Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that automates repetitive, rule-based processes that are traditionally completed by humans by using software robots, or “bots”. Through the simplification of procedures including data entry, transaction processing, and report production, it improves efficiency, accuracy, and speed. RPA is being used extensively in a variety of industries to save operating costs, boost output, and free up human labor for more strategically important, value-added tasks.
1. What is robotic process automation (RPA)?
Ans:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that automates repetitive, rule-based tasks in corporate processes using software robots, or “bots.” These tasks, such as data entry and transaction processing, mimic human interactions with digital systems. By implementing RPA, organizations can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve accuracy across various departments like finance, HR, customer support, and operations.
2. What are the differences between RPA and traditional automation techniques?
Ans:
RPA differs from traditional automation techniques in several key aspects. Unlike traditional Automation, which often requires complex integration with underlying systems and significant changes to existing infrastructure, RPA operates at the user interface (UI) level, interacting with applications and systems just like a human user would. RPA bots can navigate through multiple applications and systems without the need for custom integrations or APIs, making them highly adaptable and flexible.
3. What components make up an RPA system?
Ans:
- RPA Software is the core platform used to design, develop, deploy, and manage automation processes.
- Bots, or software agents, perform automation tasks by interacting with applications through the user interface (UI), mimicking human actions like mouse clicks, keystrokes, and data entry.
- Tools and interfaces for creating automation workflows include drag-and-drop features, code editors, and debugging tools for designing and testing scripts.
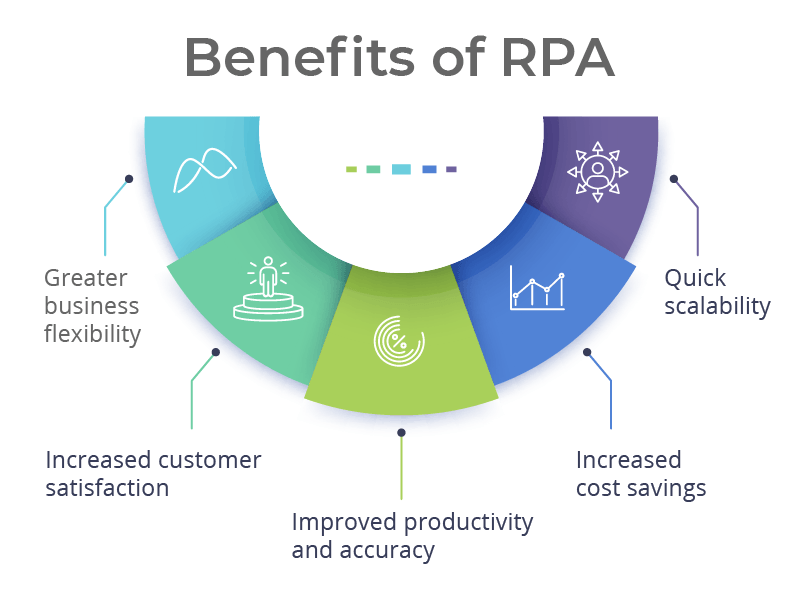
4. What are the benefits of implementing RPA in an organization?
Ans:
- Cost savings through reduced manual effort, improved resource utilization, and faster cycle times for completing tasks.
- Enhanced accuracy and quality by minimizing human errors in data processing and improving data consistency across systems.
- Faster response times and improved customer service through automated workflows and streamlined processes.
5. What industries or sectors benefit the most from RPA implementation?
Ans:
While RPA can benefit various industries, specific sectors have seen significant advantages from RPA implementation. manufacturing, and retail have particularly benefited from RPA adoption. These industries often have repetitive, rule-based processes that are ripe for Automation, such as data entry, claims processing, customer service, invoice processing, and inventory management.
6. What are the critical challenges in implementing RPA?
Ans:
- Identifying and prioritizing processes suitable for Automation, as not all processes are appropriate candidates for RPA.
- Ensuring compatibility with existing IT systems and infrastructure, including legacy systems and security protocols.
- Scaling automation initiatives across the organization while maintaining governance, control, and oversight over automation activities.
7. What metrics can be used to measure the success of an RPA implementation?
Ans:
- Increased efficiency and productivity gains in automated processes, such as faster cycle times, higher throughput, and improved resource utilization.
- Accuracy and error reduction in data processing tasks are measured by the number of errors detected and corrected before or after Automation.
- Reduction in cycle times and processing times for completed tasks, indicating improvements in workflow efficiency and responsiveness.
