
Checkpoint interviews for positions related to network security and firewall administration often include questions to assess candidates’ knowledge of Checkpoint technologies and their ability to manage and secure networks effectively. Common questions may cover topics such as firewall policies, VPN configurations, threat prevention mechanisms, and troubleshooting skills. Interviewers may ask candidates to explain how they would handle specific security scenarios, configure access control policies, or troubleshoot connectivity issues. Additionally, questions may delve into Checkpoint-specific terminology, such as Security Management Server, Security Gateway, and SmartConsole. Candidates are expected to showcase their understanding of network security concepts and demonstrate practical experience with Checkpoint’s firewall solutions during the interview process.
Q1. What is Checkpoint and what does it specialize in?
Ans:
Checkpoint is a cybersecurity company that specializes in providing solutions for network security, including firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, virtual security, cloud security, and endpoint security. It is renowned for its Checkpoint Firewall-1, which introduced stateful inspection technology.
Q2. Can you describe the Checkpoint architecture’s key components?
Ans:
The Checkpoint architecture comprises several key components, including Security Management Server, Security Gateway, SmartConsole, SmartDashboard, and various security features such as Firewall, VPN, IPS, and more. These components work together to manage, configure, and enforce security policies across the network.
Q3. Describe the purpose of the Security Management Server.
Ans:
The Security Management Server is a central component in the Checkpoint architecture responsible for managing security policies, configurations, and monitoring network activity. It acts as the central point for administrators to define, implement, and update security policies across the organization.
Q4. What is a Checkpoint Security Gateway?
Ans:
A Checkpoint Security Gateway is a dedicated device or software instance that enforces the security policies defined by the Security Management Server. It acts as the frontline defense, inspecting and controlling traffic based on the configured security rules. Security Gateways are strategically placed at network entry points to monitor and secure traffic flow.
Q5. Differentiate between a firewall and a security gateway in the context of Checkpoint.
Ans:
| Aspect | Firewall | Security Gateway | |
| Definition |
Network security device controlling traffic based on rules. |
Enforces comprehensive security policies in Checkpoint. | |
| Functionality | Basic traffic filtering. | Checkpoint’s broad security services, e.g., firewall, VPN. | |
| Deployment | Standalone or integrated. | Dedicated at network entry points. | |
| Vendor Independence | General term, multiple vendors. | Specific to Checkpoint architecture. |
Q6. Explain the function of the SmartConsole in the Checkpoint environment.
Ans:
The SmartConsole is a graphical user interface tool in the Checkpoint environment used for configuring, managing, and monitoring Checkpoint security policies. It provides administrators with a centralized platform to create and modify security policies, manage network objects, view logs, and perform various administrative tasks.
Q7. How is high availability achieved in a Checkpoint environment?
Ans:
High availability in a Checkpoint environment is achieved through the deployment of a cluster of Checkpoint Security Gateways. The clustering ensures redundancy and continuous operation. The Security Gateways synchronize state information, and in the event of a failure in one gateway, traffic is seamlessly redirected to others, minimizing downtime.
Q8. What is a Checkpoint policy, and how is it enforced?
Ans:
A Checkpoint policy is a set of rules and configurations that dictate how the Checkpoint Security Gateway should handle network traffic. It defines the allowed and denied actions for specific types of traffic based on criteria such as source, destination, service, and more. The policy is enforced by the Security Gateway, ensuring that incoming and outgoing traffic complies with the defined rules.
Q9. What are the benefits of using Checkpoint VPN solutions?
Ans:
- Remote Access: Enables secure access to the organization’s network for remote users.
- Site-to-Site Connectivity: Facilitates secure communication between geographically dispersed sites.
- Authentication: Provides robust user authentication for secure access.
Q10. What are Identity Awareness and how is it implemented in Checkpoint?
Ans:
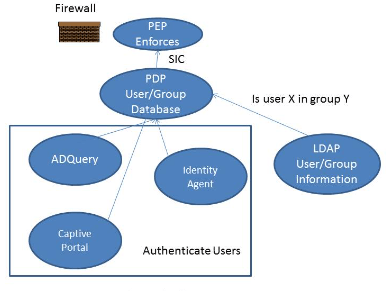
Identity Awareness: Identity Awareness is a Checkpoint feature that associates network activity with specific user identities. Implementation: Identity Awareness is implemented by integrating with identity sources such as Active Directory or LDAP.
