
- Definition and Importance
- UX vs UI Explained
- Core Principles of UX
- Core Principles of UI
- The Design Process
- Role in Product Development
- Tools and Techniques Used
- Real-world Applications
- Conclusion
Definition and Importance of UX/UI Design
UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface) design are critical disciplines in creating digital products that are both functional and enjoyable to use. UX design focuses on the overall experience a user has while interacting with a product, aiming to make it intuitive, efficient, and satisfying. It involves understanding user behaviors, needs, and motivations through research and testing to design seamless interactions and workflows.On the other hand, UI design deals with the visual and interactive elements of a product, such as buttons, icons, typography, and color schemes. It ensures that the product’s interface is visually appealing and aligns with brand identity while being easy to navigate. Together, UX User Experience and UI Design Process are essential because they directly impact how users perceive and engage with digital products. Good UX/UI design can increase user satisfaction, boost engagement, improve accessibility, and drive business success by reducing churn and increasing conversions. In today’s competitive digital landscape, investing in effective UI/UX Training is key to building products that not only meet user expectations but also provide meaningful, enjoyable experiences. In today’s digital era, users expect products that are intuitive, efficient, The Design Process and delightful. UX/UI design directly influences customer satisfaction, engagement, and retention. Well-executed UX/UI design leads to better usability, higher conversion rates, fewer errors, and ultimately drives business success by creating strong emotional connections between users and products.
Ready to Get Certified in UI/UX Design? Explore the Program Now UI/UX Design Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
UX vs UI Explained
While often used together, UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface) design refer to distinct but closely related aspects of product design. UX design is about the overall experience a user has when interacting with a product or service. It focuses on usability, functionality, typography and how smoothly users can achieve their goals. UX designers conduct research, create user personas, map out user journeys, and test prototypes to ensure the product meets real user needs and solves problems effectively. In contrast, UI design deals with the product’s visual and interactive elements the look and feel of the interface. UI designers craft layouts, choose color palettes, Design Process buttons, icons, Tools and Techniques Used and typography, and ensure that the design is consistent and aesthetically pleasing. They focus on making the product’s interface intuitive and engaging. Simply put, UX User Experience is about how the product works and the overall user journey, while UI is about how the product looks and the specific interface elements users interact with. Both disciplines work hand-in-hand to create digital experiences that are not only functional but also enjoyable and visually appealing.
Core Principles of UX Design
Effective UX design is built on several key principles:
- User-Centered Design: Designing with the users’ needs and pain points at the forefront.
- Accessibility: Ensuring the product is usable by people of all abilities.
- Usability: Making products simple, intuitive, and efficient to use.
- Consistency: Uniform design patterns and interactions across the product.
- Feedback: Providing clear, immediate responses to user actions.
- Hierarchy: Organizing information to guide users’ attention and actions.
- Empathy: Understanding and addressing user emotions and motivations.
- Clarity: Interfaces should be clear and easy to understand.
- Visual Hierarchy: Using size, color, and spacing to prioritize content.
- Consistency: Repeating visual elements and interaction patterns.
- Affordance: Visual cues that indicate how elements can be used.
- Feedback: Visual or auditory signals confirming user interactions.
- Simplicity: Avoid clutter and unnecessary design elements.
- Aesthetics: Attractive visuals improve user engagement.
- Research: Understanding user needs through interviews, surveys, and data analysis.
- Define: Synthesizing research into user personas, user journeys, and problem statements.
- Ideate: Brainstorming and sketching design solutions, wireframing.
- Design: Creating high-fidelity mockups and prototypes.
- Test: Conducting usability tests and gathering user feedback.
- Implement: Working with developers to build the product.
- Iterate: Refining the design based on analytics and further feedback.
- Design: Figma, Sketch, Adobe XD
- Prototyping: InVision, Marvel
- Wireframing: Balsamiq, Whimsical
- User Research: Optimal Workshop, Maze
- Collaboration: Miro, FigJam
