- Introduction to Private Blockch
- Public vs Private Blockchain: Key Differences
- How Does a Private Blockchain Work?
- Architecture and Components of Private Blockchains
- Benefits of Using Private Blockchains for Businesses
- Popular Private Blockchain Platforms
- Use Cases and Industry Applications
- Challenges and Future Outlook of Private Blockchains
- Conclusion
Introduction to Private Blockchain
Blockchain technology has transformed industries by introducing decentralized, transparent, and tamper-proof digital ledgers. While public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum have attracted the most attention, private blockchains have become increasingly important for enterprises requiring more control, privacy, and scalability.A private blockchain is a blockchain network where access is restricted to a specific group of participants. Unlike public blockchains, Block Chain Training which are open to anyone, private blockchains enable businesses to leverage blockchain benefits in a controlled environment. This approach allows enterprises to retain privacy, Components of Private Blockchains enforce permissions, and optimize performance, Decentralization for Enterprises making private blockchains a popular choice for supply chain management, finance, healthcare, and more.In this blog, we will explore what private blockchains are, how they function, their advantages, and why many organizations are adopting them to streamline operations and enhance trust.
Public vs Private Blockchain: Key Differences
| Aspect | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Access Control | Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, or others | Permissioned consensus (e.g., PBFT) |
| Privacy | Transparent to all participants | Data visible only to authorized users |
| Decentralization | Highly decentralized | Controlled by a single organization or consortium |
| Transaction Speed | Slower, due to large network size | Faster, fewer nodes to validate |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies, public dApps | Enterprise solutions, private consortiums |
How Does a Private Blockchain Work?
Private blockchains operate on a permissioned model where network administrators control membership and consensus participation. Key aspects include:
- Restricted Access: Only trusted participants or nodes can join the network.
- Permissioned Consensus: Consensus mechanisms focus on speed and efficiency, What is Consortium Blockchain often using algorithms like Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) or RAFT.
- Data Privacy: Transactions and data are visible only to authorized parties, maintaining confidentiality.
- Governance: A central authority or consortium governs the rules and policies of the network.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Today!
Architecture and Components of Private Blockchains
Private blockchains share several core components of Private Blockchains but incorporate additional layers for permissioning and privacy What is Decentralized Finance .
Core Components:
- Nodes: Authorized entities running the blockchain software.
- Ledger: Distributed database recording all validated transactions.
- Consensus Mechanism: Permissioned consensus protocol (e.g., PBFT, RAFT).
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts automating workflows.
- Access Control Layer: Manages identity and permissions of network participants.
- Cryptography: Ensures data integrity and security through hashing and digital signatures.
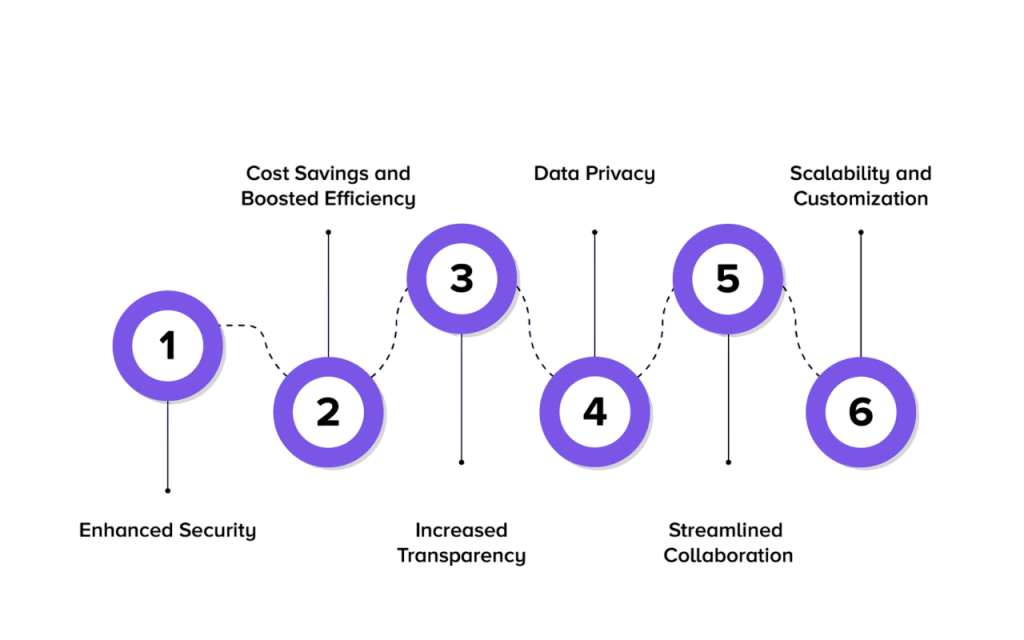
- Enhanced Privacy and Confidentiality: Data and transaction details are shared only with authorized participants, protecting sensitive business information.
