
An all-inclusive, integrated transportation management solution is offered by Oracle Corporation under the name Oracle Transportation Management (OTM). Its goal is to make business transportation and logistics operations more efficient and effective by streamlining all of the workflows involved. Providing a number of features to improve supply chain management’s visibility, control, and cost-effectiveness, OTM makes it easier to plan, carry out, and monitor transportation-related tasks.
1. What are the reasons OS-based metrics are useful?
Ans:
These are typically taken into account when keeping an eye on a certain condition. This task is readily achieved with the help of a custom script that can be written. Every time the enterprise manager is assessed, the script will be mentioned specifically. To return its value, though, is mostly up to the script.
2. What ways might the monitoring capabilities be expanded using user-defined metrics?
Ans:
These are the following:
- operating system-dependent user Specific metrics
- User-defined metrics based on SQL.
- Application-specific or custom metrics are other terms for user-defined metrics. MeasurementsWith the use of these metrics, you or an outside program can specify and gather data that the integrated Cloud Monitoring metrics are unable to.
3. How do bespoke SQL query scripts fit into metrics?
Ans:
For the same reason—that is, to monitor metrics and initiate alerts—custom calls, custom scripts, and SQL queries are all installed. This ensures that the activities run smoothly and efficiently without requiring the use of any additional services.
4. What steps are necessary to make them accessible in metrics, After establishing the features?
Ans:
The customers of Oracle TM don’t have to worry about it. This is because all necessary features become available automatically as soon as the metrics are established. One of the best things about developing metrics that meet the requirements is that they may be used for any purpose.
5. Where are the SQL-based metrics accessible?
Ans:
In essence, it can be reached via the databases’ intended home sites. They are typically contacted for deployment-related reasons when it comes to bespoke database administration. Suppose a time-saving strategy is to be taken into consideration. In that case, the functions can also be called very easily to complete tasks that are comparable or parallel without requiring additional time.
6. What are some of the most significant features that metrics offer?
Ans:
These are the following:
- Notifications pertaining to the job at hand
- Alerts from the system;
- User-taken corrective action;
- Historical collections;
- Metric monitoring;
- Features linked to allocation
7. How can metrics administrators implement unique features?
Ans:
By connecting it with the enterprise manager, administrators can easily install their custom monitoring script library for this purpose. One potential measure for effective integration is a user-defined statistic. This has the advantage of allowing users to ensure high-quality outcomes easily. For this reason, the SQL-based measure is frequently taken into account.
8. What are the two common processes in developing user-defined metrics based on the operating system?
Ans:
These are the following:
- Setting up the operating system monitoring script first;
- Registering the script as a user-defined metric;
- In certain circumstances, using the script without registration is also viable.
- Alerts from the system;
- User-taken corrective action;
- Historical collections;
- Metric monitoring;
- Features linked to allocation
9. List out any location restrictions on scripts that are normally run with user-defined metrics?
Ans:
Indeed, there is a fundamental requirement; that is, each one needs to be put in a directory to which the agent has unrestricted access. Users won’t be able to utilize any scripts that aren’t listed in the directory because they are often disregarded. If a user finds that the directory is full, they can make a new directory with whatever name they choose.
10. Why is setting up the script runtime environment important?
Ans:
This ensures that the management agent may easily implement all of the scripts for the deliberate goal. Scripts always have a limit on how much they can do, just in case. Additionally, some of them won’t function as required. Furthermore, customizing the script runtime ensures that numerous metrics can be created simultaneously without utilizing all available features or capabilities.
11. Mention one interpreter that scripts often need? In what location should it be installed?
Ans:
The interpreter that scripts often require is Perl. The host system has to have it installed. An interpreter is a computer software that, according to computer science, runs instructions written in a programming or scripting language directly without first needing to be compiled into a machine language. Program.
12. What value should the script return? What does this suggest?
Ans:
The script should return the value linked to the monitoring object. This suggests that the object is in perfect condition and may be used again. When this value is returned, it also indicates that all object-related warnings have been taken into account. In situations when returning this number takes longer than expected, users can manually retrieve it using the metric allocation tools.
