
- Introduction
- What is Edge Computing?
- How Does Edge Computing Function?
- Key Advantages of Edge Computing
- Real-World Applications of Edge Computing
- Edge Computing Examples Across Industries
- Challenges in Implementing Edge Computing
- The Future of Edge Computing in a Connected World
- Conclusion
Introduction
As technology continues to evolve, the need for efficient data processing and faster decision-making is becoming more critical. In particular, edge computing is emerging as a solution to address the challenges posed by centralized cloud computing systems. From smart devices to autonomous vehicles, edge computing is making waves across various sectors, a key topic explored in Cloud Computing Courses to help professionals understand how edge computing integrates with cloud technologies to drive innovation and improve performance. In this blog, we will dive deep into what edge computing is, its applications, and practical examples of how it is revolutionizing industries. With real-time data processing at the edge, businesses can enhance performance, reduce latency, and optimize resource use. Edge computing is also reshaping how we approach scalability, security, and privacy in an increasingly connected world. The future holds immense potential for innovation as edge computing continues to evolve and integrate with emerging technologies.
To Earn Your Cloud Computing Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cloud Computing Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
What is Edge Computing?
At its core, edge computing refers to the practice of processing data closer to its source rather than relying on a centralized cloud infrastructure. It brings computation and data storage to the “edge” of the network, where the data is generated. By reducing the need to send vast amounts of data to distant cloud servers, edge computing provides faster processing, lower latency, and more efficient resource management. This model is especially beneficial for applications that require real-time data processing, such as smart devices, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation, and can be further optimized by Understanding Containers in Cloud Computing to enhance scalability and efficiency in deploying these applications across edge and cloud environments. Edge computing also improves bandwidth efficiency by minimizing the amount of data transmitted over the network. It enhances privacy and security since sensitive data can be processed locally without being sent to centralized cloud servers. Additionally, edge computing supports scalability, enabling businesses to handle increasing data volumes from IoT devices without overloading central cloud infrastructures.
How Does Edge Computing Function?
In edge computing, devices like sensors, cameras, or IoT devices capture and process data locally rather than transferring all of it to a central server or cloud platform. Data is produced by edge devices such as sensors, cameras, or machines in real-time. Instead of sending all the data to the cloud, processing happens locally on edge devices or intermediate servers placed closer to the data source, highlighting the Differences Between On-Premise and Cloud Solutions, where edge computing enables localized data processing, reducing latency and reliance on centralized cloud infrastructure. With minimal delay, actions are taken based on the processed data, such as sending alerts or triggering machinery adjustments. For long-term storage or further analysis, only relevant or summarized data is sent to the cloud. Edge computing reduces the amount of data transmitted to the cloud, optimizing bandwidth and reducing latency. It enables real-time decision-making and automation, which is crucial for applications like smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and industrial IoT.
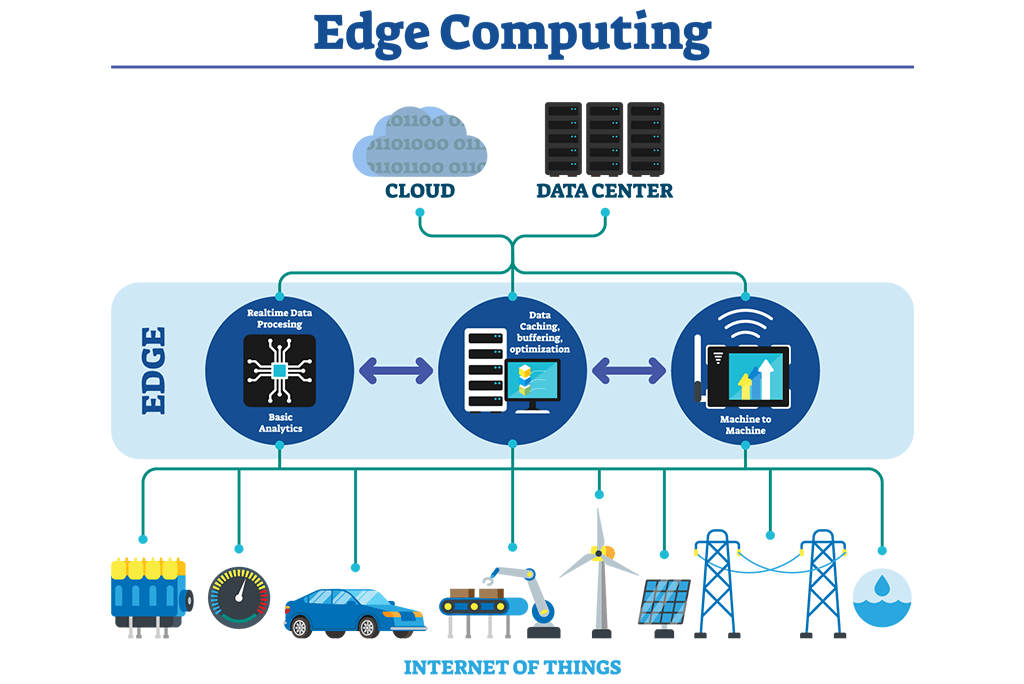
By processing data locally, edge computing also enhances security and privacy, as sensitive data can be kept on-site instead of being transmitted over networks. This distributed approach allows for greater scalability, as it can support a vast number of devices without overwhelming central systems. Additionally, edge computing improves system reliability, as local processing can continue even when connectivity to the cloud is interrupted. Additionally, edge computing improves system reliability, as local processing can continue even when connectivity to the cloud is interrupted. This decentralized model also minimizes the risk of data loss or downtime due to server failures. Edge computing supports faster response times, making it ideal for time-sensitive applications that require immediate action. Furthermore, the local processing allows for more personalized and context-aware experiences, improving user interaction in real-time. The result is a more agile, robust, and responsive computing environment across a wide range of industries.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Cloud Computing? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
Key Advantages of Edge Computing
Edge computing offers several compelling benefits that make it an attractive solution for modern technological demands:
- Reduced Latency: By processing data locally, edge computing minimizes delays, which is crucial for real-time applications.