8. What role does RPA play in digital transformation?
Ans:
RPA plays a crucial role in digital transformation by enabling organizations to accelerate their digital initiatives and achieve strategic objectives. Moreover, RPA serves as a foundational technology that makes it easier to integrate other digital technologies, such as data analytics, machine learning, and synthetic intelligence, to support business growth and continuous development.
9. What is the difference between attended and unattended RPA?
Ans:
| Feature | Attended RPA | Unattended RPA |
|---|---|---|
| Human Intervention | Requires user actions or oversight | Operates independently without human intervention |
| Trigger Mechanism | Triggered by user actions | Triggered automatically by schedules or events |
| Use Case | Customer service, support activities | Back-office tasks, data processing, report generation |
| Dependency | Dependent on human judgment or input | Autonomous, does not require human decision-making |
10. What criteria can be used to prioritize processes for automation?
Ans:
- Frequency and volume of transactions or tasks, prioritizing high-volume and repetitive processes for Automation.
- Complexity and error-proneness of manual tasks, focusing on tasks with a high likelihood of error or inconsistency.
- Potential for cost savings and efficiency gains, identifying processes that offer significant time and resource savings through Automation.
11. What is an example of a successful RPA implementation?
Ans:
A successful RPA implementation example could be a financial services company automating its account opening process. By deploying RPA bots to handle data entry, validation, and documentation tasks, the company was able to significantly reduce processing times, improve accuracy, and enhance customer satisfaction. This led to cost savings, increased productivity, and a more streamlined customer onboarding experience.
12. What is the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in RPA?
Ans:
The role of artificial intelligence (AI) is complementary to RPA by enhancing automation capabilities with advanced cognitive skills, including natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and computer vision. AI-powered RPA can handle unstructured data, make context-aware decisions, and adapt to changing scenarios more effectively. This synergy allows organizations to automate more complex tasks that require a deeper understanding of data and context.
13. What measures can be taken to ensure security and compliance in RPA implementations?
Ans:
- Implementing role-based access controls and encryption for sensitive data, restricting access to authorized users and protecting data at rest and in transit.
- Conducting regular security assessments and audits of RPA systems, identifying vulnerabilities, and implementing remediation measures to mitigate risks.
- Adhering to secure coding practices and standards like OWASP, CIS Controls, and NIST Cybersecurity Framework ensures automation scripts are free from vulnerabilities.
14. What strategies can be used to handle exceptions in RPA processes?
Ans:
Exceptions in RPA processes can be handled through exception-handling mechanisms built into automation workflows. This may involve defining specific rules and conditions to detect and handle exceptions, such as error messages, system failures, or unexpected data variations. Exception-handling strategies may include retry mechanisms, error logging, alert notifications, manual intervention workflows, or automated error resolution routines to ensure the smooth execution of RPA processes under diverse scenarios.
15. Which programming languages are commonly used in RPA development?
Ans:
- VBScript: Often used with Automation Anywhere, VBScript provides a straightforward scripting language for automating tasks within the Windows environment.
- C#: C# is supported by UiPath and Blue Prism, offering robust object-oriented programming and access to the .NET framework.
- Python: Growing in popularity due to its versatility and ease of use in Automation, Python is supported by various RPA platforms through custom integrations or scripting capabilities.
16. What methods can be used to handle dynamic elements on web pages in RPA?
Ans:
- XPath or CSS Selectors: Using dynamic XPath or CSS selectors that identify elements based on their changing attributes or positions relative to other elements on the page.
- Explicit Waits: Implementing explicit waits to wait for specific conditions or elements to become available before proceeding with automation actions.
- Dynamic Variables: Using dynamic variables to capture changing values or attributes of elements during runtime and update automation scripts accordingly.
17. What is the purpose of selectors in RPA tools?
Ans:
Selectors in RPA tools serve as unique identifiers that allow bots to locate and interact with specific UI elements within applications or web pages. These selectors define the properties or attributes of components, such as IDs, classes, names, or XPath, enabling bots to identify and manipulate them accurately during automation tasks. Selectors play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and precision of automation workflows by allowing bots to navigate through applications, input data, and perform actions on UI elements with consistency and accuracy.
18. What techniques can be used to debug RPA scripts?
Ans:
- Logging: Adding logging statements to the script to track the execution flow and output relevant information, such as variable values or error messages.
- Breakpoints: Setting breakpoints at specific lines of code to pause execution and inspect variables or states at runtime.
- Step-through Debugging: This involves stepping through the script line by line to identify discrepancies or unexpected behaviour and troubleshoot issues.
