
If you’re getting ready for an Oracle WebCenter interview, you’ve come to the right spot. In this guide, we’ll go over commonly asked Oracle WebCenter Interview Questions to enhance your confidence. Oracle WebCenter Sites allows the swift creation, deployment, and administration of a web property network, with the added feature of delegating individual website management. As a result, Oracle WebCenter professionals may encounter a variety of interview questions tailored to different enterprise roles in Oracle WebCenter jobs. This discussion provides an overview of different categories of Oracle WebCenter interview questions, aiming to assist aspiring enterprise professionals in preparing for their Oracle WebCenter interviews.
1. What is the WebCenter Portal for Oracle?
Ans:
Oracle WebCenter Portal offers capabilities for creating social networking sites, transactional websites, and enterprise portals during the design and runtime phases. It offers features unique to portals, such as delegated security, customization, page hierarchies, and navigation models.
2. How are portals and pagelets different from one another?
Ans:
Similar to a portlet, a page is a reusable user interface element that may be used on any web page, including ones that are part of other web applications or portals. Portlets were created especially for portals.
3. What is Composer by Oracle?
Ans:
Business users can edit application pages with Oracle Composer’s runtime editing tool. A new component called Oracle Composer makes it possible to edit or personalize any WebCenter portal after it has been deployed and is being used. With only a few mouse clicks, business users and end users may change any page with Oracle Composer’s incredibly user-friendly design.
4. List a few Oracle Composer components that are run-time editing.
Ans:
Web sites, J2EE apps, and Web services may all be run on the comprehensive and fully integrated Oracle Application Server, an application server that is entirely standards-based. It covers every obstacle you encounter when honing your business procedures to turn your company into an online enterprise.
5. How can I access Oracle WebCenter content?
Ans:
There are several options for accessing and navigating through the material inside your organization when using Oracle WebCenter material. To locate and view content, you have a few options: a mobile device, a desktop computer, Microsoft Office programs, or Windows Explorer.
6. Describe JCR.
Ans:
Users can access data stored in content management systems, such as Oracle WebCenter Content, Oracle Portal, or even your file system, accessible to your application, by using JCR or Java Content Repository API adapters.
7. How does the WebCenter portal application use PortalWebAssets?
Ans:
- To isolate all of the application’s static resources – such as HTML and picture files – PortalWebAssets is utilized.
- It constructs dynamic enterprise portals for extranets or intranets with Oracle WebCenter Portal.
- You may create corporate communities using the Oracle WebCenter Portal, which offers organizational and teamwork environments to engage people and link them with information through customized dashboards.
8. Is it required that the WebCenter portal application constantly be configured with insecurity?
Ans:
Actually, by default, the ADF security is configured if the developer remembers to configure the security in WebCenter. A default username and password are generated automatically as part of this. It also offers the standard pages for log-in and log-out.
9. How do you determine whether to deploy the program as a WAR or an EAR?
Ans:
The application needs to be packaged as an EAR if it uses MDS for run-time changes. WAR can be made for a basic WebCenter gateway application without any of these modifications.
10. What does jazz-data.xml serve as?
Ans:
- This file defines the rights and privileges for different user groups on different task flows that are generated in the applications.
- The user can customize the XML file system-jazz-data.xml to be used as either an ID store or a policy store. You can find the file at $DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig.
12. What do OID’s identification and policy stores look like?
Ans:
- Information about individuals and groups is stored in the identity store, and information about security policies is stored in the policy store.
- Every device’s data would have a distinct OID.
- Obtain an MIB file from the producer: The manufacturer will define OIDs. Thus, they give us the object values in a single file called Management Information Base (MIB). To obtain the MIB files, get in touch with the device’s maker.
13. What distinguishes data control? Cx from data bindings. cpx?
Ans:
The metadata from which the Oracle ADF binding objects are generated at runtime is provided by the DataBindings.cpx file, which also contains the Oracle ADF binding context for your complete application. When you register data controls on the business services, a file called DataControls.dcx is generated. Oracle ADF Business Components can’t generate this file. It recognizes the data control classes (factory classes) at the Oracle ADF model layer that enables communication between the client and the accessible business service.
