- Introduction to Supply Chain Risk Management
- Types of Risks in Supply Chains
- The Importance of Supply Chain Risk Management
- Risk Identification and Assessment Techniques
- Strategies for Mitigating Supply Chain Risks
- Role of Technology in Supply Chain Risk Management
- Case Studies: Learning from Supply Chain Disruptions
- Future Trends
- Conclusion
Introduction to Supply Chain Risk Management
In today’s globalized and interconnected economy, supply chain sustainability has become increasingly complex, spanning multiple countries, suppliers, and modes of transportation. This complexity exposes businesses to a wide array of risks that can disrupt operations,PMP Training increase costs, data analytics and damage reputation. Supply chain risk management (SCRM) is the proactive process of identifying, assessing, Learning from Supply Chain and mitigating risks to ensure continuity and resilience. It involves developing strategies to prevent disruptions and responding effectively when they occur. Effective SCRM helps companies maintain operational stability, protect profit margins, and meet customer expectations despite uncertainties.
Types of Risks in Supply Chains
Supply chain Sustainability risks can be broadly categorized into internal and external risks. Internal risks arise within the organization, such as operational inefficiencies, quality control issues, or workforce disruptions. External risks come from outside factors like Learning from Supply Chain, natural disasters,
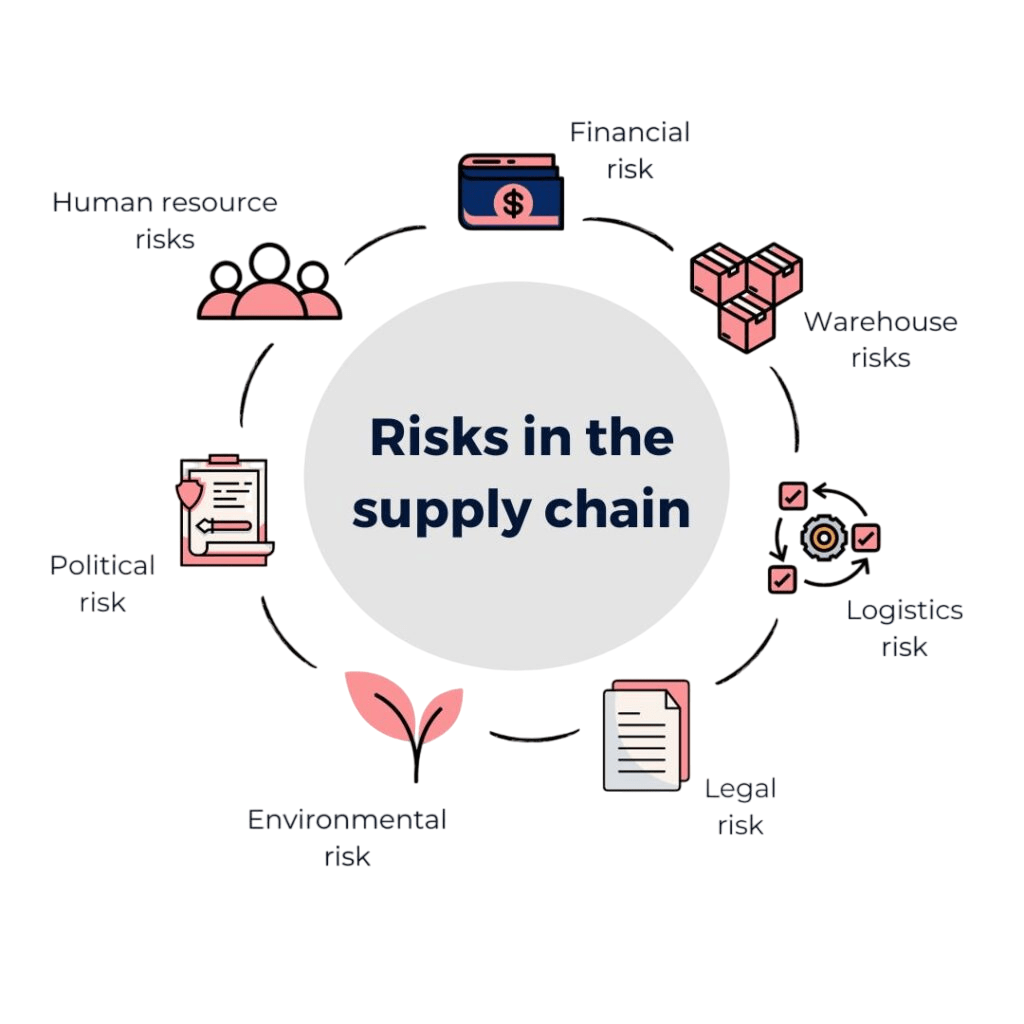
geopolitical tensions, supplier failures, cyberattacks, and economic volatility. Specific types include supplier risk (dependency on a single or unreliable supplier), Supply Chain Management Salary Breakdown demand risk (fluctuations in customer demand), transportation risk (delays or damages in transit), financial risk (currency fluctuations, credit issues), and compliance risk (regulatory changes or violations). Understanding the types of risks is essential for designing effective mitigation strategies.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
The Importance of Supply Chain Risk Management
- Supply chain Sustainability disruptions can have severe consequences, from production stoppages and lost sales to damaged brand reputation and legal penalties.
