
COBIT Interview questions are designed to evaluate a candidate’s grasp of the COBIT framework, its principles, and its practical application in IT governance. These queries may cover various aspects, including the candidate’s familiarity with COBIT components, maturity models, process attributes, and their role in achieving IT governance goals. Additionally, the questions may inquire about the candidate’s understanding of COBIT principles, policies, and their alignment with regulatory compliance. Strong responses showcase the candidate’s proficiency in implementing and enhancing COBIT processes to ensure efficient IT governance within an organizational setting.
1. What does COBIT stand for, and what does it mean?
Ans:
ContrThe Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies, or COBIT framework, offers guidance for effective IT governance and management in corporate settings.
2. What uses does COBIT serve?
Ans:
COBIT serves multiple roles by providing a framework for IT governance, aligning IT with business objectives, and aiding organizations in managing risks and ensuring compliance.
3. What are the many COBIT versions?
Ans:
COBIT has several versions, with COBIT 2019 being among the latest. Other versions include COBIT 5, COBIT 4.1, and COBIT 4.0.
4. Can you outline the five main COBIT processes?
Ans:
The five main COBIT processes are:
- Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM)
- Align, Plan, and Organize (APO)
- Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI)
- Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS)
- Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA)
5. What is the background and historical development of ISACA?
Ans:
Established in 1969 as the EDP Auditors Association, ISACA evolved into the Information Systems Audit and Control Association, addressing IT governance and management issues.
6. What does ISACA stand for, and what does it mean?
Ans:
ISACA, standing for Information Systems Audit and Control Association, is a professional association offering resources and guidance in IT governance, risk management, and information security.
7. Describe the COBIT framework’s idea of enablers.
Ans:
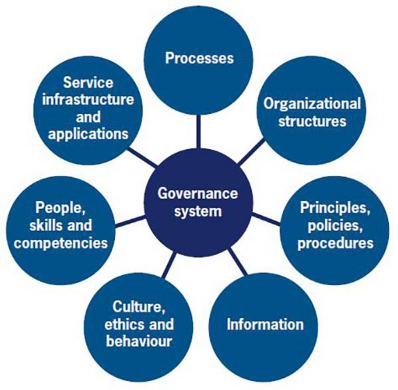
Enablers in the COBIT framework influence the success of governance and management processes, including Principles, Policies, Processes, Organizational Structures, Culture, Information, Services, and People.
8. What connection exists between governance and compliance?
Ans:
Governance in COBIT establishes the overall framework, connecting with compliance activities that ensure adherence to laws, regulations, and standards.
9. Is it necessary to use a single integrated framework?
Ans:
While not obligatory, utilizing a single integrated framework like COBIT can streamline processes, enhancing governance, risk management, and compliance efficiency.
10. Give further details regarding the enterprise’s end-to-end coverage.
Ans:
COBIT’s end-to-end coverage encompasses the entire IT governance life cycle, addressing strategic objectives, value delivery, risk management, and compliance throughout the enterprise.
11. Talk about the COBIT framework’s focus areas and management objectives.
Ans:
The COBIT framework concentrates on governance and management objectives. Governance ensures alignment with organizational goals, while management objectives focus on efficiently using IT resources.
12. List the six enablers in the COBIT framework.
Ans:
- Principles
- Policies
- Processes
- Organizational Structures
- Culture
- Information.
13. Explain the impact of the six COBIT enablers on IT governance.
Ans:
The six COBIT enablers collectively shape IT governance by providing a comprehensive approach. Principles guide decisions, Policies set direction, Processes execute activities, Organizational Structures define roles, Culture influences behaviour, and Information supports decision-making.
14. What does the Identify, Define, and Establish Processes section of COBIT serve to accomplish?
Ans:
The Identify, Define and Establish Processes section of COBIT identifies and defines governance and management objectives, establishes a governance system, and clarifies organizational responsibilities.