- Efficient Bandwidth Usage:Instead of transmitting all data to the cloud, edge computing processes data locally, saving bandwidth and reducing transmission costs.
- Enhanced Security and Privacy: Data doesn’t have to travel across long distances, reducing exposure to potential security risks and breaches. Sensitive data can be kept local.
- Increased Reliability: Edge devices can continue to operate even if the network connection to the cloud is lost, providing greater resilience and uptime.
- Cost Savings: Edge computing helps reduce cloud storage needs and associated costs by processing data at the source, which is a key consideration in understanding Public, Private & Hybrid Cloud A Complete Guide, as it highlights how edge computing can complement cloud models to optimize data processing and storage across various environments.
- Scalability: Edge computing allows organizations to scale their systems more efficiently by distributing processing power across multiple devices, reducing the need for centralized infrastructure.
- Improved Data Quality: With real-time processing, edge computing ensures that data is more accurate and timely, enabling faster and more informed decision-making.
- Enhanced User Experience: By minimizing latency and ensuring faster responses, edge computing contributes to a smoother and more responsive user experience in applications like gaming, video streaming, and autonomous systems.
Real-World Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing is becoming an integral part of many industries that rely on real-time data and fast processing. Below are some of its key applications:
Internet of Things (IoT)
In the IoT ecosystem, edge computing allows devices like smart thermostats, security cameras, and industrial sensors to process data locally. This reduces the amount of data transmitted to the cloud and allows for quicker responses to changing conditions.
Examples:
- Smart homes (e.g., lights, locks, cameras)
- Wearable devices (e.g., fitness trackers, health monitors)
Self-Driving Cars and Transportation
Autonomous vehicles generate and process massive amounts of data from sensors, cameras, and GPS systems. Edge computing allows for immediate processing, ensuring the vehicle can make decisions in real time, such as avoiding collisions or adjusting speed.
Examples:
- Real-time navigation
- Adaptive cruise control
- Obstacle detection and avoidance
Smart City Initiatives
Edge computing plays a critical role in the development of smart cities by enabling local processing of data from sensors placed throughout urban environments, a concept that is explored in Cloud Computing Courses to help learners understand how edge and cloud computing work together to enhance urban infrastructure and services.
Examples:
- Smart traffic lights and parking systems
- Public safety surveillance
- Environmental monitoring (e.g., air quality sensors)
Healthcare Innovations
In healthcare, edge computing is essential for monitoring patients in real time, especially for wearable devices that track vital signs. The local processing ensures that doctors and patients receive immediate feedback without waiting for cloud processing.
Examples:
- Real-time patient monitoring
- Wearable health devices (e.g., ECG, glucose monitors)
- Remote surgeries and telemedicine
Retail and E-commerce Enhancements
Retailers are leveraging edge computing to enhance customer experiences, improve inventory management, and personalize recommendations based on real-time data collected from customers in stores.
Examples:
- In-store personalized recommendations
- Smart inventory management systems
- Customer behavior analytics
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cloud Computing by Enrolling in Our Cloud Computing Masters Course.
Edge Computing Examples Across Industries
Smart Home Technologies
Smart home devices such as voice assistants, smart thermostats, and security cameras rely on edge computing to make immediate decisions without the need for cloud-based processing. For example, a smart thermostat can adjust room temperature based on local environmental conditions, providing immediate feedback.
Industrial IoT Applications
In industries like manufacturing and logistics, edge computing allows for faster analysis of machine data, reducing downtime, improving performance, and predicting equipment failures before they happen. Local edge devices process real-time data from machines, optimizing operations without cloud delays.
Security Surveillance Systems
Video surveillance systems use edge computing to analyze camera feeds locally, detecting anomalies, and immediately triggering alarms. This minimizes the time it takes to detect security threats and reduces the bandwidth required to transmit video footage to the cloud.
