: Creating and managing user accounts with appropriate access.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Defining roles and associating them with specific functions.
- Profile Options: Configuring system-wide parameters to control behavior.
- Data Security Policies: Implementing policies to control access to specific data subsets.
22. Explain the purpose of the Concurrent Manager in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
The Concurrent Manager in Oracle EBS is responsible for managing concurrent requests. It schedules, monitors, and executes background processes (concurrent programs) submitted by users. The Concurrent Manager ensures efficient use of system resources and provides a mechanism for running tasks concurrently.
23. What is the role of FNDLOAD in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
FNDLOAD is a utility in Oracle EBS used for migrating and downloading metadata objects between instances. It allows users to transfer configurations, setups, and personalizations, making it useful for development, testing, and deployment activities.
24. How does Multi-Org Access Control (MOAC) function in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
MOAC in Oracle EBS allows users to operate across multiple organizations within a single installation. It ensures that users see only the data relevant to their responsibilities in each organization, providing a consolidated view while maintaining data security and isolation between organizations.
25. Explain the significance of profiles in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Profiles in Oracle EBS are used to set system parameters and control application behavior. They influence the appearance and functionality of forms, concurrent programs, and other components. Profiles can be set at various levels, including site, application, and user, allowing for customization and configuration.
26. Describe the significance of Forms Personalization in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Forms Personalization in Oracle EBS enables users to customize the appearance and behavior of Oracle Forms. It allows organizations to tailor the user interface, implement business rules, and enhance user experience without modifying the underlying code. Forms Personalization is often used for making forms more user-friendly and aligned with specific business processes.
27. What is Oracle Configurator in Oracle EBS? What is its use?
Ans:
Oracle Configurator is a module in Oracle EBS that enables the configuration of complex products and services. It allows users to define and customize product options, features, and rules to meet customer-specific requirements. Oracle Configurator is often used in industries with highly configurable products, such as manufacturing and engineering.
28. What are Value Sets in Oracle EBS? Explain the different types.
Ans:
Value Sets in Oracle EBS define the valid set of values for specific attributes. There are different types of Value Sets, including:
- Independent: Contains a predefined list of values.
- Dependent: Values depend on the selection of another value.
- Table: Values come from a table.
- Pair: Two values together represent a valid combination.
29. What is the significance of the Flexfield Qualifier in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Flexfield Qualifiers in Oracle EBS are used to categorize and classify Flexfield segments. They provide additional information about the nature of the data captured by a segment. Flexfield Qualifiers help in organizing and validating data within Flexfields, ensuring accurate and meaningful representation.
30. Explain the purpose and function of a Key Flexfield in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
A Key Flexfield in Oracle EBS is used to capture unique identifiers for business entities, such as account numbers, product codes, or employee IDs. It provides a structured way to represent key information specific to an organization’s business model. Key Flexfields are often critical for identifying and differentiating records in various modules of Oracle EBS.
31. What are the different types of reports available in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Oracle EBS offers various types of reports, including:
- Standard Reports: Predefined reports provided by Oracle EBS modules.
- Ad Hoc Query Reports: Customizable reports created by users using ad hoc query tools.
- Financial Reports: Reports related to financial transactions and statements.
- Operational Reports: Reports providing operational insights across different modules.
32. How do concurrent programs differ from concurrent requests in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
In Oracle EBS, a concurrent program is a background process or executable, while a concurrent request is the user-submitted task that initiates the concurrent program. Multiple requests can run the same concurrent program concurrently, and the Concurrent Manager manages their execution.
33. What is the purpose of ‘Key Flexfield Segments’ in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
‘Key Flexfield Segments’ in Oracle EBS represent the individual components or segments within a Key Flexfield structure. They capture specific information about key business entities, such as chart of accounts, cost centers, or product codes. Key Flexfield Segments play a crucial role in identifying and categorizing data within Oracle EBS.
34. Explain the concepts of ‘SOB’ (Set of Books) and ‘LE’ (Legal Entity) in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
In Oracle EBS, a Set of Books (SOB) represents a financial reporting entity, including a chart of accounts, calendar, and currency. A Legal Entity (LE), on the other hand, is an entity recognized by law, and it may encompass one or more sets of books. Legal Entities are essential for legal and regulatory compliance.