13. What distinguishes a right outer join from a left outer join?
Ans:
| Criteria | Right Outer Join | Left Outer Join | |
| Retained Rows | All rows from the right table | All rows from the left table | |
| Unmatched Rows | Includes unmatched rows from the right table | Includes unmatched rows from the left table | |
| Matched Rows | Includes matched rows from both tables | Includes matched rows from both tables | |
| Syntax (example) | SELECT * FROM right_table RIGHT OUTER JOIN left_table ON right_table.column = left_table.column; | SELECT * FROM left_table LEFT OUTER JOIN right_table ON left_table.column = right_table.column; | |
| Short Syntax (example) | SELECT * FROM right_table NATURAL RIGHT JOIN left_table; | SELECT * FROM left_table NATURAL LEFT JOIN right_table; |
14. How do SQL functions work?
Ans:
Although SQL functions can accept parameters, they always yield a specific value.
There are two categories of SQL functions:
- Character, number, date, conversion, and general are examples of single-row functions.
- Functions with many rows, such as variance, stddev, max, min, count, and sum.
- NVL is one type of SQL General function.
- NVL2 Conditional Expressions NULLIF COALESCE
15. Describe a primary key.
Ans:
- A primary key in a database serves as a table’s unique identifier for every record.
- It establishes the foundation for relational relationships, speeds up searches, and guarantees data integrity.
- The column or columns with values that uniquely identify each row in a table are known as primary keys. For Optim to insert, update, restore, or remove data from a database table, the table needs a primary key.
16. What is the Oracle concept?
Ans:
Overview of Oracle Database One RDBMS is the Oracle Database. An object-relational database management system is an RDBMS that incorporates object-oriented characteristics, including inheritance, polymorphism, and user-defined types (ORDBMS).
17. What is the idea behind Oracle?
Ans:
An Overview of Oracle Database is one RDBMS. A relational database management system (RDBMS. that integrates object-oriented features such as inheritance, polymorphism, and user-defined types is called an object-relational database management system (ORDBMS..
18. What is the oracle’s primary purpose?
Ans:
With Oracle Functions, developers can build, execute, and grow applications without having to worry about maintaining any infrastructure. It features an interface with platform services, SaaS apps, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. The open-source Fn Project serves as the foundation for Functions.
19. What is the same across all monitoring scripts utilized for the metrics?
Ans:
The two most crucial ones are codes, which are used to verify the status of the objects under observation. The second is the code that sends the enterprise manager the results of the script. If they are intended to carry out comparable duties, users are free to store similar information in them.
20. What do the numbers next to the em_messages and em_results indicate?
Ans:
This usually includes the data pertaining to the formatted data that the enterprise manager receives back from the script. This indicates that the same has been assigned to the metrics, allowing for the completion of other tasks. A warning message alerting the user to any errors is displayed on the screen. In order to use these values for reasons other than those for which they were intended.
21. Describe the distinction between PL/SQL and SQL.
Ans:
- Oracle offers an extension for procedural programming called PL/SQL (Procedural Language/SQL., which enables more sophisticated data processing inside the databases. SQL (Structured Query Language. is used for database queries and manipulation.
- SQL is a structural query language created to manipulate relational databases. It is a declarative, detail-oriented language.
- Meanwhile, PL/SQL is a procedural language/structured query language that uses SQL as its database. It is an application-oriented language.
22. What distinguishes SQL from iSQL*Plus?
Ans:
- While iSQL*Plus is an environment, SQL is a language. With the help of a command line tool called iSQL*Plus,
- SQL instructions can be typed and immediately run against an Oracle database. While functions carry out some formatting tasks in SQL, iSQL*Plus formats data using commands.
23. Describe a sub-query.
Ans:
A subquery is a SELECT statement that is contained within another SELECT statement’s clause. The WHERE, HAVING, and FROM clauses can all contain it. A Subquery in SQL is essentially a query inside another query. Put otherwise, a subquery is a query that is incorporated within the WHERE clause of another SQL query. Crucial guidelines for subqueries: The Subquery can be inserted into many SQL clauses: clauses for WHERE, HAVING, and FROM
24. What is a VArray?
Ans:
An Oracle datatype called VArray (variable-sized array. is used to store columns with multi-valued attributes. A bounded array of values can be stored in it. A positive integer known as the array index is used to refer to each element in a VARRAY collection. The type definition states the maximum cardinality of the VARRAY. A VARRAY collection type is defined with the TYPE IS VARRAY declaration.
