
- What is Hybrid Cloud?
- How Does a Hybrid Cloud Work?
- The Core Components of Hybrid Cloud Architecture
- Key Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Computing
- When to Choose a Hybrid Cloud Platform
- Understanding Public vs. Private vs. Hybrid Clouds
- Common Hybrid Cloud Use Cases
- Challenges and Considerations for Hybrid Cloud Adoption
- The Future of Cloud is Hybrid
What is Hybrid Cloud?
In today’s fast-moving digital world, businesses must be quick, safe, and budget-friendly. Picking the right IT setup is a key choice. For years, the choice was clear stick with a safe on-premise private cloud or take advantage of the scalability of the public cloud. Today, though, there’s a third option that combines the best features of both: hybrid cloud. To understand how hybrid architectures work and how to deploy them effectively, explore Cloud Computing Training a hands-on course that covers cloud models, virtualization, orchestration, and real-world strategies for building secure, scalable cloud environments. This is the Hybrid Cloud, a smart approach that is changing how companies handle their data and applications. It’s no longer about selecting one option over the other; it’s about building a unified, flexible space that promotes innovation and growth.
How Does a Hybrid Cloud Work?
Hybrid cloud computing mixes a private cloud with public cloud services. This approach offers flexibility, cost-efficiency, and better control over sensitive data. To understand how virtualization supports this model and enables dynamic resource allocation, explore Hybrid Cloud & Hypervisors for Scalability a focused guide that explains how hypervisors manage virtual machines, balance workloads, and scale infrastructure across hybrid environments.
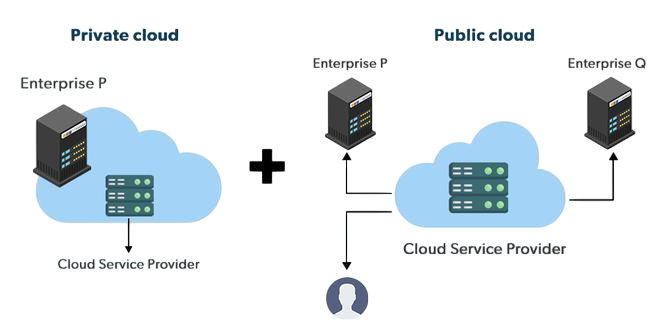
This setup lets data and apps share easily. A company might run its main apps in a private cloud but use a public cloud for more power when needed. This cloud bursting helps handle traffic spikes without buying new hardware. Good planning is important to keep everything talking securely.
Learn how to manage and deploy cloud services by joining this Cloud Computing Online Course today.
The Core Components of Hybrid Cloud Architecture
A good hybrid cloud setup involves integrating key working parts, not just linking two clouds. Knowing these parts can help show how the whole system works. To understand the foundational differences that shape hybrid strategies, explore Public Cloud vs Private Cloud a detailed comparison that explains infrastructure control, scalability, security, and cost models to help you design balanced, high-performance cloud environments.
- Public cloud infrastructure: A third-party provider, like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud, hosts this part of your setup. It has large scalability, pay-as-you-go pricing, and many services. It works well for customer apps, development, and handling different workloads.
- Private cloud infrastructure: This is your on-site data center or a cloud environment hosted privately. You have total control over hardware, security, and data regulation. It is good for storing private data, running important apps, and meeting tough compliance needs.
- Safe network connection: The link between your public and private clouds is important. Usually, a secure link, like a Virtual Private Network (VPN) or a dedicated private line (like AWS Direct Connect), creates this. It makes sure data moves between areas fast and safely.
- Single management platform: To keep things organized, a hybrid cloud platform needs one management console. This allows IT teams to handle, automate, and watch resources across both public and private areas from a central spot. This simplifies operations.
Key Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Computing
Because it has many good things, organizations are quickly using a hybrid cloud model. Control mixed with flexibility gives a strong advantage. Here are some good parts of cloud computing that come with a hybrid approach: scalability, cost optimization, and secure data segmentation. To understand how open-source platforms support these benefits, explore OpenStack in Cloud Computing a practical guide that explains how OpenStack enables private cloud control, integrates with public services, and orchestrates resources across hybrid environments.
- More Flexibility: A hybrid cloud lets you put workloads where they work best. You can make and test new things in the public cloud to be fast. Then, you can put them in the private cloud to be safe. This lets your business be quick at making new things.
- Better Security: You can keep important information like customer data and financial records on your own private infrastructure. Then, use the public cloud for things that are not as important. This way, you can follow rules like HIPAA or GDPR and still get the good things from the cloud.