19. What is the concept of object cloning in RPA?
Ans:
Object cloning in RPA involves creating a duplicate or replica of an existing object, such as a UI element or application window, to perform actions or operations without modifying the original object. Object cloning allows RPA bots to interact with multiple instances of the same object simultaneously or to preserve the state of an object for future reference.
20. What are triggers in RPA, and how do they work?
Ans:
- Time-Based Triggers: Executing automation processes at specific times or intervals, such as daily, weekly, or monthly schedules, to automate recurring tasks or processes.
- Event-Based Triggers: These triggers initiate automation processes based on specific events, such as file changes, email notifications, or database updates, enabling real-time workflow automation.
- User-Initiated Triggers: Users can manually trigger automation processes through interfaces or actions, like pressing a key or entering instructions, to initiate on-demand tasks or workflows as needed.
21. What is the concept of screen scraping in RPA?
Ans:
Screen scraping in RPA involves extracting data from the user interface (UI) of applications or web pages for processing or automation purposes. It is commonly used in scenarios where direct access to data sources is not available or feasible, such as legacy systems or unstructured documents. By extracting data from screens, RPA bots can automate data entry, data extraction, or data validation tasks with minimal manual intervention, improving efficiency and accuracy in automation workflows.
22. How can credentials be managed securely in RPA processes?
Ans:
- Credential Vaults: Storing sensitive information, such as usernames and passwords, in encrypted credential vaults or secure repositories ensures that credentials are protected from unauthorized access or exposure.
- Encryption: Encrypting credentials or sensitive data at rest and in transit using robust encryption algorithms and cryptographic protocols to prevent data breaches or unauthorized access.
- Role-Based Access Controls: Implementing role-based access controls restricts access to critical information based on user roles, ensuring only authorized users can use credentials as needed.
23. What is the role of exception handling in RPA?
Ans:
Exception handling in RPA involves identifying, capturing, and handling errors or unexpected events that occur during automation processes. This includes anticipating potential failure points, such as application errors, system failures, or data inconsistencies, and implementing mechanisms to respond to these exceptions gracefully. The role of exception handling is to ensure that RPA bots can recover from errors, resume execution, and complete tasks successfully without causing disruptions or data loss.
24. How is data manipulation and transformation handled in RPA?
Ans:
Data manipulation and transformation in RPA are crucial tasks, often executed through a combination of built-in functions, custom scripts, and external libraries tailored to the specific requirements of the automation process. In platforms like UiPath, this entails leveraging dedicated activities such as “Data Manipulation” and “Data Scraping” to efficiently process and transform data sets, ensuring accuracy and reliability throughout the automation workflow.
25. What is the concept of recording in RPA?
Ans:
Recording serves as a cornerstone in the RPA journey, facilitating the translation of human-computer interactions into automated sequences. This process entails meticulously capturing a user’s actions within the target application or system, encompassing mouse clicks, keyboard inputs, and interface navigations. Subsequently, these recorded actions are translated into automation scripts, laying the groundwork for streamlined and repeatable processes.
26. How is error handling managed in RPA scripts?
Ans:
- Adept error-handling mechanisms are imperative within RPA scripts to mitigate potential disruptions and ensure the robustness of automation workflows.
- This involves identifying potential error scenarios, using try-catch blocks to intercept exceptions, logging relevant error details, and implementing retry mechanisms for transient errors.
27. What RPA tools have been used, and which ones have been worked with?
Ans:
- Indeed, my experience spans various RPA tools, encompassing industry-leading platforms such as UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism.
- Each tool offers distinct functionalities and advantages tailored to diverse organizational needs and automation requirements.
- I’ve leveraged UiPath’s visual designer, Automation Anywhere’s integration, and Blue Prism’s scalability to deliver effective automation solutions.
28. What are the critical features of UiPath?
Ans:
UiPath stands out for its comprehensive suite of features, including an intuitive drag-and-drop visual designer, an extensive repository of pre-built activities catering to diverse automation scenarios, seamless integration capabilities with a multitude of applications and systems, cutting-edge AI-powered automation functionalities, and robust security measures tailored for enterprise-grade deployments.
29. What is the licensing model of UiPath?
Ans:
UiPath’s licensing model encompasses several tiers, meeting a variety of user and organizational requirements. These include the Community Edition, offering free access for individuals and small businesses; the Enterprise Edition, with flexible licensing options based on feature sets and scalability needs; and the Orchestrator platform for centralized management and deployment of automation assets.
