
Powerful Open-source Database PostgreSQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS) known for its robust features, extensibility, and strong emphasis on standards compliance. The development of PostgreSQL is a collaborative and community-driven effort characterized by an open-source ethos. Led by a core development team, this global community of developers and contributors works together to enhance PostgreSQL’s capabilities. PostgreSQL’s extensibility, support for multiple platforms, and commitment to internationalization make it a versatile and widely adopted database system in the software development ecosystem.
1. What is PostgreSQL, and why is it popular in the database world?
Ans:
PostgreSQL is a powerful open-source relational database management system known for its robustness, extensibility, and adherence to SQL standards. Its extensive features, including as support for complex data types, JSON processing, geographical data, and scalability, make it popular.
2. Explain the key features of PostgreSQL.
Ans:
ACID Compliance: Ensures data consistency and reliability in transactions.
Extensibility: Supports custom functions, data types, and extensions.
Advanced Indexing: Offers various indexing methods for efficient data retrieval.
Data Integrity: Enforces referential integrity with foreign key constraints.
JSON Support: Handles JSON and JSONB data types for flexible data storage.
3. What are the various data types that PostgreSQL supports?
Ans:
- Numeric Types
- Character Types
- Binary Data Types
- Date/Time Types
- Boolean Type
- Enumerated Types
4. How does PostgreSQL enable you to create new databases?
Ans:
- Use the ‘createdb’ command-line utility with ‘createdb
‘. - Within the ‘psql’ terminal, execute ‘CREATE DATABASE
;’, replacing with the desired name.
To create a new database in PostgreSQL:
5. What is a schema in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
In PostgreSQL, a schema serves as a named container or namespace within a database. Its primary purpose is to provide a structured way to organize database objects, such as tables, views, functions, and operators. By grouping related objects into schemas, PostgreSQL enhances database management and organization.
6. Describe the distinctions between PostgreSQL tables and views.
Ans:
PostgreSQL Tables:
PostgreSQL tables are physical data storage structures that hold structured data in rows and columns. They are ideal for persistently storing and managing large volumes of data.
PostgreSQL Views:
PostgreSQL views, on the other hand, are virtual representations of data derived from one or more tables or views. Views are defined by SQL SELECT statements and provide a dynamic way to access data without storing it themselves.
7. In PostgreSQL, how do you build a table?
Ans:
In PostgreSQL, the ‘CREATE TABLE’ command is used to create a table. This statement allows you to define the table’s name and its columns along with their respective data types. Additional constraints, such as primary keys or unique constraints, can also be specified as needed.
8. What is a primary key, and its important in a database?
Ans:
A primary key is a critical element in a database, serving as a unique identifier for each record within a table. It ensures data integrity by preventing duplicates, facilitates efficient data retrieval, and forms the basis for establishing relationships between tables through foreign keys.
9. How does PostgreSQL add a primary key constraint to an already existing table?
Ans:
To apply a primary key constraint to an already existing table in PostgreSQL, the ‘ALTER TABLE’ statement is used. This statement includes the ‘ADD CONSTRAINT’ clause, where you specify the primary key constraint’s name and the column(s) that constitute it.
10. What is an index, and how does it enhance the efficiency of databases?
Ans:
An index in a database is a specialized data structure designed to enhance the efficiency of data retrieval. It acts as a catalog or pointer system, allowing the database engine to swiftly locate specific records within a table. This efficiency boost is achieved by reducing the need for full-table scans when searching for data.
Indexes improve database performance by facilitating faster data retrieval, speeding up query execution, supporting sorting and grouping operations, expediting join operations, and enforcing constraints like primary keys and uniqueness.
11. What is the function of the PostgreSQL ‘pg_hba.conf ‘ file?
Ans:
The ‘pg_hba.conf’ file in PostgreSQL is responsible for managing client authentication and access control to the database server. It defines rules specifying which hosts are allowed to connect, which authentication methods are accepted, and which databases and users can access the system. This file plays a crucial role in securing and controlling access to PostgreSQL databases.
12. How do you use the command line to connect to a PostgreSQL database?
Ans:
To connect to a PostgreSQL database from the command line, use the ‘psql’ utility with the following format:
psql -U username -d database_name
Replace ‘username’ with the desired username and database_name with the target database’s name. You’ll be prompted for the password, and upon successful authentication, you can interact with the PostgreSQL database using SQL commands and queries directly from the command line.
13. Describe the ‘psql’ command-line tool’s function.
Ans:
Database Connectivity facilitates connecting to PostgreSQL databases from the command line. SQL Query Execution allows execution of SQL queries, commands, and statements interactively. Interactive Shell offers an interactive and user-friendly interface for database interaction, including auto-completion and syntax highlighting. Script Execution supports running SQL scripts and batch processing of commands, aiding in automation and maintenance.