15. Which elements make up the COBIT framework’s core?
Ans:
The fundamental components of the COBIT framework include Principles, guiding behaviour and decisions; Policies, providing direction; and Processes; the activities undertaken to achieve organizational goals.
16. Talk about the COBIT-outlined Acquire and Implement procedures.
Ans:
COBIT’s procedures for acquiring and Implementing revolve around the processes related to obtaining and implementing information systems. This encompasses acquiring technology, developing and maintaining applications, and implementing changes in existing systems.
17. What is the main objective of COBIT’s Deliver and Support processes?
Ans:
COBIT’s Deliver and Support processes aim to ensure the efficient delivery of IT services and support, aligning with the organization’s business objectives. This involves service delivery, incident resolution, and fulfilment of service requests.
18. What part do activities play in COBIT processes?
Ans:
Activities in COBIT processes denote the specific actions or tasks performed to achieve the defined outcomes of each process. They represent the operational steps to ensure that governance and management objectives are effectively met.
19. Describe the significance of COBIT’s monitoring and Evaluation procedures.
Ans:
COBIT’s monitoring and Evaluation procedures hold significance as they involve continuous assessment and measurement of IT processes. These procedures ensure alignment with organizational objectives and serve as a foundation for continual improvement by identifying areas for enhancement.
20. In what ways does COBIT make use of the idea of process reference models?
Ans:
COBIT integrates the concept of process reference models to offer a standardized framework for comprehending and managing IT processes. These models act as guides, delineating each process’s components, activities, and interactions, facilitating consistent implementation across organizations.
21. What are the primary sources of input and output for COBIT processes?
Ans:
The primary input sources for COBIT processes include organizational objectives, external regulations, and stakeholder expectations. Outputs consist of reliable Information, reports, and decisions that contribute to achieving governance and management objectives.
22. Talk about the Management domain’s function inside the COBIT framework.
Ans:
The Management domain within the COBIT framework is responsible for executing governance directives. It ensures the alignment of IT activities with business objectives, manages risks, and optimizes resource use to deliver value.
23. Explain the components of the process reference model in COBIT.
Ans:
- Processes: High-level activities designed to achieve specific governance or management objectives.
- Activities: Detailed steps within processes, outlining specific tasks and actions.
- Practices: Recommendations and best practices guiding the execution of activities.
- Metrics: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) measure the performance of processes and activities.
24. Elaborate on the areas of focus linked to COBIT governance domains.
Ans:
COBIT governance domains align IT with business strategy, ensure value delivery, manage risks, optimize resource use, and measure performance. These areas collectively contribute to effective IT governance.
25. Explain how the COBIT Governance and Management domains interact.
Ans:
The Governance domain sets objectives, priorities, and oversight, while the Management domain implements these directives, ensuring day-to-day operations align with governance objectives. They work collaboratively to achieve organizational goals.
26. Talk about the significance of accountability in COBIT governance.
Ans:
- Responsibility and Ownership: Ensuring individuals take ownership of tasks and responsibilities.
- Transparency and Trust: Promoting clarity on responsibilities for transparent and trustworthy governance.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Enforcing adherence to policies, regulations, and standards for effective risk management.
- Decision-Making and Alignment: Facilitating effective decision-making aligned with organizational goals and compliance.
- Performance Measurement: Allowing for measuring individual and team performance in governance processes.
- Continuous Improvement: Fostering a culture of constant improvement through accountability for identifying enhancements.
- Communication and Collaboration: Enhancing communication and collaboration by clearly defining responsibilities.
27. What difficulties may organizations confront when implementing COBIT governance domains?
Ans:
Organizations may face challenges such as resistance to change, inadequate resources, and difficulties defining clear roles and responsibilities while implementing COBIT governance domains.
