- Introduction to Cloud Computing
- Why Businesses Are Moving to the Cloud
- Types of Cloud Computing (Public, Private, Hybrid)
- Key Benefits of Cloud Adoption
- Cloud Service Models: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
- Major Cloud Providers: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud
- Cloud Security Best Practices
- The Role of AI and Automation in Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Career Opportunities
- Certifications for Cloud Professionals
- Common Challenges in Cloud Migration
- Future of Cloud Computing
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing, as covered in Cloud Computing Training, refers to the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the Internet (the cloud) rather than through traditional on-premises infrastructure. These services allow businesses to access resources on demand, pay only for what they use, and scale their operations without the need for significant upfront capital investments in hardware and infrastructure. The adoption of cloud computing has skyrocketed over the years, transforming how businesses operate and deliver services. Cloud computing offers flexibility, cost-efficiency, and enhanced collaboration, making it a crucial component in the modern digital transformation.
Want to Earn Your Cloud Computing Certification? Check Out Cloud Computing Online Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Why Businesses Are Moving to the Cloud
Businesses are moving to the cloud for several compelling reasons:
- Cost Efficiency: Traditional IT infrastructure requires heavy upfront hardware, software, and maintenance investments. With cloud computing, businesses can reduce capital expenditures by shifting to a pay-as-you-go or subscription-based model, where they only pay for the resources they use.
- Scalability: Cloud platforms offer businesses the ability to scale resources up or down depending on their needs. This is particularly important for companies with fluctuating demand, as they can easily adjust their cloud usage to avoid over-provisioning.
- Flexibility and Accessibility: Cloud computing allows employees to access applications and data from anywhere, on any device with an internet connection. This supports remote work, collaboration, and global operations.
- Improved Collaboration: Cloud tools play a crucial role in enabling real-time collaboration among teams, no matter where they are in the world. By leveraging shared cloud-based documents, integrated communication platforms, and efficient project management tools, teams can significantly boost their productivity and streamline workflows. If you’re interested in learning more about how these technologies work, check out this Google Cloud Computing Tutorial for a solid introduction.
- Security and Disaster Recovery: Many cloud service providers offer robust security features such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and automatic backups. In addition, cloud-based disaster recovery solutions ensure business continuity in case of unforeseen events.
- Innovation and Competitive Edge: Cloud computing allows businesses to leverage advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and big data analytics. By incorporating these technologies into their operations, companies can innovate faster and stay competitive.
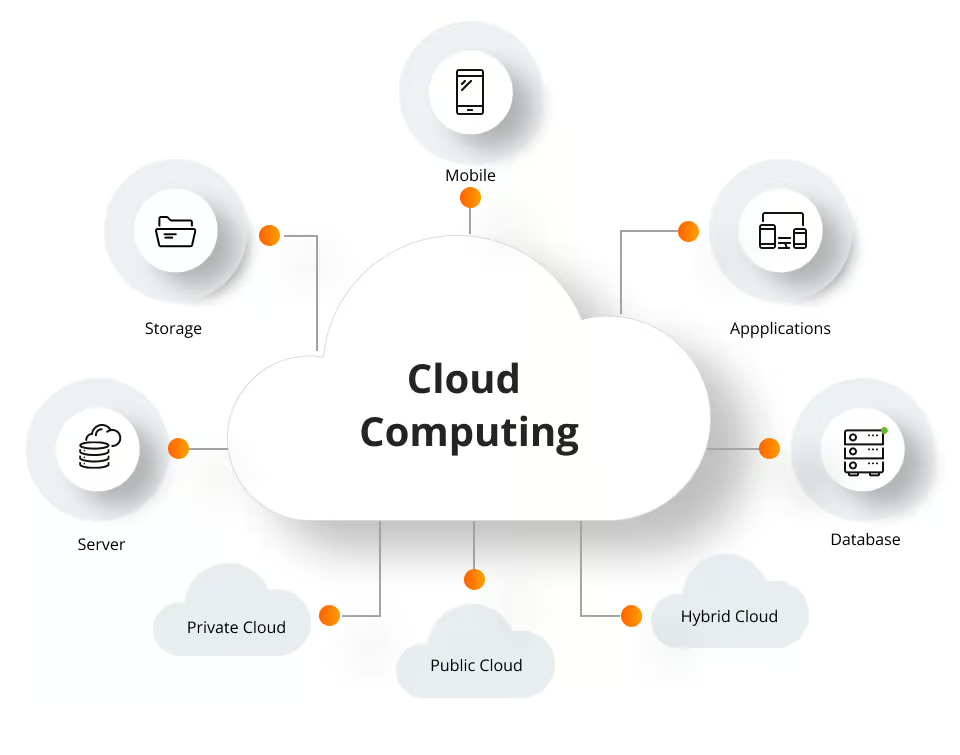
Types of Cloud Computing (Public, Private, Hybrid)
Cloud computing can be categorized into different types based on deployment models. The three most common models are public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud:
1.Public Cloud:- In a public cloud model, cloud services are provided over the Internet by third-party vendors (e.g., AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud). These services are available to the general public, and businesses share the infrastructure with other tenants.