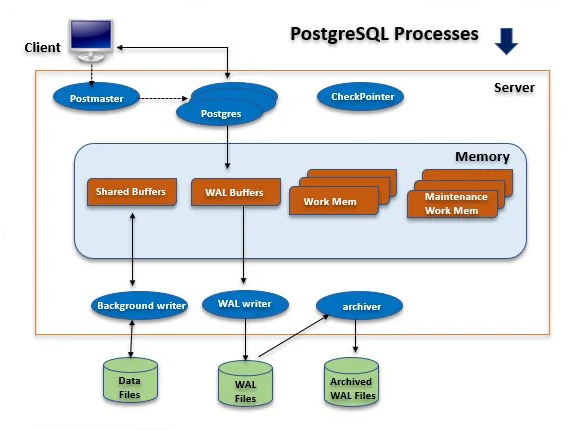
14. What is ACID compliance in the context of databases?
Ans:
ACID compliance, in the context of databases, encompasses a crucial set of properties that ensure the reliability of transactions. Atomicity guarantees that transactions are treated as indivisible units, Consistency ensures valid data changes are committed, Isolation provides separate workspaces to prevent concurrent interference, and Durability ensures permanent data storage.
15. Explain the difference between the SERIAL and BIGSERIAL data types in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
SERIAL Data Type:
In PostgreSQL, the ‘SERIAL’ data type is used to create an auto-incrementing integer column. It is commonly employed for generating unique identifier values for primary keys. The ‘SERIAL’ data type uses a 4-byte integer for the column.
BIGSERIAL Data Type:
The ‘BIGSERIAL’ data type in PostgreSQL is similar to ‘SERIAL’ but uses an 8-byte integer instead of a 4-byte integer. This means that it can accommodate much larger integer values. It is typically used when you anticipate a need for a very large number of unique identifier values, such as in tables with a massive number of rows.
16. How can you create a foreign key constraint in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
- Ensure the referenced table with a primary key or unique constraint exists.
- Use ‘ALTER TABLE’ to define the foreign key constraint, specifying the table, constraint name, and columns.
- Optionally, set actions on ‘DELETE’ or ‘UPDATE’ using ‘ON DELETE’ and ‘ON UPDATE’ clauses.
- Commit the transaction to make the constraint permanent.
To add a foreign key constraint to PostgreSQL:
17. What is a stored procedure in PostgreSQL, and how can you create one?
Ans:
A stored procedure in PostgreSQL is a precompiled collection of SQL statements designed to execute as a single unit. It encapsulates complex database operations, enhancing code modularity and reusability. To create one, you use the ‘CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION’ command, specifying the procedure’s name, input parameters, and SQL code.
18. What is a trigger, and when would you use it in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
A trigger in PostgreSQL is an automated action that responds to specific events like data changes or timing events. Triggers are used for data validation, logging, automation, complex business logic, data replication, historical data tracking, and security enforcement.
19. Explain the difference between INNER JOIN and LEFT JOIN in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
INNER JOIN:
INNER JOIN retrieves matching records from both tables based on a specified condition, excluding non-matching rows. It’s used for one-to-one or many-to-one relationships.
LEFT JOIN:
LEFT JOIN retrieves all records from the left table and matching records from the right table. Non-matching rows from the left table are included with NULL values. It’s used to preserve all rows from the left table, even if they lack matches in the right table.
20. What does Normalization entail, and why is it crucial when designing databases?
Ans:
Normalization is the process of organizing data in a relational database to reduce redundancy and improve data integrity by minimizing data duplication. Normalization is crucial in database design to prevent data anomalies, ensure efficient storage, and simplify data maintenance, leading to more robust and scalable database systems.
21. How are PostgreSQL databases backed up and restored?
Ans:
To back up a PostgreSQL database, you can use the ‘pg_dump’ command to create a logical backup of the database to a file. For restoration, you can use the ‘psql’ command to execute the SQL commands from the backup file to recreate the database. This process allows for data and schema preservation during backup and restoration.
22. What is the purpose of the ‘pg_stat_statements’ module in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
The ‘pg_stat_statements’ module in PostgreSQL serves the purpose of providing detailed statistics about the execution of SQL statements within the database. It tracks information such as query execution time, the number of times a query has been executed, and the amount of memory used by queries.
23. Explain the importance of vacuuming in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
Vacuuming in PostgreSQL is essential for maintaining database health and optimizing performance. It reclaims storage space by removing outdated or dead rows, preventing bloating of tables. Additionally, it updates statistics used by the query planner, enabling better query optimization and ensuring accurate execution plans.
24. How can you monitor PostgreSQL performance?
Ans:
Monitoring PostgreSQL performance is crucial to maintain a healthy database system. You can achieve this by utilizing built-in tools like ‘pg_stat’ views and ‘pg_stat_statements’ for query analysis.
Monitoring involves tracking metrics, analyzing query execution plans, and reviewing database logs and OS-level data to ensure efficient resource usage and proactively address any performance issues that may arise.
