
- Introduction to Cloud Computing
- History and Evolution of Cloud Computing
- Types of Cloud Computing Services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
- Key Cloud Service Providers (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Security Challenges in Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Use Cases
- Getting Started with Cloud Platforms
- Cloud Certifications and Career Paths
- Future Trends in Cloud Computing
- How to Become a Cloud Expert
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing revolutionizes how businesses and individuals store, manage, and process data. In simple terms, cloud computing refers to delivering computing services such as storage, processing, and networking over the Internet rather than relying on traditional on-premise hardware. Overview of Cloud Database model allows businesses to scale resources dynamically and enables flexibility in accessing computing power without heavy investments in physical infrastructure.Over the years, cloud computing has become an integral part of most industries, offering robust solutions for data management, collaboration, and automation. Cloud platforms provide developers and enterprises with scalable, cost-effective, and accessible resources to power applications and store vast amounts of data. This article delves into the history, types, benefits, security challenges, use cases, and career paths associated with cloud computing.
History and Evolution of Cloud Computing
The concept of cloud computing has evolved significantly since its inception. In the 1960s, computer scientist John McCarthy proposed making computing resources available to the public through time-sharing systems. This Cloud Computing Course was ahead of its time, as the technology to execute it wasn’t available then.However, the modern concept of cloud computing started taking shape in the 1990s. The arrival of virtualization technology enabled efficient resource allocation and isolation, leading to the development of virtualized environments. This, combined with the increasing popularity of high-speed Internet and web-based services, paved the way for cloud computing as we know it today. In 2006, Amazon launched Amazon Web Services (AWS), a suite of cloud services that marked the beginning of the commercial cloud computing industry. This was followed by Microsoft Azure in 2010, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) in 2011, and many other companies entering the cloud computing space. The cloud’s rise has transformed industries by enabling rapid scalability, cost reduction, and increased accessibility for businesses worldwide.
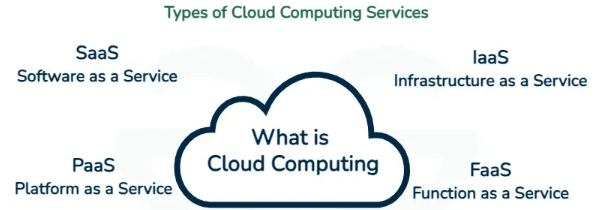
Types of Cloud Computing Services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
Cloud computing services are generally categorized into three major models, each offering varying degrees of control, flexibility, and management:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides the most fundamental computing resources over the cloud. This model allows businesses to rent IT infrastructure such as virtual machines, storage, and networking components. Users manage and configure the operating systems, applications, and databases, while the cloud provider manages the hardware infrastructure. Examples: Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, Google Compute Engine.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS provides a platform and environment for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. PaaS includes coding, testing, deployment, and hosting tools, making Step by Step Guide to Hybrid Cloud ideal for developers focused on building software without dealing with complex infrastructure management. Examples are Microsoft Azure App Services, Google App Engine, and AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
- SaaS: Software as a Service delivers fully functional software applications through the cloud. Users access these applications online, eliminating the need for local installation, updates, or maintenance. Software as a Service is typically subscription-based and is scalable according to the number of users or usage requirements. Examples are Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Salesforce.
Key Cloud Service Providers (AWS, Azure, GCP)
The major players in theCloud Computing Services market offer a broad range of services across various domains. The three primary cloud providers are:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS is the largest and most widely adopted cloud platform. It offers a wide array of services, including compute, storage, machine learning, networking, and analytics, and has a global presence across numerous regions and availability zones. Key Services like EC2, S3, RDS, Lambda, and AWS IoT.
- Microsoft Azure: Mastering AWS Cloudformation is Microsoft’s cloud platform, popular with enterprises due to its seamless integration with existing Microsoft technologies, such as Windows Server, SQL Server, and Active Directory. Key Services like Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Storage, Azure Active Directory, and Azure DevOps.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP is known for its strong data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence offerings. Google Cloud Computing Tutorial and significant data processing expertise translate into robust enterprise cloud services. Key Services like Compute Engine, Google Cloud Computing Tutorial, BigQuery, and Cloud AI.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing reduces the need for businesses to invest in expensive physical hardware and infrastructure. With a pay-as-you-go model, organizations only pay for the resources they use, which results in reduced capital expenditures. Cloud platforms offer scalability, allowing users to scale up or down based on demand. This makes it easy for businesses to adjust resources in real-time without manual intervention. Cloud environments are highly flexible, enabling users to run applications and workloads on demand.This allows businesses to experiment with new technologies, build prototypes, and innovate without worrying about hardware constraints. Guide to Cloud Security maintain high levels of availability by distributing workloads across multiple data centers and regions. This ensures uptime and reduces the risk of system failures. Cloud providers offer built-in backup and disaster recovery capabilities, ensuring business continuity in case of system failures or data loss. Leading cloud platforms invest heavily in security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and access controls. Providers also comply with industry standards, certifications, and regulations to protect user data.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Cloud Computing? Enroll in the Cloud Computing Masters Course Today!