28. What approaches may be taken to deal with these issues in the context of COBIT implementation?
Ans:
- Cultivate a Culture of Adaptability
- Deliver Comprehensive Training
- Secure Support from Top Management
- Conduct Transparent Communication
- Clarify Roles and Responsibilities
- Adopt a Phased Implementation Approach
- Apply Change Management Techniques
- Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Promote Continuous Improvement
- Align with Organizational Objectives
29. In what way do COBIT enablers enhance the overall effectiveness of the framework?
Ans:
COBIT enablers, including Principles, Policies, Processes, Organizational Structures, Culture, and Information, collectively enhance the framework’s effectiveness by providing a holistic approach to IT governance.
30. Talk about the advantages of combining COBIT with TOGAF and other frameworks.
Ans:
- Holistic Governance and Architecture
- Enhanced Risk Management
- Strategic Alignment
- Optimized Resource Utilization
- Informed Decision-Making
- Efficient Compliance Management
- Unified Process Framework
- Increased Stakeholder Confidence
- Facilitates Continuous Improvement
31. What is ITIL?
Ans:
IT service management is governed by the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, or ITIL, which offers best practices for aligning IT services to business objectives. It strongly emphasizes roles, processes, and a service lifecycle approach to improve operational effectiveness and quality.
32. In what ways can organizations tailor COBIT processes to suit their specific requirements?
Ans:
Organizations can adapt COBIT processes by tailoring controls, adjusting practices to their unique context, and aligning governance structures with their specific requirements while ensuring adherence to COBIT principles.
33. Enumerate the critical Cobit framework views.
Ans:
The fundamental COBIT framework views encompass Governance and Management, Enablers, and Implementation. These views provide a comprehensive understanding of IT governance and management practices.
34. What benefits does Cobit offer?
Ans:
COBIT delivers benefits such as improved alignment of IT with business objectives, heightened risk management, optimized resource utilization, increased stakeholder confidence, and a structured framework for efficient IT governance and management.
35. Tell me about ISACA’s history.
Ans:
Established in 1969 as the Information Systems Audit and Control Association, ISACA is a professional association for IT governance, risk management, and cybersecurity professionals. Over time, it has evolved to offer guidance and certifications, including COBIT.
36. Describe how technology helps COBIT by acting as an enabler.
Ans:
Technology is a COBIT facilitator by supporting the implementation of IT governance processes. It leverages Information, automation, and tools to enhance efficiency, transparency, and the overall effectiveness of governance practices.
37. Can you provide examples of key performance indicators (KPIs) associated with COBIT processes?
Ans:
Examples of COBIT KPIs include the percentage of projects aligned with strategic objectives, incident resolution time, compliance with policies, and the accuracy of Information provided in reports. These indicators reflect the performance of governance processes.
38. How do COBIT processes contribute to the fulfilment of strategic objectives?
Ans:
COBIT processes contribute to strategic objectives by ensuring alignment of IT activities with business goals, effective risk management, optimized resource utilization, and continuous monitoring and improvement of performance, thus supporting strategic outcomes.
39. How Was Cobit Five Developed?
Ans:
COBIT 5 was developed in response to the changing landscape of IT governance. It aimed to provide a more holistic and adaptable framework, incorporating the latest industry practices and aligning with evolving organizational needs for effective management.
40. Could you explain how COBIT has changed through the years?
Ans:
COBIT has undergone evolution to adapt to dynamic factors like technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifts in business environments. Its progression from COBIT 4.1 to COBIT 5 emphasizes a broader scope, increased flexibility, and integration with other frameworks.
41. Describe how digital ethics and COBIT relate to IT governance.
Ans:
Digital ethics and COBIT intersect within IT governance, focusing on ethical considerations in technology use. COBIT’s framework ensures ethical practices align with organizational goals, enhancing overall governance.
42. In the context of COBIT, describe the idea of continuous improvement.
Ans:
Continuous improvement in COBIT involves an iterative process of assessing, monitoring and enhancing IT governance practices. The goal is to optimize processes, align them with objectives, and adapt to evolving business and technology landscapes.