- Better Cost: Making a private data center to handle a lot of demand can cost much. With a hybrid model, you can use the public cloud and pay for what you use to handle extra traffic. This means you only pay for extra things when you need them, saving money on IT.
- More Reliable: By putting workloads in different cloud places, you stop downtime from one thing failing. Also, you can use the public cloud to grow as much as you need. This makes sure your services are always ready for customers, no matter how much they need.
- Management Difficulty: Handling resources in both public and private clouds can be tricky. IT departments might find it hard to keep track and stay in control if they lack a single platform to manage the cloud.
- Network and Security Issues: The link between your private and public setups could be easily attacked if it isn’t secure. It’s key to have consistent security rules and strong encryption across both clouds.
- Integration Expenses: The initial cost of things like network hardware and integration tools can be a large investment. Groups should include these early costs when figuring out how much the whole thing will cost them.
- Lack of Skills: Running a hybrid setup means having a team that knows about both local infrastructure and public cloud platforms. Some companies might have problems finding and keeping people who have skills in both areas.
Unlock your potential in Cloud Computing with this Cloud Computing Online Course .
When to Choose a Hybrid Cloud Platform
Hybrid cloud platforms work well in many business situations but aren’t a single solution for everyone. They are quite helpful for groups dealing with workloads that change a lot. A good example is an online store whose website traffic jumps a lot when there are holiday sales. To learn how to manage such fluctuating demand with scalable infrastructure, explore Cloud Computing Training a hands-on course that covers auto-scaling, load balancing, and cloud elasticity to ensure performance and cost-efficiency during traffic surges. These platforms are also good if a company has to follow strict rules about data and privacy, like in health care or finance. Plus, companies that have already spent a lot on their own hardware can use a hybrid approach to move to the cloud little by little, which doesn’t stop their current systems from working.
Understanding Public vs. Private vs. Hybrid Clouds
To appreciate the hybrid cloud approach, it is important to know how it is different from other options. A public cloud is like renting an apartment. You share resources and pay for space and utilities. This pay-as-you-go model works best when infrastructure can be provisioned, scaled, and managed automatically. To learn how automation supports this efficiency, explore Infrastructure as Code (IaC) in Cloud a foundational guide that explains how declarative templates, version control, and orchestration tools help streamline cloud resource management across dynamic environments. A private cloud is like owning a house; you have control and privacy but must handle all maintenance and costs. The hybrid cloud offers the benefits of both, like owning a house (private cloud) but renting a storage unit nearby(public cloud) for items you don’t always need inside. This balance provides the security and control of ownership with the scalability and affordability of renting.
Looking to master Cloud Computing? Sign up for ACTE’s Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course and begin your journey today!
Common Hybrid Cloud Use Cases
Hybrid models show their real value when put to use. Disaster recovery is a very common application of hybrid cloud computing. Instead of keeping up a second data center, which can be expensive, companies can copy their important data and apps to a public cloud. This gives them a dependable and cheaper backup option. To learn how cloud platforms like AWS simplify this process with built-in redundancy and global infrastructure, explore AWS Basics Cloud Computing a beginner-friendly guide that covers cloud storage, data replication, and disaster recovery strategies for modern businesses. Often, companies will also split up their workloads. They might keep their SAP and Oracle workloads on a private cloud, while putting their websites and mobile apps on the public cloud. This way, each app can run where it works best, which makes things run better and keeps things safer.
Boost your chances in Cloud Computing interviews by checking out our blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers!
Challenges and Considerations for Hybrid Cloud Adoption
Although there are clear advantages, moving to a hybrid cloud setup also brings its own problems, which are worth knowing about beforehand. These include integration complexity, security management, and cost tracking across environments. To prepare for these challenges and build the right expertise, explore Cloud Computing Skills a career-focused guide that covers architecture design, automation tools, and governance strategies essential for navigating hybrid cloud ecosystems.
The Future of Cloud is Hybrid
The Hybrid Cloud is not just a trend, it’s a basic change in how businesses handle their IT. It recognizes that one solution doesn’t fit all for every task. Different workloads, compliance needs, and performance goals require tailored infrastructure choices. To explore how cloud platforms support this flexibility through hybrid, public, and private models, check out Cloud Computing Training a practical course that covers multi-cloud strategies, service orchestration, and deployment techniques for building adaptable, enterprise-ready cloud environments. By mixing the security of a private cloud with the flexible ability of a public cloud, companies can build an infrastructure that fits their exact needs. This flexibility lets them change with the market, control costs, and protect important data. As tech changes, the hybrid approach offers a useful way to make sure businesses are ready for the future.





