
In this article, we will discuss the most important DBMS Interview Questions in order to make you familiar with the type of questions that can be asked during a job interview related to the Database Management System (DBMS). Basically, out of my personal experience, there is not any specific way or formula to get through an Interview Process and it totally depends on you and the type of Interviewer. But still, it’s good to be prepared on your profile for your own confidence and knowledge so that you don’t feel hesitant to answer the questions asked during an interview.
1. What is a database?
Ans:
- A database is a readily accessible, manageable, and updatable collection of logical, consistent, and organized data. Databases, is mosometimes referred to as electronic databases, are stored as a file or collection of files on magnetic disks, cassettes, and other auxiliary devices. They are designed to facilitate the productive creation, insertion, and updating of data.
- A database stly made up of objects or tables, which hold fields and records. The basic building blocks of data storage are fields that hold details about a particular component or feature of the database’s object. Data is extracted from a database in the form of queries using a database management system. Then, index it into rows, tables, and columns.
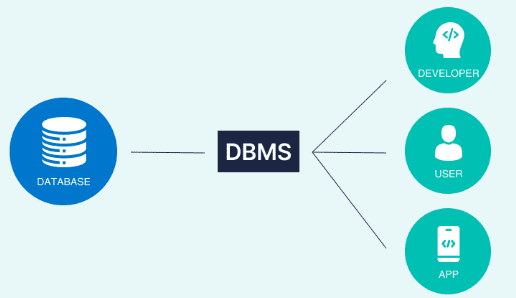
2. What is a database management system?
Ans:
A collection of tools called a database management system (DBMS. facilitates the creation and upkeep of databases for users. Stated otherwise, a database management system gives us an interface or tool to do a variety of operations, like building a database, adding data, removing data, updating data, and so forth. With DBMS, we may resolve a number of problems, including data inconsistency, data redundancy, fast access, better structure, and more. Several popular database management systems include Amazon SimpleDB.
3. Describe the drawbacks of conventional file-based systems and how DBMS is a superior option.
Ans:
Traditional file-based systems don’t have indexing, so our only option is to browse the entire website, which slows down and takes longer to get material. The other problem is inconsistency and redundancy since files frequently include redundant and duplicate data, and altering one makes the others inconsistent. Due to the disorganized nature of the data, traditional file-based solutions make data access more challenging.
Another disadvantage is that there is no concurrency control, so one operation locks the entire page instead of multiple operations working on the same file simultaneously, as with DBMS.
4. Describe a few DBMS benefits.
Ans:
Data sharing refers to the ability of numerous users to access the same database at the same time. Integrity limits, on the other hand, allow for more sophisticated data storage in a database.
- Data redundancy control: Facilitates the integration of all data into a single database in order to support a data redundancy control system.
- Data independence: The ability to modify data structure without having an impact on the structure of any active application programs. The ‘backup and recovery’ feature automatically creates a backup of the data and restores it when necessary.
- Data Security: The features required to make data storage possible are provided by a database management system
5. How does one use a view?
Ans:
- Equality Join: The most common type of join condition, this one involves connecting columns from both tables that have the same values.
- Non-Equality Join: Joins can also be performed using comparison operators, like greater than, less than, or others, in place of equality.
6. What is a procedure that is stored?
Ans:
A function that has a stored procedure within it is comparable to a collection of interconnected operations. It includes a collection of procedures that are frequently used in applications to carry out certain standard database functions. A collection of SQL statements that are kept together in a database is called a stored procedure in SQL. It can execute one or more DML operations on the database and return value based on the statements in the procedure and the arguments you pass.
7. What is a business dealing? What qualities do ACIDs have?
Ans:
A collection of tools for characterizing constraints, semantics, and data make up a data model. They also help in describing how data entities and their attributes relate to one another. Among the most widely used data models are relational, network, entity connection, and hierarchical models. You could also find out more and examine other data modeling interview questions to learn more about data models.
8. What distinguishes a stored procedure from a trigger?
Ans:
- Triggers are not callable directly, in contrast to Stored Procedures. Only questions can be connected to them. Parameters can be inserted into stored routines.
- Triggers run automatically in response to specific commands that are executed on a table. Since a procedure cannot be executed automatically, the EXEC command must be used. Triggers are mostly used to log actions taken on a table and preserve referential integrity.
9. What is a business dealing? What qualities do ACIDs have?
Ans:
A collection of database actions known as a database transaction must be handled as a whole, meaning that either every operation is carried out or not. A bank transaction from one account to another can serve as an illustration. It is necessary to do either all of the credit and debit operations or none of them. A collection of characteristics known as ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability. ensures the dependable processing of database transactions.