Q11. What are the steps of installing a Checkpoint Security Gateway.
Ans:
Installing a Checkpoint Security Gateway involves several key steps. First, ensure that the hardware meets system requirements. Next, install the Checkpoint Gaia operating system on the designated hardware. Once the OS is installed, use the configuration wizard to set basic parameters like IP addresses and interfaces. Subsequently, deploy the Security Gateway software, configure network settings, and define security policies using the SmartConsole management tool. Test the gateway’s functionality, and if necessary, troubleshoot and fine-tune configurations.
Q12. Explain the process of configuring a Security Policy in Checkpoint.
Ans:
Use SmartConsole to create rules in the “Security Policies” tab, specifying access controls for traffic based on source, destination, and services. Arrange rules and install the policy to apply changes to the Checkpoint Security Gateway. Regularly update policies to address evolving security requirements.
Q13. What are the considerations for configuring network objects and rules in Checkpoint?
Ans:
When configuring network objects and rules in Checkpoint, consider defining clear and granular network objects to represent various entities such as hosts, networks, or services. Organize rules logically, prioritizing more specific rules over general ones, and adhere to the principle of “first match.” Regularly review and optimize rule order to ensure efficient policy evaluation. Implement meaningful rule names and comments for documentation and troubleshooting purposes.
Q14. How do you implement NAT in a Checkpoint firewall?
Ans:
To implement Network Address Translation (NAT) in a Checkpoint firewall, use the SmartConsole management tool to configure NAT rules. Create a network object representing the internal IP address, define a translated address or pool for external communication, and establish NAT rules specifying source and destination translation criteria.
Q15. Describe the process of upgrading the Checkpoint version.
Ans:
To upgrade the Checkpoint version, obtain the latest software package compatible with your hardware and platform. Backup existing configurations and policies. Use the SmartUpdate tool to initiate the upgrade process, selecting the appropriate target version. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the new version, and verify system stability after the upgrade.
Q16. What is the purpose of the fw monitor command, and how is it used?
Ans:
The fw monitor command in Checkpoint is used for packet capturing and analyzing firewall traffic. It allows administrators to monitor the flow of packets at various stages in the firewall inspection process, aiding in troubleshooting and diagnosing network issues. By specifying filter and inspection points, such as interfaces or specific rules, users can capture and analyze traffic at different points within the firewall chain.
- #!/bin/bash
- # Run fw monitor with specific filters
- fw monitor -e “accept;” -o /path/to/output/file
- # Analyze the captured data as needed
Q17. How do you troubleshoot connectivity issues in a Checkpoint environment?
Ans:
To troubleshoot connectivity issues in a Checkpoint environment, start by checking firewall logs in the SmartConsole for denied traffic or rule violations. Use the fw monitor command to capture and analyze packet flow at different inspection points. Verify network object and rule configurations, ensuring correct IP addresses and services. Check for any NAT-related issues. Use diagnostic tools like ping and traceroute from both source and destination to identify potential network problems.
Q18. Can you explain the purpose of Checkpoint’s Stateful Inspection?
Ans:
Checkpoint’s Stateful Inspection is a security mechanism that monitors the state of active connections and makes decisions based on the context of the traffic. It keeps track of the state of each connection, including the source and destination addresses, ports, and sequence numbers. This enables the firewall to make informed decisions on whether to allow or deny packets based on the current state of the connection.
Q19. What is the significance of the ‘fw unloadlocal’ command?
Ans:
The fw unloadlocal command in Checkpoint is significant because it unloads the Security Policy from the local Security Gateway. This command effectively disables the enforcement of the firewall rules, allowing administrators to make changes to the policy without impacting network traffic.
Q20. How do you create and manage access control policies in Checkpoint?
Ans:
To create and manage access control policies in Checkpoint, use the SmartConsole management tool. Define network objects representing hosts, networks, and services. Create security rules specifying source, destination, and services for traffic control. Organize rules logically, with more specific rules taking precedence. Utilize object groups for efficient management. Regularly review and optimize rule order to ensure effective policy enforcement.
Q21. Explain the concept of implicit and explicit rules in a Checkpoint security policy.
Ans:
In a Checkpoint security policy, implicit rules are predefined rules that permit or deny traffic based on default settings. They are applied when no explicit match is found in the policy. Explicit rules, on the other hand, are user-defined rules that explicitly specify access controls for traffic based on defined criteria such as source, destination, and services.
