- Introduction to the Bullwhip Effect
- Causes of the Bullwhip Effect
- How the Bullwhip Effect Impacts Supply Chains
- Real-World Examples of the Bullwhip Effect
- Measurement and Detection of the Bullwhip Effect
- Strategies to Mitigate the Bullwhip Effect
- The Role of Technology in Managing the Bullwhip Effect
- Conclusion
Introduction to the Bullwhip Effect
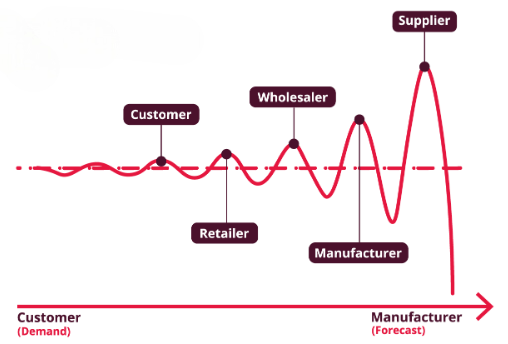
The Bullwhip Effect is a well-documented and critical phenomenon in supply chain management. It refers to how small fluctuations in consumer demand at the retail level can cause progressively larger fluctuations in orders and inventory as one moves up the supply chain, from retailers to wholesalers, manufacturers, and raw material suppliers. This demand distortion amplifies the farther it travels upstream, much like how a small flick of a whip’s handle creates a large motion at its tip. The term “bullwhip effect” captures this concept. The consequences of this amplification are often costly and disruptive. Without proper PMP Training, it can lead to excessive inventory accumulation, stockouts, longer lead times, increased warehousing and operational costs, and ultimately, poor customer service. These inefficiencies strain supplier relationships and impact overall business profitability and responsiveness. The bullwhip effect is typically caused by several contributing factors, including lack of real-time demand visibility, overreliance on forecasts, order batching, price promotions, and delays in information sharing across the supply chain. When companies fail to collaborate effectively across supply chain stages, they often respond to perceived rather than actual demand, which worsens the problem. Understanding the bullwhip effect is essential for businesses that aim to build agile and resilient supply chains. Some key strategies to mitigate it include improving information sharing, implementing just-in-time inventory practices, adopting demand-driven planning models, and investing in technologies like real-time analytics and integrated supply chain systems. Enhancing collaboration and transparency among all supply chain partners can significantly reduce demand variability and improve alignment with actual market needs. By addressing the bullwhip effect, companies can reduce waste, enhance service levels, and achieve greater efficiency across their operations.
Do You Want to Learn More About PMP? Get Info From Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Causes of the Bullwhip Effect
Several factors contribute to the bullwhip effect, each amplifying demand variability as it moves through the supply chain. One of the primary causes is demand forecast updating. In most supply chains, members do not have direct visibility into actual consumer purchases. Instead, they base their forecasts on the orders they receive from the next downstream partner. This reliance on perceived demand rather than real consumption often leads to overreactions and misaligned inventory decisions. Another contributing factor is order batching. Instead of placing frequent and consistent orders, companies often consolidate them into larger batches to reduce ordering costs or take advantage of economies of scale, which is addressed in the Phases of Project Management. While efficient for individual firms, this practice creates artificial demand spikes that propagate upstream. Price fluctuations and sales promotions also play a significant role in distorting true demand signals. Temporary discounts often lead customers and retailers to purchase more than needed, resulting in irregular buying patterns that mislead suppliers about actual market demand. Additionally, rationing and shortage gaming can significantly exacerbate demand variability. During times of product scarcity, buyers may inflate their orders in anticipation of receiving only a partial shipment. Once availability stabilizes, these inflated orders are typically canceled or reduced, causing dramatic demand swings and operational disruptions.
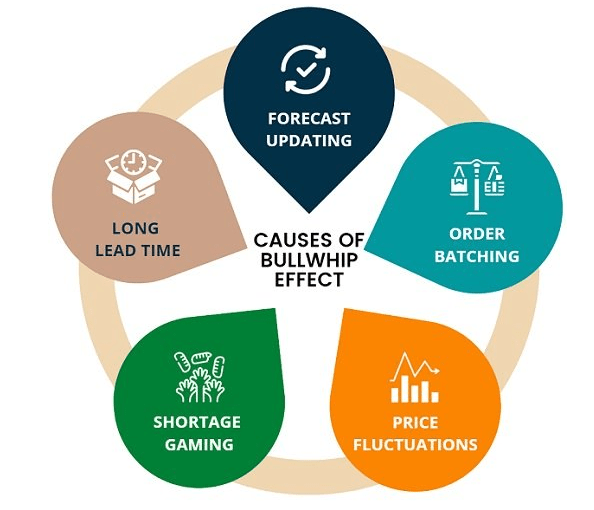
Another critical factor is the lack of communication and transparency among supply chain partners. When companies fail to share real-time data and insights, they operate in silos, making decisions based on incomplete or outdated information. This lack of coordination leads to inefficiencies and contributes to the overall instability of the supply chain. Understanding and addressing these root causes is essential for mitigating the bullwhip effect and building a more responsive, collaborative, and efficient supply chain system.