25. What is the first action it takes to execute it After a script is produced?
Ans:
Everywhere it is referenced in the scripts, the starting point for a new line must be set to em_results. If this requirement is not met, a runtime error is always displayed on the screen, and users must take note of several details in order to resolve the issue. As a result, it needs to be given top importance.
26. In what circumstances does a condition indicate a metric inaccuracy in the metrics?
Ans:
An error is indicated when a non-zero number appears on the screen or when the STDOUT and STDERR messages are not accessible at the precise location. Users must either carry out the task once more or they must make amends for the actions that are thought to have eliminated it.
27. Where in Oracle TM is the script located?
Ans:
In actuality, it ensures that updating the agent doesn’t damage the script. This ensures that the script always works regardless of the circumstances. The complete route needs to be supplied to the script when registering it in the control console. Users may only sometimes be permitted to utilize the default properties.
28. What does the term “RAC” mean?
Ans:
- Real Application Cluster is what it stands for, and it is essentially a single instance database.
- Reservations Against Cancellation, or RAC, grants you entry to the train as well as the ability to share a side lower compartment with other passengers.
- It is, in all actuality, a confirmed ticket. It results in a complete berth allocation in 99.9% of cases.
29. Describe the distinction between data types VARCHAR2 and CHAR.
Ans:
- Fixed-length strings are stored in Oracle using the CHAR data type, which can optionally be padded with space.
- Variable-length strings are stored using VARCHAR2, which uses only the necessary space. Character strings with a fixed length are stored in the CHAR file.
- If variable-length strings are stored in this type, a significant amount of disk space will be wasted. Character strings with varying lengths are stored in VARCHAR2.
30. What does “scheduling a script” mean?
Ans:
- It indicates the start time and the frequency at which the script is intended to run. The script must utilize the agent’s time zone.
- It can schedule scripts to run once during a specified period or more than once. Additionally,
- It can specify the schedule to occur at the designated hour or within a specified window of time on certain weekdays. Dates are not taken into account during scheduling.
31. Define the script by itself.
Ans:
Instead of the synopsis or other helpful data, you must specify the different parameters. They have to do with how the script operates and its surroundings. This ensures that it may be used with various range measurements with ease and that nothing is violated.
32. Describe a literal.
Ans:
A literal is a string that isn’t a column name or alias but is made up of a character, integer, or date that is present in the Select list. Scripts can be scheduled to run multiple times or only once inside a predetermined window of time. You may also set the schedule to run on a specific weekday at a given hour or within a particular time window. When scheduling, dates are not taken into consideration.
33. Describe the Oracle Database.
Ans:
An effective method for storing, retrieving, and managing structured data is the Oracle Database, a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS.. The first database made specifically for enterprise grid computing, which is the most adaptable and economical method of managing data and applications, is the Oracle Database. Large pools of modular servers and storage that meet industry standards are produced via enterprise grid computing.
34. What is SQL?
Ans:
A language called Structured Query Language (SQL. makes it possible to interact with and manipulate databases. The acronym for Structured Query Language is SQL, which is pronounced: “ess-que-el ” To communicate with a database, utilize SQ. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI. states that this language is the industry standard for relational database management systems.
35. What Do Oracle Indexes Mean?
Ans:
Oracle data structures called indexes allow for faster data retrieval, which improves database performance. They enable quicker access to particular data within a table and function similarly to an index in a boo. In Oracle, indexes are utilized to enable easy access to a table’s row. In operations, when a small percentage of a table’s rows are returned, indexes speed up access to data.
36 . How do a View and a Table vary from one another?
Ans:
- A view is a virtual table in Oracle that, in response to pre-written queries, shows data from one or more tables.
- Table, on the other hand, is a real data-containing physical storage structure. The differences between the view and table are as follows.
- The database item called a view makes it possible to create a logical subset of data from one or more tables.
- A table serves as an entity or database object used to store data in a database.
37 . How can SQL injection be avoided in Oracle?
Ans:
- Use parameterized queries and bind variables to stop SQL injection in Oracle. By ensuring that input values are handled as data, this method prevents nefarious efforts to alter the SQL query.
- Using a code injection approach, one can retrieve or manipulate data stored in the application layer by taking advantage of weaknesses in that layer.