10. Describe indexes.
Ans:
Although it requires more writes and reads, a database index is a type of data structure that speeds up data retrieval operations on a database table. Greater storage space is used to keep the extra copy of data. On a disk, data can only be kept in one order. Indexes are constructed on tables to facilitate faster searches, such as binary searches for different values, in order to provide faster access according to different values. Although these indexes require more disk space, they provide a speedier search based on many frequently queried parameters.
11. What does a DBMS checkpoint mean?
Ans:
- By using the checkpoint technique, all prior logs are permanently stored on the storage device and are deleted from the system. Two strategies that can help the DBMS recover and maintain the ACID qualities include keeping the shadow page and preserving the transaction log.
- Checkpoints are essential for a log-based recovery mechanism. Checkpoints are the lowest locations from which the database engine can resume operations following a crash. They are designated as the lowest points from which all committed data up to the crash moment can be recovered using the transaction log record.
12. What is a system of databases?
Ans:
Software for databases and database management systems is gathered together to form a database system. We can use the database system to carry out certain tasks, such as:
- There are no issues with data redundancy or inconsistency, and the data is readily stored in the database.
- DBMS software will be used to extract data from the database as needed. You may thus store, retrieve, and access data securely and precisely when you use database and DBMS software in tandem.
13. What do you mean By “Data Model,”?
Ans:
A collection of tools for characterizing constraints, semantics, and data make up a data model. They also help in describing how data entities and their attributes relate to one another. Among the most widely used data models are relational, network, entity connection, and hierarchical models. You could also find out more and examine other data modeling interview questions to learn more about data models.
14. In DBMSs, when does checkpointing happen?
Ans:
- A checkpoint represents a moment in time in the database management system’s existence. In the event of a subsequent crash, the DBMS can employ checkpoints to reduce the amount of work that needs to be done during a restart.
- Checkpoints are used to recover databases following system crashes. Checkpoints are a feature of the log-based recovery approach. Checkpoints are used when a system crash necessitates a system restart. As a consequence, we won’t have to start the transactions over.
15. What distinguishes an attribute from an entity?
Ans:
- An entity in a database is a physical object. The worker, title, division, and
- Examples of various entities in an employment database are as follows.
- An attribute is a characteristic that characterizes an entity.
- For instance, the entity “employee” may possess attributes like age, ID, and name.
16. What distinguishes non-clustered from clustered indexes?
Ans:
| Non-Clustered Index | Clustered Index |
|---|---|
| A separate structure that stores a sorted order of key values along with pointers to the actual data rows. | Determines the physical order of data rows in the table based on the indexed column(s). |
| Stored separately from the actual data rows, maintaining a distinct structure. | The table itself is the index structure, and data rows are physically sorted based on the indexed column(s). |
| Does not affect the physical order of data rows in the table; they can be stored in any order. | Dictates the physical order of data rows in the table based on the indexed column(s). |
17. What does the term “query optimization” mean?
Ans:
The process of identifying a strategy for analyzing a query with the lowest projected cost is known as query optimization. This stage appears when there are multiple algorithms and methods to accomplish the same task. Some of the advantages of query optimization include the following:
- In a shorter amount of time
- It is possible to run queries.
- Simplifies the intricacy of space and time.
18. How are NULL values the same way as zero or blank space?
Ans:
A blank space or a value of zero should not be confused with a NULL value. While blank space is a character and zero is a number, NULL indicates a value that is assigned, unavailable, unknown, or not applicable.
19. What do you mean when you talk about atomicity and aggregation?
Ans:
One relationship set can communicate with another relationship set thanks to this E-R model feature. According to this property, a database alteration must either follow every guideline or not follow any at all. Therefore, in the event that a part of the transaction fails, the entire transaction
20. What are the DBMS’s various abstraction levels?
Ans:
There are three levels of data abstraction in DBMSs.
- Physical Level: The lowest level of abstraction, the physical level, describes how data is stored.
- Logical Layer: The Logical level of abstraction comes after the Physical level. What information is kept in the database and how it is related to other information is determined by this layer.
- View degree: Only a section of the complete database is described by the highest degree of abstraction.
21. What is a model of an entity-relationship?
Ans:
Real-world objects are represented as entities in this diagrammatic approach to database architecture, and the relationships between them are specified. This technique enables the DBA workers to understand the schema rapidly. An information technology (IT. system’s relationships between individuals, things, locations, ideas, and events are shown graphically in an entity relationship diagram (ERD., often called an entity-relationship model.