25. What is a sequence in PostgreSQL, and how can you use it?
Ans:
A sequence in PostgreSQL is an auto-incrementing numeric generator commonly used for unique identifiers, such as primary keys. To use it, create a sequence with parameters using ‘CREATE SEQUENCE’, associate it with a table column, and PostgreSQL will automatically generate unique values when inserting data.
26. What are the benefits of using JSON and JSONB data types in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
Flexible Storage: Accommodate varied data shapes and formats.
Query and Indexing: Efficiently query and index JSON data.
Storage Efficiency: JSONB offers efficient storage and better performance.
Data Validation: Enforce data validation through constraints.
Interoperability: Easily exchange data with external systems.
27. Describe the PostgreSQL concept of table partitioning.
Ans:
Table partitioning in PostgreSQL is a database design approach that includes breaking a big table into smaller, more manageable portions called partitions. Each partition is essentially a separate table with its own storage location, typically based on a specific criterion, such as a range of values or a list of values from a particular column.
28. How can you create and manage roles and privileges in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
In PostgreSQL, you can create and manage roles (users or groups) and their associated privileges to control access to database objects. To do this, connect to PostgreSQL, create roles using ‘CREATE ROLE’, grant privileges using ‘GRANT’, and revoke privileges with ‘REVOKE’. You can also manage role membership, attributes, and control database access through the ‘pg_hba.conf’ file. Roles and privileges play a crucial role in securing and organizing access to your PostgreSQL database.
29. What does PostgreSQL’s ‘EXPLAIN’ statement do?
- Query Execution Plan
- Performance Tuning
- Cost Estimation
- Join Strategies
- Index Usage
30. What are Common Table Expressions (CTEs)?
Ans:
In PostgreSQL, Common Table Expressions (CTEs) are used in a similar manner as in standard SQL. CTEs can be defined within queries using the ‘WITH’ keyword, providing a way to structure and simplify complex SQL statements. They are especially valuable for recursive queries, data manipulation, and improving query readability and maintainability within the PostgreSQL database system.
31. What is Full-Text Search in PostgreSQL, and how can you implement it?
Ans:
Full-Text Search (FTS) in PostgreSQL is a powerful feature that allows you to perform advanced text-based searches on textual data within your database.
To implement Full-Text Search in PostgreSQL, enable the FTS extensions (‘pg_trgm’ and others), create a Full-Text Search index on the desired text column(s), and use the ‘@@’ operator and ‘to_tsquery’ function for text searches in your SQL queries.
32. What is replication in PostgreSQL, and how does it work?
Ans:
Replication in PostgreSQL refers to the process of maintaining multiple copies of a PostgreSQL database to ensure data redundancy, availability, and load distribution. Replication in PostgreSQL works by continuously copying data changes (using Write-Ahead Logs) from a primary database to one or more replica databases. Replicas apply these changes to stay synchronized with the primary, ensuring data redundancy, high availability, and scalability.
33. Explain the concept of high availability in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
High availability in PostgreSQL refers to the ability of a PostgreSQL database system to remain operational and accessible with minimal downtime, even in the phase of hardware failures, software issues, or other unforeseen disruptions. Achieving high availability is crucial for critical applications where uninterrupted access to the database is essential.
34. How can you implement data encryption in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
- Choose Encryption Type
- Encrypt Data at Rest
- Encrypt Data in Transit
- Manage Encryption Keys
- Authentication and Authorization
35. What is the function of PostgreSQL’s ‘pg_stat_activity’ view?
Ans:
The ‘pg_stat_activity’ view in PostgreSQL serves the purpose of providing real-time information about the current database connections and the activities they are performing. It offers insights into the state of active connections, including details like the current query being executed, the user associated with the connection, the duration of the connection, and more.
36. How do you handle database migrations in a PostgreSQL environment?
Ans:
Version Control: Use Git or similar tools for tracking schema changes.
Migration Tools: Consider using tools like Flyway or Liquibase for automation.
Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test migrations before production deployment.
Backup and Recovery: Perform database backups before applying migrations.
Rollback Strategy: Include rollback plans for failed or reversed migrations.
37. What is a foreign data wrapper (FDW), and how can you use it in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
A Foreign Data Wrapper (FDW) in PostgreSQL is an extension that enables the database to access and interact with data stored in external data sources, such as other databases, web services, or flat files, as if they were PostgreSQL tables.
Installing the necessary extension, setting up a server connection to the external data source, and creating foreign tables will enable PostgreSQL users to utilize FDWs to view and query remote data as if it were local.
38. How does PostgreSQL handle concurrent access and locking?
Ans:
PostgreSQL handles concurrent access and locking through a multi-version concurrency control (MVCC) system, which allows multiple transactions to access and modify data simultaneously while maintaining data consistency and isolation.