14. What distinguishes Trinidad skins from Trinidad configuration?
Ans:
When a WebCenter portal application is created, the configuration file is generated, named Trinidad. The purpose of this is to register the skin family that you intend to utilize throughout your application. When using the skin as a Jar file, Trinidad skins are utilized. A mapping between the Skin ID and the absolute path where the skin is located is provided by this file.
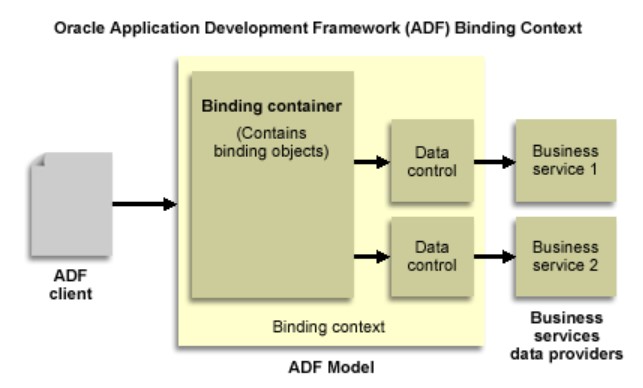
15. What do you mean by binding container and binding context?
Ans:
In order to access the binding layer, the binding context – a runtime mapping between the data controls and page specification of application pages – must be understood. It may be accessed via your js px pages’ EL expression. One request-scoped map that is used as the binding container is used to instantiate the page bindings. The EL expressions provide access to this. Additionally, it is available throughout each page request because it is a request-scoped map.
16. What kinds of bindings are there in ADF?
Ans:
The following kinds of bindings are present in ADF:
- Attribute Bindings: In an iterator binding, an attribute binding retrieves the value of a single view attribute in the current view row. #{bindings.CustomerId.InputValue}, for example
- Tree Bindings: These can be applied to trees, tables, and tree tables. It is employed to reveal table rows within the current range of the iterator bound.
- Action Bindings: When buttons or command links are dropped on the user interface, and an action has to be taken, this binding type is employed.
- Method Bindings: This binding is utilized when you wish to execute customized methods.
- Iterator Binding: In order to access the ADF binding context, the application creates this binding.
17. What distinguishes an active listener from an action taker?
Ans:
While action listeners usually carry out user interface logic and do not take part in navigation handling, actions are intended for business logic and are involved in navigation handling. A class called an action listener requests to be informed whenever a command component executes an action-packed occasion.
18. What is the scope of view?
Ans:
When a view state enters, it allocates a new view scope. To designate variables that should remain active for the length of the state, the view-state may refer to this scope. Using this scope allows you to manipulate items across several requests from the same view.
19. What distinguishes render property from visible property?
Ans:
Whether or not we want the field to be visible on the page at run time determines whether or not the visible attribute is set to true or false. Despite being hidden, the field or component is still there on the page. The component can be conditionally loaded using criteria by using the render property.
20. In ADF, how is pagination defined?
Ans:
We explain customized Using the af: iterator tag to create a custom table as a task flow is how we establish custom pagination in ADF. This presents the data collection in the same manner as a table does. We now set the number of visible rows and tie the iterator’s value property to the collection model from the ADF bindings declaration.
21. What do converters and validators mean?
Ans:
- The ADF input components are given conversion and validation capabilities by validators and converters, respectively.
- After the values are edited on the form and submitted, converters change the values on ADF forms to the kind that the application accepts.
- The input components are subjected to validations through the usage of validators.
22. How long does a JSF last?
Ans:
- Bring Back View: The FacesServet controller receives the request and extracts the view from it.
- Use request parameters: Each component’s current state is to be retrieved during the apply request values step. The FacesContext object must be used to retrieve or create the components and then their values.
- Process validations: During this stage, the validators verify the fields’ validation rules.
- Update model values: During this stage, JSF modifies the properties of your backing beans to reflect the current values of the server-side model.
- Invoke application: To handle Form submissions, the JSF controller here invokes the application action.
- Render response: During this stage, JSF shows the view together with all of its elements as they are right now.
