- Introduction to Procurement and Supply Chain Management
- Key Components of Procurement
- Overview of Supply Chain Management
- The Relationship Between Procurement and Supply Chain Management
- Importance of Effective Procurement in Supply Chains
- Challenges in Procurement and Supply Chain Management
- Strategies and Technologies Enhancing Procurement and Supply Chains
- Conclusion
Introduction to Procurement and Supply Chain Management
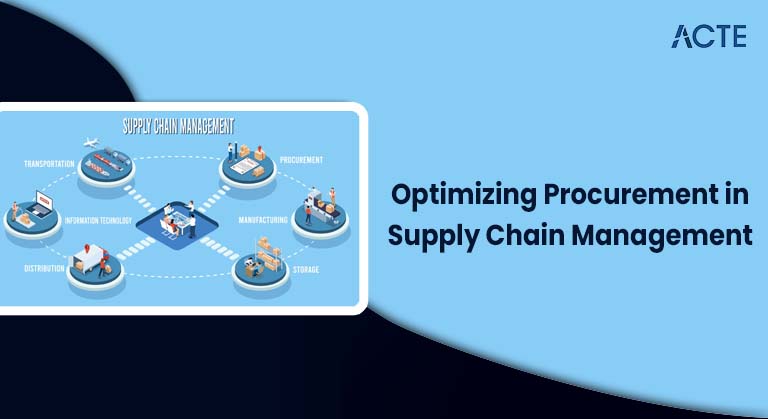
Procurement and supply chain management are two vital functions within any organization, playing a critical role in operational efficiency, cost control, and overall customer satisfaction. Procurement specifically refers to the process of sourcing and acquiring the necessary goods, materials, and services that a company requires to operate. This includes selecting suppliers, negotiating contracts, and managing supplier relationships to ensure quality and cost-effectiveness. Effective procurement helps organizations secure the right resources at the best possible prices, which directly impacts profitability and competitive advantage. On the other hand, supply chain management oversees the entire flow of goods, information, and finances from the initial stage of raw materials to the delivery of finished products to end consumers. It involves coordinating multiple activities, including production planning, inventory management, warehousing, logistics, and demand forecasting, all of which can be efficiently handled with PMP Training. The goal of supply chain management is to streamline these processes to reduce costs, improve speed, and increase reliability across the supply chain network. When procurement and supply chain management work together effectively, they ensure that companies have the right materials, in the right quantity, at the right time, and at the right cost. This coordination supports smooth manufacturing processes, reduces delays, prevents stockouts or excess inventory, and enables timely delivery to customers. The synergy between these functions is especially important as businesses operate in an increasingly globalized and competitive environment, where supply chains are complex and customer expectations are constantly evolving. Optimizing procurement and supply chain management has thus become a strategic priority. Organizations that invest in improving these areas through technology, process innovation, and skilled personnel can achieve significant cost savings, enhanced agility, and better customer service, ultimately strengthening their position in the marketplace.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Key Components of Procurement
Procurement is much more than simply purchasing goods and services; it involves a comprehensive set of activities designed to acquire these resources effectively and efficiently. At its core, procurement includes several key components such as supplier selection and evaluation, contract negotiation, purchase order management, and ongoing supplier relationship management. Each of these steps plays a crucial role in ensuring that an organization obtains quality goods and services at competitive prices, while minimizing risks and delays. Effective procurement starts with a clear understanding of the business’s specific needs. This requires close collaboration with internal stakeholders to identify precise requirements, as well as a thorough knowledge of current market conditions and supplier capabilities, which can be enhanced through What is Sprint Planning. By analyzing supplier performance, financial stability, and production capacity, organizations can make informed decisions about who to partner with. Risk management is an essential part of procurement, helping to identify potential disruptions such as supply shortages, price fluctuations, or geopolitical issues. Additionally, companies must ensure compliance with relevant laws, industry standards, and ethical guidelines to avoid legal problems and maintain their reputation. Sustainability is also becoming a critical focus area in procurement. Organizations are increasingly considering environmental and social factors when selecting suppliers, aiming to reduce carbon footprints, promote fair labor practices, and support circular economy principles. Strategic procurement goes beyond immediate cost savings.