39. What are some common performance-tuning techniques for PostgreSQL?
Ans:
- Proper Indexing
- Query Optimization
- Vacuum and Analyze
- Configuration Tuning
- Connection Pooling
40. How can you optimize a slow-running query in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
- Analyze the execution plan using ‘EXPLAIN’.
- Optimize indexes and avoid functions in ‘WHERE’ clauses.
- Rewrite and simplify complex queries.
- Use ‘LIMIT’ and ‘OFFSET’ for result set control.
- Regularly update statistics for better query planning.
To optimize a slow-running query in PostgreSQL:
41. Explain the concept of indexing strategies in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
Indexing strategies in PostgreSQL involve the creation of data structures that enhance the efficiency of query processing by facilitating rapid data retrieval. These strategies include B-tree indexing for most cases, Hash indexing for equality checks, GiST/GIN indexing for complex data types like text and arrays, and specialized indexes like SP-GiST for spatial data or BRIN for large data sets.
42. What is a role of PostgreSQL’s ‘pg_stat_bgwriter’ view?
Ans:
The ‘pg_stat_bgwriter’ view in PostgreSQL provides statistics about the background writer process, which manages the writing of modified data from memory to disk. It offers insights into checkpoint activity, buffer management, and the overall efficiency of background writes, helping database administrators optimize database performance and tune PostgreSQL configuration parameters as needed.
43. How can you identify and resolve deadlocks in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
To identify and resolve deadlocks in PostgreSQL, first monitor for deadlock incidents by enabling deadlock detection and examining database logs for related messages. When a deadlock occurs, analyze the involved transactions and the locks they’re attempting to acquire.
Use PostgreSQL’s configuration options for tuning, modify your application’s logic and locking techniques to reduce conflicts, add retry logic to handle deadlocks graciously, and regularly check for and test out scenarios for deadlock resolution.
44. What is query planning, and how does it impact query performance?
Ans:
Query planning in a relational database system (RDBMS) is essential for optimizing query performance. It finds the most efficient way to execute a query, considering the database schema, available indexes, and data statistics. Effective query planning leads to faster execution, while poor planning can cause slow and resource-intensive queries.
45. How can you monitor and analyze slow queries in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
- Enable Query Logging
- Utilize pg_stat_statements
- Use EXPLAIN and EXPLAIN ANALYZE
- Set Up Alerts
- Optimize Database and Queries
To monitor and analyze slow queries in PostgreSQL, follow these steps:
46. Explain the concept of connection pooling and its benefits in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
Connection pooling in PostgreSQL involves reusing established database connections instead of creating new ones for each client request.
This optimization reduces resource overhead, minimizes connection management complexity, enhances security, and improves overall database performance and scalability by efficiently managing concurrent connections.
47. What are some best practices for optimizing PostgreSQL for read-heavy workloads?
Ans:
Effective Indexing: Create indexes on frequently queried columns.
Regular Maintenance: Perform routine ‘VACUUM’ and ‘ANALYZE’ operations.
Caching Strategies: Implement caching mechanisms at application and database levels.
Query Optimization: Optimize SQL queries and execution plans for efficiency.
Scaling and Monitoring: Monitor performance, consider read replicas, and scale resources as necessary to handle increased read loads.
48. How can you monitor and manage PostgreSQL logs?
Ans:
To monitor and manage PostgreSQL logs, enable logging in the ‘postgresql.conf’ file, specifying the log destination and severity levels. Regularly review the logs for query performance, connection details, and errors.
Implement log rotation to prevent log files from becoming too large, archive logs for historical analysis, and consider using log analysis tools or alerting mechanisms to streamline log management and ensure the database’s reliability and security.
49. What is the autovacuum process in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
The autovacuum process in PostgreSQL is an automated maintenance mechanism that manages the removal of dead or obsolete data (also known as “dead tuples” or “dead rows”) from tables and indexes. Dead data accumulates as a result of updates and deletions in a PostgreSQL database, and if left unmanaged, it can lead to increased storage usage, degraded query performance, and potential bloat issues.
50. How do you diagnose and troubleshoot performance issues in a PostgreSQL database?
Ans:
Diagnosing and troubleshooting PostgreSQL performance issues involves gathering information, reviewing logs, monitoring queries, optimizing slow ones, adjusting configurations, considering caching and replication, and maintaining ongoing performance monitoring.
51. What is the difference between a database and a schema in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
Database:
In PostgreSQL, a database is a fundamental organizational unit that serves as a self-contained data repository. Each database operates independently, with its own unique set of tables, schemas, access permissions, and configuration settings.
Schema:
A schema in PostgreSQL is a logical container within a database used for organizing and structuring database objects. These objects can include tables, views, functions, procedures, and more.
52. Explain the purpose of tablespaces in PostgreSQL and how they are used.
Ans:
Tablespaces in PostgreSQL serve the purpose of managing the physical storage of database objects. They allow administrators to allocate and control storage separately for different parts of the database, optimizing performance, backup strategies, and data placement. Additionally, tablespaces can be used to implement table partitioning strategies, enhancing manageability and query performance for large tables.
