
- Introduction to Azure Tenant
- Key Components of an Azure Tenant
- How Azure Tenants Work
- Difference Between Azure Tenant and Subscription
- Setting Up an Azure Tenant
- Use Cases of Azure Tenant
- Best Practices for Managing Azure Tenants
- Conclusion
Introduction to Azure Tenant
An Azure Tenant is a dedicated instance of Microsoft Azure’s cloud services that represents a single organization within the Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) environment. Whenever you sign up for Complete Microsoft Azure Course, a new tenant is created, and it is linked to your Azure AD account. This tenant acts as the central management point for all resources, services, and users within an organization, providing access to cloud resources such as virtual machines, databases, and networking components in a secure manner. The Azure tenant is essential in managing identity and access control of users, devices, and applications within an organization. Azure Tenants are based on the Azure Active Directory, which is the identity and access management service provided by Microsoft. The Azure AD service allows organizations to control access to their resources and applications, whether on-premises or in the cloud. A tenant, in essence, is a container for an organization’s directory services and is used to organize and manage resources, security policies, and user identities. In a nutshell, an Azure Tenant aids organizations in safely managing and governing their cloud environment, offering control over users, applications, and resources. To understand the building blocks and what an Azure Tenant does, it is essential for IT administrators and businesses using Azure for cloud-based services.
Start your journey in Microsoft Azure by enrolling in this Microsoft Azure Training .
Key Components of an Azure Tenant
- Azure Active Directory (Azure AD): The core of an Azure Tenant is represented by Azure AD. It ensures identity management, authentication, and access control for the users and services. Azure AD supports different kinds of authentication mechanisms, such as MFA, and integrates both with Microsoft applications and third-party applications.
- Subscription: A set of resources is billed together on a subscription as it defines the billing structure associated to a tenant while an Azure tenant is a type of container hosting organizational resources in Microsoft Azure Training. Multiple subscriptions might be linked within a single instance of an azure tenant, as this provides options for scalability management.
- Resource Groups: Resources in a subscription are grouped into resource groups. Resource groups give the administrator the ability to manage related resources, such as virtual machines, storage accounts, and networks, as a single unit, making it easier to deploy and monitor applications.
- Users and roles Users, Groups & Roles Users, in their groups are pivotal in governance while controlling accessibility over cloud sources. Azure AD permits you manage User Identities by creating users in roles plus define permissions- assure secure auth all services including other resources will attain.
- Azure resources -These constitute cloud services which the user, along with services to be rendered would provision together into a tenants database, amongst virtual machines and DB.
- Signing up for Azure To create an Azure Tenant, you need to first sign up for a Microsoft Azure account. This can be done by either first creating an account on the Azure portal or through the sign-up page on Microsoft’s site. You will enter your company name and country, among other details.
- Create a New Tenant: After you have created your Microsoft Azure account, you can create a new Azure Tenant by logging into the Azure portal and navigating to the Azure Active Directory section. From there, select “Create a new tenant,” and you will be guided through the process of setting up the tenant. This includes choosing your directory name, region, and other configuration settings.
- Configure Domain and Identity Providers: Once you create the tenant, you can set up custom domains, such as your organization’s email domain, and configure identity providers like Microsoft or third-party authentication providers. You can also enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security.
- Subscription Creation: In order to use Azure resources, you must first create one or more subscriptions. Subscriptions are tied to the tenant and define the billing model for your organization’s resources. To create and manage subscriptions, navigate to the Subscriptions section in the Microsoft Azure Analysis Services. You can assign subscriptions to different departments or environments, such as production, development, or testing.
- Add Users and Assign Roles: You now have a tenant set up from which you can start adding users to your Azure AD and assign roles depending on their respective access requirements. Users may be assigned different roles like Global Administrator, User Administrator, or Contributor whereby you determine how much access and permission users would get.
- Configure Resource Groups and Resources: After you have your tenant and subscriptions in place, you can create resource groups to organize and manage your resources efficiently. Resource groups help you maintain an organized cloud environment and simplify management tasks.
- RBAC: Make use of Azure Role-Based Access Control to set permission for the right users and groups. Only specific people with assigned permissions should access certain resources, and do some administrative tasks.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Enforce multi-factor authentication for all users to increase the security and limit unauthorized access to the system. MFA involves verifying identity by multiple methods other than just usernames and passwords, which is one more layer of protection added for the user to authenticate themselves.
- Resource Groups: Organize and manage related Azure Active Directory using resource groups. This simplifies management tasks, such as monitoring and resource deployment, and ensures that resources are grouped logically.
- Naming Conventions: Establish and adhere to consistent naming conventions for your resources, subscriptions, and resource groups. This ensures easy identification, organization, and management of resources across your tenant.
- Monitor and Audit Activity: Utilize Azure’s in-built monitoring and auditing tools to track user activities, resource usage, and security events within your tenant. Use alerts to inform administrators of possible security incidents or performance issues.
- Access permissions need to be reviewed at regular intervals; therefore, reviewing and updating roles and user permission ensures they reflect job responsibilities and should have users’ access rights revoked where applicable and privileges escalation handled.