Q22. What is the purpose of the Cleanup rule in a Checkpoint policy?
Ans:
The Cleanup rule is a default rule at the end of the security policy that defines the action to be taken for traffic that doesn’t match any of the explicit rules. It typically logs the traffic and drops it, providing a security catch-all to handle unexpected or unauthorized traffic.
Q23. How can you optimize a Checkpoint security policy for performance?
Ans:
To optimize a Checkpoint security policy for performance, minimize the number of rules by consolidating where possible. Use object groups to simplify management and reduce the rule base. Prioritize rules based on frequency and specificity to expedite policy evaluation. Regularly review and remove redundant or obsolete rules. Utilize the Threat Prevention policy to offload security inspections. Employ network segmentation to minimize the scope of rules.
Q24. Describe the role of Application Control and URL Filtering in access control.
Ans:
Application Control and URL Filtering play pivotal roles in access control by regulating the types of applications and websites users can access. Application Control enables the identification and control of specific applications, preventing unauthorized or high-risk ones. URL Filtering manages web access by categorizing and controlling website access based on predefined policies.
Q25. Can you name different types of VPNs supported by Checkpoint?
Ans:
- Site-to-Site VPN: Connects different office locations securely.
- Remote Access VPN: Enables remote users to securely connect to the organization’s network.
- Client-to-Site VPN: Similar to remote access, but with a specific client-to-site connection.
Q26. How can you troubleshoot and debug security policy-related issues in Checkpoint?
Ans:
To troubleshoot security policy-related issues in Checkpoint, start by examining firewall logs in the SmartConsole for denied traffic or rule violations. Utilize the fw monitor command to capture and analyze packet flow at different inspection points. Verify network object and rule configurations for accuracy, including source, destination, and services. Use diagnostic tools like ping and traceroute to identify potential network problems.
Q27. How do you configure a site-to-site VPN in Checkpoint?
Ans:
To configure a site-to-site VPN in Checkpoint, use the SmartConsole management tool. Define VPN community objects for both local and remote sites, specifying IP addresses and shared secrets. Create VPN rules to allow traffic between the sites. Configure VPN encryption settings and tunnel properties. Install the policy on the Checkpoint Security Gateways at both ends.
Q28. Explain the difference between Main Mode and Aggressive Mode in VPN negotiations.
Ans:
- Main Mode: Main Mode is a VPN negotiation mode where a secure channel is established in multiple phases. It provides more security but involves more communication between peers.
- Aggressive Mode: Aggressive Mode is a faster VPN negotiation mode that requires fewer exchanges between peers. However, it offers lower security compared to Main Mode.
Q29. What is VPN tunnel initiation and how is it configured?
Ans:
- VPN Tunnel Initiation: The process of creating a secure communication channel between two VPN gateways is referred to as VPN tunnel initiation. It entails haggling over authentication and encryption preferences.
- Configuration: Configure VPN tunnel initiation by defining VPN properties, including encryption algorithms, authentication methods, and VPN peer settings.
Q30. How can you troubleshoot VPN-related issues in Checkpoint?
Ans:
To troubleshoot VPN-related issues in Checkpoint, start by checking VPN logs in the SmartConsole for error messages or connection failures. Verify that the VPN community settings, including IP addresses and shared secrets, match on both ends. Use the VPN tunnel diagnostics tool to check the status of VPN tunnels. Inspect firewall rules to ensure proper traffic flow between VPN peers.
Q31. What are the different types of reports available in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
In Oracle E-Business Suite, various types of reports are available, including Financial Reports, Operational Reports, Management Reports, and Ad Hoc Query Reports. These reports cover areas such as General Ledger, Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, Inventory, Purchasing, and more.
Q32. How do concurrent programs differ from concurrent requests in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
In Oracle EBS, a Concurrent Program is a program that performs a specific task, while a Concurrent Request is a user’s request to run a Concurrent Program. Multiple requests can be associated with a single Concurrent Program, allowing users to execute the same program with different parameters.
Q33. What is the purpose of ‘Key Flexfield Segments’ in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Key Flexfield Segments in Oracle EBS are used to capture and represent essential information in the accounting structure. They allow for a flexible and customizable way to define chart of accounts segments, enabling organizations to adapt the accounting structure to their specific business needs.