35. What is the significance of the ‘Document Sequence’ in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
The ‘Document Sequence’ in Oracle EBS refers to the unique identifier assigned to financial transactions or documents. It ensures that each transaction receives a distinct identifier for tracking and reporting purposes. Document Sequences help maintain data integrity and provide a systematic way to organize financial information.
36. Explain the purpose of Auto Invoice in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Auto Invoice in Oracle EBS automates the process of importing and validating external invoices into the Accounts Receivable module. It allows organizations to efficiently process large volumes of invoices, reducing manual effort and ensuring accuracy in financial transactions.
37. Describe the different types of tables in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Oracle EBS includes various types of tables, such as:- Transaction Tables: Store transactional data.
- Setup Tables: Hold configuration and setup information.
- History Tables: Maintain historical records of data changes.
- Interface Tables: Temporary storage for data before processing.
- Flexfield Tables: Store flexfield-related information.
38. What are the key tables in Oracle General Ledger?
Ans:
Some key tables in Oracle General Ledger include:
- GL_JE_BATCHES: Stores journal entry batches.
- GL_JE_HEADERS: Contains journal entry headers.
- GL_JE_LINES: Stores journal entry lines.
- GL_CODE_COMBINATIONS: Holds code combinations for the chart of accounts.
39. What is Subledger Accounting (SLA) in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Subledger Accounting (SLA) in Oracle EBS is a rules-based accounting engine that centralizes accounting functions for subledger modules (e.g., Payables, Receivables). SLA allows organizations to define and enforce accounting policies consistently across various subledgers, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
40. Explain the functions and uses of Flexfield Value Sets.
Ans:
Flexfield Value Sets in Oracle EBS define the valid set of values that can be used for a specific flexfield segment. They control data entry, validation, and display of flexfield segments. Value Sets can be of various types, such as Independent, Dependent, Table, or Pair, offering flexibility in capturing and validating data.
41. How does the Flexfield structure work in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
The Flexfield structure in Oracle EBS allows users to define and customize data entry forms by adding segments. These segments capture specific information about business entities, such as accounts or cost centers. Users can configure the Flexfield structure to match their organization’s unique requirements, providing flexibility in data representation.
42. Describe the significance of ‘Concurrent Request Set’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
A Concurrent Request Set in Oracle EBS is a collection of related concurrent requests that are submitted and executed together. It enables users to group and manage multiple requests as a single unit, streamlining the execution of complex business processes with specific sequencing requirements.
43. What is the purpose of ‘DFF’ (Descriptive Flexfield) in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
- Descriptive Flexfields (DFF) in Oracle EBS allow users to capture additional information beyond the standard fields available in data entry forms.
- They provide a customizable way to collect and store descriptive data related to specific business entities, enhancing the depth of information recorded in the system.
44. How does the Flexfield open interface work in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
The Flexfield open interface in Oracle EBS allows users to import and update Flexfield values using predefined interfaces. It provides a mechanism for mass data entry and updates, enabling organizations to efficiently manage Flexfield information across various modules.
45. Explain the significance of Concurrent Request ‘Phase’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
The Concurrent Request ‘Phase’ in Oracle EBS represents the current stage or status of the concurrent request execution process. Phases include pending, running, completed, etc. Monitoring the phase helps users track the progress of concurrent requests and identify potential issues in the execution flow.
46. What is ‘Concurrent Program Execution’ in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Concurrent Program Execution in Oracle EBS refers to the process of running concurrent programs or background processes. Users submit concurrent requests, and the Concurrent Manager manages the execution of these programs. Concurrent Program Execution allows users to perform tasks like running reports, data processing, and batch jobs concurrently with online operations.
47. Describe the Flexfield Value Set Validation process in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
- Flexfield Value Set Validation in Oracle EBS ensures that data entered for Flexfield segments adheres to predefined rules and values.
- It validates user input against the configured Value Set, ensuring data accuracy and integrity. Value Set Validation helps maintain consistency in data representation.
48. How does the ‘Concurrent Manager’ monitor and control jobs in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
The Concurrent Manager in Oracle EBS monitors and controls concurrent jobs by scheduling, prioritizing, and executing concurrent requests. It manages the concurrent program execution lifecycle, allocates resources, and ensures the efficient utilization of system resources to meet user-defined priorities and service levels.