43. What role does COBIT play in guaranteeing adherence to legal requirements?
Ans:
- Framework for IT Governance:
- Risk Management
- Control Objectives and Practices
- Alignment with Industry Standards and Regulations
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
- Performance Measurement
- Audit Support
44. Give the COBIT framework’s definition of “governance reporting.”
Ans:
Governance reporting in COBIT involves communicating pertinent Information about IT governance to stakeholders. This practice ensures transparency, accountability, and details for well-informed decision-making.
45. What is the significance of incorporating other IT governance frameworks with COBIT?
Ans:
Adding other IT governance frameworks to COBIT significantly improves coverage and flexibility. It helps businesses take advantage of many frameworks, resulting in a more thorough and customized approach to IT governance.
46. Define continuous improvement about COBIT.
Ans:
Continuous improvement in COBIT refers to the ongoing process of refining IT governance practices. It entails regular assessment, adjustment, and optimization of processes to align with organizational objectives and improve overall effectiveness.
47. Describe the function of COBIT in decision-making and board-level involvement.
Ans:
COBIT supports decision-making by providing a structured approach to IT governance. It facilitates board-level involvement by offering insights into IT-related risks, ensuring alignment with business goals, and enabling informed decision-making.
48. Talk about the benefits and difficulties of incorporating vendor management techniques into COBIT.
Ans:
Integrating vendor management into COBIT enhances control over external relationships, ensuring vendor alignment with organizational goals. Challenges may include integration complexities and the need for robust monitoring to ensure compliance and performance.
49. What tactics may improve the COBIT process’s efficiency and effectiveness?
Ans:
Strategies for improving COBIT processes include regular assessments, training initiatives, automation, clear communication, and alignment with business objectives. Continuous monitoring, feedback, and adaptation contribute to enhanced efficiency and effectiveness.
50. How can businesses use COBIT procedures to evaluate and quantify their performance?
Ans:
Businesses can leverage COBIT procedures for performance evaluation by establishing key performance indicators (KPIs), conducting regular assessments, and comparing actual outcomes against expected results. This quantitative approach helps measure and improve overall performance.
51. Explain the key differences between COBIT and ITIL
Ans:
| Feature | COBIT | ITIL | |
| Focus |
Broad framework for IT governance |
Specific framework for IT service management | |
| Objective | Ensures effective IT governance | Enhances IT service management processes | |
| Scope |
Encompasses end-to-end IT governance |
Primarily focuses on the IT service lifecycle | |
| Emphasis | Business alignment, risk management, compliance | Service delivery and continual improvement | |
| Processes |
Encompasses a wide range of IT processes across the enterprise |
Centers around service lifecycle stages (e.g., service design, transition) | |
| Framework Structure |
Comprises five principles, seven enablers, and a process reference model |
Includes service lifecycle stages, processes, functions, roles, and a service catalog | |
| Lifecycle Approach | Utilizes a broad lifecycle approach for IT processes and governance | Follows specific lifecycle phases for IT services (strategy, design, transition, operation, continual improvement) | |
| Audience | Targets business executives, IT managers, and auditors | Appeals to IT service management practitioners and professionals | |
| Metrics and KPIs | Emphasizes key performance indicators (KPIs) related to IT governance | Focuses on metrics and KPIs for service quality and delivery | |
| Integration with Other Frameworks | Aligns with various standards and frameworks | Commonly integrated with COBIT, ISO/IEC 20000, and other frameworks |
52. What does the process of transitioning to COBIT 5 entail?
Ans:
The process of transitioning to COBIT 5 entails evaluating existing IT governance practices, aligning them with COBIT 5 principles, and implementing necessary adjustments. This includes familiarizing oneself with the COBIT framework, defining governance objectives, and adapting processes for improved IT governance effectiveness.
53. Talk about how COBIT helps process improvement adhere to Six Sigma concepts.
Ans:
COBIT supports Six Sigma-driven process improvement by offering a framework for optimizing IT governance processes, ensuring efficiency, and minimizing defects. Its integration with Six Sigma principles enhances quality, reduces variability, and fosters better organizational outcomes.