23. How does setting immediate true on a button differ from setting immediate faithful on a text field?
Ans:
When a button’s immediate property is actual, the command’s action and ActionListeners, which include the JavaServer Faces implementation’s default ActionListener will be carried out during the request processing lifecycle’s Apply Request Values phase as opposed to waiting until the Call upon the Application stage. When it comes to text fields, by default, the Process Validators phase combines the validation and conversion of values.
24. What is communication between portlets?
Ans:
When an action in another triggers a response in one portlet, this is known as inter-portlet communication. It serves as a link for communication between two portlets. One portlet, for instance, has a checkbox with a list of products in it. The other portlet shows the details of the selected product when I select it from the list and click submit.
25. What is the Oracle Web Center’s annotation process?
Ans:
Without opening and sharing the document, Oracle Web Center annotations can be used to highlight, remark on, or conceal security information on the document preview.
26. In the Oracle Web Center, how may users share documents?
Ans:
In the Oracle Web Center, users can annotate documents to add comments, highlight text, or conceal sensitive information. To transmit a link to a document, large files don’t need to be emailed.
27. What is Oracle Web Center’s usage of libraries and folders?
Ans:
Document groups in libraries are automatically assigned security, and users can organize and save documents locally or in the cloud using folders. Users can use drag-and-drop to upload or inspect documents into folders. It is possible to choose metadata when checking in to locate documents afterward.
28. Who is the Oracle Web Center Presenter?
Ans:
Users can utilize Oracle’s digital asset management tools by creating a picture gallery using the Presenter function in Oracle Web Center. Modal dialogues, detailed descriptions, and alt tags are used to navigate the photographs in the gallery.
29. How does the composer view operate in the Oracle Web Center?
Ans:
The composer view in Oracle Web Center allows users to select and move things in the gallery manually. This solution uses a single page with JSP x pages, standard references to other libraries, prefixes referring to web center-specific capabilities, JavaScript, cascading style sheets, and inline CSS. Using standard markup, a verbatim block allows users to insert functions at specific points in a dynamic page.
30. How do fancy boxes in the Oracle Web Center interact with the jQuery function?
Ans:
The jQuery function associates images with fancy boxes after document loading. After that, it moves into areas unique to web centers, such as the DT list template. Retrieve properties from the node object by iterating over it. When the eight F iterator generates an anchor tag using picture data from the node object, the template begins. It is possible to use standard markup with the value attribute. Image descriptions are provided in the title section by the server image names.
31. What is the purpose of Oracle’s J developer?
Ans:
Presenter templates are made with Oracle’s J developer. A free integrated development environment called Oracle JDeveloper makes it easier to create Java-based apps by covering every stage of the application lifecycle. JDeveloper provides complete end-to-end development services for Oracle applications and platforms.
32. What is a Java Server faces component in Oracle Web Center?
Ans:
In Oracle Web Center, a Java Server encounters a fragment—a section of code that makes up a part of a Java Server in one of the portal application’s nodes. With the help of the web center UI, this code may create a portal item, export it from the J developer, and import it into the web center.
33. What does Oracle Web Center’s adaptive design mean?
Ans:
- Oracle Web Center’s adaptive design refers to the portal template’s capacity to adjust to tablet and mobile browser windows.
- ODI 19C: If specific criteria are met—for instance, when a query contains joins and complicated predicates that make it challenging to estimate cardinality accurately the Optimizer will select an adaptive plan.
- The Optimizer can postpone the plan decision for a statement until execution time by using adaptive plans.
34. What is the Oracle Web Center adaptable template sample?
Ans:
The Oracle Web Center adaptive template sample makes use of the media query dot CSS file and styles folder from the Web Center portal project. To build the template, right-click on it and select a JSF page template. The facet will be used by pages that use the flexible template.
35. In Oracle Web Center, what is the purpose of jQuery?
Ans:
- Through a Google CDN, jQuery enhances the web center’s headers and offers viewport functions for various screen widths.
- One little JavaScript library that aims to “write less, do more” is called jQuery. jQuery is designed to make using JavaScript on your website more simpler.
- Many typical operations that need multiple lines of JavaScript code to complete are wrapped into methods that may be called with just one line of code by jQuery.