- One scenario is when a user enters required data, and it either needs to be properly filtered, not strongly typed, and executed unexpectedly, or the user enters a SQL statement in its place.
38. In Oracle, how can you get the current time and date?
Ans:
The SQL function “SYSDATE” can be used to obtain the current date and time in Oracle. It provides the precise current time and date displayed by the system. You have an easy choice in any scenario:
- Use SYSDATE whether the time spent on the database server or during your session is of interest to you.
- Use a function that returns the session time zone if it’s for your session.
- Use a function that returns the database time zone if it’s for the database server.
39. What does the COMMIT statement aim to achieve?
Ans:
All modifications are finalized and applied permanently in Oracle by using the COMMIT command. Data durability and consistency are ensured inside a transaction to the database. The COMMIT statement initiates a new unit of work and concludes the current unit of work that is being performed. All modifications performed by SQL data change statements and SQL schema statements during the unit of work are committed, with the exception of DROP SCHEMA. See Statements for more on SQL data change statements and SQL schema statements.
40. Why is the UNIQUE restriction in place?
Ans:
In order to prevent duplicate entries, the UNIQUE constraint in Oracle is used to make sure that the values in a particular column or group of columns are unique and varied throughout the table.
To guarantee that every value in a column is unique, apply the UNIQUE constraint. The UNIQUE and PRIMARY KEY constraints ensure a column’s or a group of columns’ uniqueness. A UNIQUE constraint is inherently included in a PRIMARY KEY constraint.
41. Describe normalization.
Ans:
Normalization is an essential database design procedure to minimize data redundancy and reliance. Normalization improves data integrity and eases maintenance by dividing data into several tables, each with a distinct function. By optimizing database efficiency, this method guarantees consistent and dependable information retrieval and storage.
42. Describe the distinction between UNION ALL and UNION.
Ans:
The “UNION” operator in SQL queries removes duplication by combining and returning unique rows from several SELECT statements. On the other hand, “UNION ALL” incorporates all rows—duplicates included—while combining the outcomes of several queries. Whether you require all entries or want unique results will determine which option to select.
43. What does the GROUP BY clause mean?
Ans:
The objective behind SQL is that the GROUP BY clause is used to classify and group rows from a table according to particular field values. It makes it possible to apply aggregation functions—such as COUNT, SUM, AVG, and so on—to these groups, resulting in summarised data that facilitates data analysis.
44. What is Foreign Keys?
Ans:
In relational databases, a foreign key refers to the primary key of one table in another, creating a relationship between the two tables. When retrieving and modifying data across related tables, this connection guarantees consistency and accuracy by upholding referential integrity and enforcing data integrity.
45. What does the NVL function aim to achieve?
Ans:
- Oracle’s NVL function replaces null values with a defined replacement value. This guarantees more efficient data processing as well as precise query and computation output.
- The NVL function accepts two arguments: The name of the expression to be evaluated is taken in the first parameter and the second argument.
46. What does the ROLLBACK statement mean?
Ans:
- In order to ensure data integrity and return the database to its former consistent state, the Oracle ROLLBACK statement is used to undo any uncommitted changes performed during a transaction.
- When a transaction is COMMITTED, its modifications are finalized and made available to all sessions.
- Conversely, a ROLLBACK statement reverses any changes made by the current transaction.
- All InnoDB locks that were set during the current transaction are released by both COMMIT and ROLLBACK.
47. What distinguishes a Primary Key from a Candidate Key?
Ans:
- A Candidate Key and a Primary Key have important responsibilities in Oracle SQL, although they are not the same.
- A Primary Key is a selected Candidate Key that acts as the primary means of record identification, enabling effective data organization and retrieval.
- In contrast, a Candidate Key is a unique identifier for every record in a table.
48. Describe a subquery.
Ans:
A subquery is a SQL query inside another query; it’s also known as a nested query. It is employed to obtain information that will be utilized in the main inquiry. Circumstances or computations. Subqueries increase the flexibility of a query by allowing the retrieval of data from several tables or the application of aggregates for more accurate outcomes.
49. Describe the distinction between a function and a stored procedure.
Ans:
A Stored Procedure and a Function have different functions in database management. A stored procedure is a collection of SQL statements created to carry out particular actions, frequently involving data modification. A function, on the other hand, is frequently used to return a single value that has been calculated or transformed and utilized in SQL queries.