- Improved Transaction Speed and Scalability:With fewer nodes and permissioned consensus, private blockchains process transactions faster than public blockchains.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower energy consumption and reduced need for complex consensus algorithms cut operational costs Block Chain Training .
- Governance and Compliance: Businesses can implement custom rules, identity verification, and comply with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
- Auditability and Transparency: Immutable ledgers provide verifiable audit trails, increasing trust among stakeholders.
- Customization and Flexibility: Private blockchains can be tailored to specific business needs, integrating easily with legacy systems.
- Hyperledger Fabric: A modular framework from the Linux Foundation supporting permissioned networks with plug-and-play consensus and privacy.
- Corda: Developed by R3, optimized for financial services with strong privacy features.
- Quorum: An enterprise Ethereum-based What is Cloud Mining blockchain by JPMorgan Chase, focusing on permissioned environments.
- MultiChain: Open-source blockchain platform emphasizing simplicity and enterprise adoption.
- Chain: Focused on permissioned blockchain solutions for financial institutions.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking provenance, reducing fraud, and enhancing transparency while keeping sensitive data confidential.
- Banking and Finance: Secure interbank settlements, Know Your Customer (KYC) processes, and syndicated loans with privacy controls.
- Healthcare: Secure sharing of patient records between authorized providers Blockchain Certification Training while complying with data privacy regulations.
- Government and Public Services: Transparent voting systems, identity management, and secure data sharing between agencies.
- Real Estate: Managing property titles, leases, and transactions with reduced fraud and streamlined processes.
- Manufacturing: Ensuring quality assurance and tracking production data within trusted partner networks.
- Limited Decentralization: Centralized control might reduce trust compared to public blockchains.
- Interoperability: Integrating with public blockchains and other systems remains complex.
- Adoption Barriers: Organizations need technical expertise and cultural changes to implement blockchain effectively Best Blockchain Programming Language .
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Navigating evolving legal frameworks can be challenging.
To Explore Database in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Database Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Benefits of Using Private Blockchains for Businesses
Private Blockchains for Businesses offer multiple advantages to enterprises looking to optimize their processes:
Popular Private Blockchain Platforms
Several platforms have been designed or adapted to support private blockchain deployments:
Use Cases and Industry Applications
Private Blockchains for Businesses have seen adoption across various sectors:
Want to Learn About Database? Explore Our Database Interview Questions and Answers Featuring the Most Frequently Asked Questions in Job Interviews.
Challenges and Future Outlook of Private Blockchains
Challenges:
Future Outlook:
Despite challenges, private blockchains are poised for growth driven by increasing demand for secure, Integrating , Components of Private Blockchains, scalable, supply chain and compliant distributed ledgers. Advances in interoperability, hybrid blockchain models, and enterprise blockchain consortia will further unlock their potential.
Conclusion
private blockchains offer enterprises a powerful way to harness blockchain technology while maintaining control over data, participants, and network governance. Their scalability, privacy, and customization make them ideal for business applications where security and efficiency are paramount.As blockchain technology matures, Integrating , Private Blockchains for Businesses, Block Chain Training supply chain management, Decentralization for Enterprises private blockchains will continue playing a pivotal role in transforming industries, enabling secure collaboration, and driving innovation within trusted networks.