
- Introduction to Cloud Computing
- Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Challenges in Cloud Computing
- Future Trends in Cloud Computing (2025)
- Conclusion
Cloud computing offers several key characteristics, including scalability, flexibility, cost-efficiency, and accessibility. These features enable businesses to quickly adapt to changing demands, reduce infrastructure costs, and improve operational efficiency by outsourcing data storage and processing to third-party providers. Cloud Computing Courses also enhances collaboration by allowing remote access to applications and data, fostering innovation and faster decision-making. The business impact includes improved agility, reduced time to market, enhanced customer experience, and a more competitive edge in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cloud Computing Certificate? View The Cloud Computing Online Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of different computing services like storage, processing power, and software over the internet on demand. Business and personal computing no longer have to physically house or operate their own data centers or servers using cloud computing, instead accessing those services over the internet, sometimes called “the cloud.” It also brought an end to capital expenditure in that cloud services are usually a pay-per-use model, a concept that is integral to Data Movement and Transformation in Azure Data Factory, where efficient, cost-effective data management is a key benefit of cloud solutions. Users scale their resources up or down, so they pay for what they use instead of shelling out the huge amounts that could be involved with the hardware and software. The same cloud can be used for collaboration, ease of access, and even faster application deployment. As cloud computing technologies evolve, businesses are leveraging them for tasks such as data storage, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and Internet of Things (IoT) integration. There are public clouds, private clouds, and hybrid clouds, each with a different level of control, security, and management. The advancement has made the operation of more companies move their business to the cloud, and it is a vital component of modern business infrastructure. Organisations may consider cloud computing fully if it means understanding its characteristics, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing:
Several key characteristics that define cloud computing and are different from other traditional computing models:
- On-demand Self-service: The service provided by the cloud for users to provision, manage, and monitor their own computing resources without involving the cloud provider directly is similar to the flexibility and control offered in the Guide to GitLab Features & Setup, where users can manage their repositories, pipelines, and integrations independently. It includes the self-provisioning of virtual machines, storage, software applications, among others.
- Broad Network Access: Cloud services are accessible over the internet, and they support a wide range of devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets. This characteristic allows users to connect and use cloud resources from virtually anywhere in the world, provided they have internet access.
- Resource Pooling: Cloud providers pool their computing resources (e.g., storage, processing power, memory) to serve multiple customers, utilizing multi-tenant models. This dynamic resource allocation enables efficiency, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Fast Elasticity: Cloud services are structured to scale according to customer demand. Whether it’s during peak utilization times or low-traffic periods, users could dynamically adjust resources on-the-fly without involving manual intervention, similar to how Docker Containers on AWS allow for scalable and efficient deployment of applications in the cloud environment. This elasticity ensures that organizations stay agile and cost-effective.
- Measured Service: The cloud computing resources are metered and billed according to usage. Clients are charged according to their consumption, which can be a huge cost-saving factor for businesses. The measured service allows for pay-as-you-go pricing models, where users only pay for the resources they actually use, whether that’s storage, bandwidth, or compute power.
- Multi-tenancy: Cloud services are shared among several customers, or tenants, making it possible to efficiently utilize resources. Data for each user is logically isolated, ensuring security and privacy in the same physical infrastructure.
To Earn Your Cloud Computing Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cloud Computing Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
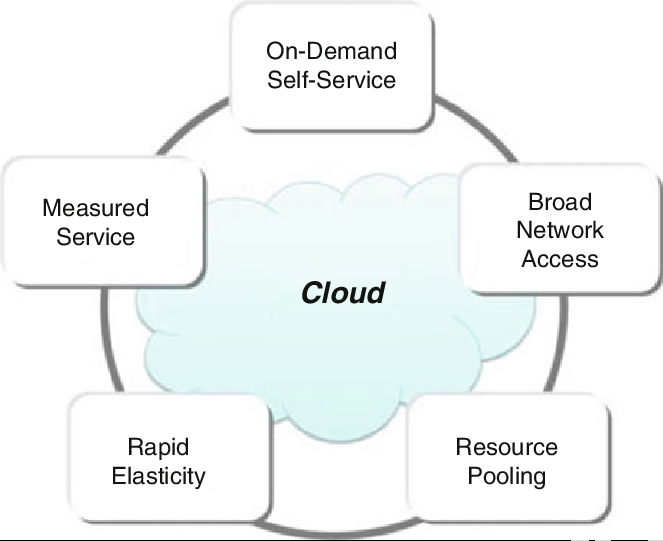
All these features help organizations use cloud services effectively to provide flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cost Efficiency traditional IT infrastructure calls for a huge amount of upfront investment in hardware, software, and maintenance. Cloud computing does away with these capital expenses as it employs a pay-as-you-go model where users can pay only for whatever resources they require. They can scale up or scale down the resource usage as needed. The model will both save financial outlay and enhance operational efficiency. Scalability Cloud Computing Courses allows businesses to scale their IT resources based on demand. A business may want to expand its infrastructure for the launch of a new product or scale down resources when the business is slow. It is easy to do so using the cloud, and scalability guarantees that organizations will always have the right resources at the right time. Flexibility and Agility Cloud services provide unprecedented flexibility, where organizations can access a wide variety of applications, tools, and infrastructure on-demand.