50. What distinguishes a non-correlated subquery from a related subquery?
Ans:
A Correlated Subquery in SQL differs from a Non-correlated Subquery based on how the two interact with the Outer Query. For every row that is processed, a Correlated Subquery influences the Outer Query’s execution by referencing values from that query. Conversely, a Non-correlated Subquery functions autonomously, acquiring information without depending on the context of the Outer Query.
51. What is a sequence In Oracle?
Ans:
In Oracle, a sequence is a type of database object that generates progressively distinct numeric values. It is frequently used to supply tables with primary key values. Sequences guarantee the uniqueness of every value and allow for step-by-step incrementation or decrementation. This improves data simplicity and integrity.
52. Why is the UNIQUE restriction in place?
Ans:
- In order to prevent duplicate entries, the UNIQUE constraint in Oracle is used to make sure that the values in a particular column or group of columns are unique and varied throughout the table.
- To guarantee that every value in a column is unique, apply the UNIQUE constraint. The UNIQUE and PRIMARY KEY constraints ensure a column’s or a group of columns’ uniqueness.
- A UNIQUE constraint is inherently included in a PRIMARY KEY constraint.While sessions enable user interactions, transactions have an impact on data.
53. What distinguishes an alias from a synonym?
Ans:
- Although the terms “alias” and “synonym” are used interchangeably in the context of databases, they have different functions.
- A synonym is a different word for an item that helps make difficult searches easier to understand.
- An Alias, on the other hand, temporarily renames a table or field in a query to improve readability.
54. Describe the distinction between a cold and hot backup.
Ans:
- The availability and timing of a Hot Backup and a Cold Backup in Oracle databases vary.
- Users can access data while the database is up and running by taking a hot backup.
- A Cold Backup, on the other hand, is carried out when the database is offline, guaranteeing data consistency but momentarily limiting user access.
55. What’s an index bitmap?
Ans:
In Oracle, a Bitmap Index is a type of data structure that effectively displays binary properties such as True or False or Yes/No. It indexes data using bitmaps, in which each bit represents a distinct attribute value. This indexing technique reduces disk I/O, which improves query performance and speeds up queries with numerous characteristics.
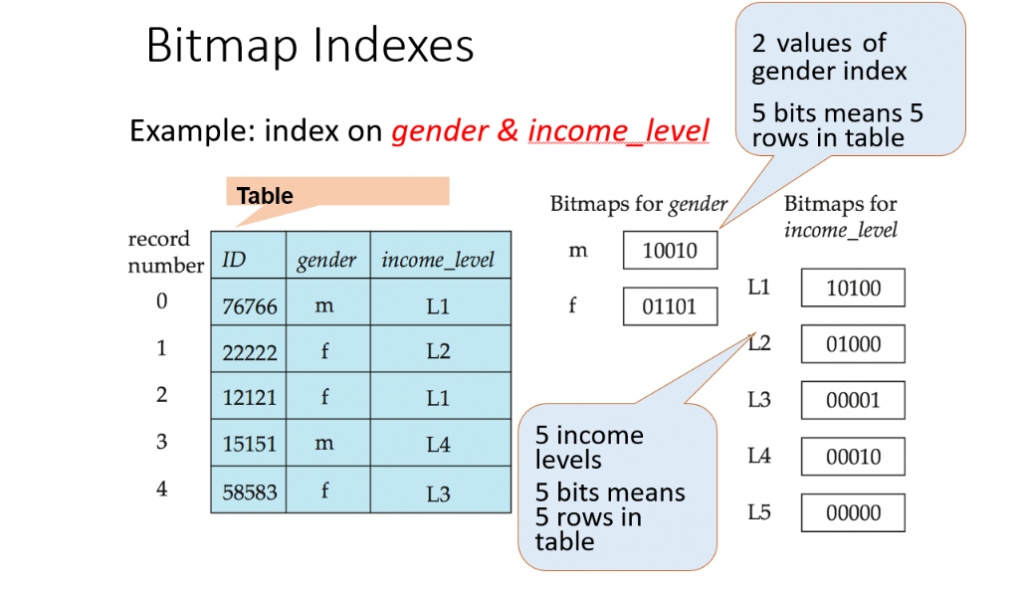
56. Describe the difference between a stored procedure and a database trigger.
Ans:
Although they are both database objects, a stored procedure and a database trigger have different functions. A stored procedure is a set of reusable SQL statements that may be manually invoked. In contrast, a trigger is automatically executed in reaction to particular events, such as changes in data. While Stored Procedures are called by application code, triggers are event-driven.