30. What is the process for deploying robots in UiPath?
Ans:
- Deploying robots in UiPath is orchestrated seamlessly through the UiPath Orchestrator platform, serving as a centralized hub for managing automation resources.
- Leveraging Orchestrator, organizations can efficiently deploy robots to designated machines or virtual environments, ensuring optimal resource allocation and streamlined execution of automation processes.
31. What are the limitations of UiPath?
Ans:
While UiPath boasts an array of powerful features, it’s essential to acknowledge certain limitations inherent to the platform. These may include dependencies on the Windows operating system for execution, potential constraints in handling complex decision-making processes and cognitive tasks (though advancements in AI capabilities are continually addressing this), and scalability considerations in large-scale deployments necessitating meticulous planning and resource allocation strategies.
32. What steps are involved in scheduling processes in UiPath?
Ans:
Scheduling processes in UiPath are facilitated through the robust capabilities of the UiPath Orchestrator platform. The platform empowers users to define intricate automation schedules tailored to specific triggers and dependencies. By leveraging Orchestrator’s scheduling functionalities, organizations can orchestrate automation tasks to run at designated times or intervals, optimizing resource utilization and ensuring the seamless execution of automation workflows.
33. What distinguishes attended robots from unattended robots in [Tool Name]?
Ans:
- Attended robots in [Tool Name] are designed to work alongside human users, performing tasks under human supervision and often triggered by user actions.
- They excel in scenarios where human judgment or intervention is required during the automation process.
- Unattended robots, on the other hand, operate autonomously without human intervention, executing tasks according to predefined schedules or triggers.
34. How is version control managed in [Tool Name]?
Ans:
- In [Tool Name], version control is managed through dedicated features or integrations using Git-style version management systems.
- This enables users to monitor modifications made to automation projects over time, maintain multiple versions of workflows, and collaborate effectively in team environments.
- Version control ensures transparency, facilitates collaboration and helps in reverting to previous versions if needed.
35. What is the role of the control room in [Tool Name]?
Ans:
The control room in [Tool Name] serves as a centralized hub for managing and monitoring automation processes. It provides functionalities such as scheduling, monitoring, logging, and auditing of robot activities. Additionally, the control room facilitates deployment, scalability, and governance of automation assets, ensuring efficient orchestration and management of the RPA ecosystem.
36. What methods can be used to identify processes that are suitable for automation?
Ans:
Identifying processes suitable for Automation involves assessing criteria such as rule-based tasks, repetitive nature, volume, frequency, and potential for error reduction or efficiency gains. Techniques like process mining, stakeholder interviews, and analysis of process metrics can help identify suitable candidates for Automation, ensuring maximum return on investment and business value.
37. What does the process documentation phase entail in RPA implementation?
Ans:
- The process documentation phase in RPA implementation involves documenting the current state of the process to be automated, including its steps, inputs, outputs, exceptions, and dependencies.
- This documentation serves as a blueprint for designing automation workflows and ensures alignment between business requirements and automation solutions.
- It also facilitates knowledge transfer, training, and troubleshooting throughout the RPA lifecycle.
38. What methods can be used to analyze the ROI of automating a process?
Ans:
Analyzing the ROI of automating a process involves evaluating factors such as cost savings, efficiency gains, error reduction, increased productivity, and revenue generation resulting from Automation. This analysis compares the costs and benefits associated with implementing and maintaining the automation solution over its expected lifespan, helping organizations make informed decisions about prioritizing automation initiatives.
39. What criteria can be used to evaluate the scalability of an automated process?
Ans:
Evaluating an automated process’s scalability involves assessing its ability to handle increasing workload demands, user volumes, and transaction volumes without compromising performance or reliability. This evaluation considers factors such as system architecture, resource utilization, capacity planning, and the scalability of underlying technologies to ensure that the automation solution can adapt and grow with the organization’s needs.
40. What are the risks associated with automating a process?
Ans:
Automating a process entails risks such as technical challenges, process complexity, integration issues, data security concerns, compliance risks, and potential impacts on employee morale or job displacement. Mitigating these risks requires thorough planning, stakeholder engagement, robust governance frameworks, and continuous monitoring throughout the automation journey.
41. What methods can be used to optimize processes for automation?
Ans:
Optimizing processes for Automation involves:
- Streamlining workflows.
- Standardizing inputs and outputs.
- Eliminating unnecessary steps.
- Reducing manual intervention wherever possible.