54. Describe the connection between COSO and COBIT.
Ans:
COSO and COBIT share a robust connection in governance and risk management. While COSO focuses on broader internal controls, COBIT complements it by providing specific IT governance practices, ensuring a comprehensive approach to organizational governance.
55. How does COBIT’s information security management connect with ISO/IEC 27001?
Ans:
COBIT’s information security management aligns with ISO/IEC 27001 by offering a structured approach to managing and securing information assets. It guides the implementation and sustainability of an effective information security management system, ensuring compatibility with ISO/IEC 27001 standards.
56. Describe the function of COBIT’s Organizational Structures component.
Ans:
COBIT’s component on Organizational Structures defines roles, responsibilities, and organizational relationships within IT governance. It establishes effective decision-making, accountability, and communication, creating a framework for clear governance structures aligned with business objectives.
57. Discuss the integration points between COBIT and the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI).
Ans:
COBIT and the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) integrate at various junctures. Both frameworks concentrate on process improvement, with COBIT emphasizing IT governance processes and CMMI addressing overall organizational processes. Integration enhances overall maturity, efficiency, and effectiveness in delivering quality products and services.
58. How does the COBIT framework organize and structure its processes?
Ans:
COBIT organizes and structures its processes into Governance and Management domains, encompassing areas like Evaluate, Direct and Monitor, Align, Plan and Organize, Build, Acquire, and Implement, and Deliver, Service, and Support. This structure ensures comprehensive coverage of IT governance practices.
59. Describe the role that organizational structures play in the COBIT framework.
Ans:
Organizational structures in COBIT define the hierarchy, roles, and responsibilities within IT governance. They play a pivotal role in establishing clear lines of authority, accountability, and communication, ensuring effective decision-making and alignment with organizational objectives.
60. What does it mean to use COBIT 5 to implement NIST cybersecurity?
Ans:
Implementing NIST cybersecurity using COBIT 5 involves aligning COBIT’s risk management and security principles with NIST’s cybersecurity framework. This ensures a structured approach to identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity threats, enhancing overall security posture.
61. Does COBIT 5 address how management and governance are related?
Ans:
COBIT 5 addresses the synergy between management and governance by aligning IT processes with business objectives. Emphasizing effective communication, risk management, and accountability, it promotes a cohesive approach to achieving organizational goals through sound governance and management practices.
62. Who Makes Use of Cobit 5?
Ans:
COBIT 5 finds application among IT professionals, governance and risk management teams, auditors, and business leaders. Its wide-ranging utility spans across diverse industries, aiding organizations of all sizes in establishing effective IT governance and management practices for sustained success.
63. In what ways does the Process Reference Model help businesses comply with regulations?
Ans:
- Standardization of Processes
- Documentation and Traceability
- Risk Management
- Continuous Improvement
- Measurable Metrics
- Cross-Functional Integration
64. What distinguishes COBIT 5 from COBIT 4 Framework in terms of importance?
Ans:
COBIT 5 surpasses the COBIT 4 Framework with its more adaptable and comprehensive approach to IT governance. Emphasizing integration with overall enterprise governance, flexibility in adapting to evolving technologies, and alignment with contemporary business practices, COBIT 5 introduces governance principles and enablers for tailored processes. Its iterative lifecycle supports continuous improvement, making it ideal for dynamic business environments. While COBIT 4 laid the foundation, COBIT 5 stands out for its responsiveness to modern IT complexities, providing a scalable and robust governance framework.
65. Describe the connection between the needs for regulatory compliance and COBIT Policies.
Ans:
COBIT Policies serve as guidelines aligning IT processes with business goals and legal requirements, ensuring regulatory compliance. They provide a structured approach to meet industry standards and regulations.
66. Describe the function of the COBIT framework’s Principles.
Ans:
- Addressing Stakeholder Requirements:
- Spanning the Entire Enterprise:
- Utilizing a Unified Framework:
- Facilitating a Comprehensive Perspective
- Distinguishing Governance from Management
- Meeting Governance Obligations
67. Explain the concept of process attributes in the COBIT framework.
Ans:
Process attributes in COBIT refer to the characteristics defining the effectiveness and efficiency of a process. These attributes, including performance, capability, practices, and outcomes, aid in assessing process maturity and performance.