How the Bullwhip Effect Impacts Supply Chains
- Demand Amplification: Small fluctuations in customer demand can cause progressively larger variations upstream in the supply chain. This distortion leads suppliers to overreact, creating inefficiencies.
- Excess Inventory: To buffer against uncertain demand signals, companies often hold excessive inventory. This results in higher holding costs, increased risk of obsolescence, and wasted resources.
- Poor Forecasting Accuracy: The Bullwhip Effect causes demand data to become unreliable as it moves up the chain. This reduces the accuracy of forecasts, leading to misaligned production schedules, highlighting the importance of adaptability found in The Most Important Benefits of Blended Learning.
- Longer Lead Times: Because suppliers react to exaggerated demand swings by adjusting production quantities, lead times tend to increase. Longer lead times further worsen the effect, creating a vicious cycle.
- Increased Costs: Fluctuations force manufacturers and distributors to change production rates frequently, leading to higher operational costs, such as overtime, expedited shipping, and inefficient machine setups.
- Reduced Service Levels: Inventory shortages and surpluses caused by demand variability can lead to stockouts or overstocks. This negatively impacts customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Strained Relationships: The Bullwhip Effect often results from poor communication and lack of transparency among supply chain partners. This can cause mistrust, conflicts, and difficulties in collaboration.
- MIT Beer Distribution Game: This classic simulation game, often used in PMP Training, demonstrates the Bullwhip Effect by mimicking a beer supply chain.
- Retailers’ Order Variability: In the game and real life, retailers’ changing orders to buffer stock cause exaggerated demand signals for upstream suppliers.
- Procter & Gamble’s Diapers Case: P&G observed that retailers’ fluctuating orders of diapers caused large swings in their production schedules and inventory levels, illustrating the Bullwhip Effect in a real product line.
- Upstream Production Swings: Due to variable orders from retailers, manufacturers often respond with significant changes in production volume, creating inefficiencies and higher operational costs.
- COVID-19 Panic Buying: The pandemic intensified the Bullwhip Effect as consumers panic-bought PPE and other essentials, leading retailers and distributors to place excessive orders upstream, causing massive inventory imbalances.
- Inventory Imbalances: Such panic-driven ordering created supply shortages and overstocks across the supply chain, revealing how external shocks amplify the Bullwhip Effect.
- Lessons on Supply Chain Visibility: These examples highlight the need for transparent communication and real-time data sharing to reduce demand distortion and better manage inventory and production during disruptions.
- Improve Communication and Information Sharing: Sharing real-time sales and inventory data among all supply chain partners reduces uncertainty and helps align production with actual demand, minimizing distortions.
- Implement Collaborative Planning: Joint demand forecasting and production planning between suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers help synchronize activities and avoid overreactions to demand changes.
- Reduce Order Batch Sizes: Smaller, more frequent orders decrease variability and prevent large spikes in demand upstream, smoothing the flow of goods and information, similar to practices emphasized in What are Scrum Ceremonies.
- Stabilize Prices and Avoid Promotions: Frequent price changes and promotions can cause artificial demand spikes. Maintaining stable prices reduces sudden order fluctuations driven by consumers’ forward buying behavior.
- Lead Time Reduction: Shortening production and delivery lead times allows supply chain partners to respond more quickly and accurately to actual demand changes, reducing the need for excessive safety stock.
- Use Advanced Technology and Analytics: Tools like demand sensing, machine learning, and integrated ERP systems improve forecast accuracy and provide visibility, helping to detect and respond to demand changes faster.
- Align Incentives Across the Supply Chain: Designing contracts and incentive structures that encourage truthful reporting of demand and discourage gaming the system helps reduce order variability and promotes cooperation.
Would You Like to Know More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Now!