42. What does the concept of process mining in RPA entail?
Ans:
Process mining in RPA involves analyzing event logs and data captured from existing IT systems to discover, monitor, and improve business processes. It utilizes techniques such as process discovery, conformance checking, and performance analysis to visualize process flows, identify bottlenecks, uncover deviations from expected behaviours, and optimize processes for Automation.
43. What strategies can be used to handle process variations in RPA implementations?
Ans:
Handling process variations in RPA implementations involves designing flexible automation solutions capable of adapting to different scenarios, exceptions, and business rules. This may entail using conditional logic, exception-handling mechanisms, parameterization, and dynamic decision-making to accommodate variations in input data, process flows, and environmental conditions, ensuring robust and resilient automation workflows.
44. What methods can be used to collaborate with business stakeholders during RPA implementation?
Ans:
- Collaborating with business stakeholders during RPA implementation involves engaging in open communication, understanding their requirements, and aligning automation initiatives with strategic business goals.
- This collaboration entails conducting stakeholder interviews, workshops, and demos to gather feedback, prioritize automation opportunities, and ensure that the automation solution meets the needs of the business users.
45. What does business process modeling mean in the context of RPA?
Ans:
- Business process modelling in RPA involves visually representing business processes using standardized notation such as BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation).
- This modelling technique allows stakeholders to map out current and future state processes, identify inefficiencies, and define automation opportunities.
- It serves as a blueprint for designing automation workflows and facilitates clear communication between business and technical teams throughout the RPA lifecycle.
46. What methods can be used to ensure alignment between business objectives and RPA initiatives?
Ans:
Ensuring alignment between business objectives and RPA initiatives requires a holistic approach that involves engaging with key stakeholders, understanding organizational priorities, and prioritizing automation opportunities that deliver tangible business value. This alignment is achieved by continuously evaluating automation projects against strategic goals, measuring their impact on key performance indicators (KPIs), and adjusting priorities as needed to maximize ROI and business impact.
47. What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring RPA success?
Ans:
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring RPA success incorporate measurements like cost reductions and increases in process efficiency, error reduction, cycle time reduction, throughput increase, resource utilization, customer satisfaction, and compliance adherence. These KPIs help assess the impact of Automation on business outcomes and inform decision-making throughout the RPA journey.
48. What strategies can be used to manage change during RPA implementation?
Ans:
- Change management during RPA implementation includes communication, stakeholder engagement, training, and assessing readiness to prepare employees for automation.
- This includes addressing concerns, managing resistance to change, and providing support to employees transitioning to new roles or responsibilities.
- Additionally, establishing governance frameworks and change control processes helps mitigate risks and ensure the smooth implementation of automation initiatives.
49. What is an example of a business case for implementing RPA?
Ans:
- A business case for RPA implementation could involve automating repetitive data entry tasks in a finance department to improve accuracy, reduce processing time, and free up employees for higher-value activities.
- Implementing RPA leads to cost savings, increased productivity, improved data quality, and enhanced efficiency, yielding a positive ROI and competitive advantage.
50. What methods can be used to assess the impact of RPA on existing business processes?
Ans:
Assessing the impact of RPA on existing business processes involves analyzing metrics such as process cycle time, mistake rates, resource utilization, as well as customer satisfaction before and after automation implementation. This analysis helps quantify the benefits of Automation, Determine what needs to be improved, and streamline procedures to maximize effectiveness. And effectiveness.
51. What strategies can be used to integrate RPA with existing systems and applications?
Ans:
Integrating RPA with existing systems and applications involves leveraging APIs, web services, and integration platforms to create smooth data sharing and communication amongst various systems. This integration enables RPA robots to interact with and automate tasks across multiple applications, databases, and platforms, enhancing end-to-end process automation and interoperability.
52. What role do APIs play in RPA integrations?
Ans:
Application Programming Interfaces, or APIs, are essential to RPA integrations by providing standardized interfaces for interacting with external systems and applications. RPA robots leverage APIs to extract data, trigger actions, and exchange information with backend systems, enabling seamless integration and Automation of business processes across the enterprise.
53. What challenges are faced when integrating RPA use antiquated systems?
Ans:
- It can be challenging to combine RPA with outdated systems due to obsolete technologies, a lack of standardization, complex data formats, limited API support, and security concerns.
- To overcome these obstacles, cooperation and technical know-how are needed with IT teams, and innovative solutions tailored to the specific requirements of legacy systems.
