
- Introduction
- Grid computing: what is it?
- Important Features of Grid Computing
- Cloud computing: what is it?
- Important Features of Cloud Computing
- A Comprehensive Comparison of Grid and Cloud Computing
- Important Distinctions Between Cloud and Grid Computing
- Conclusion
Introduction
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources, offering flexibility, scalability, and easy management through a pay-as-you-go model. It is particularly suited for applications that require rapid scaling and easy access from anywhere, with the infrastructure managed by third-party providers. On the other hand, grid computing focuses on harnessing the power of multiple distributed systems to work collaboratively on large-scale computational tasks, often for scientific or research purposes. Cloud Computing Course specialized network and is optimized for parallel processing of complex jobs. While cloud computing prioritizes accessibility and cost-effectiveness, grid computing emphasizes high-performance computing for intensive, resource-heavy tasks. By understanding these differences, organizations can better leverage each technology to meet their specific needs.
Grid computing: what is it?
Grid computing enables the distribution of large workloads across multiple machines, accelerating execution by parallelizing tasks. This is particularly effective in fields like climate modeling, molecular research, and big data analysis. Additionally, it enhances fault tolerance by redistributing tasks during system failures, ensuring continuous processing. Grid computing allows organizations to maximize existing infrastructure, optimizing resource allocation without needing new hardware investments. Although Master Docker Entrypoint can be more complex to set up than cloud computing, grid computing provides a powerful solution for specialized tasks requiring immense computational power. Grid computing also supports collaborative efforts by allowing multiple organizations or institutions to contribute resources to a shared computational task. This collective approach enables access to vast amounts of computational power, making it feasible to tackle problems that were previously unattainable. Furthermore, grid computing offers flexibility in workload distribution, allowing tasks to be allocated based on available resources, optimizing efficiency and performance across the network.
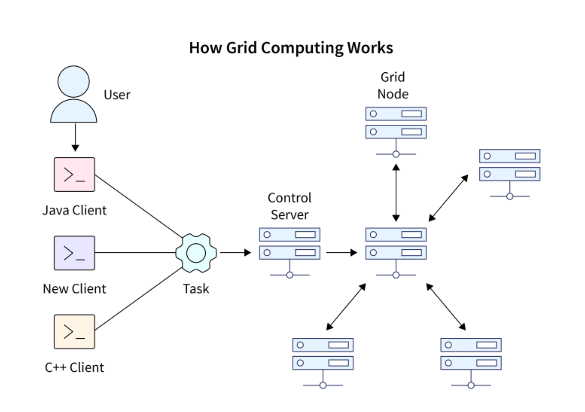
Important Features of Grid Computing
- Resource Sharing: Enables multiple groups or organizations to share computational resources, such as processing power, storage, and networking, efficiently.
- High Performance: Leverages the combined processing capabilities of multiple systems to execute complex computations at a much faster rate.
Learn the fundamentals of Cloud Computing with this Cloud Computing Online Course .
- Parallel Processing: Breaks down complex tasks into smaller sub-tasks, which are processed simultaneously across multiple systems, increasing efficiency and reducing execution time.
- Scalability: Allows for the addition of more resources or systems to the grid, enhancing its overall performance as demand grows.
- Load Balancing: Distributes workloads evenly across available resources to ensure that no single system is overburdened, improving system utilization.
- Fault Tolerance: Ensures the system can continue functioning even if some nodes fail, by redistributing tasks to other available systems in the grid.
- Cost Efficiency: Utilizes existing infrastructure to perform large-scale tasks, minimizing the need for expensive dedicated supercomputers or servers.
- Distributed Data Processing: Allows Azure Data Box Secure Data Transfer Solution to be processed across various locations, improving the accessibility and speed of data retrieval.
- Specialized Networks: Requires a dedicated, high-speed network to interconnect the systems and manage the communication between them effectively.
- Dynamic Resource Allocation: Provides the ability to allocate resources based on real-time demand, optimizing performance and ensuring that resources are used efficiently.
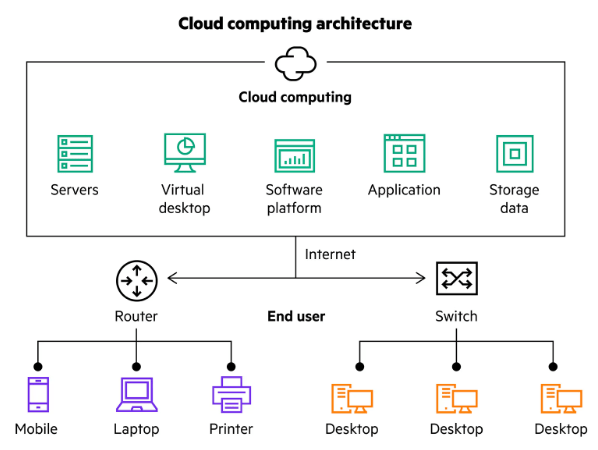
- On-Demand Services: Customers only pay for the resources they use and can access them as needed, providing flexibility and cost savings.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Resources can be easily scaled up or down based on demand, allowing businesses to adjust as needed without overprovisioning.
- Centralized Management: Cloud services are managed and maintained by third-party vendors, reducing the burden on businesses and ensuring efficient operation.
- Easy to Use: Cloud platforms typically offer simple-to-use APIs or web interfaces that make it easy to set up, manage, and maintain resources.