57. What is the Common Table Expression (WITH. purpose?
Ans:
Common Table Expressions (CTEs., like the WITH clause, are used to improve query readability and streamline intricate SQL queries. It makes it simpler to refer to and work with data by enabling users to establish temporary result sets within a query. This helps to simplify complex queries into smaller, more manageable components, which enhances maintainability and efficiency.
58. What does the “HAVING” clause mean?
Ans:
The objective of SQL’s “HAVING” clause, especially when used in conjunction with a GROUP query, is to filter the results following the application of grouping. The ‘HAVING’ clause operates on grouped data, which is different from the ‘WHERE’ clause, which filters rows before grouping. By putting constraints on aggregated values, you can get hold of particular subsets of grouped data that satisfy particular requirements.
59. Describe the Oracle Transactions context and the attributes of ACID.
Ans:
The ACID qualities are essential to Oracle Transactions because they guarantee the consistency and dependability of data manipulations. The abbreviation integrity of the database ensures that committed changes are kept forever, even in the event of a system failure.
60. What Does Oracle Mean by an Execution Plan?
Ans:
In Oracle, an execution plan is a tactical blueprint that describes how the database engine will carry out a given SQL query. It offers the database optimizer a thorough, step-by-step manual on how to set of fundamental principles known as Isolation and Durability dictate how transactions behave. A Transaction’s atomicity guarantees that it is interpreted as a single, indivisible piece of work, meaning that either all of its modifications are applied or none at all.
61. Describe the distinction between an Oracle user and a schema.
Ans:
- Tables, views, and procedures are examples of database objects that are logically contained in an Oracle schema.
- In contrast, a User is an account that grants access to a particular schema and has its name and password.
- A User may possess more than one Schema, although there is just one User connected to the Schema.
62. What distinguishes a non-clustered index from a clustered index?
Ans:
- The physical arrangement of rows in a table is determined by a clustered index, which reorganizes the data to conform to the index.
- A non-clustered index, on the other hand, refers to the positions of rows without changing the actual data order.
- It is a different structure. A table may have more than one non-clustered index but only one clustered index.
- Performance is affected by this distinction: Non-clustered Indexes are excellent at accelerating data retrieval for certain columns, whereas Clustered Indexes are effective for range queries because of their data order.
63. Which three qualities define a main key?
Ans:
- SQL Primary Key: Advantages, Characteristics, and Applications
- Each primary key column, or columns, has the following properties:
- By refusing to accept any duplicate values, it enforces uniqueness.
- A primary key uniquely identifies every field.
- There can only be one primary key per table.
- The maximum length for primary columns is 900 bytes.
- Null values are not permitted in a main key column.
64. What is the Oracle database’s logical and physical structure?
Ans:
The Oracle database allows logical space for every piece of data. Data blocks, extents, segments, and tablespaces are the logical building blocks for allocating database space. The data is physically kept on disk as data files. Operating system blocks are used to store the data in the data files.
65. Which three physical parts make up an Oracle database?
Ans:
- Structures for Physical Storage
- Overview of Physical Storage Facilities
- Temporary and data files.
- An Oracle Database-created physical file on persistent storage that includes data structures like tables and indexes is called a data file.
66. What is the Oracle DBMS’s internal structure?
Ans:
SAP Foundation: Oracle Database Internal Architecture. The database and the Oracle instance are the two primary parts of the Oracle Database Internals. The memory structures and Oracle background processes that are launched when the database is started make up the Oracle instance, which is the static portion of the Oracle system.
67. Which model describes a database’s internal organization?
Ans:
The database’s physical storage structure is described in the internal level’s internal Schema. A physical schema is another name for the internal Schema. The physical data model is employed. It serves to specify the manner in which information will be kept in a block.