22. In DBMS terminology, what do you mean by an entity, an entity type, and an entity set?
Ans:
- Entity: An entity is an actual object that possesses attributes that are nothing more than the characteristics of the object. An example of an entity is an employee. Empath, Emname, and other properties are possible for this creature.
- Entity Type: An entity type is a group of entities that share comparable characteristics. In general, one or more connected tables in a database are referred to as an entity type. Because of this, entity type might be regarded as a characteristic that makes an entity distinctive. Aspects like department, empid, empname, and so forth can be assigned to an employee.
- Entity Set: An entity set in a database is an assembly of all the entities belonging to a particular entity type. A group of workers, a group of businesses, or a group of people are a few examples of entity sets.
23. What does “transparent DBMS” mean to you?
Ans:
A type of database management system called a transparent DBMS hides its actual physical structure from users. The term “physical structure,” which can also refer to “physical storage structure,” describes how data is stored on a disk and relates to the DBMS’s memory management. Transparencies in DBMS refers to the ability of a DBMS system to provide the user with a transparent distribution.
24. What are Relational Algebra’s unary operations?
Ans:
- PROJECTION and SELECTION are the unary operations of relational algebra. Unary operations are those that involve just one operand.
- Three unary procedures are RENAME, PROJECTION, and SELECTION.
- In SELECTION, relational operators such as as =,=,>=, and others are used.
25. What is an RDBMS?
Ans:
- An abbreviation for relational database management systems is relational database management systems . Table indices and data records are tracked using it. An RDBMS is a kind of database management system that uses structure to locate and retrieve information about other database entries.
- An RDBMS is a database management system that makes it easy to administer, update, add, remove, and alter relational databases. The majority of the time, RDBMS uses the SQL language because it is widely used and easily understood.
26. What kinds of data models exist?
Ans:
There are several data modes, and these include:
- Relational model,
- network model, and
- hierarchical data model
- Relationship-Entity model
27. Describe a Relation and a Relation Schema.
Ans:
A set of characteristics that specify a relationship is called a relation schema. An alternative name for it is table schema. The table’s name is specified. The relation schema is the blueprint that allows us to describe how data is organized into tables. This contains no data or blueprint. A set of tuples defines a relation. A connection is an assemblage of related characteristics that are distinguished by common characteristics.
- Let t1, t2, t3,…, tn be the set of tuples included in the relation r. An ordered list of n values (t=1. (v1, v2,…., vn). makes up each tuple.
28. What is the relationship’s degree?
Ans:
One of the characteristics of a relationship’s relation schema is its degree. The number of times one entity happens in relation to the number of times another entity occurs is known as a degree of connectedness or cardinality. The three degrees of relation (M: M. are one-to-one one-to-many and many-to-one.
29. Describe a Relationship.
Ans:
- A connection involving two or more. A relationship is defined as the association of two or more entities. There are three different kinds of relationships in a database management system:
- One-to-One: In this scenario, any object’s record can be connected to the record of another object. One record of any object can be linked to numerous records of other objects in a one-to-many (many-to-one. scenario. Many-to-many: This type of linking allows n records of one object to be connected to numerous records of another.
30. What drawbacks do file processing systems have?
Ans:
The following are file processing system drawbacks:
- Data redundancy, inconsistency, lack of security Data access is challenging
- Restricted sharing of data
- Data integrity
- Accessing concurrently is not feasible
- Isolation of data
- Atomicity issue
31. In DBMS, what is Data Abstraction?
Ans:
- Data abstraction in a database management system is the technique used to keep users from seeing unimportant facts. User interaction with the database is made possible by the intricate data structures that make up database systems.
- For instance, systems with a straightforward graphical user interface (GUI. don’t require complex processing. Data abstraction is, therefore, necessary to maintain user engagement and simplify data access. Data abstraction separates the system into layers, making it possible to explain and specify the task clearly.
32. Why is it advised to utilize DBMS? And explain its benefits.
Ans:
Some of the main benefits of DBMS are as follows:
- Regulated Redundancy: By consolidating all data into a single database and avoiding data duplication due to data being stored in a single location, DBMS provides a mechanism to manage data redundancy inside the database.
- Data Sharing: Since several application apps and all users share the same database, data can be shared simultaneously across multiple users in a DBMS.
- Backup and Recovery Facility: DBMSs come with a feature called “backup and recovery” that automatically creates data backups and recovers them when needed, relieving the strain of repeatedly making data backups.
- Integrity restraints need to be upheld: Integrity restraints need to be upheld. The refined data is kept in the database in accordance with DBMS.