53. What is the role of the ‘pg_clog’ and ‘pg_xlog’ directories in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
In PostgreSQL, the ‘pg_clog’ directory tracks the status of transactions in the database by recording whether transactions are active, committed, or aborted.
Conversely, the ‘pg_xlog’ directory, also known as the write-ahead log (WAL), stores a continuous stream of transaction log records. These records capture changes made to the database before they are applied to actual data files.
54. List the benefits of using PostgreSQL as a JSON store.
Ans:
- Schema Flexibility: Adaptable data modeling for evolving structures.
- Data Integrity: Enforces data validity and rules.
- Advanced Querying: Powerful JSON operators and functions.
- Indexing: Improved JSON data retrieval performance.
- Full-Text Search: Efficient searching within JSON documents.
55. How does PostgreSQL handle concurrent transactions and isolation levels?
Ans:
PostgreSQL uses Multi-Version Concurrency Control (MVCC) and SQL-standard isolation levels to handle concurrent transactions. MVCC creates separate data versions for each transaction, allowing for concurrent reading and writing. PostgreSQL offers four isolation levels, giving developers control over data consistency and concurrency.
56. What is the purpose of the ‘pg_locks view’, and how can it be used for troubleshooting?
Ans:
The ‘pg_locks’ view in PostgreSQL serves the purpose of providing insights into the current state of locks within the database. It helps identify lock conflicts, detect deadlocks, analyze lock types, monitor long-running transactions, and understand the status of locks within the database, aiding in diagnosing and resolving concurrency-related problems efficiently.
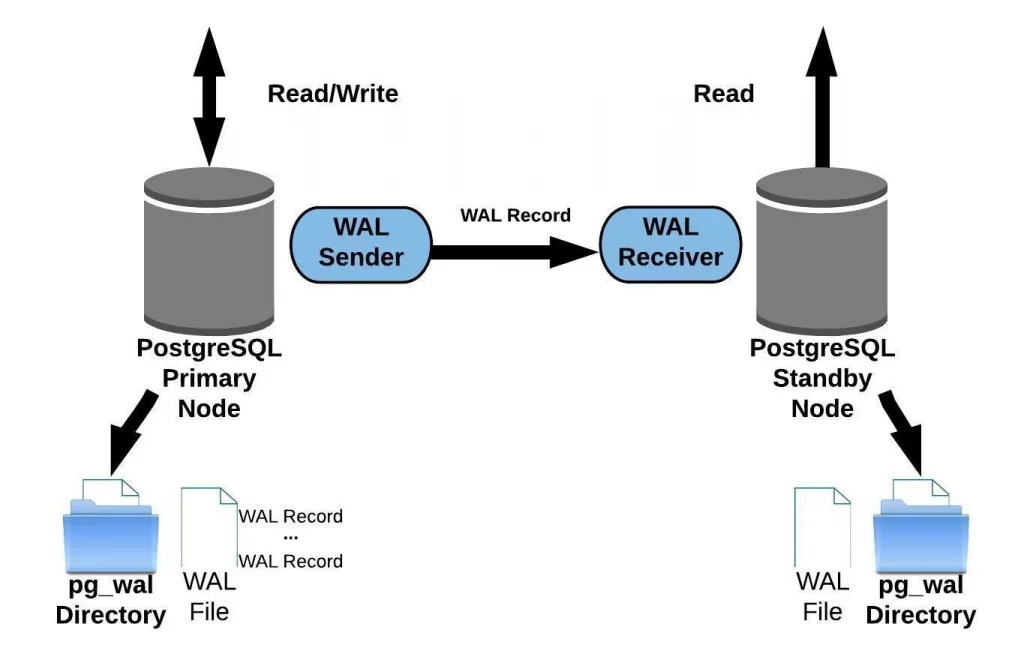
57. Explain the concept of a write-ahead log (WAL) in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
The Write-Ahead Log (WAL) in PostgreSQL is a critical mechanism for ensuring data durability and recovery. It records changes to the database in a sequential log before they are written to the actual data files. This allows PostgreSQL to recover the database to a consistent state in case of crashes or failures by replaying the log, ensuring data integrity and reliability.
58. What is a savepoint in PostgreSQL, and how can it be used in transactions?
Ans:
In PostgreSQL, a savepoint is a named point within a transaction to which you can later roll back if needed. It allows you to create a kind of “bookmark” in the middle of a transaction, enabling you to partially undo changes made within that transaction while preserving the rest of the work.
59. Describe the use cases for unlogged tables in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
Unlogged tables in PostgreSQL find utility in scenarios where data durability and recovery are not paramount. They are well-suited for temporary data storage, high-performance logging, and audit trails.
Additionally, unlogged tables are valuable for performance-critical workloads and ephemeral data storage, as they bypass the Write-Ahead Log (WAL) and minimize write overhead.