68. What Are The Three Approval Steps That You Must Comply With In The Qas Approval Procedure?
Ans:
- To Obtain permission from the system administrator
- To be approved with department assistance
- To receive permission from the requested owner
69. What are the constituents of Oracle database’s logical database structure?
Ans:
In the Oracle database, the logical database structure consists of two primary parts:
- Surfaces for tables
- Schema objects in the database
- Tablespaces for SYSTEM and SYSAUX
- UNDOTBS1 tablespace, TEMP tablespace, USERS tablespace.
70. What is the data abstraction’s physical level?
Ans:
- GeeksforGeeks: Data Abstraction and Data Independence Internal or Physical Level The lowest level of data abstraction is this one.
- It explains the exact method by which the data is kept in memory. The same is true for file organization techniques like hashing and B+ trees, as well as access techniques like sequential or random access.
71. What is a table that is nested?
Ans:
- In Oracle, a nested table is a form of data that has columns for storing attributes with multiple values. A whole subtable can be contained in a nested table.
- A nested table in relational databases is a table embedded in another table. In a nested table, individual elements can be added, changed, and removed.
72. Describe the objective of the Oracle Data Pump tool.
Ans:
The Oracle Data Pump tool is crucial for operations like database migration, system upgrades, and data consolidation since it provides a quick and effective way to export and import massive volumes of data. With the help of this application, users can select data subsets, compression choices, and parallel execution to maximize efficiency and have more control over the export and import procedures.
73. How do schema objects work?
Ans:
Tables, indexes, databases, views, synonyms, triggers, functions, procedures, and packages are examples of schema objects. Users establish logical structures called schema objects. Tables and indexes are examples of objects that contain data; other objects, such as views and synonyms, can have definitions. Be aware that a tablespace and a schema are unrelated.
74. What makes up the Oracle database’s physical database structure?
Ans:
The physical database structure consists of the following: greater than equal to one control file, greater than equal to two redo log files, and greater than equal to one data file. The term “physical structures” refers to those that the operating system can view and manipulate, such as the actual files used to store data on disk. The operating system is unaware of logical structures; they are generated and identified by the Oracle database server.
75. Explain how Varchar and Varchar2?
Ans:
Oracle has two data types, Varchar and Varchar2, for storing character strings of different lengths. Varchar2 has a maximum storage capacity of 4000 bytes, whereas Varchar can only hold 2000 bytes of characters. All of the characters defined during the declaration will be stored in Varchar. Characters that were not used will have more room, thanks to Varchar2.
76. What is an Oracle table?
Ans:
Oracle Database, a table is a fundamental and structured database object used to store and organize data in a tabular format. It represents a collection of related data entries arranged in rows and columns, where each column corresponds to a specific attribute or field, and each row contains a record or data instance. Tables serve as the primary means of organizing and managing data within the Oracle Database system. The structure of an Oracle table is defined by its schema, which outlines the columns along with their respective data types and constraints.
77. In Oracle, how are comments represented?
Ans:
There are two ways we can represent comments in Oracle:
Before the line begins, there are two dashes (–.. One assertion
Regarding the statement block, we can represent it as comments using /*—— */.
78. How do the database, tablespace, and data file relate to each other?
Ans:
One or more tablespaces, or logical storage units, can be found in an Oracle database. All of the data in a database is stored in these tablespaces combined. One or more files, known as data files, make up each tablespace. The physical formats of the data files follow the specifications of the operating system that Oracle is executing on.
79. What is DML?
Ans:
To access and manage data in the current objects, we employ Data Manipulation Language or DML. The select, insert, update, and delete DML statements are used.
Oracle’s RAW datatype Binary data with variable length or byte string values are stored in the RAW datatype. A raw in a table can have a maximum size of 32767 bytes.
80. What do Oracle’s Aggregate functions do?
Ans:
Oracle’s aggregate functions are a set of powerful tools in the SQL language that enable users to perform calculations on a set of values and return a single, summarized result. These functions are particularly useful in data analysis and reporting, allowing for the extraction of meaningful insights from large datasets. Commonly used aggregate functions in Oracle include COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, and MAX. The COUNT function tallies the number of rows in a specified column or the number of non-null values.
81. What Does a View Mean?
Ans:
A logical table based on one or more tables or views is called a view. A view does not physically store data. Base tables are those tables that serve as the foundation for views. Views in database management systems are virtual tables that are produced by SQL queries or Structured Query Language whenever the user asks for data based on certain requirements rather than the entirety of the table’s contents.