36. What are Adaptive plans?
Ans:
The Universal Marketing Dictionary explains adaptive planning. Adaptive planning is a framework for iteratively organizing various information flows, analyses, concerns, and viewpoints that come together to generate strategic decisions.
37. What does Oracle Web Center’s service bus look like?
Ans:
By connecting documents to support requests, the service bus in Oracle Web Center is a link that makes troubleshooting easier with interest-checking Maximiser and Excel diagnostic suggestions.
38. How is the Oracle Web Centerset homepage doing?
Ans:
During design or runtime, the Oracle Web Center homepage can be configured in the ADF config file. The default template is loaded at runtime when the index.html file is executed.
39. What is Oracle Web Center’s primary sidebar?
Ans:
Oracle Web Center’s primary sidebar supports both wide and narrow columns. The Find Documents page and the View Documents page are the two primary pages utilized in Oracle WebCenter Content. When you log into Oracle WebCenter Content for the first time, the Find Documents page appears.
40. In Oracle Web Center, what CSS media queries are used?
Ans:
Styles under 60 can be overridden using CSS media queries. Compared to style sheets that employ the handheld media type, CSS3 media queries are more adaptable and efficient. Here are a few explanations for this: Increased Control To create a more responsive design, developers can use media queries to control several design components, including screen size, orientation, resolution, and aspect ratio.
41. Describe XML. What is the Web service’s use of XML?
Ans:
Support records and XML representations of service requests receive the variable. Information interchange between computer systems, including webpages, databases, and outside apps, is supported by XML. Data can be easily transmitted as XML files over any network by using predefined rules, which the recipient can utilize to read the data efficiently and precisely.
42. How does the system take advantage of process debugging?
Ans:
In the process, debugging, count, and index variables are used. Three elements make up the debugging procedure
- Find: Identify the surprising behavior that needs to be altered.
- Identify: Ascertain the reason behind the strange conduct.
- Fix: Put in place a solution that will stop unexpected behavior from occurring in the future.
43. What is a ticketing system for calls?
Ans:
A management tool used to handle and organize customer service requests is called a ticketing system. Cases and issues, sometimes referred to as tickets, must be correctly stored with pertinent user data. Administrators, managers, and customer service personnel should all find the ticketing system easy to use.
44. How do the changes made to the XML document work out?
Ans:
The aggregate support list will take the place of the XML document when all requests and amendments have been made. Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations are the standard method for converting XML data into various formats (XSLT). To convert XML documents into HTML, plain text, or other XML schemas, utilize the integrated XSLTRANSFORM function. XSLT uses stylesheets to transform XML into different data types.
45. How may Siebel Web Service be added to the service register?
Ans:
Operations and support documentation are provided by registering Siebel Wisdom. External customers can access Siebel functionality through inbound Web services. A bespoke user interface (UI) that aims to examine and alter Siebel service requests is one example. Siebel applications can request external apps through outbound Web services.
46. What function does the Fizz Buzz service serve?
Ans:
The FizzBuzz problem is resolved in the FP style by a single, brief function called fizzBuzz, which accepts an input called n and returns an array containing both strings and numbers. The function returns the proper string or integer after using a ternary operator to determine whether the current number is divisible by 3, 5, or 15.
47. What distinguishes pagelets from portals?
Ans:
Much like a portlet, a page is a reusable user interface element that can be utilized on various web pages, including those integrated into other web applications or portals.
48. Can you describe the MDS Repository Directory?
Ans:
When people want to view the content they saved after customizing their blogs the following day, we have a directory named MDS repository directory that we use to accomplish this. Before every run, it is used to save or remove settings. Choose Application Properties by right-clicking on the application. Choose Run->MDS from the program properties menu. Choose the necessary options from the Directory content.
49. What is Composer for Oracle?
Ans:
- Business users can edit application pages with Oracle Composer’s runtime editing tool.
- A new component called Oracle Composer makes it possible to edit or personalize any WebCenter portal after it has been deployed and is in use.
50. What do the OID’s Identity Store and Policy Store mean?
Ans:
Information about individuals and groups is stored in the Identity Store, and information about security policies is stored in the Policy Store. An Oracle database is used to operate Oracle Internet Directory as an application. Oracle Net Services, an operating system-independent database connectivity solution from Oracle, is used to connect it to the database.