68. Describe the importance of the COBIT Process Reference Model for attaining IT governance transparency.
Ans:
- Structured Framework
- Clear Process Documentation
- Defined Roles and Responsibilities
- Maturity Assessments
- Compliance Guidance
- Auditability
- Performance Measurement
69. Describe the part that good communication plays in resolving COBIT implementation-related issues.
Ans:
Effective communication is crucial for successful COBIT implementation. It ensures stakeholders comprehend their roles, responsibilities, and the changes introduced by COBIT. Clear communication fosters collaboration and addresses concerns during the implementation process.
70. What role do Policies play in the overall design of COBIT?
Ans:
COBIT Policies form the foundation for governance, guiding decision-making and behavior. Aligned with business goals, legal requirements, and industry standards, these policies are integral to the overall design of the COBIT framework.
71. Describe the process of integrating the main components of the COBIT framework in a comprehensive manner.
Ans:
Integrating COBIT components involves aligning governance processes, Principles, and enablers. This comprehensive approach includes defining policies, designing processes, implementing controls, measuring performance, and continuous improvement for an effective IT governance framework.
72. Talk about how people have a part in making sure COBIT is implemented successfully.
Ans:
People play a critical role in COBIT implementation, contributing through commitment, skills, and understanding of COBIT Principles. Training personnel, fostering a compliance culture, and raising awareness are essential for successful COBIT integration within an organization.
73. Describe the role that information plays in assisting COBIT procedures.
Ans:
Information is a crucial enabler in COBIT procedures, supporting decision-making, risk management, and performance measurement. Effective information management ensures COBIT processes are well-informed, responsive, and aligned with organizational goals.
74. Talk about how an organization’s culture affects the adoption of COBIT principles.
Ans:
Organizational culture shapes the adoption of COBIT principles. A culture valuing transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement aligns well with COBIT. Conversely, a resistant or non-collaborative culture may impede effective adoption and implementation of COBIT principles.
75. Describe how each COBIT component affects IT governance procedures.
Ans:
COBIT’s Principles, Processes, Frameworks, and Practices collectively shape IT governance procedures. Principles guide decisions, Processes enable execution, Frameworks provide structure, and Practices offer guidelines. Together, they establish effective governance procedures, ensuring alignment with organizational objectives, risk management, and continuous improvement.
76. What role do services play in achieving the COBIT goals?
Ans:
Services in COBIT involve delivering IT capabilities. They play a pivotal role in achieving goals by ensuring effective design, implementation, and operation of IT services. Services support organizational objectives, enhance efficiency, and contribute to overall governance by delivering value and meeting stakeholder needs.
77. Examine the interconnectedness among the various components of COBIT.
Ans:
COBIT’s interconnected components, including Principles, Processes, Frameworks, and Practices, ensure a holistic and integrated approach to IT governance. Principles guide Process design, executed within Frameworks using established Practices. This interplay establishes a comprehensive governance structure, aligning IT with business goals, managing risks, and fostering continuous improvement.
78. Explain the relationship between COBIT Policies and regulatory compliance requirements.
Ans:
COBIT Policies are pivotal for aligning with regulatory requirements. They serve as controls, mapping out how IT processes adhere to legal frameworks and standards. Adherence to COBIT Policies ensures practices that facilitate compliance, establishing a transparent and accountable governance structure meeting regulatory expectations.
79. Describe how accountability and performance measurement relate to each other in COBIT procedures.
Ans:
In COBIT, accountability and performance measurement are intertwined. Accountability ensures individuals are responsible for their roles within IT processes. Performance measurement, defined by KPIs and metrics, evaluates process effectiveness. Together, they promote transparency, showcasing individual contributions to objectives and overall performance alignment with organizational goals in a continually improving governance environment.