- Data independence: Essentially, it indicates that changing the data format won’t change how any application apps are structured.
33. What distinguishes the where clause from the having clause?
Ans:
- HAVING is used to create a condition for a group or an aggregate function in a select statement.
- The WHERE clause is selected before grouping. Rows are chosen by the HAVING clause after grouping.
- Unlike the HAVING clause, the WHERE clause is not allowed to use aggregate functions.
34. What is a business dealing? What qualities do ACIDs have?
Ans:
A database transaction is a group of related database activities that need to be handled collectively, i.e., all or none of the actions that need to be carried out. An example that works well is a bank transaction involving many accounts. The characteristics of ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability). guarantee the consistent processing of database transactions.
35. Describe Join.
Ans:
- Combining data from two or more tables based on a shared column is possible with an SQL Join. In database management systems, a join is an operation that combines data from two or more tables according to a common column.
- It makes it possible to retrieve pertinent and related data by merging entries from multiple tables that share a value in a particular field.
- Join methods are essential for data processing and querying in relational databases. Joining tables can produce complex linkages that enable the retrieval of large and valuable amounts of data.
36. What Is Identity?
Ans:
A column called Identity, often known as AutoNumber, generates numerical values on its own. Although start and increment values can be adjusted, most DBAs keep them at 1. Numbers are also generated via a GUID field, but the value is fixed. Indexing the identity/GUID columns is not required.
37. What does SQL view mean?
Ans:
A view is a virtual table made from the result set of a SQL query. To do this, we can utilize the create view syntax. In SQL Server, a VIEW is comparable to a virtual table that holds information from one or more tables. It does not physically exist in the database and does not contain any data. Distinct inside a database. It includes a list of pre-written SQL queries to retrieve information from the database
38. What applications does view serve?
Ans:
View is used for the following purposes:
- A user may be able to query the view but only part of the base database.
- Simplify and merge several tables into a single virtual table by using views.
- Views can function as aggregated tables, where the database engine compiles data into tables (sum, average, etc.. and shows the resulting results next to the data.
- Views may mask the intricacy of the data.
- Views use incredibly little storage space; the database keeps track of a view’s specifications, not a duplicate of every piece of information it shows.
- Views may provide more security based on the SQL engine being used.
39. What Is a Trigger?
Ans:
A code associated with adding, modifying, or removing data is called a trigger. The code is executed automatically when the query linked with a table is executed. Triggers are helpful in preserving the integrity of databases. A trigger can invoke an action, but as actions are independent of the trigger’s method of invocation, an infinite number of triggers can be generated. A function and a stored procedure are comparable in that they both consist of a group of combined activities. It contains a number of routines that are commonly employed in applications to do database operations.
40. What is the DBMS normalization process used for?
Ans:
- The technique of structuring a database’s attributes to lessen or completely eradicate data redundancy—having the same data but at different locations..
- The goal of normalization is to eliminate from the relational table any duplicate data and abnormalities from the database.
- Normalization examines new data types used in the table and helps to eliminate complexity and redundancy.
- The big database table should be split up into smaller tables and connected by relationships.
- It prevents redundant data or groupings into a table that is not repeated.
- It lessens the likelihood that anomalies will arise in a database.
41. What distinguishes a stored procedure from a trigger?
Ans:
Unlike Stored Procedures, triggers are not callable directly. They can only be connected to questions. Parameters can be inserted into stored routines. Triggers run automatically in response to specific commands that are executed on a table. Since a procedure cannot be executed automatically, the EXEC command must be used. The primary use of triggers is to preserve referential integrity and log actions taken on a table.
42. What is the normalization of databases?
Ans:
It is a technique for evaluating relation schemas to get the following desired properties by looking at their main keys and functional dependencies:
- Reducing the amount of redundancy
- Minimizing Inconsistencies in Insertion, Deletion, and Update Smaller relation schemas that might satisfy the requirements are created from relation schemas that don’t match the properties.
43. How do indexes work?
Ans:
- A database index is a type of data structure that increases the speed at which data can be retrieved from a database table. Still, it also requires more writes and storage capacity to hold the additional copies of data.
- Data can only be stored in one order on a disc. It is intended to give faster search times through the use of binary searches for various variables.
- To access based on various values. Table indexes are created with this objective in mind. Although these indexes require more disc space, they enable faster searches using a number of often requested characteristics.
44. What distinguishes non-clustered from clustered indexes?
Ans:
The indexes that decide how data is stored on a disc are called clustered indexes. Therefore, there can only be one clustered index per database table. Logical ordering, as opposed to physical ordering of data, is defined by non-clustered indexes. Usually, a tree is created, the leaves of which point to disc records. A B-tree or B+ tree is used for this.