51. What is The Portal Web Assets project?
Ans:
By default, this project is launched whenever a webcenter application is developed. It is used to hold the project’s static material, such as HTML and photos. To lessen the load on the primary application server, we can also independently execute this project on different servers. Our task is to eliminate the dependencies.
52. What is communication between portlets?
Ans:
When an action in another triggers a response in one portlet, this is known as inter-portlet communication. It serves as a link for communication between two portlets. One portlet, for instance, has a checkbox with a list of products in it. The other portlet shows the details of the selected product when I select it from the list and click submit.
53. What are some of the parts that Oracle Composer uses for edits during runtime?
Ans:
- Custom Actions
- Show Detail Frame
- Adjustable Panel
- Customizable Layout
54. Describe MDS.
Ans:
The repository for some deployed applications’ metadata is called an MDS or Metadata Repository. When the user commits run-time modifications, they are stored and deployed as an MDS on the server.
55. What function does Oracle Fusion’s Page Composer serve?
Ans:
Extensibility Guide for Oracle Fusion Applications CRM, In Oracle Fusion CRM, Page Composer is meant for simple user interface altering functions, such as showing and hiding regions, fields, and tables, changing the order of regions, or changing a dashboard page layout. It can also be used to add or remove items from the Resource Library that have already been predefined.
56. How does the web center portal application use Portal WebAssets?
Ans:
The application’s static resources, such as HTML and image files, are all divided into different folders using PortalWebAssets. Oracle Net Services, an operating system-independent database connectivity solution from Oracle, is used to connect it to the database. The database resides on a different host.
57. What distinguishes render property from visible property?
Ans:
Whether or not we want the field to be visible on the page at run time determines whether or not the visible attribute is set to true or false. Despite being hidden, the field or component is still there on the page. To conditionally load the component according to a criterion, utilize the render property.
58. How do you always configure security in your web center portal application?
Ans:
- By default, the ADF security is configured if the developer doesn’t configure the security in WebCenter.
- A default username and password are generated automatically as part of this. It also offers the standard pages for log-in and log-out.
59. How do you determine if an EAR should be deployed for the application?
Ans:
- The application needs to be packaged as an EAR if it includes runtime modifications made with MDS.
- WAR can be built for a basic WebCenter Portal application without any such changes.
60. What kinds of bindings are there in ADF?
Ans:
The following kinds of bindings are present in ADF:
- Bindings of attributes: In the current view row of the iterator binding, this binding is used to obtain the value of a single view attribute. #{bindings.CustomerId.InputValue}, for example
- Bindings in Trees: Tables, tree tables, and trees all use this. It is employed to reveal table rows within the current range of the iterator bound.
- Bindings of Action: This binding style is applied when command links or buttons are placed on the user interface and demand that something be done with them. On them, we can apply data control operations such as Create, Delete, First, Last, Commit, Rollback, and so on.
61. What is Composer for Pages?
Ans:
The tool you use to modify the text on the pages of your websites is called Page Composer. With Page Composer, you can see a breakdown of each page on your website visually. Your content is organized into sections and lists on every page. These sections and lists contain content that you update or add to.
62. What do converters and validators mean?
Ans:
The ADF input components are given conversion and validation capabilities by validators and converters, respectively. After the values are edited on the form and submitted, converters change the values on ADF forms to the kind that the application accepts. The input components are subjected to validations through the usage of validators.
63. What differentiates Data Control Dux from Data Bindings Cx?
Ans:
The metadata from which the Oracle ADF binding objects are generated at runtime is provided by the DataBindings.cpx file, which also contains the Oracle ADF binding context for your complete application. DataControls.dcx is the When you register data controls on the business services, a file called DataControls.dcx is generated. Oracle ADF Business Components can’t generate this file.
