
Oracle BPM (Business Process Management) is a robust suite designed to facilitate the modeling, execution, and enhancement of business processes within organizations. Built on the BPMN 2.0 standard, it empowers business analysts and process owners through tools like Process Composer for intuitive process design. The platform integrates seamlessly with Oracle SOA Suite, allowing the orchestration of services and processes.
1. What is business process management?
Ans:
Business process management (BPM) is the methodical process of improving an organization’s workflow to make it more efficient, effective, and able to change with the times. A business process is an action or series of actions designed to achieve a particular organizational objective.
2. What is the definition of process management?
Ans:
Process management is ensemble of activities of planning and monitoring performance of a business process. The phrase is used to describe the management of manufacturing and business processes. While there are similarities between business process re-engineering and business process management (BPM), they are not the same.
3. What is the BPM industry?
Ans:
The field of operations management known as business process management, or BPM, is dedicated to managing and streamlining a company’s business processes in order to increase corporate performance.
4. What is the difference between validating and cross checking?
Ans:
- Validation and crosschecking serve similar purposes but differ in their approaches.
- Validation focuses on confirming the accuracy of a single set of data or information, ensuring it meets specific criteria or standards.
- On the other hand, crosschecking involves comparing information from multiple independent sources to verify consistency and identify discrepancies.
5. What is Level 0, Level 1 backup?
Ans:
A level 0 incremental backup, which is base for a subsequent incremental backups, copies all the blocks containing data, backing data file up into a backup set just as storing data files in a backup set in the same way as a complete backup. The two types of level 1 incremental backups are as follows:
- A differential backup, which backs up all the blocks changed after recent incremental backup at level 1 or 0.
- A cumulative backup, which backs up all the blocks changed after most recent incremental backup at level 0.
6. What is Oracle BPM Process Spaces REST API ?
Ans:
The Oracle BPM Process Spaces REST API allows developers to interact with the Oracle BPM Process Spaces programmatically. It provides the capabilities for managing Process Spaces, including the creating, updating, and retrieving information about spaces, streamlining integration with external systems.
7. How do you go about backing up online redo logs?
Ans:
Regardless of how the backup is executed—hot or cold—online redo logs should never, ever be included in it. The reasons for this are two-fold. First, physically cannot backup a hot online redo log, and second, there is a precisely zero need to do so in first place because an archive redoes log is, by definition, backup copy of formerly on-line log. There is, however, more practical reason: backing up online logs increases the risk that will lose.
8. What is the backup set?
Ans:
- RMAN can store backup data in the logical structure called a backup set, which is the smallest unit of an RMAN backup.
- A backup set is made up of data from one or more data files, control files, archived redo logs, and server parameter files.
9. What is the auxiliary channel in RMAN? When do I need this?
Ans:
An auxiliary channel is the link to auxiliary instance. If do not have automatic channels configured, then before issuing DUPLICATE command, manually allocate at least one auxiliary channel within a same RUN command. An auxiliary database is used when creating a duplicate database or performing a table space point-in-time recovery. The host for this database may be the same or different.
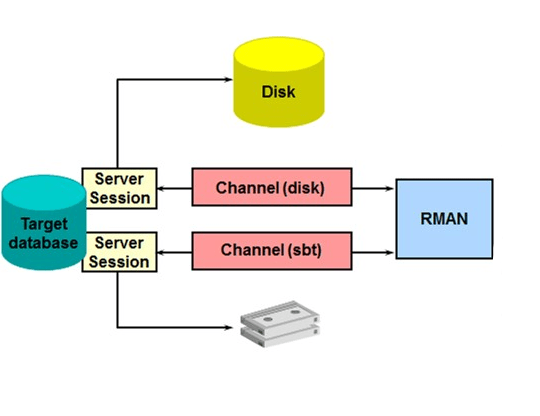
10. What is channel? How to enable parallel backups with RMAN?
Ans:
- Use ALLOCATE CHANNEL command to manually allocate a channel, which is the connection between RMAN and a database instance.
- To enable parallel backups, allocate the multiple manual channels in a run block or configure parallelism.
