
- Introduction to Cyber Extortion
- Common Types of Cyber Extortion
- Ransomware Attacks and Extortion
- Doxxing and Threatening Disclosure
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
- Phishing and Identity Theft Extortion
- Psychological Manipulation in Cyber Extortion
- Legal and Financial Impacts of Cyber Extortion
- Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cyber Extortion
Cyber extortion is a form of digital crime in which attackers demand money or other forms of compensation from individuals, organizations, or governments by threatening to cause harm, disrupt services, or expose sensitive data. These threats are carried out through sophisticated cyberattacks, using malware, social engineering, or exploiting vulnerabilities. Cloud Computing Course has become a significant concern due to the rise in digital reliance, exposing critical infrastructure, businesses, and individuals to risks. Key characteristics of cyber extortion include anonymity (often achieved through cryptocurrencies and the dark web), global reach, and the ability to inflict widespread damage. With the rise in remote work and cloud storage, the attack surface has expanded, making cybersecurity a critical priority for individuals and organizations.
Gain in-depth knowledge of Cloud Computing by joining this Cloud Computing Online Course now.
Common Types of Cyber Extortion
Cyber extortion manifests in various forms, each leveraging specific tactics to coerce victims into paying ransom or complying with demands in Microsoft Azure Analysis Services. Common types include:
- Doxxing: Threatening to release sensitive personal or organizational data.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Disrupting services until a ransom is paid.
- Ransomware Attacks: Encrypting files and demanding payment for decryption.
- Phishing and Identity Theft Extortion: Exploiting stolen credentials to demand money.
- Cyberbullying and Psychological Manipulation: Using fear tactics to manipulate victims.
- How Ransomware Works: Typically delivered via phishing emails, infected downloads, or software vulnerabilities. Once executed, the ransomware locks critical files and displays a ransom note.
- Famous Ransomware Attacks: Examples include WannaCry, Petya, and REvil attacks, which caused billions of dollars in damages globally.
- Preventing Ransomware: Effective measures include maintaining regular backups, updating systems, employing endpoint protection, and training employees in recognizing phishing attempts.
- How Doxxing Works: Attackers gather data through social engineering, breaches, or open sources like social media.
- Impacts of Doxxing: Victims face reputational damage, privacy violations, and psychological distress. For businesses, it can lead to loss of customer trust and legal repercussions.
- Defense Against Doxxing: Measures include using privacy settings, limiting online sharing of personal information, and employing robust data encryption.
- How Phishing Works: Attackers send emails or messages that appear legitimate, tricking victims into providing personal details or downloading malicious files.
- Consequences of Identity Theft: Victims may face financial fraud, unauthorized access to accounts, and reputational harm.
- Preventing Phishing Attacks: Educate users about phishing tactics, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA), and deploy anti-phishing tools.
- These psychological tactics often target the victim’s sense of urgency, exploiting the fear of reputational damage or financial loss.
- By instilling panic, attackers aim to cloud judgment, making it more likely that victims will make hasty decisions, such as paying the ransom or complying with demands without proper consideration.
- Victims may also experience a sense of shame, isolation, or confusion, further intensifying their vulnerability.
- To counteract these methods, Understanding GCP Analytics for organizations to have pre-established crisis response plans and trained professionals who can assess the situation objectively.
- Legal and mental health support should also be readily available to help victims navigate these distressing scenarios.
- Additionally, fostering a culture of resilience, with clear communication channels and regular training, can reduce the psychological impact of such attacks and strengthen overall defenses.
- Technology-Based Solutions: Employ firewalls, Docker in Linux Software Development, intrusion detection systems, and encryption. Regularly update and patch systems to prevent vulnerabilities.
- Employee Training: Educate employees about cybersecurity best practices, phishing recognition, and response protocols.
- Regular Backups: Maintain secure and up-to-date backups of critical data to recover from ransomware attacks without paying a ransom.
- Incident Response Plans: Develop and test a response plan to minimize downtime and damage during a cyberattack.
- Collaboration with Authorities: Report incidents to law enforcement or cybersecurity agencies to address extortion attempts effectively.
- Adopting Zero Trust Models: This security framework ensures that no entity, whether inside or outside the organization, is trusted by default.
Each type has unique attack vectors and consequences, necessitating tailored defenses and awareness campaigns.