49. What are ‘Concurrent Request Sets’ and their use in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Concurrent Request Sets in Oracle EBS are collections of concurrent requests that are submitted and executed together as a single unit. They allow users to streamline and automate the execution of multiple concurrent requests, making it easier to manage complex business processes with specific sequencing requirements.
50. Explain the purpose of ‘SOB’ (Set of Books) in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
A Set of Books (SOB) in Oracle EBS represents a financial reporting entity with a specific chart of accounts, calendar, and currency. It provides the framework for financial transactions and reporting. SOBs are essential for organizing financial data and ensuring accurate financial statements and compliance.
51. What is the significance of Oracle Forms and Reports in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Oracle Forms and Reports are integral components of Oracle EBS, providing a user-friendly interface for data entry and reporting. Oracle Forms allow users to interact with the application, entering and retrieving data, while Oracle Reports facilitate the generation of various types of reports, supporting decision-making processes.
52. Explain the difference between ‘Responsibility’ and ‘Request Group’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
In Oracle EBS, a Responsibility defines a user’s access and privileges, including the menu options available to them. A Request Group, on the other hand, is a collection of concurrent programs grouped together for easier assignment to responsibilities. While responsibilities control overall access, request groups govern access to specific concurrent programs.
53. What is the ‘Concurrent Processing’ architecture in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Concurrent Processing in Oracle EBS is the architecture that manages and executes background processes, known as concurrent programs. It includes components like the Concurrent Manager, which schedules and monitors concurrent requests, and the concurrent programs, which perform tasks such as running reports and batch jobs.
54. How does ‘Table Registration’ work in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
- Table Registration in Oracle EBS involves registering tables in the Oracle E-Business Suite database to make them visible and accessible to Oracle Forms and Reports.
- This process ensures that custom tables can be used seamlessly within the application, allowing for integration and reporting capabilities.
55. Describe the importance of ‘Key Flexfield Structure’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
The Key Flexfield Structure in Oracle EBS defines the arrangement and organization of segments within a Key Flexfield. It plays a crucial role in capturing unique identifiers for business entities, ensuring consistency and standardization in representing key information specific to an organization’s business model.
56. What is the use of ‘FNDLOAD’ in Oracle EBS? How is it beneficial?
Ans:
‘FNDLOAD’ is a utility in Oracle EBS used for downloading and uploading metadata objects and configurations between instances. It facilitates the migration of setups, personalizations, and customizations, saving time and effort in development, testing, and deployment activities.
57. Explain the role and significance of the ‘Application Object Library’ (AOL) in Oracle EBS.
The Application Object Library (AOL) in Oracle EBS provides a set of common services and utilities used by Oracle applications. It includes features such as security, concurrent processing, profile options, and Flexfields. AOL ensures consistency, standardization, and shared functionality across the Oracle E-Business Suite.
58. What is the ‘Flexfield Value Set’ security feature in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
‘Flexfield Value Set’ security in Oracle EBS allows administrators to control access to specific values within a Flexfield Value Set. It helps enforce data security policies by restricting user access to only authorized values, ensuring that sensitive or confidential information is protected.
59. How does ‘AutoPatch’ function in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
‘AutoPatch’ in Oracle EBS is a tool used for applying patches and updates to the application. It automates the patching process, handling tasks such as copying files, generating reports, and updating database objects. ‘AutoPatch’ streamlines the patching procedure, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring a consistent application environment.
60. Explain the process of defining ‘Concurrent Programs’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Defining Concurrent Programs in Oracle EBS involves configuring the background processes that perform specific tasks. This includes specifying the executable, parameters, and options for concurrent programs. Once defined, concurrent programs can be associated with responsibilities and request groups for user access and execution.
61. What are the different types of Flexfield Event Points in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Flexfield Event Points in Oracle EBS are triggered at different stages of data entry. Some types include:
- Pre-Validation Event: Triggered before data validation.
- Post-Validation Event: Triggered after data validation.
- Post-Update Event: Triggered after data is saved.