Q34. Explain the concepts of ‘SOB’ (Set of Books) and ‘LE’ (Legal Entity) in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
SOB (Set of Books): A Set of Books in Oracle EBS represents a financial reporting entity. It includes a chart of accounts, accounting calendar, and currency. Each SOB maintains its own set of financial records and reports.
LE (Legal Entity): Legal Entities represent organizations recognized by legal authorities. In Oracle EBS, LE is a financial reporting concept and is associated with an SOB. Legal Entities are used to comply with legal and regulatory requirements.
Q35. What is the significance of the ‘Document Sequence’ in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
The Document Sequence in Oracle EBS is a unique identifier assigned to transactional documents. It ensures that each document has a distinct number for tracking and audit purposes. Document Sequences are often associated with various Oracle EBS modules like General Ledger, Purchasing, and Payables.
Q36. Explain the purpose of Auto Invoice in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
Auto Invoice in Oracle EBS automates the process of importing and validating external invoices from various sources. It allows for the creation of invoices in Oracle Receivables without manual entry, reducing errors and improving efficiency. Auto Invoice supports integration with other modules and external systems.
Q37. Describe the different types of tables in Oracle EBS.
Ans:
- System Tables
- Transaction Tables
- Base Tables
- Interface Tables
- Flexfield Tables
Q38. What are the key tables in Oracle General Ledger?
Ans:
Key tables in Oracle General Ledger include GL_CODE_COMBINATIONS for the chart of accounts, GL_JE_HEADERS and GL_JE_LINES for journal entries, GL_BALANCES for account balances, and GL_LEDGERS for ledger information. These tables collectively manage financial data storage and retrieval in Oracle General Ledger.
Q39. What is Subledger Accounting (SLA) in Oracle EBS?
Ans:
Subledger Accounting (SLA) in Oracle EBS is a framework that allows for the centralization of accounting rules and the generation of accounting entries for subledger transactions. It provides a standardized way to create and manage accounting entries across different subledger applications.
Q40. Explain the functions and uses of Flexfield Value Sets.
Ans:
Flexfield Value Sets in Oracle EBS are used to define valid values for flexfields. They control the values that users can enter in flexfield segments. Value Sets enable flexibility and validation in capturing data, ensuring consistency and accuracy in information stored in flexfields.
Q41. How do you optimize a Checkpoint security policy for better performance?
Ans:
Optimizing a Checkpoint security policy for better performance involves streamlining the rule base by minimizing the number of rules and consolidating where possible. Prioritize rules based on frequency and specificity to expedite policy evaluation. Use object groups to simplify management and reduce rule complexity. Regularly review and remove redundant or obsolete rules.
Q42. Explain the purpose of State Synchronization in a clustered environment.
Ans:
State Synchronization in a Checkpoint clustered environment ensures that the connection and state information of established connections are synchronized between cluster members. This allows for seamless failover, where if one member fails, another can take over and continue processing existing connections without disruption.
Q43. What is the significance of SecureXL in Checkpoint performance optimization?
Ans:
SecureXL is a hardware acceleration technology in Checkpoint that offloads intensive packet processing tasks to dedicated hardware. It significantly enhances firewall and VPN performance by accelerating key operations such as packet inspection, connection tracking, and encryption, resulting in improved throughput and reduced CPU utilization.
Q44. How can you monitor and analyze resource utilization in a Checkpoint environment?
Ans:
To monitor and analyze resource utilization in a Checkpoint environment, use the SmartView Monitor tool to assess CPU, memory, and disk usage on the Security Gateway. Review performance graphs and logs to identify patterns and anomalies. Utilize the “cpstat” command for real-time statistics and diagnose issues. Regularly check system alerts and logs for indications of resource constraints or potential bottlenecks. Implement proactive monitoring practices to ensure optimal performance and timely resolution of resource-related issues in the Checkpoint environment.
Q45. Describe the purpose and implementation of Checkpoint Threat Emulation.
Ans:
Checkpoint Threat Emulation is a feature that proactively detects and prevents unknown threats by analyzing files in a virtual sandbox environment. Suspicious files are emulated to observe their behavior, enabling the detection of advanced malware and zero-day threats before they can harm the network.
Q46. What is SandBlast, and how does it enhance security in Checkpoint?
Ans:
SandBlast is a comprehensive threat prevention solution in Checkpoint that combines multiple security technologies. It includes Threat Emulation, Threat Extraction, Anti-Bot, Anti-Virus, and URL Filtering. SandBlast enhances security by providing advanced protection against a wide range of cyber threats, including unknown and sophisticated attacks.