60. How do you perform a cross-database query in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
- Connecting to your PostgreSQL instance.
- Explicitly referencing the target database, schema, and table in your SQL query.
- Ensuring you have the necessary permissions for both databases involved.
- Executing the query using a PostgreSQL client or CLI.
Performing a cross-database query in PostgreSQL involves:
61. Explain window functions in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
Window functions in PostgreSQL are analytical functions that run calculations over a number of rows connected to the current row within a result set. These functions allow you to perform calculations, aggregations, and ranking operations while considering the context of neighboring rows. Window functions are typically used in complex analytical queries and reporting to gain insights into data trends.
62. What is a recursive common table expression (CTE), and when would you use it?
Ans:
A recursive common table expression in SQL, including PostgreSQL, is a powerful feature that allows for self-referential queries within a single SQL statement.
It’s particularly useful when dealing with hierarchical or graph-like data structures, such as organizational charts, file systems, or network graphs.
63. How can you pivot data from rows to columns in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
In PostgreSQL, you can pivot data from rows to columns using the ‘crosstab’ function provided by the ‘tablefunc’ module, which must be installed and enabled to use this feature. Pivoting is typically used to transform data from a normalized format (rows) into a denormalized format (columns), making it easier to analyze and visualize.
64. What are lateral joins, and how do they differ from regular joins?
Ans:
Lateral joins, introduced in SQL, including PostgreSQL, are a specialized type of join that allows correlated subqueries to reference columns from the preceding tables in the query.
Lateral joins allow subqueries to reference columns from preceding tables, making them suitable for dynamic and context-aware calculations, while regular joins operate independently of preceding tables and don’t have this referencing capability.
65. Explain the purpose of the ‘WITH RECURSIVE’ clause in SQL queries.
Ans:
‘WITH RECURSIVE’ in SQL allows for creating recursive common table expressions (CTEs) that reference themselves. It’s used for hierarchical and recursive data processing, such as navigating organization structures or file systems, by iteratively querying and building results until a termination condition is satisfied.
66. How do you use the ‘pg_stat_statements’ extension to analyze query performance?
Ans:
- To use ‘pg_stat_statements’ for query performance analysis in PostgreSQL, enable and configure it, then access the collected statistics through the ‘pg_stat_statements’ view.
- Analyze the data to identify and optimize slow or frequently executed queries, improving database performance over time.
67. What is a materialized view in PostgreSQL, and when is it useful?
Ans:
A materialized view in PostgreSQL is a database object that stores the result of a precomputed query as a physical table. It provides a static snapshot of data, unlike regular views, which are virtual and execute queries on-demand. Materialized views are useful in scenarios where you want to improve query performance and reduce execution time by storing and accessing precomputed or summary data efficiently.
68. How can you optimize queries that involve large tables in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
- Strategic indexing and partitioning.
- Efficient query writing and careful schema design.
- Regular maintenance with ‘VACUUM’ and ‘ANALYZE’.
- Consider using LIMIT to restrict result sets.
- Implement aggregate functions for data summarization.
69. Describe the benefits of using table inheritance in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
It allows you to create a structured hierarchy of tables, simplifying data organization and code management. By inheriting properties and constraints from a parent table, child tables can efficiently reuse common structures, reducing redundancy. This approach also enables performance optimization, as each child table can be optimized individually, enhancing query speed.
70. What tools and methods are available for migrating data to PostgreSQL from other databases?
Ans:
Migrate data to PostgreSQL from other databases using tools like pg_dump, pg_restore, third-party ETL tools (e.g., Apache Nifi, Talend), and specialized migration tools like AWS DMS, Microsoft Data Migration Assistant, Oracle SQL Developer, and IBM Data Movement Tool. These tools offer flexibility and efficiency for various migration scenarios.
71. Explain the Foreign Data Wrapper (FDW) extension in PostgreSQL and its use cases.
Ans:
The Foreign Data Wrapper (FDW) extension in PostgreSQL is a useful tool that allows you to access and edit data from distant data sources as if they were local tables in your PostgreSQL database.
It basically gives you the ability to connect to other databases, APIs, or data sources and query them without any hassle from within your PostgreSQL environment.
72. How do you import and export data in various formats (e.g., CSV, JSON) in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
- Use the ‘COPY’ command for importing and exporting data.
- Specify file formats like CSV or JSON with appropriate options.
- PostgreSQL provides functions like ‘json_agg()’ and ‘jsonb_agg()’ for working with JSON data.
- These methods facilitate flexible and efficient data transfer between the database and external formats.
73. What is the purpose of the ‘COPY’ command in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
The ‘COPY’ command in PostgreSQL imports and exports data between the database and external files in various forms such as CSV, JSON, or binary. It offers efficient data transfer, making it suited for tasks such as data migration, bulk loading, and data exchange with external applications.