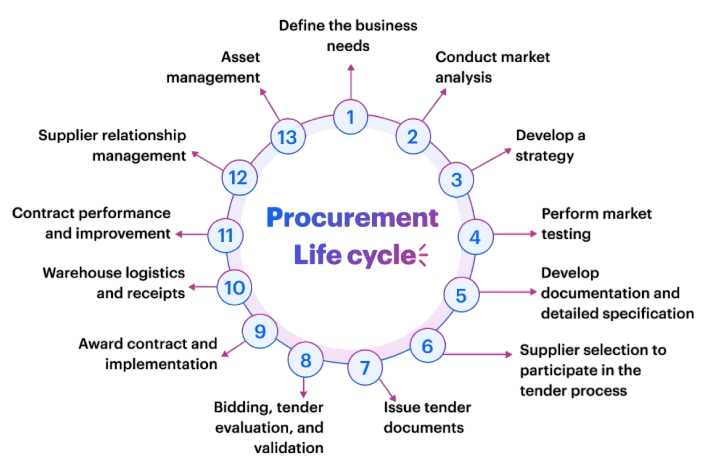
It involves long-term planning and building collaborative relationships with suppliers to drive innovation, improve quality, and create additional value. By working closely with suppliers, companies can co-develop new products, streamline processes, and adapt more quickly to market changes. Overall, procurement is a dynamic, strategic function that plays a vital role in achieving an organization’s broader business goals and competitive advantage.
Overview of Supply Chain Management
- Definition and Purpose: Supply Chain Management (SCM) involves coordinating and managing the flow of goods, information, and finances from raw material sourcing to product delivery, aiming to meet customer demand efficiently.
- Key Components: SCM includes procurement, production, inventory management, transportation, warehousing, and distribution, all integrated to create a seamless process.
- Supply Chain Planning: Effective SCM requires demand forecasting, capacity planning, and scheduling to balance supply with customer needs and minimize costs, supported by principles from What is Total Productive Maintenance.
- Collaboration and Coordination: Strong communication among suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers is essential to synchronize activities and respond quickly to market changes.
- Technology Integration: Modern SCM leverages digital tools like ERP systems, IoT, AI, and analytics to enhance visibility, automate processes, and improve decision-making.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks such as supply disruptions, demand fluctuations, or geopolitical issues ensures supply chain resilience and continuity.
- Performance Measurement: Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as delivery time, inventory turnover, and order accuracy help assess and optimize supply chain effectiveness.
- Interconnected Functions: Procurement is a critical subset of supply chain management focused on sourcing and purchasing goods and services, while supply chain management covers the entire flow from raw materials to end customers.
- Procurement as a Starting Point: Effective procurement ensures the supply chain begins with high-quality materials, reliable suppliers, and cost-effective contracts, setting the foundation for smooth operations supported by PMP Training.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Procurement manages supplier selection, negotiation, and evaluation, which directly impacts supply chain reliability, cost control, and quality standards.
- Inventory and Cost Control: Procurement decisions influence inventory levels and costs by determining purchase quantities, timing, and pricing, affecting the overall supply chain efficiency.
- Risk Mitigation: Both procurement and supply chain management collaborate to identify and manage risks related to supplier disruptions, market volatility, and compliance issues, ensuring continuity.
- Collaboration and Communication: Close coordination between procurement and other supply chain functions such as logistics, production, and sales helps align purchasing strategies with demand and operational needs.
- Technology Integration: Digital tools like e-procurement systems and supply chain software enable seamless data sharing, enhance transparency, and improve decision-making across procurement and supply chain activities.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, and pandemics can interrupt supply lines, causing delays, shortages, and increased costs.
- Supplier Reliability: Ensuring suppliers consistently meet quality, delivery, and compliance standards is challenging, especially when working with multiple or global vendors.
- Cost Management: Fluctuating raw material prices, transportation fees, and tariffs make controlling procurement and supply chain costs difficult, demonstrating Why is Retrospection Needed to continuously improve processes.
- Demand Forecasting: Accurately predicting customer demand is complex but essential; errors lead to overstocking or stockouts, both costly to the business.
- Technology Integration: Integrating new digital tools with legacy systems can be complicated and costly, often requiring change management and employee training.
- Sustainability Pressure: Increasing regulatory requirements and consumer expectations push companies to adopt eco-friendly practices, which can increase complexity and cost.