54. What strategies can be used to handle data synchronization between systems in RPA?
Ans:
- Handling data synchronization in RPA requires robust data mapping, transformation, and validation to ensure consistency and accuracy across systems.
- This involves using RPA capabilities like data scraping and manipulation to synchronize data in real-time or batch mode based on integration needs.
55. What role does machine learning play in RPA?
Ans:
Machine learning (ML) dramatically enhances robotic process automation (RPA). ML gives robots the ability to learn from data, adjust to changing environments, and make wise decisions on their own. Because ML algorithms can identify trends, forecast results, and optimize workflows based on past data and real-time input, they can improve automation processes.
56. How is cognitive automation implemented in RPA processes?
Ans:
Implementing cognitive Automation in RPA involves integrating AI technology, including machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing (NLP), into automation workflows. This enables robots to understand unstructured data, extract insights from documents, images, and videos, and perform complex cognitive tasks such as language translation, sentiment analysis, and image recognition.
57. What is the concept of self-learning robots in RPA?
Ans:
- Self-learning robots in RPA refer to intelligent automation solutions that can continuously improve and adapt their behaviour over time without human intervention.
- These robots use advanced machine learning algorithms to analyze data, learn from experience, and optimize their performance autonomously, resulting in more efficient and adaptive automation.
58. What are the limitations of traditional RPA, and how can they be overcome?
Ans:
- Traditional RPA is limited in handling complex decision-making, cognitive tasks, and unstructured data.
- These limitations can be overcome by integrating Artificial Intelligence technologies, such as computer vision, natural language processing, and machine learning, into automation workflows.
- By leveraging AI capabilities, organizations can enhance the capabilities of RPA robots to handle a broader range of tasks and scenarios effectively.
59. What steps can be taken to implement process orchestration in RPA?
Ans:
Implementing process orchestration in RPA involves coordinating and managing end-to-end automation workflows across multiple systems, applications, and environments. This includes defining dependencies, sequencing tasks, handling exceptions, and monitoring execution to ensure smooth and efficient automation processes. Additionally, it enables better resource utilization and enhances the overall performance of automated workflows.
60. What is the concept of hyper-automation?
Ans:
Hyperautomation is an approach to Automation that combines RPA with complementary technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, process mining, and analytics to automate complex business processes end-to-end. This holistic approach aims to maximize automation coverage, efficiency, and agility by leveraging a diverse set of automation tools and technologies tailored to specific business needs.
61. What strategies can be used to explain the benefits of RPA to non-technical stakeholders?
Ans:
Communicating RPA’s benefits to non-technical stakeholders involves highlighting tangible outcomes such as cost savings, efficiency gains, error reduction, and improved customer experience. Using real-world examples, case studies, and demonstrations can help illustrate the impact of RPA on business processes and outcomes clearly and compellingly.
62. What strategies can be used to address resistance to change during RPA implementations?
Ans:
- Handling resistance to change in RPA implementations requires proactive communication, stakeholder engagement, and change management strategies.
- This includes addressing concerns, providing training and support, soliciting feedback, and demonstrating the value of RPA through pilot projects and success stories.
- Building a culture of collaboration and empowerment can also help overcome resistance and foster buy-in from stakeholders.
63. What strategies can employ to align and manage stakeholder expectations in RPA projects?
Ans:
Managing stakeholder expectations in RPA projects involves setting clear goals, defining success criteria, and maintaining open communication throughout the project lifecycle. This includes regular updates, progress reports, and stakeholder meetings to ensure alignment between project objectives and stakeholder needs. Proactively managing expectations helps build trust and confidence in the RPA initiative.
64. What strategies can be used to prioritize tasks and manage time effectively in RPA projects?
Ans:
Prioritizing tasks and managing time effectively in RPA projects involves:
- Defining clear objectives.
- Breaking down tasks into smaller milestones.
- Allocating resources based on project priorities.
65. What role do interpersonal skills play in RPA projects?
Ans:
Interpersonal skills play a crucial role in RPA projects by facilitating collaboration, communication, and teamwork among project stakeholders. These skills include active listening, empathy, conflict resolution, and relationship building, which help foster a positive work environment, build trust, and drive successful project outcomes. Additionally, strong interpersonal skills enable effective negotiation and help align diverse interests toward common goals.
66. What measures can be taken to ensure that RPA processes comply with regulatory requirements?
Ans:
Ensuring RPA processes are compliant with regulatory requirements involves:
- Conducting thorough risk assessments.
- Identifying relevant regulations and standards.
- Implementing controls to mitigate compliance risks.