64. How does Trinidad Config differ from Trinidad Skins?
Ans:
| Aspect | |||
| Purpose | Configuration of application-wide settings and behaviors. | Styling and appearance customization for UI components. | |
| Scope | Global settings affecting the entire Trinidad application. | Primarily focuses on the visual presentation of components. | |
| Content | Includes parameters related to behavior, navigation, and more. | Contains definitions for skin styles, colors, and images. | |
| Inheritance | Supports inheritance, allowing settings to be inherited by child pages. | Supports inheritance to ensure consistent styling across pages. | |
| File Types | Typically stored in trinidad-config.xml or similar files. | Stored in CSS files or skin-declaration XML files. |
65. What Are the Policy Store And Identity Store In Oid?
Ans:
While the Policy Store is designed to store information on privacy regulations, the Identity Store is used to store data about businesses and customers. An Internet protocol called Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is used to access information directories. A distributed database application called a directory service is made to handle the entries and properties in a directory. Clients using LDAP can access various directory services according to entries.
66. What is the difference between data bindings CPX and DataControl.DCX?
Ans:
The DataBindings carry the Oracle ADF binding context for your entire utility. Cpx file, which also provides the metadata from which the Oracle ADF binding objects are generated during runtime. When you register for information controls on the business offerings, the DataControls dcx file is generated. The Oracle ADF model layer statistics control instructions (factory training) that enable communication between the buyer and the available enterprise carrier are identified.
67. What Distinguishes Trinidad.Config From Trinidad.Skins?
Ans:
Trinidad. Config report is generated when a WebCenter Portal application is being created. The pores and skin-circle of the relatives you plan to utilize throughout your complete software are registered using this. Trinidad.When we employ skin as a Jar record, skins are used. A mapping between the Skin ID and the actual course where the pores and skin are located is provided by this record.
68. What Are The Terms Binding Container And Binding Context?
Ans:
- The binding context, which is utilized to gain access to the binding layer, is a runtime mapping between the record controls and page definitions of the software’s pages.
- It is accessible through your jspx pages’ EL expression.
- An example of a request-scoped map is the binding field.
- To instantiate the web page bindings. Through the EL expressions, this is accessible. Additionally, any web page request can access it at some point due to its request-scoped mapping.
69. What types of bindings does ADF support?
Ans:
ADF supports various binding styles, including attribute bindings for retrieving unmarried view attribute values, tree bindings used in tables, tree tables, and trees, method bindings for custom methods, and iterator bindings for accessing the ADF binding context, granting access to collected data and looping through record objects.
70. What Distinguishes An Action From An Action Listener?
Ans:
While action listeners usually exercise consumer interface good judgment and do not engage in navigation dealings, actions are intended for business common sense and participation in navigation dealings. The class action listener wishes to be notified while a command thing fires an action event.
71. Describe A View Scope.
Ans:
- As it enters, a view-nation assigns a new view scope. To assign variables that must exist in the nation at some point, this scope can be referred to within the view state.
- Using this scope to manipulate objects across a series of requests from a single view is advantageous.
72. What Distinguishes Render Property From Visible Property?
Ans:
Depending entirely on whether we want to view the field on the website at run time or not, the visible assets are prepared to be genuine or phony. Despite being hidden, the section or piece still exists on the webpage. The component is conditionally loaded using the render assets in accordance with a set of criteria.
73. What Do Converters And Validators Mean?
Ans:
The ADF entry components are given validation and conversion capabilities by validators and converters, respectively. After the values are modified at the form and submitted, converters change the values on the ADF bureaucracy to the kind that the application allows. Validations are applied at the additives entry point.
74. What Is The JSF Life Cycle?
Ans:
The FacesServet controller receives the request and extracts the considered information from it.
- Validations of processes: In order to validate the validation, this phase uses the validator rules in the fields.
- Update version values: Using an update to your backing beans’ homes, JSF updates the server-aspect model’s actual values in this part.
- Render response: In this section, JSF presents the view of its cutting-edge country along with all of its extras.
75. What Is The Distinction Between Using Immediate accurate In A Text Field And Immediate proper On A Button?
Ans:
The command’s action and ActionListeners, including the default ActionListener provided by the JavaServer Faces implementation, can be completed at some point in the Apply Request Values section of the request processing lifecycle when on the spot is appropriate on a button, as opposed to being ready until the Invoke Application stage. When a textual content subject is involved, the Process Validators segment transforms and verifies values jointly using default. But setting this to “on the spot” makes it possible if you want access to the issue charge during the Apply Request Values process.