Q47. Explain the Checkpoint Anti-Bot and Anti-Virus features.
Ans:
Anti-Bot: Protects against botnet infections by identifying and blocking communication between infected devices and command and control servers.
Anti-Virus: Scans files for known malware signatures and prevents the execution of malicious files. It provides real-time protection against viruses, worms, and other malware.
Q48. How do you configure and manage Identity Awareness in Checkpoint?
Ans:
To configure and manage Identity Awareness in Checkpoint, integrate the firewall with an Identity Awareness-enabled source such as Active Directory or LDAP. Define identity sources and query users and groups. Configure Access Role objects to associate users with specific roles based on their identity attributes. Utilize these roles in security policies to enforce granular access controls.
Q49. What is the role of ThreatCloud in Checkpoint security?
Ans:
ThreatCloud is Checkpoint’s collaborative security infrastructure that collects and analyzes threat intelligence from a global network. It provides real-time threat data, enabling Checkpoint devices to make informed security decisions. ThreatCloud enhances security by leveraging collective intelligence to identify and block emerging threats.
Q50. How do you generate and analyze compliance reports in Checkpoint?
Ans:
To generate and analyze compliance reports in Checkpoint, use the SmartConsole management tool. Define compliance rules based on regulatory requirements or organizational policies. Run predefined compliance reports or customize them as needed. Analyze the reports for compliance violations, security gaps, or policy deviations.
Q51. Explain the role of SmartEvent in Checkpoint reporting and analysis.
Ans:
SmartEvent is Checkpoint’s event analysis and reporting tool. It plays a crucial role in reporting and analysis by providing insights into security events, trends, and potential threats. SmartEvent consolidates log data, correlates events, and generates visual reports to help administrators monitor and analyze the security posture of the network.
Q52. How can you customize and schedule reports in SmartEvent?
Ans:
The “Logs & Monitor” page of the SmartConsole management interface is where you can schedule and edit reports in SmartEvent. Specify the fields and criteria you want in your own report templates. Establish the settings for the report, including the time intervals and data sources. Pre-schedule the automated creation and delivery of the tailored reports. Convenient and proactive monitoring and analysis in the Checkpoint environment can be achieved by making use of the scheduling options to guarantee timely report delivery.
Q53. Describe the process of exporting and archiving log data in Checkpoint.
Ans:
- Source Ip address
- Destination Ip address
- IP protocol TCP &UDP
- IP protocol information we have which are nothing but TCP/UDP port numbers, TCP sequence number &TCP flags
Q54. What is the Checkpoint SmartConsole, and how is it used in administration?
Ans:
Checkpoint SmartConsole is the primary graphical user interface for Checkpoint administration. It is used to configure, manage, and monitor security policies, objects, and settings on Checkpoint Security Gateways. SmartConsole provides a centralized platform for administrators to interact with different Checkpoint modules and features.
Q55. Explain the purpose of the Checkpoint Dashboard and how it aids in monitoring.
Ans:
The Checkpoint Dashboard is a visual interface in SmartConsole that provides a real-time overview of the security status and performance of the Checkpoint environment. It aids in monitoring by presenting key metrics, such as threat indicators, traffic statistics, and system health, allowing administrators to quickly assess the security posture of the network.
Q56. How can you manage and configure network objects using SmartConsole?
Ans:
In SmartConsole, managing and configuring network objects in Checkpoint involves navigating to the “Objects” tab. Create new network objects representing hosts, networks, or services. Organize objects into folders for efficient management. Utilize object groups to simplify rule definitions. Modify object properties as needed and apply changes.
Q57. Describe the functionalities of SmartView Monitor in SmartConsole.
Ans:
SmartView Monitor in SmartConsole provides real-time monitoring and reporting capabilities for Checkpoint security devices. It allows administrators to visualize network activity, monitor VPN and gateway performance, and analyze traffic patterns. SmartView Monitor displays live and historical data through interactive graphs and charts, enabling quick identification of network issues.
Q58. How do you use SmartView Tracker for log analysis and troubleshooting?
Ans:
To use SmartView Tracker for log analysis and troubleshooting in Checkpoint, open the SmartConsole management tool and navigate to the “Logs & Monitor” tab. Filter and search logs based on specific criteria, such as time range, source, and destination. Analyze log entries to identify security events, policy violations, or connectivity issues.Utilize the detailed information in logs for troubleshooting and diagnosing network problems.