82. How do images get added to a database?
Ans:
Type of Long Raw Data Can be applied to databases to store images. This data type can be used to store binary data with a 2GB length. Binary data, sometimes referred to as BLOB (Binary Large OBject. data, is one way to store photos. This entails saving the picture file straight to the database after converting it to a binary representation. January 23, 2023
83. In what contexts are DECODE and CASE statements used?
Ans:
These statements are used in Oracle for data value modification and work similarly to the if-then-else statement. While DECODE is exclusively utilized in SQL statements, CASE can function as a PL/SQL construct. DECODE is limited to operating as a function within SQL. In PL/SQL, CASE can be a useful stand-in for IF-THEN-ELSE. If you swap out CASE in the example below with Then, DECODE returns an error.
84. What do Oracle database objects mean?
Ans:
Among the objects in an Oracle database are:
- Tables are collections of components arranged both horizontally and vertically.
- A virtual table created from one or more tables is called a view.
- Indexes are a way to fine-tune record processing performance.
85. Describe the Oracle ANALYZE command.
Ans:
- The command “ANALYZE” enables the user to manipulate an index, table, or cluster in different ways. It facilitates:
- To determine which table or cluster’s migrated and chained rows are.
- To verify an object’s structure and gather data regarding the things that users utilize and store it in the data dictionary.
83. What kinds of joins do subqueries use?
Ans:
To compare and integrate particular rows of data from two or more tables in a database, use a join. The different joins consist of the following:
- To join a table with itself, use self-join.
- To combine some dissimilar and matching data from many tables, use an outer join.
- Equi-join: a join criterion that yields only rows with values that are comparable.
84. In Oracle, what is MERGE, and how does one merge two tables?
Ans:
Data from two tables can be merged later using the merge statement. In accordance with the criteria given in the query, it extracts data from the source table and inserts or changes it in the destination table. Applications for data warehousing can benefit from the merge command.
85. In Oracle, what is the NULL value?
Ans:
A NULL value denotes unknown or missing data. A column is referred to as null or containing null if it is empty in a row. Any column that isn’t constrained by integrity constraints related to NOT NULL or PRIMARY KEY can include null values. When it is unknown what the true value is or when the value would have no significance.
86. When is the creation of a SYSTEM tablespace?
Ans:
When a database is built in the Oracle database system, a SYSTEM tablespace is automatically created. It is always online and has all of the database’s data dictionary tables in it. The data dictionary is made up of the metadata for the tablespace SYSTEM, which is always used to store SYSTEM data, which includes information on tables, indexes, sequences, and other objects. A SYSTEM tablespace, which is the first tablespace produced when a database is formed, is a need for any Oracle database.
87. What do the numbers in Oracle version 9.3.0.5.0 mean?
Ans:
The Oracle version number represents the following:
The release numbers for the following databases are available: 9 for major databases, 3 for database maintenance, 0 for application servers, and 5 for component-specific releases.
88. What is bulk copy denoted by number • 0.In Oracle,?
Ans:
Data from tables and views can be imported and exported using bulk copy or BCP. It does not replicate the same data structure. Its process for transferring data is rapid, and users can easily take a backup of their data. Using bulk copy reduces processing overhead significantly. Data can be loaded into earlier Oracle databases using the ODP.NET Bulk Copy functionality. For direct path loading, the ODP.NET Bulk Copy functionality is subject to the same fundamental limitations and integrity requirements.
89. What kinds of data are temporal?
Ans:
- Date Datatype
- Datatype for Timestamp Data
- Interval Datatype
- To store date, time, and time-interval data, use temporal data types.
For consistency and validation, temporal types work better than character strings for storing this data.
90. Describe PL/SQL.
Ans:
An extension of SQL, which is utilized in Oracle, is PL/SQL. Procedural languages’ processing power and SQL’s ability to manipulate data are combined in PL/SQL to produce extremely potent SQL queries. Procedural languages like PL/SQL are made especially to support SQL statements in their syntax. The Oracle Database server compiles and stores PL/SQL program units inside the database. Additionally, for maximum efficiency, SQL and PL/SQL execute within the same server process at run-time.