- Advantages: Cost-efficient, scalable, and has no need for infrastructure management
- Disadvantages:: Less control over data security and privacy, shared resources. 2.Private Cloud:
- A private cloud is a cloud environment used exclusively by a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider but is not shared with other businesses.
- Advantages: Greater control over security, performance, and data privacy.
- Disadvantages: Higher costs for setup and maintenance, less scalability compared to public cloud. 3.Hybrid Cloud:
- Hybrid cloud combines public and private clouds, allowing businesses to move workloads between them based on their needs. This provides flexibility and optimization of existing infrastructure, with the ability to leverage the public cloud for non-sensitive workloads while keeping critical applications and data in a private cloud.
- Advantages: Flexibility, scalability, and control over sensitive data.
- Disadvantages: Complexity in management and integration between cloud environments
Earn Your Cloud Computing Certification, Gain Insights From Leading DevOps Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
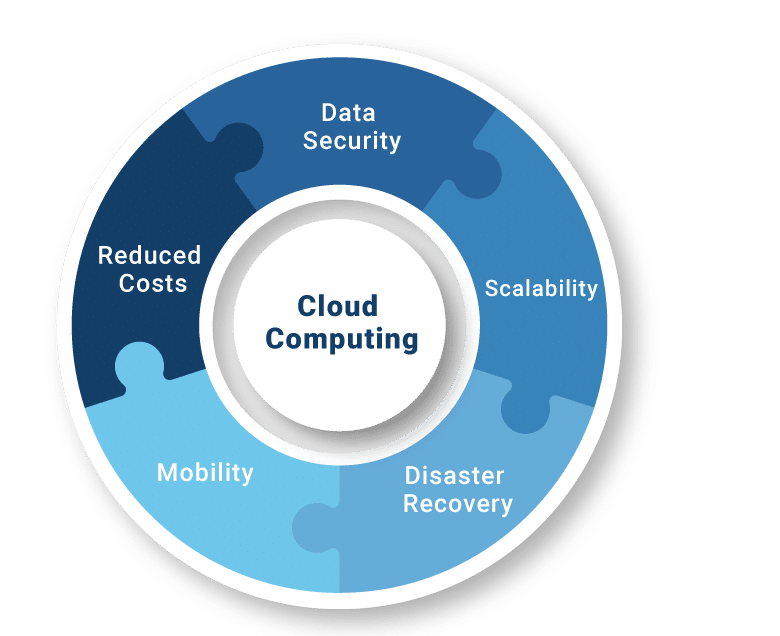
Key Benefits of Cloud Adoption
Cloud adoption offers businesses several significant benefits:
- Cost Savings: By reducing the need for expensive hardware and infrastructure, cloud computing helps businesses save on capital expenditures. Additionally, the pay-as-you-go model ensures that businesses only pay for the resources they actually use.
- Enhanced Agility: Cloud computing enables businesses to quickly deploy new applications and services, iterate faster, and adapt to market changes. This agility leads to quicker innovation and a competitive advantage.
- Security and Reliability: Cloud providers invest significantly in securing their infrastructure and ensuring consistent uptime. With the help of resources such as Cloud Computing Training, users can better understand advanced security measures like encryption, access control, and regular backups that help minimize the risk of data breaches and service disruptions.
- Global Reach: With cloud infrastructure distributed across the globe, businesses can easily expand their operations and serve customers from various regions without significant physical infrastructure investment.
- Collaboration and Remote Work: Cloud-based tools facilitate better communication and collaboration, supporting distributed teams and remote work environments.
Cloud Service Models: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
Cloud services are typically divided into three main service models:
1.Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):- IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet. Businesses can rent virtual machines, storage, networking, and other infrastructure components from cloud providers. IaaS allows businesses to manage and control their infrastructure without the complexity of maintaining physical hardware.
- Example Providers: AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, Google Compute Engine. Platform as a Service (PaaS):
- PaaS offers a platform that allows businesses to develop, run, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. PaaS provides developers with tools, databases, and runtime environments to build applications more efficiently.
- Example Providers: Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Service, AWS Elastic Beanstalk. Software as a Service (SaaS):
- SaaS delivers software applications over the Internet on a subscription basis. Businesses can access applications like email, customer relationship management (CRM), and project management tools directly from the cloud without needing to install or maintain them.