Q59. What is the role of the Checkpoint Management Server in the overall architecture?
Ans:
The Checkpoint Management Server is a critical component in the overall architecture, serving as the central hub for managing and configuring security policies across Checkpoint Security Gateways. It stores and organizes policy settings, logs, and configurations, ensuring consistency and coordination among multiple gateways. The Management Server facilitates tasks such as policy updates, software deployment, and monitoring through the SmartConsole management tool.
Q60. How do you perform backups and restores of the Management Server?
Ans:
To perform backups and restores of the Checkpoint Management Server, use the built-in tools in the SmartConsole management tool. Access the “Backup” section to create regular backups of the Management Server configuration, including policies and logs. Specify backup locations and schedules based on organizational needs. In case of a failure or need to restore, use the “Restore” option to retrieve the saved configuration.
Q61. Explain the process of upgrading the Checkpoint Management Server.
Ans:
To upgrade the Checkpoint Management Server, obtain the latest compatible software package and verify system requirements. Prior to the upgrade, perform a backup of the Management Server’s configuration using the SmartConsole management tool. Run the upgrade package on the Management Server, following on-screen instructions for the specific version. During the process, existing configurations and policies are preserved.
Q62. How can problems pertaining to the Management Server be resolved?
Ans:
To resolve problems with the Checkpoint Management Server, troubleshoot using the SmartConsole management tool and review logs for errors. Restart services or the server if necessary. Verify network connectivity and ensure adequate system resources. Check disk space and resolve any storage issues. Consult Checkpoint documentation, knowledge base, or support for specific error codes and recommended solutions.
Q63. What are some best practices for securing the Checkpoint environment?
Ans:
Securing a Check Point environment involves implementing a comprehensive set of measures to fortify the network infrastructure. It begins with a steadfast commitment to keeping software and firmware up-to-date, ensuring the latest security patches are applied. Strong authentication, including multi-factor authentication, is paramount for safeguarding administrator access.
Q64. How do you ensure that your security policy aligns with industry compliance standards?
Ans:
Aligning your security policy with industry compliance standards involves a thorough understanding of regulatory requirements and the integration of these mandates into your security framework. Begin by identifying the relevant compliance standards applicable to your industry, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. Tailor your security policy to address the specific controls and safeguards mandated by these standards.
Q65. Describe the importance of regularly updating and patching the Checkpoint installation.
Ans:
Regularly updating and patching the Check Point installation is crucial for maintaining a secure and resilient network. These updates often include critical security patches that address vulnerabilities, safeguarding the system against emerging threats and potential exploits. By staying current with updates, organizations ensure that their Check Point infrastructure is equipped with the latest security features, bug fixes, and performance enhancements.
Q66. How can you monitor and respond to security threats using Checkpoint features?
Ans:
Monitor and respond to security threats effectively with Check Point features by leveraging its advanced threat detection tools such as intrusion prevention systems (IPS) and threat intelligence feeds. Configure real-time logging and monitoring to track network activities and set up alerts for suspicious behavior.This proactive approach, coupled with a well-defined incident response plan, enables quick identification, containment, and remediation of security threats in the Check Point environment.
Q67. Explain the Checkpoint licensing model and its components.
Ans:
Checkpoint’s licensing model is based on Software Blades, modular security functionalities activated as needed, like firewall and antivirus. Licensing is typically user, device, or throughput-based. Subscription services include threat prevention updates and access to ThreatCloud. This flexible model allows organizations to customize their security solutions and scale according to their specific requirements.
Q68. How do you manage licenses in a Checkpoint environment?
Ans:
Managing licenses in a Checkpoint environment involves using the License Management Portal (LMP) or the License Administration Tool (LAT) to view, activate, and update licenses. Access the UserCenter portal for license downloads and renewals. Regularly monitor license usage and expiration dates, ensuring compliance with the organization’s needs. Automated tools and periodic audits assist in optimizing license allocation and maintaining a secure and properly licensed Checkpoint environment.
Q69. Describe the process of activating and updating licenses in Checkpoint.
Ans:
To activate and update licenses in Checkpoint, access the License Management Portal or use the License Administration Tool. Retrieve license information from the UserCenter portal, and apply the license activation key in the management interface. Regularly check for updates through the same portals and install them using the SmartUpdate tool. This ensures that the Checkpoint environment is equipped with the latest features, security patches, and subscription services, maintaining optimal functionality and protection.