11. Is it possible to specific tables using the RMAN DUPLICATE feature?
Ans:
Yes, it is possible to duplicate the specific tables using the RMAN (Recovery Manager) DUPLICATE feature in the Oracle Database. The DUPLICATE command in RMAN allows to create a copy of a database or a subset of a database, and can use the TABLES clause to specify the tables want to duplicate.
12. What is the purpose of Oracle BPM Worklist API?
Ans:
The Oracle BPM Worklist API allows the developers to programmatically interact with BPM Worklist. It can be used for a tasks such as querying and updating task information, managing task assignments, and integrating the BPM functionality into other applications.
13. How do verify integrity of image copy in RMAN environment?
Ans:
- To verify the integrity of image copies in an Oracle RMAN environment, use the ‘RESTORE … VALIDATE’ command.
- Connect to RMAN, and execute this command specifying the files you want to validate.
- For example, you can validate all image copies with ‘RESTORE DATABASE VALIDATE’.
- Review the results to ensure the integrity of the backups, and address any reported issues for data reliability and recoverability.
14. Explain Oracle BPM Metadata Service (MDS) in process development.
Ans:
The Oracle BPM Metadata Service (MDS) is used for the storing metadata related to the business processes, including process definitions, rules, and other artifacts. It facilitates the versioning, reuse, and consistency across the different projects.
15. Describe the procedures for a TIME-based recovery from a hot backup.
Ans:
Specify the recovery point, mount the database, restore files using ‘RESTORE DATABASE;’, recover to the target point, and open the database with ‘ALTER DATABASE OPEN RESETLOGS;’. Verify success, optionally update statistics, and perform checks for functionality.
16. Explain steps to perform point in time recovery with backup.
Ans:
- Need to list the database incarnations by using the list incarnation command.
- Shutdown database.
- Startupc a mount the database.
- Issue reset database to incarnation to reset incarnation.
- Restore database using the restore command.
- Recover the database.
- Open database using resetlogs command.
17. What are correlation sets in Oracle BPM?
Ans:
Correlation sets in Oracle BPM are used to be correlate messages or events related to the specific process instance. They define criteria for matching incoming messages to appropriate process instance, ensuring a proper coordination and data association.
18. What is the difference between obsolete RMAN backups and expired RMAN backups?
Ans:
| Aspect | Obsolete Backups | Expired Backups | |
| Definition |
Backups that are no longer considered usable |
Backups that have exceeded their retention policy | |
| Cause | Typically due to a change in backup strategy | Result of reaching the configured retention period | |
| Visibility | Visible in RMAN catalog views | Not displayed in RMAN catalog views | |
| Deletion |
Must be manually deleted using RMAN commands |
Automatically deleted by RMAN when expired |
19. Explain callback in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
- A callback in Oracle BPM refers to ability to invoke an external service or process and receive the response asynchronously.
- It is significant for the handling long-running or asynchronous interactions with an external systems.
20. What is Oracle BPM Expression Language?
Ans:
The Oracle BPM Expression Language is the language used to define expressions and conditions within the process models. It allows for a dynamic evaluation of values, conditions, and calculations, enhancing flexibility of process modeling.
21. How do clone databases using RMAN?
Ans:
The Two commands available in RMAN to clone database:
- Duplicate the target database to.
- Restore.
22. What is the difference between CATALOG vs NOCATALOG?
Ans:
CATALOG: In Oracle RMAN, CATALOG involves storing backup metadata in a dedicated recovery catalog, providing centralized management and historical tracking across multiple databases.
NOCATALOG: In contrast, NOCATALOG stores metadata directly in the target database’s control file, offering a simpler, localized approach.
23. What is a short lock in tibco iProcess?
Ans:
Normally, TIBCO iProcess Workspace sets this standard lock. The user releases or keeps a work item, removing a brief lock. Should short locks remain after an iProcess Workspace crash, for example, restarting iProcess Engine is the only method to release the short lock.
24. What is the difference between cumulative and differential backups?
Ans:
Differential backup: This is a default type of incremental backup which backs up all the blocks changed after most recent backup at level n or lower.
Cumulative backup: Backup all the blocks changed after the most recent backup at level n-1 or lower.
25. What is a long lock in tibco iProcess?
Ans:
An eternal lock that can only be released by the user who is holding it with the sal_llock_frm_init() function. TIBCO iProcess Workspace typically does not use long locks, but SAL SDK programmes and the TIBCO iProcess Objects Client may set them. Any iProcess user who locks a work item in this manner cannot access it again until it is manually unlocked. Restarting iProcess Engine has no effect on long locks.