- Testing: Lookback, UsabilityHub
- Development Handoff: Zeplin, Abstract
- User interviews and surveys
- Usability testing (remote and in-person)
- A/B testing
- Card sorting for information architecture
- Heatmaps and analytics for behavior tracking
To Explore UI/UX in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive UI/UX Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Core Principles of UI Design
UI design principles ensure visual harmony and effective interaction:
The Design Process
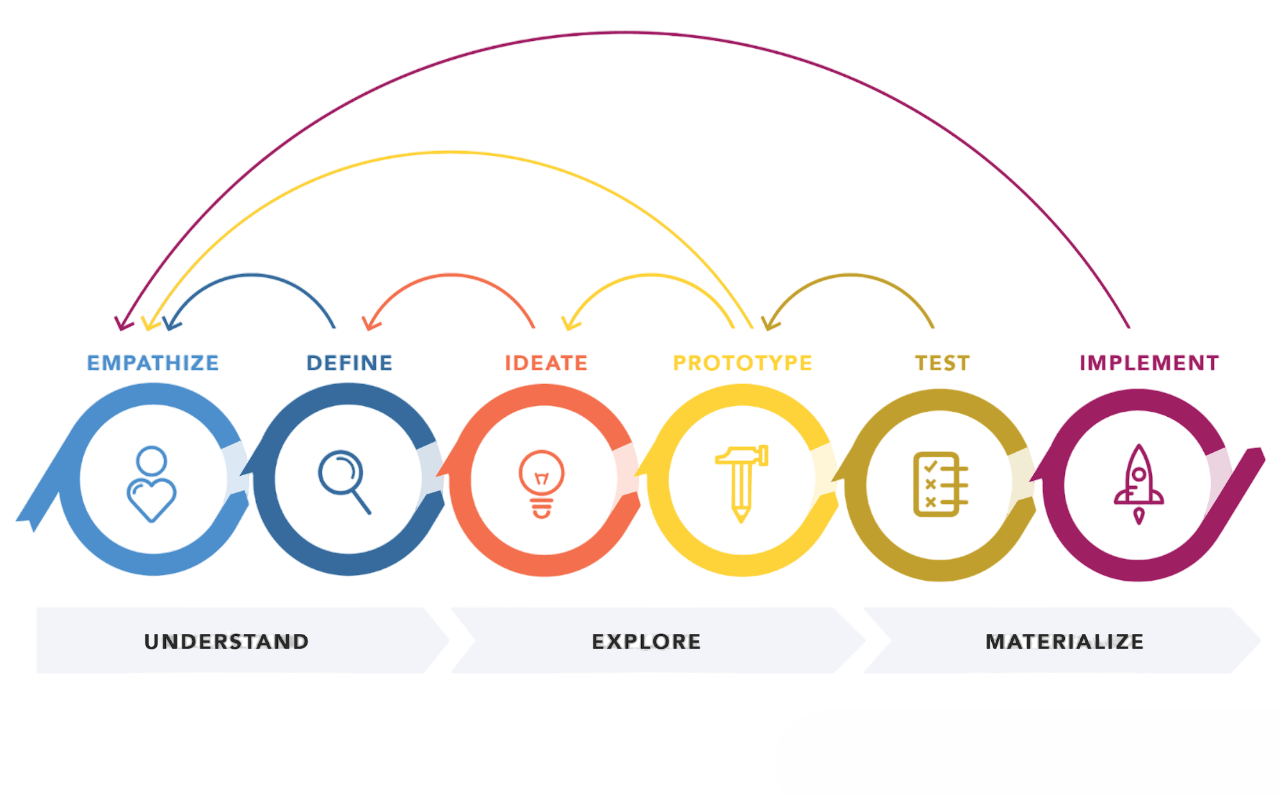
This iterative process ensures the product evolves according to user needs and business goals.
Looking to Master Machine Learning? Discover the UI/UX Design Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Role in Product Development
UX/UI designers collaborate closely with product managers, developers, marketers, and stakeholders to create products that meet user needs and business objectives.UX and UI User Interface design play vital roles throughout the product development lifecycle, ensuring that digital products are both user-friendly and visually compelling. UX designers typically get involved early in the process, conducting user research, defining user personas, typography and mapping out user journeys to understand the needs and pain points of the target audience. Their insights guide the product’s overall structure, features, and flow, helping to create intuitive and efficient solutions.
UI designers come in once the framework is established, focusing on translating these functional requirements into attractive and consistent visual designs. They design interfaces that are easy to navigate, accessible, and aligned with the brand’s identity, ensuring a cohesive user experience. Together, Digital Marketing Training User Interface collaborate closely with product managers, developers, and stakeholders to iterate designs based on user feedback and testing. Their combined efforts help minimize usability issues, reduce development costs, and increase user satisfaction and engagement, ultimately contributing to the product’s success in the market.Together, they ensure the product is functional, user-friendly, and visually engaging.
Tools and Techniques Used
Common Tools:
Techniques:
Preparing for UI/UX Design Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on UI/UX Design Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Real-world Applications
UX/UI User Interface is integral to creating effective digital products solutions across a wide range of industries, each with unique user needs and challenges. In e-commerce, the focus is on streamlining shopping and checkout processes, minimizing cart abandonment by simplifying navigation, speeding up payment flows, and providing clear product information to enhance customer satisfaction and boost sales. In the healthcare sector, UX/UI designers prioritize accessibility and security by crafting patient portals that allow easy appointment scheduling, medical record access, typography and telehealth services, ensuring patients of all ages and abilities can manage their health conveniently. Within finance, UX/UI design simplifies complex data dashboards, transforming vast amounts of financial information into clear, actionable insights for both professionals and consumers. This helps users make informed decisions with confidence. In education, engaging learning platforms are developed to foster interactive and personalized experiences that motivate learners, support different learning styles, and improve knowledge retention through intuitive interfaces and multimedia content. For enterprise software, usability improvements are critical to boost employee productivity, reduce errors, and shorten training times, ensuring that business tools integrate smoothly into daily workflows. Finally, in the world of mobile apps, responsiveness and intuitive navigation are essential, as users expect fast, seamless experiences on devices of all sizes. Designers focus on touch-friendly interfaces, quick load times, Tools and Techniques Used and easy access to core features to keep users engaged on the go. Beyond these industries, UX/UI design also plays a transformative role in sectors like travel, gaming, government services, and more, continuously adapting to emerging technologies and user expectations. By prioritizing user-centered design principles, businesses can create digital products that are not only functional but also delightful and inclusive.
Conclusion
UX/UI design is a dynamic field blending creativity, psychology, and technology to create meaningful digital experiences. Whether you are starting a career or scaling your expertise, understanding core principles, mastering the design process, Tools and Techniques Used and staying updated on tools and trends are vital for success. With a focus on users and business goals, user Interface, The Design Process shapes the future of digital interaction.