45. How Does Denormalization Occur?
Ans:
Duplicate data is added to one or more tables as part of the database optimization process known as denormalization. The process of structuring data in a database is called normalization. It involves building tables and defining linkages between those tables in accordance with rules intended to safeguard the information as well as increase database flexibility by getting rid of redundant information and inconsistent dependencies.
46. In SQL, what is CLAUSE?
Ans:
A clause in SQL is a section of a query that lets you customize or filter how your data is retrieved. A SQL built-in function called a clause aids in retrieving the necessary records from a database table. A conditional phrase, such as the name of a column or certain terms, is given to a sentence. The stated statements in the expression are the basis for the calculation of the outcome by the clause.
47. Describe LiveLock.
Ans:
The Processes that repeatedly alter their states to block one another and prevent further progress are said to be in a state known as livelock. Starvation is the effect of a process being continuously denied resources or coming from a deadlock or livelock.
48. Describe QBE.
Ans:
- A visual/graphical method of retrieving data from a database utilizing skeleton tables as query templates is called “query-by-example.” It is used to explicitly enter sample values into a query template in order to describe what has to be done.
- QBE is an extremely powerful tool that doesn’t require the user to know any programming languages in order to obtain the information they need. In QBE, queries are expressed using skeleton tables.
49. Why does embedded SQL require cursors?
Ans:
An object known as a cursor is used by application programs to store and process query results row by row. SQL statements are expressions that manipulate a set of data and produce a new set of data in return. Conversely, host language programs operate one after the other. To navigate, utilize cursors. A group of records generated by one of the code’s SQL SELECT statements. A pointer and a cursor are comparable.
50. What is the DBMS normalization process used for?
Ans:
Database normalization is the process of organizing a database’s properties to reduce or eliminate data redundancy (having the same data but in various places.The goal of normalization:
- It is used to eliminate duplicate data and strange database entries from the relational table.
- Normalisation reduces complexity and redundancy by evaluating newly used data types in the table.
- Dividing a large database table into smaller tables and using relationships to link them is a smart approach.
- It stops the entry of duplicate data.
- Both into a database and without any repeating groups.
- It makes irregularities in a database less likely.
51. What distinguishes a database state from a database schema?
Ans:
- Database schema refers to the overall structure of the database, whereas database state refers to the collection of data stored in a database at a certain moment in time.
- The database schema represents the basic layout or structure of the database. It shows how data is arranged and related to one another, as well as the logical view of the database. The term “database state” describes the content that is present in the database at any one time.
52. What is SQL used for?
Ans:
- The main function of Structured Query Language, or SQL, is to work with relational databases by importing, updating, and modifying data.
- To communicate with a database, utilize SQL. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI. states that this language is the industry standard for relational database management systems. SQL statements are used for operations like updating and retrieving data from databases.
53. Describe what a primary key and a foreign key are.
Ans:
- A foreign key, which is a specific field or field in one database table that serves as the primary key of another table, is used to connect two or more tables. Primary keys are used to identify records in database tables uniquely.
- For instance, there are two tables: Employee and Department. ‘ID,’ a field or column shared by both tables, serves as the primary key for both the Employee and an additional subquery. The AdventureWorks2022 sample database, which may be downloaded from the Microsoft SQL Server Samples and Community Projects homepage, is needed for this article.
54. What distinguishing features set a primary key apart from a unique key?
Ans:
Below is a list of a few inconsistencies:
- The main difference between the Unique and Primary keys is that the former can have null values at any time.
- Each table can have more than one unique key, but there can only be one main key per table.
55. What does the SQL phrase “sub-query” mean?
Ans:
- A query enclosed in another query is called a sub-query. Because it can be located inside the outer query, it is sometimes referred to as an inside query.
- A subquery is a query that is nestled inside another subquery or a SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement. The AdventureWorks2022 sample database, which may be downloaded from the Microsoft SQL Server Samples and Community Projects homepage, is needed for this article.
56. What is the purpose of the DROP command, and how does it differ from the TRUNCATE, DELETE, and DROP command
Ans:
- A table, database, index, or view that already exists in a database can be deleted using the DDL DROP command.
- The primary distinctions between the DROP, TRUNCATE, and DELETE commands are as follows:
- Tables can be removed from the database using the DDL commands DROP and TRUNCATE. Upon table deletion, all related permissions and indexes are also removed. These two actions should only be used in dire situations because they cannot be undone.
- The command DELETE, nevertheless, is a DML statement that can remove rows from a table and also be rolled back.
