
- Introduction to Cloud-First Strategy
- Key Components of a Cloud-First Strategy
- The Benefits of Adopting a Cloud-First Approach
- Challenges of Implementing a Cloud-First Strategy
- Cloud-First vs. Traditional IT Strategy: A Comparative Overview
- Steps to Successfully Implement a Cloud-First Strategy
- The Future of Cloud-First Strategies: Trends to Watch
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cloud-First Strategy
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, businesses are increasingly adopting cloud computing as a central component of their IT strategies. One of the most forward-thinking approaches in cloud adoption is the Cloud-First Strategy. This strategy signifies a commitment to using cloud-based technologies as the primary option for deploying and managing IT infrastructure and services. A Cloud-First Strategy involves prioritizing the cloud for new applications, services, and IT infrastructure over on-premise or legacy solutions, which can be better understood through Cloud Computing Courses. Essentially, when a company faces a decision about whether to adopt a new solution or migrate an existing one, the default choice is to select a cloud-based option, unless there are compelling reasons to opt for a traditional approach. This strategy has become crucial for companies seeking to maintain competitiveness, agility, and scalability in an increasingly cloud-driven business world.
To Explore Cloud Computing in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cloud Computing Online Course To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Key Components of a Cloud-First Strategy
A Cloud-First Strategy involves several essential components that align with modern business objectives. These components create a cohesive framework for adopting and leveraging cloud technologies effectively:
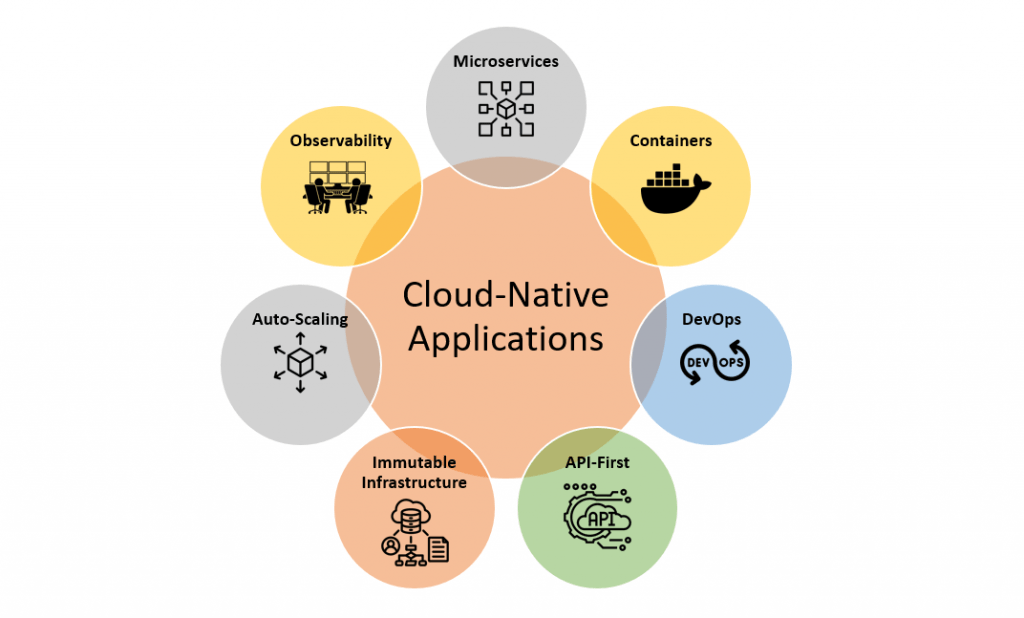
- Cloud-Native Applications: Cloud-native applications are designed specifically to run in the cloud and leverage cloud computing’s inherent scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. They are typically built using microservices, containerization, and DevOps principles, allowing organizations to continuously innovate and scale efficiently.