Ransomware Attacks and Extortion
Ransomware is a leading cyber extortion tool. Malicious software encrypts a victim’s files, rendering them inaccessible. Attackers then demand payment, often in cryptocurrency, in exchange for the decryption key. High-profile ransomware attacks have targeted hospitals, Investment Banking, and government institutions, causing operational paralysis.

Doxxing and Threatening Disclosure
Doxxing involves the collection and publication of private, sensitive, or personally identifiable information (PII) to intimidate or extort individuals or organizations. In Understanding Multitenancy, attackers often threaten to release confidential information unless their demands are met.
Start your journey in Cloud Computing by enrolling in this Cloud Computing Online Course .
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
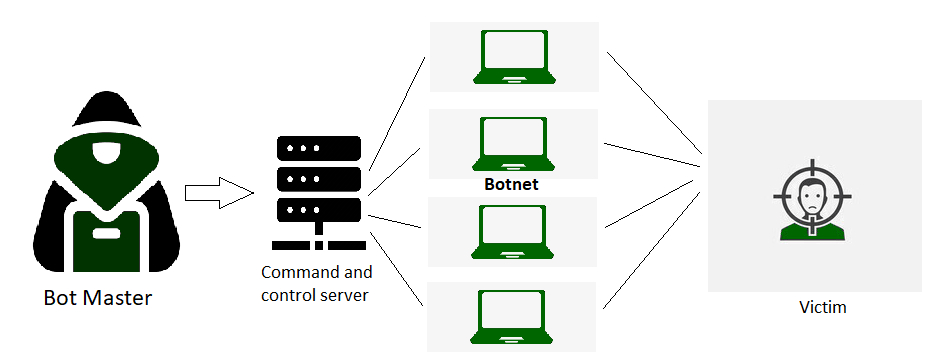
Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks disrupt a target’s network or servers by flooding them with overwhelming traffic, often exploiting network vulnerabilities or using botnets. In extortion-based DoS attacks, attackers demand ransom under the threat of launching or continuing these disruptive actions. The result is significant downtime, leading to financial losses, a damaged reputation, and frustrated users. Cloud Computing Course can target both small businesses and large corporations, affecting online services, e-commerce platforms, and critical infrastructure. The intensity and sophistication of these attacks are increasing, with attackers often using amplification techniques to maximize impact. To prevent such attacks, organizations can implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and DDoS mitigation tools while ensuring their infrastructure is scalable to handle traffic spikes. Regular security audits and employee training also play a crucial role in defending against evolving cyber threats.
Phishing and Identity Theft Extortion
Phishing involves fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information like passwords or credit card details by impersonating trustworthy entities. Cyber extortionists use stolen identities to blackmail victims.
Psychological Manipulation in Cyber Extortion
Want to lead in Cloud Computing? Enroll in ACTE’s Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course and start your journey today!
Legal and Financial Impacts of Cyber Extortion
Cyber extortion has significant legal and financial repercussions for both individuals and organizations. Financially, it leads to costs such as ransom payments, recovery expenses, operational downtime, and potential regulatory fines. Legally, victims of data breaches or those failing to protect customer data may face lawsuits, while non-compliance with data protection regulations, such as the GDPR, can result in severe penalties. Regulatory implications are also substantial, as governments enforce strict cybersecurity and reporting standards, making it crucial for organizations to implement robust security protocols. Additionally, cyber insurance can help mitigate financial losses, but policies often come with conditions, such as the need for preventive measures and adherence to reporting timelines, which highlight the importance of proactive security strategies.
Are you getting ready for your Cloud Computing interview? Check out our blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers!
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Effective prevention and mitigation strategies, which combine technology, policies, and training, are critical to combating cyber extortion.
Conclusion
Cyber extortion remains a pressing challenge in the digital age, with evolving attack techniques and increasing sophistication. Understanding these threats and implementing robust prevention strategies are vital for safeguarding sensitive data, maintaining operations, and protecting reputations. By fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness and leveraging advanced technologies, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to Cloud Computing Course. Additionally, timely detection and response to potential threats play a crucial role in minimizing damage. Collaboration between government agencies, law enforcement, and private sector entities can help track cybercriminal activity and strengthen defenses. Regular training and awareness campaigns for employees can also mitigate human errors that often lead to breaches. Investing in strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and comprehensive backup systems ensures that even in the event of an attack, organizations can recover swiftly without compromising their data.