57. What distinguishes UNION from UNION ALL in particular?
Ans:
- When connecting data from two or more tables, UNION and UNION ALL are both utilized. However, UNION eliminates duplicate rows and chooses the unique rows after combining the data from the tables. In contrast, UNION ALL does not eliminate duplicate rows and only chooses every row from the tables.
- The results of two or more tables are combined in UNION and UNION ALL. While the UNION ALL result set returns every row from both tables, the UNION result set is devoid of duplicate rows. The time of UNION ALL’s execution is less than the UNION execution time since duplicate rows are not eliminated.
58. In DBMSs, what is a Correlated Subquery?
Ans:
- A subquery is a query that is written inside another query or nested query. An outer query’s correlated subquery is run for every row in the outer query.
- A subquery that references a table column that is not included in its FROM clause is known as a correlated subquery: the projection clause or the where clause may contain the column.
59. What integrity standards does the DBMS have?
Ans:
Integrity rules in database management systems primarily consist of two types.
- Entity integrity is an important criterion that states that a main key’s value can never be NULL.
- This rule relates to the foreign key and requires that a foreign key be the primary key of another relation or have a NULL value.
60. What does the DBMS’s E-R model entail?
Ans:
- The Entity-Relationship model, or E-R model as it is known in relational databases, is based on the idea of entities and the relationships that exist between them.
- An entity-relationship model, or ER model, uses an entity-relationship diagram (ER Diagram. to illustrate how a database is structured. An ER model is a database’s layout or blueprint that can be used as a database.
61. In a DBMS, what is a functional dependency?
Ans:
- For instance, if a relation ‘R1’ includes two attributes, Y and Z, then Z is functionally dependent on Y, and the functional dependency between these two qualities can be expressed as Y->Z.
- When the determinant characteristics determine the dependent attributes, this is known as a fully functional dependency. For instance, the Employee’s name, address, and other personal details are fully determined by their employee ID number in the database of employees. In DBMS, a relationship between dependent characteristics of any table is referred to as functional dependence on one another.
62. What distinguishes a stored procedure from a trigger?
Ans:
Triggers are not callable directly, in contrast to Stored Procedures. Only questions can be connected to them. Parameters can be inserted into stored routines. Triggers run automatically in response to specific commands that are executed on a table. Since a procedure cannot be executed automatically, the EXEC command must be used. Triggers are mostly used to log actions taken on a table and preserve referential integrity.
63. What does the term “data warehousing” mean?
Ans:
Data warehousing is the process of collecting, extracting, analyzing, and importing data from various sources and storing it in a single database. A data warehouse is core data from relational databases and transactional systems fed into this data analytics repository. An organization’s historical data that supports decision-making is gathered in a data warehouse
64. Describe the distinction between an extension and an intent in a database.
Ans:
- Database schema, commonly referred to as intention, is what defines the description of a database. It is defined at every stage of the database design and usually doesn’t change.
- On the other hand, the number of tuples in a database at any given time is measured by extension. The value of a database snapshot, sometimes referred to as an extension of a database, is dynamic and changes as tuples are added, modified, or obliterated within the database.
65. Describe the distinction between a DBMS’s DELETE and TRUNCATE commands.
Ans:
- DELETE instruction: This command removes rows from a table according to the condition specified in the WHERE clause. Only the rows specified by the WHERE clause are deleted. It can be rolled back if needed. It is sluggish since it maintains a log in order to lock the table row before deleting it.
- TRUNCATE command: In a database, the TRUNCATE command is used to eliminate every entry from a table. A DELETE command without a WHERE clause is comparable to it. A database table’s whole contents are erased. If needed, it can be rolled back. (Truncate can be undone depending on the version of the database, however. It’s challenging and may cause data loss.
66. Describe the exclusive lock and a shared lock during a database transaction.
Ans:
A database lock is a technique that stops several database users from simultaneously altering the same record. A single database user or session that obtains a lock prevents any other database user or session from editing the data until the lock is released.
- Shared Lock: A shared lock allows many transactions to hold locks on the same data item and is required for reading data items.
- Multiple transactions can read the data items thanks to a shared lock.
- Exclusive Lock: An exclusive lock is placed on any transaction that is going to execute a write operation. This type of lock only permits one transaction at a time, preventing any database inconsistencies.
67. Describe the various DBMS normalization formats.
Ans:
- Unique Key: A unique key is the same as a primary key, except that unique keys allow NULL values to be entered in columns while primary keys do not. Primary keys containing NULL values are unique keys.