80. Describe the idea of maturity models in terms of COBIT’s continuous improvement framework.
Ans:
Maturity models in COBIT’s continuous improvement framework illustrate the evolutionary stages of IT processes, guiding organizations from initial development to optimization. These models aid in assessing and advancing process maturity over time, ensuring continual improvement and alignment with business objectives.
81. How can organizations identify KPIs for their COBIT processes?
Ans:
Organizations can pinpoint Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for COBIT processes by aligning them with business goals, regulatory requirements, and stakeholder expectations. A systematic approach involves defining objectives, selecting relevant metrics, and ensuring KPIs are measurable, achievable, and linked to overall organizational success.
82. What steps should organizations take to define suitable KPIs for their COBIT processes?
Ans:
To define appropriate KPIs for COBIT processes, organizations should:
- Clearly articulate process objectives.
- Align KPIs with business goals and stakeholder needs.
- Select measurable indicators.
- Ensure KPIs are realistic and aligned with organizational priorities.
- Periodically review and adjust KPIs to reflect changing business environments.
83. Describe the function of COBIT’s feedback systems for continuous improvement.
Ans:
COBIT’s feedback systems facilitate continuous improvement by collecting, analyzing, and incorporating feedback on IT processes. They provide insights into performance, areas for enhancement, and alignment with governance objectives. This iterative feedback loop ensures that organizations can adapt and optimize processes over time.
84. Talk about the function of benchmarking in the COBIT framework’s performance measurement.
Ans:
Benchmarking in the COBIT framework involves comparing organizational performance against industry best practices. This role aids in identifying performance gaps, setting realistic improvement targets, and fostering a culture of continuous enhancement by leveraging insights from successful peers within the industry.
85. Talk about the significance of regular audits and assessments for gauging COBIT success.
Ans:
Regular audits and assessments are critical for evaluating COBIT success by ensuring adherence to established policies, controls, and regulatory requirements. These processes provide an independent evaluation of IT governance practices, identify areas for improvement, and instill confidence among stakeholders in the effectiveness of COBIT implementation.
86. Describe the ways in which COBIT governance decision-making is supported by performance assessment.
Ans:
Performance assessment in COBIT informs governance decision-making through a data-driven approach. By evaluating KPIs and metrics, decision-makers gain insights into the effectiveness and efficiency of IT processes. Informed decisions can be made to optimize resources, mitigate risks, and align IT activities with strategic business objectives.
87. Talk about tactics to deal with reluctance to change in the COBIT process of continuous improvement.
Ans:
To address reluctance to change in COBIT’s continuous improvement, organizations can:
- Communicate the benefits of change.
- Involve stakeholders in decision-making.
- Provide training and support.
- Demonstrate success through pilot projects.
- Foster a culture that embraces innovation and continuous improvement.
88. Describe the connection between COBIT process optimization and performance measurement.
Ans:
COBIT process optimization and performance measurement are intertwined. Performance metrics provide insights into process effectiveness, highlighting areas for improvement. Optimization efforts are guided by these insights, ensuring that changes are targeted, measured, and contribute to overall performance enhancement aligned with organizational goals.
89. Explore methods for organizations to sustain commitment to continuous improvement in COBIT governance.
Ans:
Organizations can sustain commitment to continuous improvement in COBIT governance by:
- Cultivating a culture that values learning and adaptability.
- Recognizing and celebrating achievements in improvement.
- Providing ongoing training and development opportunities.
- Encouraging collaboration and knowledge-sharing.
- Regularly reviewing and updating improvement goals to align with evolving business needs.
90. Describe the meaning of the COBIT Process Reference Model’s maturity levels.
Ans:
The maturity levels in the COBIT Process Reference Model represent stages in evaluating an organization’s process capability. Ranging from Level 0 (Nonexistent) to Level 5 (Optimized), each level signifies an evolution in process maturity, indicating higher control and optimization.