These components work together to enable organizations to manage and scale their cloud resources securely, efficiently, and cost-effectively.
How Azure Tenants Work
Azure Tenants are built to offer a single management point for all the cloud resources and services within an organization. Upon signing up for an Azure account, you receive a unique tenant ID that will serve as the identifier for your organization’s Azure Active Directory, or Azure AD. The tenant ID is used to secure and organize your cloud resources, user access, and configurations. The basic function of an Azure Tenant revolves around Azure Active Directory, managing identities and authentication for the users, devices, and applications within the tenant. Azure Active Directory ensures that only authorized individuals can access resources, thereby providing central control over security and access policies.
Dive into Microsoft Azure by enrolling in this Microsoft Azure Training today.
One or more subscriptions are associated with every Azure Tenant. A subscription establishes the scope for your Azure services and resources, like virtual machines, storage accounts, or databases, and ties a specific billing model to them. Organizations may have several subscriptions under one tenant; this is what allows organizations to separate different environments, regions, or cost centers. Resources within the tenant are grouped into resource groups within which users can group and manage related Azure resources. Resource groups make it easy to deploy and manage applications, hence monitor and track services within the tenant. Besides these, Azure DNS Management can also be aligned with other Azure services such as, Azure Security Center and Azure Policy in order to ensure better governance, compliance, and security management across the overall organization.
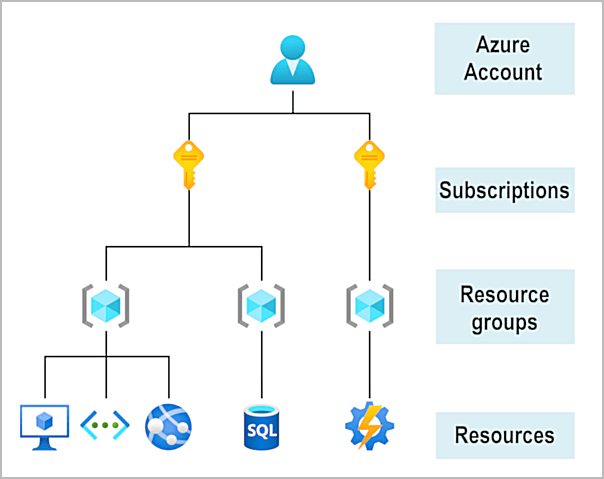
Difference Between Azure Tenant and Subscription
The terms “Azure Tenant” and “Azure Subscription” are sometimes used with the same meaning, but they refer to two separate concepts under the Azure platform. In summary, Microsoft Azure Training is responsible for identity and access management, while an Azure Subscription represents the container for cloud services and resources. A tenant can have multiple subscriptions, but a subscription can only belong to one tenant.
Setting Up an Azure Tenant
Ready to excel in Cloud Computing? Enroll in ACTE’s Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course and begin your journey today!
By following these steps, you can successfully set up and configure an Azure Tenant that suits your organization’s needs.
Use Cases of Azure Tenant
Azure Tenants are primarily used to handle identities, authentication, and access control within an organization. Organizations can easily manage their users’ access to applications, resources, and services both in the cloud and on-premises using Azure Active Directory (Azure AD). In addition, MFA and conditional access policies can be executed to boost security. Multi-Subscription Management Large organizations with different departments use multiple subscriptions within a single Azure Tenant to separate billing, resources, and environments. This approach allows businesses to scale and manage resources effectively while maintaining proper isolation between different areas of the business. The Azure Tenants are a central part of the hybrid cloud architectures. Organizations can integrate their on-premises Active Directory with Azure AD in order to provide a hybrid identity solution. The users can thus access both the on-premises and the cloud-based resources using the same credentials. Azure Tenants are required for managing compliance and governance across an organization’s cloud environment. With Azure Policy, Microsoft Azure Portal, and Azure Blueprints, administrators can enforce organizational standards, security configurations, and compliance requirements. With Azure Tenants, organizations can collaborate with external partners by sharing certain resources, like applications, through Azure AD B2B collaboration features. This is useful when managing access to joint projects or services shared with external stakeholders.
Boost your chances in Microsoft Azure interviews by checking out our blog on Microsoft Azure Interview Questions and Answers!
Best Practices for Managing Azure Tenants
The effective management of an Azure Tenant requires best practices in security, organization, and governance.
Conclusion
The basic building block of any organization’s Azure environment is the Azure Tenant. It acts as a centralized platform for managing identities, subscriptions, and resources within the cloud. Understanding the components and operations of an Azure Tenant can help organizations optimize their cloud infrastructure for security, scalability, and efficiency.Proper management and adherence to best practices with Microsoft Azure Training can help organizations streamline resource management, improve security, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. From managing multiple subscriptions to ensuring access control with Azure AD, tenants provide the foundation for secure and organized cloud environments.Understanding Azure Tenants will become key to business success in the cloud as more and more organizations are shifting into it, with an increased focus by IT administrators, business leaders, and cloud architects on proper and secure management of their cloud environment as the complexity is getting bigger with the ever-expanding and continuously increasing growth.