Virtual and Augmented Reality
AR/VR applications require ultra-low latency to provide users with a seamless experience. Edge computing can process data at the source, providing the necessary performance for immersive experiences without cloud dependency.
Autonomous Vehicles
Edge computing is crucial for autonomous vehicles, as it allows them to process sensor data in real-time, enabling immediate decision-making for safe navigation, a concept that aligns with Understanding Private Cloud Computing by showcasing how localized computing resources can enhance performance and security in specialized environments like autonomous vehicle systems.
Healthcare and Remote Monitoring
In healthcare, edge computing supports real-time monitoring of patient data, enabling quicker responses to medical emergencies. Devices like wearables can process health metrics locally, providing instant alerts to both patients and healthcare providers without cloud delays.
Smart Cities
Edge computing enhances smart city infrastructure by processing data from various sensors in real-time, such as traffic monitoring systems, waste management sensors, and public safety cameras. This enables quicker responses and more efficient urban management.
Retail and Customer Experience
In retail, edge computing enables personalized customer experiences by analyzing data from in-store sensors, kiosks, or smart shelves. This allows for real-time inventory tracking, dynamic pricing, and personalized promotions, improving overall customer satisfaction.
Challenges in Implementing Edge Computing
While edge computing provides numerous benefits, it also comes with certain challenges. Decentralized systems can introduce new vulnerabilities if edge devices aren’t properly secured. Managing and maintaining numerous edge devices across a wide geographical area can be complex and resource-intensive. Ensuring data consistency between local edge devices and the cloud can be difficult, especially when devices are disconnected from the network. Scaling edge computing networks to accommodate a growing number of devices can be challenging, particularly when managing resources and ensuring efficient operation across a large system. Edge computing involves processing sensitive data locally, raising concerns about data privacy and compliance with regulations such as GDPR. Ensuring proper encryption and secure data handling at the edge is critical to protect user information.

Edge devices are often distributed over vast geographical areas, and their reliability depends on the quality of local network connections. Network outages or instability can impact real-time data processing and system performance.With a wide variety of edge devices from different manufacturers, ensuring that they work seamlessly together can be challenging. Compatibility issues between devices and platforms can complicate deployment and maintenance.Many edge devices operate in remote or power-constrained environments, making energy efficiency a crucial consideration. Ensuring that devices consume minimal power while maintaining performance is a significant challenge in edge computing systems.
The Future of Edge Computing in a Connected World
- The future of edge computing looks promising, with the increasing adoption of technologies like 5G and AI, which will play a crucial role in shaping Cloud Deployment Models by enabling more efficient data processing and enhancing the integration of edge computing with cloud environments.
- The combination of 5G’s ultra-low latency and edge computing’s ability to process data locally will enable even faster, more reliable applications.
- Moreover, the integration of AI and machine learning at the edge will enhance the capabilities of edge devices, making them more intelligent and capable of handling complex tasks.
- As industries continue to expand their use of IoT and smart technologies, edge computing will become more vital in ensuring fast, efficient, and secure data processing.
- Whether it’s in healthcare, transportation, or manufacturing, edge computing is set to play a central role in shaping the future of our connected world.
- As edge computing continues to evolve, the need for robust security measures will become increasingly critical to safeguard sensitive data processed locally.
- The expansion of 5G networks will further accelerate the deployment of edge computing solutions, providing faster connections and enabling real-time decision-making for applications in various sectors.
- With advancements in hardware and software, edge devices will become more powerful, capable of handling even more sophisticated tasks without relying on the cloud.
- Additionally, the growing demand for autonomous systems and real-time analytics will push the boundaries of edge computing, making it a cornerstone of the next wave of technological innovation.
- As a result, edge computing will not only transform industries but also enable new, previously unimaginable use cases, further enhancing our digital ecosystem.
Go Through These Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer to Excel in Your Upcoming Interview.
Conclusion
Edge computing is rapidly transforming how data is processed, stored, and analyzed, offering significant benefits such as reduced latency, improved security, and enhanced performance. From IoT and autonomous vehicles to healthcare and smart cities, edge computing is revolutionizing industries by enabling real-time decision-making and reducing reliance on centralized cloud systems. As the technology matures and 5G networks take hold, edge computing is poised to become even more integral to the digital landscape, driving innovation and efficiency across sectors. With the ability to process data locally, edge computing also helps minimize bandwidth usage, making it ideal for remote or resource-constrained environments, a concept that is thoroughly covered in Cloud Computing Courses to help professionals understand its impact on modern cloud architectures and IoT applications. The integration of AI and machine learning at the edge will further amplify its potential, allowing devices to become smarter and more autonomous. As edge computing continues to expand, it will play a pivotal role in supporting the next generation of connected devices and services, ensuring a more responsive and scalable digital ecosystem.