- Alternate Key: An alternate key is any candidate key that was not chosen to be the primary key. An attribute that can only accept values from one table and is shared by an attribute in another table is known as a foreign key.
- Composite Key: A composite key consists of two or more columns combined so that it can allow every tuple in a table to have a unique identity.
68. What is a business dealing? What qualities do ACIDs have?
Ans:
A collection of database actions known as a database transaction must be handled as a whole, meaning that either every operation is carried out or not. A bank transaction from one account to another can serve as an illustration. It is necessary to do either all of the credit and debit operations or none of them. A collection of characteristics known as ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability. ensures the dependable processing of database transactions.
69. Describe the distinctions between a DBMS’s 2-tier and 3-tier architectures.
Ans:
- The two-tier design With this client-server architecture, client apps communicate with the server’s database directly and without the need for middleware.
- For example, a railway reservation system or a contact management system integrated into MS-Access.
- The three-tier design increases the system’s safety and accessibility by putting a layer between the client and the server and providing users with a graphical user interface. The database system is contacted by the server-side application, which in turn connects with the client-side application in this arrangement.
- Creating a registration form that has a button, label, text field, or other a sizable webpage on the Internet, for instance.
70. Distinguish between the physical and logical designs of databases.
Ans:
A relational database structure is mapped onto or transformed from the conceptual schema (also known as an ER schema. from the high-level data model. The physical storage architecture, record placement, and index creation are specified for the stored database.
There are two phases to the mapping process:
- Data model-dependent yet independent of system mapping modifying the schemas to conform to a particular DBMThe following factors are commonly considered when choosing physical database design options.Transaction throughput, Response time, and Space Utilisation.
- DDL commands that specify the selected DBMS language schemas at the conceptual and external levels of the database system. Database design is divided into several phases. Logical database design and physical database design are two of them. The three-level design of a database management system (DBMS., which guarantees data independence, is typically the foundation for this division.
71. What do make-shift tables mean? When do they come in handy?
Ans:
Tables designated as temporary are those whose contents are only retained for the length of the transaction or that are only used for a single session. Most frequently, temporary tables are used to accommodate special rollups or demands related to application processing. Unlike a permanent table, a temporary table does not have space assigned to it when it is constructed. The table’s space will be dynamically allocated when rows are added. Use the CREATE GLOBAL TEMPORARY TABLE command in Oracle to create a temporary table.
72. Define Entity type extension.
Ans:
- The process of integrating similar entity types into a single type, which is subsequently grouped as an entity set, is known as entity type extension.
- Extension of the entity type refers to the entity set that is made up of a grouping of entities of a specific entity type.
73. In DBMs, what does conceptual design mean?
Ans:
- The database design process includes requirements analysis and collection, conceptual modeling, logical database design, and database implementation.
- Conceptual design is the initial stage of the database design process. The objective at this point is to build a database that is independent of physical details or database software.
- As a result of this process, a conceptual data model represents the essential data items, characteristics, connections, and limitations of a certain issue area.
74. Describe indexes.
Ans:
Although it requires more writes and reads, a database index is a type of data structure that speeds up data retrieval operations on a database table. Greater storage space is used to keep the extra copy of data. On a disk, data can only be kept in one order. Indexes are constructed on tables to facilitate faster searches, such as binary searches for different values, in order to provide faster access according to different values. Although these indexes require more disk space, they provide a speedier search based on many frequently queried parameters.
75. What is the primary objective of RAID technology?
Ans:
- Redundant Array of Inexpensive (or “Independent”. Disks is what the acronym RAID stands for.
- RAID is a method for combining many hard drives (two or more. into a single logical unit.
- RAID was developed to get around traditional disk storage’s fault tolerance and performance constraints. It can outperform a single hard drive or a group of separate hard drives in terms of fault tolerance and throughput.
76. Elucidate the significance of database partitioning.
Ans:
- Data partitioning is the process of dividing a logical database into separate components in order to enhance availability, performance, and manageability.
- Some of the factors that make database partitioning crucial are as follows:
- Gives you access to major areas of a partition. Information can be spread, and less expensive storage can be used to store data.
77. Describe how the DML Compiler works.
Ans:
DML statements are transformed into query language that the query evaluation engine can understand by the DML Compiler. A DML compiler is required because DML is a collection of grammar parts that resemble other programming languages that need to be compiled. Therefore, it’s essential to work on the queries with the correct output after compiling the code in a language that the query evaluation engine can comprehend.
78. What is Relational algebra?
Ans:
- A collection of operations that take one or two relations as input and produce a new relationship are called operations in relational algebra, a procedural query language—fundamentals of the relational model.