- Example Providers:Google Workspace, Microsoft Office 365, Salesforce.
Major Cloud Providers: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud
The three major players in the cloud computing market are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Each offers a comprehensive set of services and solutions, with varying strengths and capabilities:
1.Amazon Web Services (AWS):- AWS is the largest and most widely adopted cloud platform. It offers a vast array of services, including computing, storage, networking, databases, machine learning, and more. In this ecosystem, the role of an AWS Solutions Architect is crucial for designing scalable and cost-effective cloud solutions. AWS has a strong presence in industries like e-commerce, gaming, and media.
- Strengths: Wide range of services, global infrastructure, enterprise-grade solutions. 2.Microsoft Azure:
- Azure is the second-largest cloud provider and is particularly strong in hybrid cloud solutions. Azure integrates well with Microsoft products like Windows Server, SQL Server, and Active Directory, making it an attractive option for businesses already using Microsoft technologies.
- Strengths: Hybrid cloud capabilities, enterprise integration, strong presence in industries like government and healthcare. 3.Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
- In the comparison of Google Cloud vs AWS, GCP is recognized for its strong features in data analytics, machine learning, and open-source tools. It’s commonly chosen by companies that work heavily with big data, and its Kubernetes service is a major part of its containerization support.
- Strengths: Big data, AI, and machine learning services, containerization, and open-source technologies.
Cloud Security Best Practices
Ensuring the security of cloud infrastructure is critical for businesses adopting cloud computing. Here are some best practices for cloud security:
1.Identity and Access Management (IAM):- Use strong IAM policies to control who can access cloud resources. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) and enforce the principle of least privilege to minimize access to sensitive data and services. 2.Data Encryption:
- Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access. Use encryption standards like AES-256 for data storage and SSL/TLS for data transmission. 3.Regular Audits and Monitoring:
- Conduct regular audits of cloud resources and security policies. Cloud-native monitoring tools like AWS CloudTrail, Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud Audit Logs are used to track and analyze activity in real time. 4.Backup and Disaster Recovery:
- Implement automated backup solutions to ensure that critical data is regularly backed up and can be restored quickly in the event of a failure. 5.Compliance:
- Ensure that your cloud infrastructure adheres to relevant industry standards and regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
The Role of AI and Automation in Cloud Computing
With the rise of AI and automation, their role in Cloud Computing Training is becoming more significant. Technologies such as machine learning and natural language processing empower cloud providers to deliver intelligent services that streamline operations like predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and automated decision-making.
Key ways AI and automation are transforming cloud computing:
- 1.Predictive Analytics: AI-powered tools analyze data to predict future trends and behaviors, improving decision-making and resource optimization.
- 2.Automated Infrastructure Management: Cloud platforms use automation to dynamically scale resources, manage workloads, and handle routine maintenance tasks.
- 3.AI-driven Security: AI and machine learning help identify potential security threats, automate threat detection, and respond faster to incidents.
Cloud Computing Career Opportunities
Career in Cloud Computing offers diverse opportunities across various roles, including:
- Cloud Architect: Designs cloud infrastructure and solutions for businesses.
- Cloud Engineer: Implements and manages cloud infrastructure and services.
- Cloud Security Engineer:Secures cloud environments and ensures compliance.
- Cloud Consultant:Advises businesses on cloud adoption strategies and implementations.
- Cloud Developer:Develops applications and services hosted on the cloud.
Certifications for Cloud Professionals
Several certifications can help professionals advance their cloud computing careers:
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect (Associate/Professional)
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Fundamentals/Associate
- Google Cloud Certified – Professional Cloud Architect
- CompTIA Cloud+
- Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP)
Common Challenges in Cloud Migration
Migrating to the cloud can be complex and challenging. Some common challenges include:
- Data Security and Privacy: Ensuring sensitive data is protected during migration and remains compliant with regulations.
- Cost Management: Managing and optimizing cloud spending can be difficult, especially without a clear understanding of usage patterns.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Integrating cloud infrastructure with on-premises systems can require significant effort and resources.
- Downtime During Migration: Minimizing downtime and service disruptions during migration is critical for business continuity.
Future of Cloud Computing
The future of cloud computing looks promising, with continued growth driven by the rise of emerging technologies like AI, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Key trends shaping the future of cloud computing include:
- Edge Computing: As IoT devices proliferate, Future of IoT will bring computation closer to data sources, reducing latency and enhancing performance.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing will continue to grow, allowing developers to build applications without worrying about infrastructure management.
- Increased Focus on Security and Compliance: With the growing adoption of the cloud, security and regulatory compliance will remain top priorities for businesses. As cloud computing evolves, it will continue to drive innovation and enable businesses to stay competitive in an increasingly digital world.