26. What are key components of Oracle BPM Suite?
Ans:
The key components include the Oracle BPM Studio (for process modeling), BPM Composer (for business users to participate in process design), BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) engine, Business Rules engine, and BPM Workspace (for task management and monitoring).
27. What is the role of the BPMN engine in Oracle BPM?
Ans:
- The BPMN engine is responsible for an executing business processes based on BPMN models created in Oracle BPM Studio.
- It interprets process definitions, manages process instances, and facilitates a flow of activities as defined in BPMN diagrams.
28. Explain BPMN and its significance in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
BPMN is a standard notation for a business process modeling. It provides the graphical representation of business processes, making them easily understandable by both the technical and non-technical stakeholders. In Oracle BPM, BPMN is used for a modeling and defining business processes.
29. How does Oracle BPM integrate with the other Oracle products?
Ans:
Oracle BPM can integrate with the other Oracle products through the various integration mechanisms, like Oracle SOA Suite for service-oriented architecture, Oracle ADF (Application Development Framework) for building the rich user interfaces, and Oracle WebCenter for a content and collaboration services.
30. Explain concept of Human Workflow in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
- Human Workflow in Oracle BPM refers to involvement of human users in the business processes.
- It allows for definition of tasks, assignments, and notifications that require a human interaction.
- Oracle BPM provides BPM Workspace for users to manage and complete assigned tasks.
31. What is the Business Rule in Oracle BPM?
Ans:
A Business Rule in Oracle BPM is the set of conditions and actions that define a specific business logic. Business rules are used to make the decisions within business processes, and can be managed and modified independently of process, promoting agility and flexibility.
32. Explain concept of Human Workflow in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
- Human Workflow in Oracle BPM refers to involvement of human users in the business processes.
- It allows for definition of tasks, assignments, and notifications that require human interaction.
- Oracle BPM provides BPM Workspace for users to manage and complete assigned tasks.
33. What is Oracle BPM Composer?
Ans:
Oracle BPM Composer is the web-based tool that allows the business users to participate in a design and modification of business processes. It provides the user-friendly interface for users who are not necessarily technical experts but have the valuable insights into business process.
34. Explain the difference between Oracle BPM and Oracle SOA Suite.
Ans:
While Oracle BPM focuses on a business process modeling, execution, and optimization Oracle SOA Suite is the primarily designed for service-oriented architecture, providing the framework for developing and managing services. However, these two products can work together to provide comprehensive solution for a business process management and integration.
35. How does Oracle BPM handle process monitoring and analytics?
Ans:
Oracle BPM provides BPM Workspace for users to monitor and manage tasks. Additionally, it integrates with the Oracle BAM (Business Activity Monitoring) for real-time monitoring and analytics, providing the insights into a process performance and efficiency.
36. Explain the difference between Oracle BPM and Oracle SOA Suite.
Ans:
While Oracle BPM focuses on a business process modeling, execution, and optimization, Oracle SOA Suite is the primarily designed for service-oriented architecture, providing the framework for developing and managing services. However, these two products can work together to provide comprehensive solution for a business process management and integration.
37. Explain the difference between process and task in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
- In Oracle BPM, a process is the collection of related activities that work together to achieve the business goal.
- A task, on other hand, is a single unit of work within a process.
- Tasks can be automated or manual and are used to represent steps in a business process.
38. What is the significance of BPMN Gateway in Oracle BPM?
Ans:
BPMN Gateways in Oracle BPM represent a decision points or branching within process. They control the flow of process based on conditions or events, enabling creation of more complex and a dynamic process structures.
39. How does Oracle BPM handle exception handling in business processes?
Ans:
Oracle BPM provides the mechanisms for handling exceptions in the business processes. This includes the ability to define the error handling activities within a process, catch and handle faults, and implement compensation activities to revert the changes in case of errors.
40. Explain process versioning in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
- Process versioning in Oracle BPM allows for management of different versions of business process.
- This is crucial when making changes to the process while instances of older version are still running.
- It ensures a new process instances use the updated version while existing instances of continue with original version.