74. Describe the process of setting up and configuring logical replication in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
To set up logical replication in PostgreSQL, enable the feature, create a publication defining the data to replicate, establish a subscription on the subscriber side, initialize the subscription, monitor using system views, implement error handling and security, and optimize performance. Logical replication offers flexibility for replicating specific data and transformations in PostgreSQL databases.
75. How can you integrate PostgreSQL with other data sources (e.g., NoSQL databases, APIs)?
Ans:
To integrate PostgreSQL with external data sources like NoSQL databases and APIs, you can use built-in features like Foreign Data Wrappers (FDW), custom scripts, ETL tools, middleware like GraphQL, and CDC techniques.
Additionally, options like message queues, data pipelines, and replication methods provide flexibility for seamless data integration, enabling PostgreSQL to collaborate effectively with various data sources.
76. What is row-level security (RLS) in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
Row-level security (RLS) in PostgreSQL is a security feature that enables fine-grained control over data access. It allows database administrators to define policies specifying which rows of data users can access based on conditions. RLS operates transparently for users and applications, ensuring that authorized users see only the data they are permitted to view or manipulate.
77. How can you implement SSL/TLS encryption for PostgreSQL connections?
Ans:
- Generate SSL/TLS certificates.
- Configure PostgreSQL’s ‘postgresql.conf’ for SSL.
- Update ‘pg_hba.conf’ to specify SSL usage.
- Reload PostgreSQL to apply the changes.
- Install client certificates and connect securely using SSL settings.
To implement SSL/TLS encryption for PostgreSQL connections:
78. What are role attributes in PostgreSQL, and how do they impact user management?
Ans:
Role attributes in PostgreSQL are characteristics associated with database roles that play a crucial role in user management and access control within the database system.
These attributes influence how roles interact with the database and the privileges they possess. Role attributes include the superuser status, which grants extensive administrative powers, and the designation as a login role, which allows users to connect to the database.
79. Describe the purpose of role membership in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
Role membership in PostgreSQL serves the purpose of organizing and managing user access and permissions within the database. It allows roles to be grouped hierarchically, where one role can be a member of another.
80. Explain how to restrict access to specific schemas or tables in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
To restrict access to specific schemas or tables in PostgreSQL, use the ‘GRANT’ and ‘REVOKE’ commands to assign or remove privileges for roles or users. Organize roles hierarchically to manage permissions collectively, and set default privileges for consistent access control. These methods provide fine-grained control over schema and table access, enhancing security and data protection in PostgreSQL databases.
81. How is Row-level security (RLS) in PostgreSQL implemented?
Ans:
Row-level security (RLS) in PostgreSQL is implemented by defining security policies using ‘CREATE POLICY’, assigning policies to roles with ‘ALTER TABLE’, and enabling RLS with ‘ENABLE ROW LEVEL SECURITY’. PostgreSQL automatically enforces policies during queries, filtering rows based on policy conditions.
82. How do you audit and log PostgreSQL database activity for security purposes?
Ans:
- Enable logging in ‘postgresql.conf’.
- Configure log parameters like ‘log_statement’ and ‘log_duration’.
- Specify log directory and file names.
- Secure log file access permissions.
- Consider using extensions like pgAudit for advanced auditing capabilities.
83. What is streaming replication in PostgreSQL, and how does it work?
Ans:
Streaming replication in PostgreSQL is a high-availability and data replication technique that allows a standby database server to keep a precise copy of the primary database in real-time.
Streaming replication in PostgreSQL involves the continuous transfer of Write-Ahead Logging (WAL) files from the primary server to standby servers in real-time.
84. Describe the role of the ‘pg_stat_replication’ view in monitoring replication.
Ans:
The ‘pg_stat_replication’ view in PostgreSQL is essential for monitoring replication. It provides real-time data on replication connections, states, WAL location, and lag, enabling administrators to maintain replication health and reliability in the database cluster.
85. How can you set up synchronous replication in PostgreSQL for high availability?
Ans:
- Configure synchronous standbys on the primary server.
- Enable hot standby mode on standby servers.
- Restart PostgreSQL services.
- Ensure network connectivity for real-time data synchronization.
To set up synchronous replication for high availability in PostgreSQL:
86. Explain the purpose of automatic failover and how it can be configured.
Ans:
Automatic failover is a crucial feature in high-availability database setups, such as PostgreSQL streaming replication with multiple standbys. Its purpose is to ensure uninterrupted database operation by quickly promoting a standby server to become the new primary when the primary server fails.
To configure automatic failover, you can use tools like repmgr, Patroni, or pgPool-II, which monitor the primary’s status and initiate the failover process when a failure is detected.
87. What is the difference between warm standby and hot standby in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
Warm Standby:
Warm standby, or asynchronous replication, involves standby servers that are not fully up-to-date with the primary, potentially leading to data lag in read-only operations. Failover may result in some data loss.
Hot Standby:
Hot standby, or synchronous replication, maintains real-time synchronization between standby and primary servers, minimizing data lag and ensuring immediate readiness for failover with minimal data loss.