67. What methods can be used to stay updated on the latest trends and developments in RPA?
Ans:
- Regularly reading industry publications
- Attending webinars and conferences
- Participating in online forums and communities
- Networking with peers and experts in the field
68. What certifications or training programs can be completed in RPA?
Ans:
Can complete a certifications and training programs in various RPA platforms such as UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism. These certifications cover topics ranging from basic automation ideas to complex subjects like machine learning, cognitive Automation, and process optimization. Additionally, attending online forums, webinars, and industry conferences offers insights and networking opportunities with RPA professionals, helping to stay informed about emerging technologies and best practices.
69. What is the career progression path for RPA professionals?
Ans:
The career progression path for RPA professionals typically begins with entry-level roles such as RPA developer or analyst, where individuals gain hands-on experience in building and deploying automation solutions. As they gain expertise, they may advance to roles such as RPA architect, solution consultant, or project manager, where they are responsible for designing and leading automation initiatives at an organizational level.
70. What can envision for the future of RPA technology?
Ans:
- The future of RPA technology is promising, With ongoing developments in machine learning, artificial intelligence, and process automation.
- RPA is expected to become more intelligent, adaptive, and autonomous, with robots capable of handling increasingly complex tasks and decision-making processes.
- RPA is expected to integrate more with advanced technologies like robotic process intelligence, process mining, and low-code platforms, enhancing overall business automation and efficiency.
71. What methods can be used to ensure scalability and resilience in RPA implementations?
Ans:
In the next five years, RPA is expected to evolve into a more mature and ubiquitous technology with widespread adoption across industries and sectors. We can see RPA solutions becoming more intelligent, scalable, and resilient, with robots capable of autonomously learning, adapting, and optimizing processes in real-time. Additionally, RPA is likely to become more integrated with other technologies, such as AI, analytics, and cloud computing, enabling organizations to achieve greater levels of Automation and innovation in their operations.
72. What strategies can employ to ensure scalability and resilience in RPA implementations?
Ans:
Ensuring scalability and resilience in RPA implementations involves:
- Designing robust automation architectures.
- Leveraging scalable infrastructure and cloud resources.
- Implementing best practices for deployment, monitoring, and management of automation assets.
73. What are the ethical considerations in RPA implementation?
Ans:
Ethical considerations in RPA implementation include:
- Ensuring data privacy and security.
- Avoiding biases and discrimination in automation decisions.
- Promoting transparency and accountability in automation processes.
- Mitigating potential social and economic impacts of Automation on workers and communities.
74. What is the concept of self-healing robots in RPA?
Ans:
Self-healing robots in RPA refer to automation solutions capable of detecting and resolving errors or anomalies in automation processes autonomously, without human intervention. These robots leverage advanced monitoring, analytics, and machine learning capabilities to identify issues, diagnose root causes, and apply corrective actions in real time, ensuring continuous operation and resilience of automation workflows.
75. What strategies can be use to handle unstructured data in RPA?
Ans:
Handling unstructured data in RPA involves leveraging AI technologies such as natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and text analytics to extract, interpret, and process information from documents, images, and other unstructured sources. This may include techniques such as document classification, entity recognition, sentiment analysis, and optical character recognition (OCR) to transform unstructured data into structured formats that can be processed and analyzed by RPA robots.
76. What strategies can employ to address resistance to RPA adoption?
Ans:
To overcome resistance to RPA adoption, it’s essential to communicate the benefits of Automation, involve stakeholders in the decision-making process, address concerns and misconceptions, provide training and support, and demonstrate the value of RPA through pilot projects and success stories. Additionally, fostering a culture of innovation, collaboration, and continuous improvement can create a positive environment conducive to RPA adoption and success.
77. What methods can be used to ensure continuous improvement in RPA processes?
Ans:
- Ensuring continuous improvement in RPA processes involves establishing feedback mechanisms, monitoring performance metrics, analyzing automation results, and identifying opportunities for optimization and refinement.
- This may include conducting regular reviews and retrospectives, soliciting feedback from stakeholders, and implementing changes and enhancements to automation workflows based on lessons learned and evolving business requirements.
78. What is the role of process discovery in RPA implementation?
Ans:
- Process discovery in RPA implementation involves analyzing and documenting existing business processes to identify automation opportunities and define automation requirements.
- This includes mapping process flows, reporting tasks, inputs, outputs, and exceptions, and capturing relevant metrics and data points.
- Process discovery helps ensure that automation solutions are aligned with business needs and objectives, leading to more effective and successful RPA implementations.