This flexibility helps businesses adapt quickly to market changes and innovate faster. Enhanced Collaboration Cloud computing allows teams to work together in real-time, irrespective of their location. With cloud-based applications like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365, users can collaborate on documents, projects, and tasks from anywhere, thereby enhancing productivity and efficiency. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Most cloud providers offer integrated disaster recovery solutions, which safeguard data from loss. In the case of hardware failure or disaster, data can be recovered in a matter of time from the cloud, and there will be minimum disruption to the business operations. Automatic Software Upgrades of the software are undertaken by the providers of the cloud services, thus upgrading the systems all the time, which will include recent features and the security patches in place. No more hassle is put on an organization to undertake update management and implementation. All this makes cloud computing a powerful tool for contemporary businesses to achieve optimal performance without costs, promote collaboration, and innovation.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cloud Computing by Enrolling in Our Cloud Computing Masters Course.
Challenges in Cloud Computing
While cloud computing offers many advantages, it comes with several challenges that businesses need to address to maximize its potential.
- Security and Privacy: Security continues to be a major issue when organizations implement cloud computing. Placing sensitive information in a third-party data center exposes them to risks of access by unauthorized individuals, data breach, and cyberattacks. Cloud providers should maintain strong security protocols such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audit. The other issue that creates complexity for companies dealing with sensitive information is regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. .
- Downtime and Service Reliability: Cloud services are dependent on the provider’s infrastructure, and service outages or downtime can disrupt business operations. While most cloud providers offer service level agreements (SLAs) to guarantee uptime, unexpected issues such as hardware failures, network disruptions, or natural disasters can cause temporary service interruptions. Organizations should have contingency plans in place, including backup systems and disaster recovery strategies.
- Compliance and Legal Issues: One of the major issues while using cloud services is compliance with industry regulations and standards, a challenge that can be addressed through solutions like AWS Transit Gateway Simplifying Network Connectivity, which ensures secure and compliant network configurations across multiple cloud environments. Data storage and protection laws vary across different regions. An organization should ensure that the cloud provider complies with all the relevant regulations, especially in the case of sensitive or personal data. In such cases, non-compliance may lead to hefty fines and legal consequences.
- Vendor Lock-In: Because proprietary technologies may make it difficult to move workloads between providers, vendor lock-in is another concern when selecting a cloud provider. Organizations might find themselves in a position of paying higher prices, with little flexibility to change contract terms if needed. Organisations should factor this into their decision-making and ensure that they have an exit strategy in place.
- Latency and Performance: In cloud services, internet connectivity will be used to access the information. Poor internet connectivity or the instability of connectivity can cause some latency issues, and applications where some real-time processing is required will be degraded from performance when operating in the cloud. Organizations need to evaluate the likelihood of cloud-related latency impacting business operations and could use hybrid clouds or edge computing for applications sensitive to latency requirements.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing (2025)
Cloud computing will continue to change its face. A few major trends are predicted to shape the face of cloud technology by 2025.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing will trend as companies want real-time data processing. Data doesn’t need to be sent to remote cloud servers; instead, the edge computing process lets data process near the source of the data—IoT devices or distant sensors. It reduces latency and ensures true-time data processing, essential for applications such as autonomous vehicles, industrial IoT, and smart cities.
- Artificial Intelligence and Cloud Integration: The more AI and machine learning emerge to integrate with cloud computing, the more AI-driven cloud services we should expect, which can be efficiently managed and secured using tools like the Guide to AWS SSO, ensuring seamless and secure access to these advanced services. The cloud will be enhanced with tools and services for automation, predictive analytics, and data analysis, allowing businesses to take advantage of AI without requiring deep in-house expertise.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: The Organizations are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud environments, combining on-premises data centers with private and public clouds. This approach provides greater flexibility, resilience, and risk mitigation by avoiding dependence on a single cloud provider.
- 5G and Cloud Synergy: The rollout of 5G networks will bring better network speed and bandwidth to cloud computing, which will improve the delivery of cloud services more reliably and more rapidly on applications including data-intensive ones such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and real-time video streaming.
- Quantum Computing: Though it is still in its infancy, there is a potential role for quantum computing in the future of cloud computing. Quantum cloud computing services may help businesses solve complex problems in areas like cryptography, drug discovery, and optimization that normal computers cannot.
Are You Preparing for Cloud Computing Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Conclusion
It fundamentally changed how business operates: Cloud computing gives unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. In cloud computing, three main features-the on-demand self-service, resource pooling, and rapid elasticity-endow organizations with streamlined operations to innovate rather than managing infrastructure. There are, however, many challenges associated with the vast adoption of cloud computing. The key concerns in business about moving to the cloud include issues such as security, compliance, and vendor lock-in. Organization will be able to access the full benefits of cloud computing by addressing the above-mentioned concerns and ensuring that the right measures are in place. Cloud computing will evolve in the future with improvements in edge computing, AI, and hybrid cloud strategies. All these trends promise to enhance the capabilities of cloud services and enable organizations to optimize their workflows, improve decision-making, and stay competitive in an increasingly digital world. Cloud Computing Courses has become the necessary tool for the modern business world. With this in mind, organizations need to understand its characteristics, benefits, and challenges so that they can harness the power of the cloud to drive growth and innovation. As cloud technologies continue to evolve, companies that embrace these advancements will be well-positioned for success in the future.