62. Describe the functions of ‘Document Sequencing’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Document Sequencing in Oracle EBS assigns unique identifiers to financial transactions or documents. It ensures a systematic order for document creation and provides a coherent sequence for reporting and auditing purposes.
63. What is the role of ‘System Administrator’ in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
The System Administrator in Oracle EBS is responsible for managing and maintaining the E-Business Suite environment. This role involves tasks such as user administration, security setup, concurrent processing management, and system configurations.
64. How is a ‘Flexfield Structure’ used in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
- Flexfield Structures to match their unique data entry requirements.
- A Flexfield Structure in Oracle EBS defines the arrangement of segments within a Flexfield.
- It is used to capture and store data specific to an organization’s business model.
65. Explain the use and purpose of ‘Concurrent Processing’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Concurrent Processing in Oracle EBS allows users to run multiple background processes simultaneously. It includes tasks like running reports, data processing, and batch jobs. Concurrent Processing enhances system efficiency by enabling users to perform tasks concurrently with online operations.
66. What is the significance of the ‘MO: Security Profile’ in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
‘MO: Security Profile’ in Oracle EBS is used to control access to multiple organizations (Multi-Org). It ensures that users see only the data relevant to their responsibilities within each organization, maintaining data security and integrity.
67. Describe the process of managing ‘Concurrent Request’ priorities in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Managing Concurrent Request priorities in Oracle EBS involves assigning priority levels to concurrent requests. This determines the order in which requests are processed by the Concurrent Manager. Higher priority requests are given precedence in the processing queue.
68. Explain the functionality and use of ‘Workflow’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Workflow in Oracle EBS automates and streamlines business processes. It defines, manages, and tracks the flow of information, tasks, and approvals among users or systems. Workflow ensures efficient and standardized process execution across the organization.
69. What is ‘Profile Option’ and how is it used in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
- A ‘Profile Option’ in Oracle EBS is a customizable setting that controls the behavior of the application. It can be set at various levels, including site, application, and user.
- Profile Options allow administrators to tailor the application’s functionality to meet specific business requirements.
70. Describe the significance of ‘Key Flexfield Qualifiers’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Key Flexfield Qualifiers in Oracle EBS categorize and provide additional information about Flexfield segments. They play a vital role in organizing and validating data within Flexfields, ensuring accurate and meaningful representation of key information specific to an organization’s needs.
71. What is the role of ‘Key Flexfield Value Sets’ in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
‘Key Flexfield Value Sets’ in Oracle EBS define the valid set of values that can be used for individual segments within a Key Flexfield. They play a crucial role in controlling and validating data entry, ensuring that key information is accurately represented.
72. Explain the concept of ‘Concurrent Program Library’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
The ‘Concurrent Program Library’ in Oracle EBS is a repository that stores definitions of concurrent programs. It includes information about the executable, parameters, and options required for program execution. This central library simplifies the management and maintenance of concurrent programs across the E-Business Suite.
73. Describe the process of managing ‘Key Flexfield Segments’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Managing ‘Key Flexfield Segments’ in Oracle EBS involves defining and configuring individual components within a Key Flexfield structure. This process allows users to customize and organize the capture of key business information according to specific organizational needs.
74. What is ‘Flexfield Value Set Security’ in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
- ‘Flexfield Value Set Security’ in Oracle EBS is a feature that allows administrators to control user access to specific values within a Flexfield Value Set.
- It enhances data security by restricting users to authorized values and ensuring compliance with organizational policies.
75. How does ‘FNDLOAD’ aid in migration processes in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
‘FNDLOAD’ in Oracle EBS is a utility used for downloading and uploading metadata objects and configurations between instances. It aids in migration processes by facilitating the transfer of setups, personalizations, and customizations. This simplifies development, testing, and deployment activities.
76. Explain the functionality of ‘Concurrent Program Requests’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
‘Concurrent Program Requests’ in Oracle EBS represent user-submitted tasks that initiate the execution of concurrent programs. While the Concurrent Manager oversees the execution of these requests, users may keep an eye on their status and advancement. This functionality is essential for running reports and background processes.
77. What is the purpose of ‘Flexfield Security’ in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
‘Flexfield Security’ in Oracle EBS allows administrators to control user access to specific Flexfields based on responsibilities. It ensures that users can only view and update data within authorized Flexfields, enhancing data security and integrity.