Q70. How can you use Checkpoint API for automation and scripting tasks?
Ans:
Checkpoint provides a RESTful API that allows for automation and scripting tasks. By leveraging the API, you can automate routine management tasks, deploy configurations, and extract information from the Checkpoint environment programmatically. Use programming languages like Python or tools such as cURL to interact with the API, enabling streamlined integration with other systems, orchestration, and the automation of security operations, ultimately improving efficiency and reducing manual intervention in Checkpoint environments.
Q71. Describe scenarios where scripting or automation would be beneficial in Checkpoint administration.
Ans:
Scripting and automation in Checkpoint administration prove beneficial in scenarios such as bulk configuration changes, where repetitive tasks like adding or modifying rules across multiple gateways can be streamlined. Automated log analysis and reporting help quickly identify and respond to security incidents. For backup and recovery, scripting can ensure regular and consistent data backups. Scaling and provisioning resources, especially in dynamic environments, become more efficient with automation, reducing manual errors.
Q72. What scripting languages are commonly used for Checkpoint automation?
Ans:
Commonly used scripting languages for Checkpoint automation include Python, which offers versatility and readability, and Bash for quick, scriptable tasks. Additionally, tools like Ansible, leveraging YAML, and RESTful APIs, facilitate automation and configuration management. These languages provide flexibility and ease of integration, enabling administrators to automate various tasks and streamline Checkpoint security operations effectively.
Q73. How do you keep up with the latest Checkpoint technology trends and updates?
Ans:
Staying current with the latest Checkpoint technology trends involves regularly visiting the official Checkpoint website for announcements, releases, and documentation updates. Subscribing to newsletters, participating in online forums, and following Checkpoint on social media platforms provide additional sources of real-time information. Engaging in industry conferences and webinars, as well as networking with peers, helps stay informed about emerging trends and best practices in Checkpoint security solutions.
Q74. Can you discuss any Checkpoint certifications you hold or plan to pursue?
Ans:
- Check Point Certified Security Administrator (CCSA): Foundation-level certification.
- Check Point Certified Security Expert (CCSE): Advanced certification for security professionals.
- Check Point Certified Master Architect (CCMA): Expert-level certification. Planning to pursue additional certifications based on career goals and evolving Checkpoint technologies.
Q75. How would you approach continuous learning in the field of Checkpoint administration?
Ans:
Continuous learning in Checkpoint administration involves regularly reviewing official documentation, participating in webinars, and exploring online forums to stay informed about updates and best practices. Subscribing to industry publications and blogs helps keep abreast of emerging trends. Engaging in hands-on labs and practical exercises enhances proficiency, while pursuing relevant certifications validates expertise.
Q76. How can you integrate Checkpoint security with cloud services like AWS or Azure?
Ans:
Integrating Checkpoint security with cloud services like AWS or Azure involves deploying Checkpoint Virtual Security Gateways (VSX) within the cloud environment. Utilize Checkpoint CloudGuard to extend security policies seamlessly, ensuring consistent protection across on-premises and cloud environments. Leverage cloud-native features like AWS Security Groups or Azure Network Security Groups in conjunction with Checkpoint’s advanced threat prevention capabilities.
Q77. Describe the considerations for securing cloud-based environments using Checkpoint.
Ans:
Securing cloud-based environments with Checkpoint involves several considerations. Firstly, deploy Checkpoint CloudGuard for native integration with cloud platforms, ensuring consistent security policies. Utilize network segmentation to isolate workloads and limit lateral movement.
Q78. How would you handle a security incident in a Checkpoint environment?
Ans:
In the event of a security incident in a Checkpoint environment, promptly activate the incident response plan. Utilize Checkpoint logs and monitoring tools to identify the scope and nature of the incident. Isolate affected systems using firewall rules and implement mitigation measures. Engage Checkpoint’s threat intelligence feeds for real-time updates. Conduct a thorough post-incident analysis to strengthen preventive measures and ensure continuous improvement in the security posture.
Q79. What forensic tools and methodologies can be employed with Checkpoint logs?
Ans:
Checkpoint logs can be analyzed using forensic tools like Wireshark and volatility, allowing for detailed examination of network and system activity. Export logs in a standardized format and integrate them into SIEM systems for comprehensive analysis. Maintain a strict chain of custody for log data to ensure its reliability in legal contexts.