88. What are the various backup methods available in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
- pg_dump: Logical backup in SQL format.
- pg_dumpall: Exports entire database cluster.
- pg_basebackup: Physical snapshot backup.
- Continuous Archiving: Enables point-in-time recovery.
- Third-party Tools: External backup solutions.
Various PostgreSQL backup methods:
89. How do you perform a point-in-time recovery in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
To perform a point-in-time recovery (PITR) in PostgreSQL, ensure a recent base backup, restore it, copy archived WAL files, specify the recovery point in ‘recovery.conf,’ and start PostgreSQL for precise data recovery to the desired time.
90. Explain the concept of Continuous Archiving and Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR) in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
Continuous Archiving and Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR) in PostgreSQL is a mechanism for ensuring data integrity and enabling precise recovery. Continuous Archiving involves regularly copying Write-Ahead Log (WAL) files to a safe location, preserving a continuous history of database changes. This ensures that data can be recovered up to the moment before a failure, providing a reliable means of data protection and restoration in PostgreSQL.
91. What is the importance of the ‘pg_wal’ directory in backup and recovery operations?
Ans:
- Stores Write-Ahead Log (WAL) files.
- Enables continuous archiving for history.
- Facilitates point-in-time recovery.
- Ensures data integrity and consistency.
- Essential for disaster recovery scenarios.
The ‘pg_wal’ directory in PostgreSQL is vital for backup and recovery:
92. How can you automate backup and restore operations in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
Automating backup and restore operations in PostgreSQL involves implementing scheduled tasks and utilizing various tools and methods. You can schedule backups using tools like cron jobs, which run ‘pg_dump’ or ‘pg_basebackup’ commands at specified intervals. Alternatively, third-party solutions such as Bacula or cloud-based services provide advanced automation and management features.
93. Describe the importance of query optimization in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
Query optimization in PostgreSQL is crucial for database performance and efficiency. It ensures that database queries are executed in the most efficient manner, reducing response times and resource consumption. Efficient queries lead to improved user experiences, minimized server loads, and cost savings in terms of hardware and maintenance.
94. How do you analyze query execution plans using the ‘EXPLAIN ANALYZE’ command?
Ans:
To analyze query execution plans in PostgreSQL using the ‘EXPLAIN ANALYZE’ command, simply prefix your SQL query with it and execute. PostgreSQL then generates a plan detailing how the query will be processed, including table access, join methods, and index usage.
‘EXPLAIN ANALYZE’ provides actual execution times, aiding in pinpointing performance bottlenecks and areas for optimization. This valuable tool assists administrators and developers in fine-tuning the database schema and SQL statements for improved query performance.
95. What are the key factors to consider when designing indexes in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
- Query Patterns: Understand common query types.
- Column Selectivity: Assess data uniqueness and distribution.
- Index Types: Choose suitable index types.
- Composite Indexes: Consider multiple column coverage.
- Maintenance Impact: Be aware of overhead during data changes.
When designing indexes in PostgreSQL, focus on these key factors:
96. Explain the role of the query planner and optimizer in PostgreSQL.
Ans:
The query planner and optimizer in PostgreSQL collaborate to enhance query performance. The query planner dissects SQL queries, crafting multiple execution plans and estimating their respective costs, leveraging statistics and index information.
Subsequently, the optimizer selects the most efficient plan among the options generated by the query planner, with the intention of reducing query execution time and resource consumption.
97. How can you monitor and optimize memory usage in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
Monitoring and optimizing memory usage in PostgreSQL involves configuring parameters like ‘shared_buffers’ and ‘work_mem’ in the ‘postgresql.conf’ file to allocate memory efficiently based on available resources. Additionally, utilizing monitoring tools like ‘pg_stat_statements’ and ‘pg_stat_activity’ helps track memory consumption and identify performance bottlenecks for optimization.
98. What are the benefits of using connection pooling in PostgreSQL?
Ans:
- Resource Efficiency
- Improved Scalability
- Faster Response Times
- Connection Reuse
- Reduced Errors
99. What is the purpose of the ‘pg_stat_progress_vacuum’ view?
Ans:
The ‘pg_stat_progress_vacuum’ view in PostgreSQL serves the purpose of providing real-time information about the progress of vacuum operations within the database. It offers insights into ongoing vacuum processes, including the specific tables being vacuumed, the number of dead tuples removed, and the current phase of the vacuum operation.
100. How do you detect and resolve performance bottlenecks in a PostgreSQL database?
Ans:
Detecting and resolving performance bottlenecks in PostgreSQL involves systematic steps. Monitor database metrics, analyze query performance, and optimize queries by refactoring SQL and utilizing indexing.
Adjust configuration parameters, implement connection pooling, and conduct routine maintenance. Consider hardware upgrades and load balancing for scalability. Establish monitoring and alerting for proactive issue detection and resolution.