79. What is the approach to user acceptance testing (UAT) in RPA projects?
Ans:
User acceptance testing (UAT) in RPA projects involves working with business users to define test scenarios and acceptance criteria, validating automation workflows against user requirements, and ensuring they meet functional, performance, and usability standards. Any issues identified are addressed before obtaining stakeholder approval for deployment, ensuring that the final solution aligns with business needs and expectations.
80. What are the key factors to consider when selecting an RPA tool?
Ans:
Essential things to think about before choosing an RPA tool include functionality, scalability, ease of use, integration capabilities, vendor support, licensing model, and total cost of ownership. Organizations should evaluate RPA tools based on their specific automation requirements, technical infrastructure, and strategic objectives and select a tool that best fits their needs and priorities.
81. What methods can be used to manage the lifecycle of RPA bots?
Ans:
- Managing the lifecycle of RPA bots involves several stages, including bot development, testing, deployment, monitoring, maintenance, and retirement.
- Throughout each stage, it’s essential to track bot performance, ensure compliance with organizational policies and standards, and periodically review and update automation processes to reflect changes in business requirements or technology landscape.
82. What approaches can be taken to manage version upgrades and maintenance in RPA deployments?
Ans:
Handling version upgrades and maintenance in RPA deployments involves establishing robust change management processes, scheduling regular maintenance windows, and testing new releases in a controlled environment before deploying them to production. This ensures that upgrades are implemented smoothly, minimize disruptions to automation workflows, and maintain system stability and reliability.
83. What role does change management play in RPA projects?
Ans:
Change management plays a crucial role in RPA projects by facilitating the adoption of automation solutions, managing resistance to change, and ensuring that organizational stakeholders are aligned and supportive of automation initiatives. This involves communication, training, stakeholder engagement, and establishing governance structures to guide the implementation and integration of RPA into existing business processes.
84. What strategies can be used to mitigate the risks associated with RPA implementation?
Ans:
- Mitigating risks associated with RPA implementation involves conducting thorough risk assessments, identifying potential pitfalls, and implementing mitigation strategies to address them.
- This may include establishing robust governance frameworks, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, implementing security controls, providing training and support to users, and continuously monitoring and evaluating automation processes for potential risks and vulnerabilities.
85. What is the concept of a virtual workforce in RPA?
Ans:
- The concept of a virtual workforce in RPA refers to a scalable and flexible workforce comprised of software robots capable of executing repetitive, rule-based tasks across digital systems and applications.
- These virtual workers operate autonomously, 24/7, without the need for breaks or supervision, enabling organizations to achieve significant productivity gains, cost savings, and operational efficiency improvements.
86. What is the role of analytics in optimizing RPA processes?
Ans:
Analytics play a critical role in optimizing RPA processes by providing insights into automation performance, identifying areas for improvement, and enabling data-driven decision-making. This includes analyzing process metrics, identifying bottlenecks, detecting patterns, and predicting outcomes to optimize automation workflows, enhance efficiency, and drive continuous improvement in RPA initiatives.
87. What methods can used to manage exceptions caused by system errors in RPA?
Ans:
Handling exceptions caused by system errors in RPA involves implementing robust exception-handling mechanisms, such as try-catch blocks, retry logic, and error logging, to gracefully handle unexpected scenarios and ensure the reliability and resilience of automation workflows. Additionally, proactive monitoring and alerting systems help detect and respond to errors in real time, minimizing their impact on business operations.
88. What is the concept of attended automation in RPA?
Ans:
- Attended Automation in RPA refers to automation solutions that work alongside human users to augment their productivity and efficiency.
- Attended automation involves human-robot collaboration, where robots assist users with repetitive tasks and provide real-time support, in contrast to unattended automation, which operates autonomously in the background.
89. What strategies can be used to foster innovation in RPA projects?
Ans:
Fostering innovation in RPA projects involves creating a culture of experimentation, creativity, and continuous improvement within the organization. This includes encouraging collaboration between business and IT teams, providing opportunities for training and upskilling, promoting knowledge sharing and idea generation, and incentivizing innovative solutions that create competitive advantage and commercial value.
90. What strategies can be used to ensure data security in RPA implementations?
Ans:
Ensuring data security in RPA implementations involves implementing strong controls like access restrictions, encryption, data masking, and secure authentication. Organizations should also conduct regular security assessments, follow best practices and compliance standards, and provide training to raise awareness about data security risks. Continuous monitoring of data access and usage further enhances security measures.