Q80. Explain the role of Checkpoint in managing network address translation (NAT).
Ans:
Checkpoint plays a pivotal role in managing Network Address Translation (NAT) by providing a flexible and configurable solution for mapping private internal IP addresses to public external addresses. NAT is crucial for conserving IPv4 address space and enhancing security by masking internal network structures. Checkpoint allows administrators to define NAT policies, enabling dynamic or static translation based on specific network requirements.
Q81. Describe the process of configuring and troubleshooting VPN tunnels.
Ans:
Configuring and troubleshooting VPN tunnels in Checkpoint involves defining VPN communities, specifying encryption settings, and establishing secure communication channels between gateways. Administrators configure VPN settings such as encryption algorithms, authentication methods, and tunnel parameters. Troubleshooting encompasses checking tunnel status, reviewing logs for connectivity issues, and verifying configuration consistency between gateways.
Q82. What is Checkpoint Endpoint Security, and how does it complement network security?
Ans:
Checkpoint Endpoint Security is a comprehensive solution designed to secure end-user devices, including laptops, desktops, and mobile devices. It complements network security by extending protection beyond the perimeter, safeguarding endpoints against various threats such as malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks. The solution includes features like antivirus, firewall, threat prevention, and data loss prevention, providing a layered defense strategy.
Q83. How can you ensure endpoint security compliance in a Checkpoint environment?
Ans:
Ensuring endpoint security compliance in a Checkpoint environment involves configuring and enforcing security policies consistently across all endpoints. Use Checkpoint Endpoint Security features such as antivirus, firewall, and endpoint compliance checks to enforce security measures. Regularly update security definitions and conduct automated scans to detect and remediate vulnerabilities. Implement centralized management to monitor endpoint status, enforce policies, and respond to security incidents promptly.
Q84. How can you configure user authentication in a Checkpoint environment?
Ans:
Configure user authentication in a Checkpoint environment by integrating with external authentication servers like LDAP or Microsoft Active Directory. Utilize Checkpoint’s Identity Awareness feature to associate network activities with specific user identities. Implement user-based access controls, defining policies based on user groups or roles. Enable multi-factor authentication for enhanced security.
Q85. Describe the integration of Checkpoint with external authentication services.
Ans:
Checkpoint seamlessly integrates with external authentication services, such as LDAP or Microsoft Active Directory, to enhance user authentication. By leveraging Identity Awareness, Checkpoint associates network activities with specific user identities, enabling user-based access controls. This integration streamlines authentication processes, allowing organizations to enforce security policies based on users and groups defined in external directories.
Q86. How do you collaborate with other IT teams for effective security management?
Ans:
Collaboration with other IT teams for effective security management involves regular communication to align security policies with network and system configurations. Coordinate closely to ensure firewall rules and security measures are consistent across the infrastructure. Engage in joint vulnerability assessments and incident response drills to enhance overall readiness.
Q87. Describe a situation where effective communication was crucial in Checkpoint administration.
Ans:
In a complex Checkpoint administration scenario, a critical security incident occurred that required swift response and coordination. Through effective communication channels established with network and system administrators, we were able to share real-time information about the incident’s nature and potential impact. This collaborative effort enabled a faster identification of the root cause, allowing the Checkpoint team to implement immediate firewall rule adjustments and containment measures.
Q88. How does Checkpoint adapt to emerging technologies like IoT and mobile security?
Ans:
Checkpoint adapts to IoT and mobile security with advanced threat prevention and identity management, ensuring specific controls for IoT devices and extending protection to mobile endpoints.
Q89. Describe the challenges and opportunities associated with securing modern IT architectures.
Ans:
Securing modern IT architectures presents challenges due to the complexity of hybrid and multi-cloud environments, increased attack surfaces, and sophisticated cyber threats. The dynamic nature of containerized and serverless applications introduces new vulnerabilities. Managing user access across diverse platforms adds complexity.
Q90. How can Checkpoint be integrated into a DevOps workflow?
Ans:
Integrating Checkpoint into a DevOps workflow involves leveraging automation and orchestration tools. Checkpoint provides APIs and integrations with popular DevOps tools like Terraform and Ansible. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) practices can be used to define security policies alongside infrastructure configurations, ensuring security is built into the development process.