78. Describe the significance of ‘Key Flexfield Compilation’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
‘Key Flexfield Compilation’ in Oracle EBS is the process of validating and compiling the configuration of Key Flexfields. It ensures that changes to Flexfield structures are correctly implemented and that any customization or extension adheres to the defined rules and structure.
79. Explain the use of ‘Concurrent Manager Recovery’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
- ‘Concurrent Manager Recovery’ in Oracle EBS is a feature that helps recover and restart concurrent managers in the event of failures or disruptions.
- It ensures the continuous and reliable operation of the Concurrent Manager, preventing data loss or process interruptions.
80. What is the role of ‘Flexfield Value Set’ in the validation process in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
‘Flexfield Value Set’ in Oracle EBS defines the set of valid values that can be used for Flexfield segments. During the validation process, the system checks that entered values conform to the predefined Value Set, ensuring data accuracy and integrity within Flexfields.
81. How does ‘Flexfield Security’ differ from ‘Profile Options’ in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
‘Flexfield Security’ controls user access to specific Flexfields based on responsibilities, ensuring data security within those Flexfields. ‘Profile Options’ are system-wide settings that influence the behavior of the application but don’t restrict access to specific data. While both impact system configuration, ‘Flexfield Security’ focuses on data access within Flexfields, while ‘Profile Options’ affect application behavior globally.
82. Explain the process of managing ‘Key Flexfield’ values in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Managing ‘Key Flexfield’ values involves defining, configuring, and maintaining the valid set of values for each segment within a Key Flexfield. This process ensures that data entered aligns with the defined values, providing consistency and accuracy in representing key business entities.
83. What is the ‘Concurrent Processing Program’ and its function in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
The ‘Concurrent Processing Program’ in Oracle EBS refers to background processes or concurrent programs that run simultaneously with online operations. These programs perform various tasks, such as generating reports, processing data, and executing batch jobs, enhancing system efficiency and user productivity.
84. Describe the use and process of ‘Flexfield Structure’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
‘Flexfield Structure’ in Oracle EBS defines the arrangement and organization of segments within a Flexfield. Users can customize Flexfield Structures to capture and represent specific data elements unique to their organization. The process involves configuring the structure to meet business requirements and ensure accurate data capture.
85. How does the ‘Flexfield’ framework enhance data capture in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
The ‘Flexfield’ framework in Oracle EBS provides a highly customizable structure for capturing and representing data. It allows users to define and organize data elements (segments) based on business needs, ensuring flexibility and adaptability. This framework enhances data capture by accommodating unique organizational requirements without the need for extensive customization.
86. Explain the role of ‘Concurrent Processing Manager’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
The ‘Concurrent Processing Manager’ in Oracle EBS, also known as the Concurrent Manager, is responsible for scheduling, managing, and executing concurrent requests or background processes. It allocates resources, monitors request execution, and ensures the efficient use of system resources for concurrent processing tasks.
87. What is the significance of ‘Flexfield Value Set’ security profiles in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
- Flexfield Value Set’ security profiles in Oracle EBS control user access to specific values within Flexfield Value Sets.
- They enhance data security by restricting users to authorized values, ensuring that only valid and authorized information is entered and maintained.
88. Describe the purpose and use of ‘Key Flexfield’ in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
‘Key Flexfield’ in Oracle EBS serves as a customizable data structure for capturing and representing key business entities. It allows users to define segments and values specific to their organization’s needs, providing a systematic way to organize and categorize data.
89. How does ‘AutoPatch’ help in managing patches in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
‘AutoPatch’ in Oracle EBS is a tool used for automating the application of patches and updates. It streamlines the patching process by handling tasks such as copying files, generating reports, and updating database objects. ‘AutoPatch’ ensures consistency and reduces the risk of errors during the patching procedure.
90. What is the ‘Flexfield Structure Code’ and its importance in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
The ‘Flexfield Structure Code’ in Oracle EBS is a unique identifier associated with a specific Key Flexfield structure. It is used to distinguish between different Flexfield configurations. The ‘Flexfield Structure Code’ is important for maintaining and managing multiple Flexfield structures within the same Oracle EBS instance.