- High-profile events such as the COVID-19 pandemic, natural disasters like the 2011 Japan earthquake, and trade wars have highlighted vulnerabilities in global supply chains.
- Effective risk management ensures business continuity by minimizing the impact of disruptions Stages in the Supply Chain Management .
- It also enables companies to gain a competitive advantage through greater agility and responsiveness.
- By managing risks proactively, businesses can reduce costs associated with delays, inventory stockouts, and emergency sourcing, ultimately safeguarding profitability and customer loyalty.
- Organizations employ various strategies to mitigate supply chain Sustainability risks.
- Diversification of suppliers reduces dependency on a single source and spreads risk. Establishing strong supplier relationships facilitates collaboration and early warning of issues.
- Inventory buffers or safety stocks provide a cushion against delays or shortages. Implementing dual sourcing or nearshoring can reduce exposure to geopolitical or transportation risks.
- Contracts with clear risk-sharing clauses and contingency Successful Supply Chain Strategy plans help manage financial and operational uncertainties.
- Agile supply chain practices, such as flexible manufacturing and demand-driven replenishment, enhance responsiveness.
- Regular audits and monitoring ensure compliance and early detection of risks.
- The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami disrupted suppliers of automotive and electronics components, highlighting the risks of geographic concentration.
- Companies like Toyota adapted by diversifying suppliers and increasing inventory buffers.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, companies with strong digital supply chain visibility and agile sourcing strategies were better positioned to handle demand shocks and supplier shutdowns Key Features of Supply Chain Management.
- The blockage of the Suez Canal in 2021 demonstrated the vulnerability of critical shipping chokepoints, prompting firms to reassess logistics routes and inventory strategies.
- These cases emphasize the need for proactive risk identification, contingency planning, and investment in resilience.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Risk Identification and Assessment Techniques
The first step in supply chain risk management is identifying potential risks through methods like brainstorming sessions, supplier audits, historical data analysis, and scenario planning. Risk assessment involves evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of each identified risk, often using risk matrices or scoring systems. Advanced approaches include Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), PMP Training which assesses possible failure points and their effects, Learning from Supply Chain, mitigation and supply chain mapping, which visualizes the entire supply chain network to identify vulnerable nodes. Quantitative models such as Monte Carlo simulations can forecast risk outcomes under various scenarios. Accurate risk identification and assessment lay the foundation for effective mitigation.
Strategies for Mitigating Supply Chain Risks
Role of Technology in Supply Chain Risk Management
Role of Technology in Supply Chain plays a pivotal role in enhancing supply chain risk management capabilities. Digital supply chain platforms integrate data from multiple sources to provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, shipments, and supplier performance What is Supply Chain Management. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets to predict risks such as demand fluctuations or supplier failures.
Blockchain technology increases transparency and traceability, helping to verify the authenticity of goods and transactions. Internet of Things (IoT) sensors monitor conditions during transport, such as temperature and humidity, alerting managers to potential quality issues. Cloud computing and data analytics facilitate faster decision-making and scenario planning, mitigation enabling companies to respond swiftly to emerging risks.
Want to Pursue a PMP Master’s Degree? Enroll For PMP Master Program Training Course Today!
Case Studies: Learning from Supply Chain Disruptions
Preparing for a PMP Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on PMP Interview Questions and Answers
Future Trends
The future of supply chain risk management will be shaped by ongoing globalization, technological advances, and evolving risks such as cyber threats and climate change. Increasingly, companies will adopt integrated risk management frameworks that encompass financial, Role of Technology in Supply Chain, Learning from Supply Chain operational, mitigation and reputational risks. Enhanced data analytics and AI will improve predictive capabilities, allowing for earlier interventions Understanding the Bullwhip Effect in Supply Chain. Sustainability considerations will become central, as environmental risks impact supply chain reliability. Collaboration across the supply chain ecosystem, including suppliers and logistics providers, will be essential to building resilience. Ultimately, companies that prioritize comprehensive and adaptive risk management will gain competitive advantage by maintaining uninterrupted operations and meeting customer demands even in turbulent times.
Conclusion
In conclusion, supply chain risk management is vital for navigating the complexities of modern global supply chains. By Role of Technology in Supply Chain, systematically identifying risks, data analytics , assessing their impacts, and implementing strategic mitigation measures supported by technology, PMP Training organizations can safeguard their operations and thrive despite uncertainties. Investing in supply chain resilience is no longer optional but a critical business priority for long-term success.