- Relational algebra is a set of operations. The main characteristic of relational algebra is its resemblance to algebra with a numerical focus. There are just a few fundamental operations in relational algebra.
79. What is Relational Calculus?
Ans:
- Relational Calculus is a non-procedural query language that uses mathematical predicate calculus in place of algebra. Essential math concepts such as algebra, differential equations, integration, and so forth are different from relational calculus.
- For this reason, it is also known as predicate calculus.Two versions of relational calculus exist. Calculus of Domain Relationships and Relational calculus in a tuple.
80. What does “durability in DBMS” mean?
Ans:
The impact of a system failure, even if it occurs before all of the changes are recorded on the disc. As soon as the DBMS notifies the user that the transaction has been properly finished, it should continue. This attribute is known as durability. A transaction is guaranteed to be safe against system failure in non-volatile memory after it is committed to the database. This is known as durability.
81. Describe System R. Of its two main subsystems, how many exist?
Ans:
The IBM San Jose Research Center designed and constructed System R between 1974 and 1979. System R was the first to use SQL, the common language for relational data queries, and the first to show that a relational database management system (RDBMS. could provide better transaction processing performance. It’s a functional prototype that shows how to design a Relational System that can be used for real-world issues and situations.
The following are System R’s two main subsystems:
- Research Storage System
- Relational Data System
82. How can one interact with an RDBMS?
Ans:
It is necessary to use Structured Query Language (SQL. to connect with the RDBMS. We can provide feedback to the database using SQL queries, and once the queries have been performed, the database will provide us with the necessary output.
83. What does “simultaneous, proactive, and retroactive update” mean to you?
Ans:
- Proactive Update: The database is updated with these modifications prior to its real-world implementation.
- Retroactive updates: These are made to a database after it has been used in real-world operations.
- Simultaneous Update: These changes are implemented in the real world and the database at the same time.
84. Describe what is meant by generalization and specialization.
Ans:
The process of defining a set of subclasses for a specific object type is called specialization. All of the traits and relationships of the parent object will be present in every subclass. Subclasses may then have additional characteristics and connections that are particular to them. Finding connections and shared characteristics among a collection of entities and then creating a common superclass for them is the process of generalization.
85. In relation to indexes, what does the Fill Factor idea mean?
Ans:
The percentage of remaining space on each leaf-level page that is tightly packed with content is referred to as the “fill factor .”Typically, the default value is 100.
86. What is index hunting, and how does it enhance the efficiency of queries?
Ans:
- Enhancing an index collection is known as index hunting. This is carried out because indexes enhance both query processing speed and query performance.
- It helps to enhance query performance in the following ways: Making Use of The best queries are recommended by the query optimizer.
- Metrics like index, query distribution, and performance are utilized to verify the impact. Databases are designed to be optimal for a limited set of issue queries.
87. Describe what a stalemate is and provide a solution.
Ans:
When two transactions wait for an unavailable resource, or while another process is suspended, a deadlock happens. By mandating that all transactions acquire all locks simultaneously, deadlocks can be prevented. Therefore, stopping one of the transactions and deleting the partially finished work is the only method to end the stalemate.
88. When is it appropriate to use an index?
Ans:
As long as the query volume to the table containing the indexed column is reasonable and not constantly loaded, it can occasionally be acceptable performance-wise to utilize an index for convenience purposes for columns containing unique data.
89. What kinds of joins are there?
Ans:
- Inner Join: An inner join only shows the matched rows from both tables based on the join criteria that were entered. Rows that satisfy the join criteria are joined together.
- Left Join: A join on the left returns every row from the left table (also referred to as the first table. and any rows from the right table that match (sometimes referred to as the second table.. If there isn’t a match, NULL values are displayed in the columns of the right table.
- Correct Join: A The complete opposite of left joins is a right join. All of the rows from the right table, as well as the matching rows from the left table, are given back. If there isn’t a match in the left table, NULL values are displayed in the columns.
- Full Outer Join: All records, including those that were mismatched, are retrieved from both tables using this join. If a record in the other table does not match, NULL values are displayed in its columns.
- Cross Join: Also called a Cartesian join, a cross join combines every row from two tables to produce a Cartesian product.
90. Define Stated Join Conditions.
Ans:
Join procedures are commonly used in SQL queries to combine data from different tables based on the associations created by main and foreign keys. Joins provide a way to retrieve data that is scattered across several tables and to join and analyze relevant data. They contribute significantly to the creation of reports, the provision of insightful information, and the support of decision-making processes by making use of the relationships between tables in relational databases.