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud computing removes the need for significant upfront investments in physical hardware, as users only pay for what they actually use.
- High Availability and Reliability: Cloud providers implement redundant systems and backup mechanisms to ensure services remain available with minimal downtime.
- Security: Robust security measures, including encryption, Azure SSO to Secure And Scalable Authentication, and access control, are implemented to protect data and maintain compliance with industry standards.
- Automatic Software Updates: Cloud services automatically handle software updates and patches, ensuring users always have the latest features and security enhancements.
- Global Accessibility: Cloud services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, facilitating remote work and global collaboration.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud providers often include disaster recovery features, enabling businesses to recover from system failures quickly and efficiently.
Unlock your potential in Cloud Computing with this Cloud Computing Online Course.
Cloud computing: what is it?
Cloud computing enables users to quickly scale resources up or down based on demand, making it ideal for dynamic applications such as web hosting, software development, and data storage. It offers a wide range of services, including Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), allowing businesses to choose the most suitable solution for their needs. Unlike grid computing, which focuses on distributing tasks across multiple machines for high-performance computing, Cloud Computing Course away much of the complexity, providing users with a simplified, user-friendly interface to manage resources. Security and data privacy are also a priority for cloud providers, who implement advanced encryption techniques and strict access controls to safeguard data. Cloud services enable businesses to innovate faster and focus on core competencies without the burden of managing physical infrastructure. Additionally, the global reach of cloud computing allows users to access services and data from anywhere in the world, further enhancing collaboration and operational efficiency.
Take charge of your Cloud Computing career by enrolling in ACTE’s Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course today!
Important Features of Cloud Computing:
A Comprehensive Comparison of Grid and Cloud Computing
| Feature | Grid Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A distributed computing paradigm that solves complex issues by utilizing several separate systems. | A service approach in which online computing resources are made available whenever needed |
| Resource Ownership | Resources are owned by several separate organizations or entities. | Centralized cloud service providers own and manage the resources. | Resource Sharing | Entails pooling resources from many businesses or people. | In a centrally controlled resource pool, customers only pay for the resources they utilize. |
| Primary Focus | Scientific simulations and other specialized jobs require high-performance computing (HPC) | Hosting and general-purpose computing for a range of services and Applications of Cloud Computing. |
| Scalability | Restricted by the system’s architecture and the quantity of associated resources. | Extremely scalable; users can swiftly adjust resources to meet demand. |
| Service Model | Users frequently set up or maintain the system individually; there is no standard service model. | Pay-per-use, on-demand business model using APIs and managed services. |
| Cost Structure | Because of hardware setup, resource management, and maintenance, it is frequently more expensive. | Pay-as-you-go models are frequently more affordable for little or medium-sized requirements. |
| Accessibility | A specialized network is used to access resources, and typically, particular configurations are needed. | Resources with user-friendly interfaces are readily available online. |
| Flexibility | Less adaptable; resources are made especially to complete predetermined tasks. | Extremely adaptable; customers can set up a range of services and apps. |
| Example Use Cases | Weather forecasting, data-intensive applications, simulations, and scientific research. | Storage, machine learning, web hosting, software as a service (SaaS), and more. |
Boost your chances in Cloud Computing interviews by checking out our blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers!
Important Distinctions Between Cloud and Grid Computing
Grid computing requires users to manage their own infrastructure, often for high-performance tasks like scientific simulations, while cloud computing offers managed, on-demand resources for a variety of applications, from hosting websites to enterprise software. Grid computing has limited scalability and higher initial costs, requiring specialized infrastructure, whereas cloud computing is highly scalable with a flexible pay-as-you-go pricing model. Cloud services also simplify user experience, offering reduced management effort, while grid computing gives more control but needs complex setup and maintenance. Cloud providers handle infrastructure, ensuring performance, fault tolerance, and accessibility with built-in redundancy and global collaboration features, making it user-friendly and cost-effective. Grid computing is ideal for resource-intensive tasks that need distributed computing power, while cloud computing supports a broader range of performance needs, from basic hosting to complex enterprise operations. The setup complexity of grid computing requires specialized knowledge, whereas cloud computing offers a simpler, AWS Outposts Powering Hybrid Cloud pre-configured deployment process. Grid computing typically involves owning or managing the physical infrastructure, leading to significant capital investment, while cloud computing eliminates this by outsourcing infrastructure to third-party providers. Cloud services provide automatic updates and maintenance, reducing the need for manual intervention. Grid computing, on the other hand, requires careful planning and manual configurations for fault tolerance and disaster recovery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while both cloud computing and grid computing offer powerful, scalable resources, they serve distinct purposes. Cloud computing stands out for its flexibility, scalability, and ease of use, making it ideal for general-purpose applications and on-demand services with low overhead. Cloud Computing Course offers cost efficiency, centralized management, and broad access to a variety of services, catering to businesses and individuals who need quick and dynamic computing resources. On the other hand, grid computing excels in high-performance, data-intensive scenarios, such as scientific simulations and research, where specialized computational power is required. It involves a more complex setup and is best suited for tasks demanding intense processing over extended periods. Ultimately, the decision between the two depends on specific needs: cloud computing is perfect for convenient, versatile tasks, while grid computing is the better choice for specialized, resource-demanding activities.