- Data Security and Privacy: Handling large volumes of sensitive data across multiple partners increases risks of cyberattacks, data breaches, and compliance violations.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
The Relationship Between Procurement and Supply Chain Management
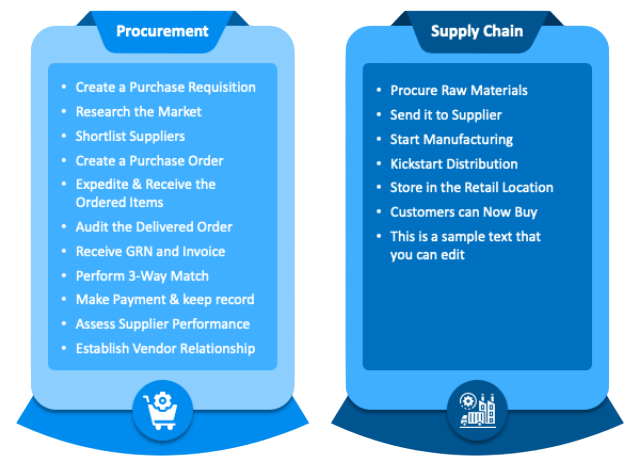
Importance of Effective Procurement in Supply Chains
Effective procurement plays a vital role in the overall success and efficiency of supply chains by ensuring that high-quality materials and services are available when needed and at competitive prices. One of the primary benefits of strong procurement practices is the reduction of operational disruptions. Delays from suppliers or the receipt of substandard goods can cause significant setbacks in production schedules and delivery timelines, ultimately affecting customer satisfaction. Procurement helps mitigate these risks by carefully selecting and managing suppliers, ensuring reliability and consistency. Another important aspect is the development of strong, collaborative relationships with trusted suppliers. These relationships contribute significantly to supply chain resilience, allowing companies to better withstand market volatility, unexpected demand changes, or crises such as natural disasters or pandemics, which can be monitored using What are Agile Metrics. When procurement teams work closely with suppliers, they can quickly adapt to disruptions and find alternative solutions that maintain continuity. Strategic procurement also acts as a catalyst for innovation. By partnering with suppliers, companies can jointly develop new products, improve existing processes, and incorporate cutting-edge technologies. This collaboration drives continuous improvement and helps organizations maintain a competitive edge in dynamic markets. Moreover, ethical procurement practices are increasingly important as businesses commit to sustainability and corporate social responsibility goals. By prioritizing suppliers who adhere to environmental standards and fair labor practices, procurement aligns the supply chain with broader ethical values and regulatory requirements. Ultimately, procurement influences key supply chain performance metrics such as cost control, product quality, and delivery reliability. Because of this, it serves as a fundamental driver of supply chain excellence and long-term business success. Organizations that invest in effective procurement are better equipped to optimize operations and satisfy their customers consistently.
Looking to Master PMP? Discover the PMP Master Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Challenges in Procurement and Supply Chain Management
Strategies and Technologies Enhancing Procurement and Supply Chains
To overcome the challenges faced in procurement and supply chain management, organizations are increasingly adopting advanced strategies and leveraging cutting-edge technologies. One important approach is supplier segmentation and risk assessment, which allows companies to identify and prioritize critical suppliers that have the greatest impact on operations. By focusing attention and resources on these key suppliers, organizations can better manage potential risks and ensure continuity of supply. Collaborative planning and improved demand forecasting are also vital for enhancing the alignment between procurement and production teams. When both functions work closely together, they can anticipate needs more accurately, optimize inventory levels, and reduce delays or shortages, highlighting the differences in Project Life Cycle vs Product Life Cycle. Additionally, the adoption of lean and agile methodologies helps businesses increase responsiveness to market changes while minimizing waste throughout the supply chain. On the technology side, digital procurement platforms are transforming traditional processes by automating sourcing, bidding, and contract management. These platforms simplify supplier interactions, reduce manual errors, and speed up procurement cycles. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning further enhance procurement by enabling predictive analytics. These tools analyze vast amounts of data to forecast demand, monitor supplier performance, and identify risks before they escalate. Blockchain technology is becoming increasingly important for supply chains with complex networks. Its decentralized and secure ledger improves transparency and traceability by providing an immutable record of transactions, which helps prevent fraud and ensures compliance. Meanwhile, Internet of Things (IoT) devices offer real-time visibility by tracking inventory levels and shipment locations, enabling faster and more informed decision-making. Together, these innovations empower organizations to make smarter decisions, improve operational efficiency, and strengthen risk management capabilities, thereby driving more resilient and agile supply chains.
Preparing for a PMP Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on PMP Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Procurement and supply chain management are fundamental pillars that support overall business success by ensuring the smooth and efficient flow of goods, services, and information across organizations and global markets. When these functions are effectively integrated, procurement plays a key role in strengthening supply chain resilience by securing reliable sources of materials and fostering strong supplier relationships. This integration also helps reduce operational costs by optimizing purchasing decisions and improving inventory management. Furthermore, it drives innovation by enabling collaboration between suppliers and internal teams to develop new products and improve processes. Sustainability is another important benefit, as coordinated procurement and supply chain management allow businesses to adopt eco-friendly practices, minimize waste, and comply with environmental regulations. Despite these advantages, organizations still face significant challenges in managing procurement and supply chains, which PMP Training can help address. Globalization has increased complexity by expanding supplier networks and exposing supply chains to geopolitical risks. Demand variability adds unpredictability, requiring businesses to be more agile in adjusting their operations. Technological disruptions are reshaping traditional supply chain models, forcing companies to continuously adapt and invest in digital tools. To address these challenges, adopting strategic approaches such as supplier segmentation, risk assessment, and collaborative planning is essential. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things are transforming how procurement and supply chains operate, enabling greater transparency, predictive insights, and real-time tracking. As global markets continue to evolve rapidly, businesses that prioritize optimizing procurement and supply chain management will be better positioned to compete effectively, achieve sustainable growth, and deliver superior value and service to their customers. Investing in these areas is no longer optional but a critical component of long-term business strategy.