41. What is the Oracle BPM MDS (Metadata Services) repository?
Ans:
The Oracle BPM MDS repository is used to store and manage a metadata, including the process models, rules, and other artifacts.
It provides the centralized location for a storing and versioning artifacts, promoting reusability and consistency across the different projects.
42. How can integrate external systems or services with Oracle BPM?
Ans:
Oracle BPM supports the integration with external systems through the web services, service connectors, and adapters. Service connectors enable interaction with external services, while the adapters provide connectivity to the various technologies and systems, including a databases, ERP systems, and more.
43. How does Oracle BPM support business activity monitoring (BAM)?
Ans:
Oracle BPM integrates with the Oracle BAM to provide real-time monitoring and analytics capabilities. BAM allows an organizations to track key performance indicators (KPIs), monitor process performance, and generate a reports to gain insights into business processes.
44. How can you secure Oracle BPM processes?
Ans:
- Oracle BPM provides a security features such as user authentication, authorization, and role-based access control.
- Users can be assigned the specific roles, and access to tasks and processes can be controlled based on roles.
45. What is correlation in Oracle BPM?
Ans:
Correlation in Oracle BPM is association of messages or events related to the specific process instance. It is important for the handling asynchronous processes and ensures that a messages are correctly matched to an appropriate process instance, allowing for the accurate process coordination and execution.
46. Explain role of Oracle BPMN Engine in process execution.
Ans:
The Oracle BPMN Engine is responsible for an interpreting and executing BPMN process definitions. It manages flow of activities, handles task assignments, and ensures correct sequencing of process steps based on BPMN models created in the Oracle BPM Studio.
47. Explain dynamic process in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
In Oracle BPM, a dynamic process allows for a flexibility in process execution by enabling runtime modification of process structures. This means that certain aspects of process can be altered without stopping or redeploying an entire process.
48. What is the Oracle BPM Worklist?
Ans:
- The Oracle BPM Worklist is the user interface that allows the participants to view and manage their tasks in a business processes.
- Users can access the Worklist to perform a tasks assigned to them, view task details, and interact with process.
49. What is the difference between subprocess and multi-instance subprocess?
Ans:
A subprocess in Oracle BPM is the reusable unit of work within a process, while multi-instance subprocess is the subprocess that can be executed multiple times in parallel, often based on the collection or condition.
50. Explain the correlation set in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
- A correlation set in Oracle BPM is used to correlate a messages or events related to the specific process instance.
- It defines criteria for matching incoming messages to appropriate instance, ensuring a proper coordination and data association.
51. How does Oracle BPM handle compensations in business processes?
Ans:
Compensations in Oracle BPM are used to be undo or compensate for work that has performed in case of errors or exceptions. Compensation activities are defined within process and are executed when needed to revert a changes made during process execution.
52. What is the Oracle BPM process dictionary?
Ans:
- The Oracle BPM process dictionary is the repository for storing the reusable artifacts such as data objects, business rules, and service definitions.
- It promotes the consistency and reusability across the processes by providing centralized location for managing shared resources.
53. How can I implement error handling in Oracle BPM processes?
Ans:
Error handling in the Oracle BPM involves use of fault policies, catch events, and compensation activities. Fault policies define how system should respond to specific errors, catch events capture and handle faults during the process execution, and compensation activities revert changes made in case of the errors.
54. Explain dehydration in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
- Dehydration in the Oracle BPM involves persisting process instances to database when they are not actively executing.
- This helps free up a system resources while retaining the state of process.
- Dehydrated instances can be rehydrated when needed to be resume execution.
55. Explain roles and participants in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
Roles in Oracle BPM represent the set of responsibilities or tasks, while participants are individuals or groups assigned to roles. Roles are used to define the access permissions and responsibilities within process, and participants are assigned to be roles based on functional responsibilities.
56. What is the purpose of Oracle BPM Process Spaces feature?
Ans:
Oracle BPM Process Spaces provide the collaborative environment for a business analysts, developers, and the other stakeholders to work together on modeling and refining a business processes. It supports the versioning, discussions, and annotations to enhance collaboration.
57. Explain the role of Oracle BPM Sensor framework.
Ans:
The Oracle BPM Sensor framework is used for a monitoring and collecting runtime data from the business processes. Sensors can be defined to capture the specific data points at a various stages of process execution, providing the insights into a performance and behavior.