76. What is Inter-portlet communication?
Ans:
Verbal communication between ports occurs when a movement in one portlet prompts a response in another portlet. It is a bridge for vocal communication between two ports. For instance, one portlet has a checkbox with a product list on it. Once I select an item from the catalog and click, The specifics of the corresponding product are presented via the other portlet upon submission.
77. Why Is Faces-config.Xml In Use?
Ans:
To define all page-to-page navigation rules and to check in resources such as custom validators and controlled beans for a Framework application, use the faces-config.Xml document.
78. Which XML file is used to configure your framework applications?
Ans:
- Configure: Trinidad-config.Xml
- Although any generic web application can be configured using the web.xml file, using the Struts framework requires you to define a few Struts-specific configuration options in this file.
79. What Does Adfc-config.Xml Serve As?
Ans:
The configuration record for an ADF unbounded project flow is found in the adfc-config.Xml report. The unbounded venture flows, manage flows, and sports metadata are included in this file.
80. Describe the components that make up Oracle Forms Services.
Ans:
Client:
- The client submits the HTTP requests in Oracle forms.
- Creates a Listener Database: The information retrieved from the database.
Servlet:
- It initiates, stops, and communicates with the Forms Runtime Process.
- Forms Runtime Process: It runs the code included in a specific forms application.
81. Mention the new features that Oracle Form Services.
Ans:
The features of Oracle Form Services are as follows:
- Schedule forms’ runtime prestart;
- Integrate with Oracle Access Manager;
- Improve network statistics reports.
The following features are supported: forms metric agent, Unicode column support, guiMode configuration parameter, URL support for picture items and iconic buttons, and Oracle actual user experience insight.
82. Describe the distinctions between OPEN_FORM, NEW_FORM, and CALL_FORM.
Ans:
- NEW_FORM: It ends the current form and replaces it with the indicated new form;
- OPEN_FORM: It opens the indicated new form without suspending or replacing the parent form.
- CALL_FORM: It initiates a new form and transfers control to it.
83. Which Oracle Forms Configuration files are listed?
Ans:
Among the configuration files for Oracle Forms are:
- Base HTML files (base.htm)
- Environment
- CFG
- Base HTML files (base.htm, basejini.htm, basejpi.htm, and baseie.htm)
84. What is the maximum length of the Record group Column in an Oracle Forms Report?
Ans:
Record group column names must be longer than 30 characters at most. Record groups come in a variety of forms, such as query record groups, state record groups, and nonQuery record groups.
85. Mention the order in which the forms’ firing triggers occur.
Ans:
When forms open, the following sequence of firing triggers occurs: Pre-form, Pre-block, Pre-recorded, Pre-text-item, When-new-form-instance.
86. Mention the distinction between a list item and a LOV.
Ans:
Oracle Forms compares the current value of the text item when the LOV for validation is set to True. Oracle Forms compares the text item’s current value to the values in the first column of the LOV when the validation LOV is set to True. List items are items, whereas LOV is a property. While love can have one or more columns, a list item can only have one.
87. Describe how two columns can use the same LOV.
Ans:
- By bypassing the return values in global values and utilizing the global values in the code,
- we may use the same LOV for two columns.
- Go to Home > Highlight Cells Rules > Conditional Formatting > Duplicate Values.
88. Mention what bind variables are; in Excel, how do you compare data across two columns.
Ans:
- In report 6i, the select statement’s single parameter is substituted with the bind variables.
- The following steps are a common way to compare two columns in Excel:
- Choose both data columns → Navigate to the Home menu, then select Find & Select, Go To Special, Row Differences, and finally click OK.
89. How do you loop through the records and items in a given block?
Ans:
- Use NEXT_FIELD to iterate over items in a given block.
- NEXT_RECORD to iterate through records in a block to iterate through both items and records in a defined block.
90. What does it mean to reverse engineer or convert an FMX file back into an FMB file?
Ans:
To make sure they are recovered, an FMX cannot be reverse-engineered or converted back to an FMB file. Using an Oracle database as a source, Oracle Forms creates a default form that displays and modifies data. The “executable” (*. fmx), which is interpreted by the forms runtime module, is created by compiling the source form (*. fmb).