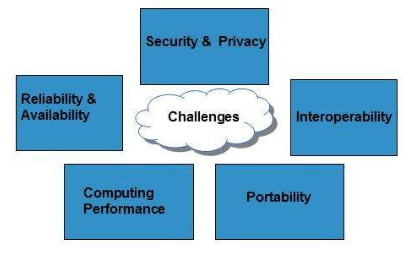
Security Challenges in Cloud Computing
While cloud computing offers many benefits, it also introduces security challenges that must be addressed to protect sensitive data and applications:
- Data Privacy and Compliance: Storing data in the cloud raises concerns about compliance with local regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA. Ensuring that cloud providers meet these standards is critical to maintaining data privacy.
- Access Control: Managing access to cloud resources can be complex, especially with large teams and distributed systems. Proper Cloud Computing Platforms and Services and authorization mechanisms must be in place to prevent unauthorized access.
- Data Encryption: While cloud providers offer encryption, organizations must ensure that data is adequately encrypted in transit and at rest. A failure to implement encryption could expose sensitive data to security risks.
- Vendor Lock-in: Organizations may face difficulties switching cloud providers due to the complexity of moving data and applications from one provider to another.
Cloud Computing Use Cases
Cloud computing is applied in various industries for a wide range of purposes. Some everyday use cases include:
- Data Storage and Backup: Cloud storage solutions like AWS S3 and Azure Blob Storage provide scalable, cost-effective ways for businesses to store and back up data.
- Website Hosting:Cloud platforms allow organizations to host websites and web applications with high availability and performance. Popular platforms like Amazon Web Services and Azure support content delivery and website scaling.
- Big Data and Analytics: Cloud Computing Course facilitates big data processing and analytics, with services like AWS Certified Solutions, Azure Synapse, and Google BigQuery helping businesses analyze large datasets efficiently.
- Machine Learning and AI: Cloud providers offer managed services for machine learning and artificial intelligence, enabling developers to build and deploy predictive models without worrying about infrastructure.
- Software Development and Testing: Cloud platforms enable developers to provide testing and development resources using tools likeAWS Certified Solutions, Azure DevOps, and Google Cloud Computing Tutorial.
Getting Started with Cloud Platforms
To get started with cloud platforms, individuals and businesses should Select a Cloud Provider and Choose a cloud provider (AWS, Azure, GCP) based on your needs.Please create an Account to Set up an account with the chosen cloud provider and familiarize yourself with its services.Learn Basic Cloud Concepts Understand the fundamentals of cloud computing, including IaaS, PaaS, Software as a Service , And various deployment models. Explore Free Tiers Most cloud providers offer free tiers with limited usage, allowing users to experiment and learn without incurring costs. Start with Hands-On Projects Build simple cloud-based applications to get practical experience.
Go Through These Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer to Excel in Your Upcoming Interview.
Cloud Certifications and Career Paths
Cloud computing offers numerous certification programs that validate your expertise in cloud technologies, opening up various career opportunities. Popular certifications include the AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate/Professional, which demonstrates your ability to design and deploy scalable systems on Amazon Web Services, the Microsoft Certified Administrator Associate, which validates skills in managing Azure resources and services, and the Hybrid Cloud Hypervisors for Scalability Tutorial, which focuses on designing and managing solutions on Google Cloud Platform. These certifications can lead to careers as cloud architects, cloud engineers, or DevOps engineers, with increasing demand for cloud professionals across industries. As more businesses migrate to the cloud, the need for skilled cloud professionals continues to grow, making cloud certifications a valuable asset for career advancement.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing
The future of cloud computing is poised for exciting developments. Edge Computing of IoT devices and low-latency applications will push for more edge computing solutions, where data processing occurs closer to the data source rather than centralized cloud data centers. AI and Automation Cloud platforms will continue to leverage AI and automation tools for tasks such as resource optimization, workload management, and security threat detection. Cloud Computing Course As quantum computing advances, cloud providers will start offering quantum computing services, which could revolutionize industries such as cryptography and drug development.
How to Become a Cloud Expert
- Learn Cloud Fundamentals: Understand the core principles and services of cloud computing.
- Gain Hands-On Experience: Practice with real-world projects and cloud services.
- Pursue Certifications: Obtain certifications from AWS, Azure, or GCP to validate your expertise.
- Stay Updated: Cloud technologies evolve rapidly, so keep learning about new services and trends.
- Network with Cloud Professionals: Join cloud communities, attend conferences, and collaborate on projects to expand your network.