58. How does Oracle BPM handle long-running processes?
Ans:
Oracle BPM supports the long-running processes through the features like dehydration and instance state persistence. Dehydration allows the system to store the state of inactive process instances, and state persistence ensures that process state is retained even if the server is restarted.
59. What are Adaptive Case Management (ACM) features in Oracle BPM?
Ans:
Adaptive Case Management in the Oracle BPM allows for a dynamic and flexible handling of unstructured processes.
It enables the knowledge workers to make ad-hoc decisions and collaborate on cases, providing the more flexible approach to handling the unpredictable work scenarios.
60. Explain the difference between synchronous and asynchronous communication in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
Synchronous communication involves the immediate interactions, where a sender waits for a response, while asynchronous communication allows for the delayed interactions, and sender does not wait for an immediate response. Oracle BPM supports both the synchronous and asynchronous communication patterns.
61. How can you achieve fault tolerance in Oracle BPM processes?
Ans:
Fault tolerance in Oracle BPM involves the designing processes to handle errors gracefully. This includes the implementing fault policies, retry mechanisms, and compensation activities to ensure that system can recover from the unexpected issues without compromising data integrity.
62. Explain subprocess pool in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
- A subprocess pool in the Oracle BPM is a mechanism for reusing the subprocesses across multiple parent processes.
- It allows for creation of shared subprocesses that can be invoked by a different processes, promoting reusability and consistency.
63. How does Oracle BPM support mobile applications?
Ans:
Oracle BPM provides the mobile support through the Oracle BPM Worklist Mobile, allowing users to access tasks and participate in processes from mobile devices. This enhances flexibility and accessibility of a BPM applications.
64. What is the purpose of Oracle BPM Business Indicator?
Ans:
Oracle BPM Business Indicators are used to measure and track the specific metrics within a business process. These indicators can be associated with the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to provide the insights into performance and efficiency of the process.
65. What is the Oracle BPM API?
Ans:
The Oracle BPM API (Application Programming Interface) allows the developers to programmatically interact with the Oracle BPM processes and services.
It can be used for a tasks such as starting processes, querying task information, and integrating the BPM functionality into other applications
66. Explain the difference between a sequential and parallel gateway in BPMN.
Ans:
- A sequential gateway in BPMN controls a flow of a process by making decisions based on conditions, allowing the only one path to be executed.
- A parallel gateway, on other hand, enables the multiple paths to be executed simultaneously, often used for a parallel branching in a process.
67. How does Oracle BPM handle versioning of business rules?
Ans:
Oracle BPM allows for a versioning of business rules through Oracle Business Rules component. This enables management of different rule versions, ensuring that changes to the business rules do not impact existing processes using the previous rule versions.
68. Explain role of Oracle BPM Process Analytics component.
Ans:
- Oracle BPM Process Analytics provides the advanced analytics and reporting capabilities for a monitoring and analyzing business processes.
- It allows organizations to create a custom dashboards, reports, and charts to gain insights into the process performance and trends.
69. What is Oracle BPM simulation feature, and how is it beneficial?
Ans:
Oracle BPM simulation allows the users to model and simulate business processes to analyze and optimize performance. It helps in understanding a impact of changes, identifying the bottlenecks, and making informed decisions to improve the overall process efficiency.
70. How can model user interactions in Oracle BPM processes?
Ans:
User interactions in Oracle BPM are modeled using the human tasks. These tasks can be defined as a manual tasks, user tasks, or service tasks with user interactions, allowing for integration of human participants in execution of business processes.
71. What is BPMN Data Object, and how is it used in Oracle BPM?
Ans:
In BPMN, a Data Object represents information that is used or produced by the process. In Oracle BPM, Data Objects are used to model data consumed or generated by the process activities, providing clarity on information flow within process.
72. Explain BPMN Message Events and their role in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
BPMN Message Events in Oracle BPM represent communication between the different processes or process instances.
They are used for a sending and receiving messages between processes, enabling the coordination and interaction in a distributed environment.
73. Explain Oracle BPM Document Service.
Ans:
The Oracle BPM Document Service allows for management and manipulation of documents within the business process. It provides the features such as document creation, retrieval, update, and deletion, enabling processes to interact with an external document repositories.