Real-World Examples of the Bullwhip Effect
Measurement and Detection of the Bullwhip Effect
Detecting the bullwhip effect is a critical step toward improving supply chain efficiency and responsiveness. One of the most commonly used methods involves analyzing the variance in orders relative to the variance in actual sales or customer demand. A widely accepted metric for this analysis is the variance amplification ratio. This ratio compares the variability of orders placed by a supply chain entity to the variability of the demand it receives. When this ratio is significantly greater than one, it indicates that the supply chain member is reacting more aggressively to demand changes than necessary, signaling the presence of the bullwhip effect. Advanced analytics and modern supply chain visibility tools further enhance the ability to detect the bullwhip effect, helping to explain Why Do Scrum Masters Get Paid so Much. These technologies enable real-time monitoring of demand patterns, inventory levels, and order behavior across all stages of the supply chain. By identifying abnormal fluctuations, bottlenecks, and unexpected order patterns, companies can proactively address inefficiencies before they escalate. The use of machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics also supports early warning systems that flag unusual demand shifts or order surges. In addition to variance-based analysis, monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) provides further insight. Metrics such as inventory turnover rates, order cycle times, forecast accuracy, and fill rates serve as valuable indicators of supply chain health. A sudden drop in inventory turnover or a consistent mismatch between forecasted and actual demand may point to bullwhip-related issues. Overall, detecting the bullwhip effect requires a combination of quantitative analysis and real-time monitoring. By leveraging data-driven tools and continuously assessing performance metrics, businesses can identify the early signs of demand distortion and take corrective actions to maintain a stable, efficient supply chain.
Looking to Master PMP? Discover the PMP Master Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Strategies to Mitigate the Bullwhip Effect
The Role of Technology in Managing the Bullwhip Effect
Technology plays a vital role in mitigating the bullwhip effect by enhancing data integration, visibility, and decision-making across the supply chain. One of the foundational tools is the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system, which integrates data across various departments such as procurement, production, sales, and inventory management. This centralized access to real-time information enables more synchronized operations and reduces the delays and miscommunications that often contribute to demand distortion. Advanced analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) significantly enhance demand forecasting and scenario planning. By analyzing historical data, market trends, and external factors, these tools generate more accurate forecasts and allow companies to simulate the impact of various demand and supply scenarios. This improves responsiveness and reduces the tendency to overreact to fluctuations. Supply chain visibility platforms are another critical technology, supporting the core concepts of What is Business Agility. These systems allow real-time data sharing among supply chain partners, promoting transparency and collaboration. Enhanced visibility ensures that all stakeholders are working with the same demand and inventory information, minimizing misinterpretation and over-ordering. The use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags has revolutionized inventory tracking. These technologies provide precise, real-time insights into product location, condition, and movement, allowing for better inventory control and reduced safety stock requirements. Blockchain technology adds another layer of trust and security by offering tamper-proof transaction records. This fosters greater confidence among supply chain partners and improves traceability. Additionally, cloud computing enables scalable, collaborative platforms where stakeholders can access and update information continuously, regardless of location. Together, these technologies create a connected, transparent, and intelligent supply chain ecosystem that is far more resilient to demand volatility and less prone to the bullwhip effect.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s PMP Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Conclusion
The bullwhip effect is a fundamental and persistent challenge in supply chain management, leading to significant inefficiencies, inflated costs, and reduced customer satisfaction. It arises when small fluctuations in consumer demand become increasingly exaggerated as they move upstream through the supply chain. This distortion causes businesses to overreact by placing larger orders, stockpiling inventory, or adjusting production schedules unnecessarily. The result is often excessive inventory, stockouts, longer lead times, and poor service levels. These inefficiencies can strain supplier relationships, reduce profitability, and impair a company’s ability to respond effectively to real market needs. Understanding the root causes and consequences of the bullwhip effect is critical for supply chain leaders aiming to improve coordination and resilience. Factors such as demand forecast inaccuracies, order batching, price fluctuations, lack of transparency, and poor communication between partners, which are addressed in PMP Training, contribute to this phenomenon. By identifying and addressing these drivers, organizations can implement targeted strategies to reduce variability and align supply more closely with actual demand. Technology plays a vital role in mitigating the bullwhip effect. Tools such as ERP systems, advanced analytics, AI-driven forecasting, and supply chain visibility platforms allow companies to share real-time data, improve forecasting accuracy, and foster greater collaboration across the supply chain. IoT and blockchain technologies further enhance inventory tracking and transactional transparency. As global supply chains grow in complexity and interdependence, managing the bullwhip effect is becoming increasingly essential for achieving operational excellence. Businesses that successfully minimize its impact can reduce waste, improve responsiveness, and gain a competitive advantage in today’s dynamic market landscape. Addressing the bullwhip effect is not just a tactical necessity but a strategic imperative for long-term success.