74. How does Oracle BPM support role-based access control (RBAC)?
Ans:
Oracle BPM supports RBAC through assignment of roles to users and participants. Access permissions and responsibilities are defined based on these roles, ensuring that users have appropriate level of access to tasks and processes based on roles.
75. What is Oracle BPM Test Framework?
Ans:
- The Oracle BPM Test Framework is the tool for automated testing of a BPM processes.
- It allows the developers to create and execute test cases to validate the behavior of processes, ensuring reliability and correctness of implemented solutions.
76. What is Oracle BPM Process Spaces REST API?
Ans:
The Oracle BPM Process Spaces REST API allows the developers to programmatically interact with the Oracle BPM Process Spaces. It provides the capabilities for creating, updating, and managing Process Spaces, as well as a retrieving information about them.
77. How does Oracle BPM support business rule versioning and deployment?
Ans:
Oracle BPM supports the business rule versioning through the Oracle Business Rules. Rules can be versioned and deployed independently of process, allowing for management of rule changes without affecting overall process.
78. Explain the concept of subprocess call activity in BPMN.
Ans:
- A subprocess call activity in the BPMN represents invocation of a subprocess within parent process.
- It allows for modularization and reuse of subprocesses, enhancing maintainability and promoting the modular design approach.
79. What is Oracle BPM Exception Management Framework?
Ans:
The Oracle BPM Exception Management Framework provides the standardized approach for handling exceptions in the business processes.
It allows for the definition of exception policies, which specify how different types of the exceptions are handled during process execution.
80. Explain the concept of process templates in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
- Process templates in Oracle BPM are predefined process structures that serve as a starting points for creating a new processes.
- They encapsulate best practices and standardization, allowing for consistent creation of a processes across the organization.
81. What is Oracle BPM Process Asset Manager (PAM)?
Ans:
The Oracle BPM Process Asset Manager is the component that allows organizations to manage and reuse process assets are process templates, rulesets, and documents. It promotes the reusability and consistency across the different projects.
82. What is Oracle BPM Composer and how differ from Oracle BPM Studio?
Ans:
Oracle BPM Composer is the web-based tool that allows the business users to participate in design and modification of business processes. It provides the simplified interface compared to the Oracle BPM Studio, making it more accessible to users who are not necessarily technical experts.
83. Explain subprocess compensation in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
Subprocess compensation in the Oracle BPM involves defining a compensation activities within a subprocess.
These activities are executed if error occurs in the subprocess, allowing for a reversal or compensation of work done in subprocess.
84. How can you implement conditional branching in Oracle BPM processes?
Ans:
- Conditional branching in the Oracle BPM is implemented using an exclusive gateways.
- These gateways route flow of the process based on a specified conditions, allowing for a decision-making within the process.
85. What is the significance of Oracle BPM Data Association feature?
Ans:
Oracle BPM Data Association is used to define how data is transferred between the activities in a process. It specifies the how input and output data are associated with variables used in different activities, ensuring the proper data flow within the process.
86. How can model time-based events in Oracle BPMN?
Ans:
Time-based events in Oracle BPMN are modeled using the intermediate timer events. These events trigger based on a specified time intervals or schedules and can be used to control the timing of the activities within a process.
87. What is Oracle BPM Process Lifecycle Service (PLS)?
Ans:
The Oracle BPM Process Lifecycle Service provides APIs for managing and controlling lifecycle of BPMN processes. It allows for the operations such as deploying, undeploying, and initiating processes programmatically.
88. How does Oracle BPM handle stateful processes?
Ans:
Oracle BPM supports the stateful processes through use of process instances. Each process instance represents the unique execution of process, and state of the process is maintained as long as instance is active.
89. Explain Oracle BPM Message Exchange Framework.
Ans:
- The Oracle BPM Message Exchange Framework facilitates communication between the different BPM processes.
- It allows the processes to exchange messages in loosely coupled manner, enabling integration and collaboration between the different parts of a business.
90. Explain subprocess boundary events in Oracle BPM.
Ans:
Subprocess boundary events in the Oracle BPM are attached to specific subprocess and trigger based on a specified conditions. They allow for handling exceptions or events at level of subprocess, influencing the overall flow of process.