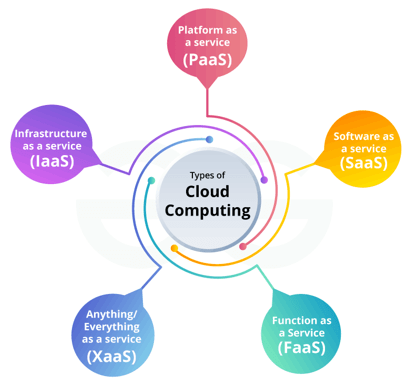
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): One of the key elements of a Cloud-First Strategy is leveraging IaaS. This involves outsourcing the management of hardware infrastructure to cloud providers, which can be complemented by Getting Started with Docker Pull for efficient container management. By using IaaS, companies can avoid the capital costs and complexities associated with on-premise hardware while gaining the flexibility to scale resources based on demand.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS provides a ready-to-use platform for building, deploying, and managing applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure. A Cloud-First Strategy often involves adopting PaaS for faster development cycles, reduced complexity, and improved time-to-market for applications.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Instead of maintaining software and updating it in-house, organizations using a Cloud-First approach rely heavily on SaaS solutions. Cloud-based software tools offer access to essential applications via the internet, significantly reducing maintenance overhead and ensuring users always have access to the latest features.
- Cloud Security and Compliance: Security is a fundamental concern in any IT strategy, and a Cloud-First Strategy places a strong emphasis on ensuring that cloud services meet the required security and compliance standards. Adopting cloud security best practices, such as encryption, identity and access management (IAM), and regular audits, is critical to maintaining data privacy and protecting against threats.
- Data Security Concerns: Storing data in the cloud raises security concerns, particularly for sensitive or regulated information. Companies must ensure that they have the necessary security measures in place, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and strict access controls, to protect data and maintain compliance with regulatory standards.
- Resistance to Change: Employees and leadership may be resistant to adopting cloud technologies due to familiarity with legacy systems or concerns about the transition process, but Understanding Docker Push can help ease the migration to cloud-based environments by streamlining container deployment. Overcoming this resistance requires clear communication, training, and a well-defined migration plan to ensure a smooth transition.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: In many cases, businesses have existing on-premise systems that must be integrated with new cloud-based solutions. Ensuring seamless interoperability between cloud and legacy infrastructure can be complex and may require custom solutions.
- Vendor Lock-In: Cloud providers offer a variety of services, but relying too heavily on a single provider can lead to vendor lock-in. Organizations need to carefully consider their cloud provider strategy and explore multi-cloud or hybrid cloud approaches to avoid being overly dependent on one vendor.
- Assess Current IT Landscape: Before adopting a Cloud-First strategy, conduct a thorough assessment of your current IT infrastructure, applications, and workloads. Identify which systems are best suited for cloud migration and which may need to remain on-premises for the time being.
- Define Clear Objectives and Metrics: Establish clear business objectives for your cloud adoption and define key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the success of your cloud initiatives. This could include cost savings, speed to market, and operational efficiency.
- Develop a Migration Plan: Carefully plan your cloud migration to minimize disruption and downtime. This involves deciding which applications or workloads will be moved to the cloud first and setting realistic timelines for each phase, with the integration of GraphQL APIs for AWS AppSync to enhance data fetching and management.
- Select the Right Cloud Provider: Choose the cloud provider that best aligns with your business needs. Consider factors such as service offerings, cost, security features, and the provider’s support for hybrid or multi-cloud environments.
- Train Employees and Foster Cloud Culture: Ensure that your employees are equipped with the knowledge and skills to succeed in the cloud environment. Providing ongoing training and fostering a cloud-first mindset across your organization will help drive adoption and maximize the benefits of the strategy.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Cloud platforms are increasingly incorporating AI and machine learning capabilities, which can be leveraged by businesses to gain insights from their data and automate processes. Expect to see more AI-powered cloud services that help businesses become more intelligent and agile.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies are becoming essential for organizations looking to balance performance, cost, and security, with a deeper Understanding GCP Analytics to optimize cloud resource utilization and data insights. Many businesses will continue to adopt hybrid and multi-cloud models, combining private and public cloud services to optimize workloads efficiently. A hybrid approach allows companies to maintain sensitive data on-premises while leveraging the scalability of public cloud platforms. Multi-cloud strategies also help organizations avoid vendor lock-in by distributing workloads across multiple providers, enhancing flexibility and resilience.
- Edge Computing: Edge Computing is another emerging trend that will complement cloud strategies by bringing computation and data storage closer to the data source. This reduces latency and enables faster processing, making it particularly valuable for IoT devices, real-time analytics, and autonomous systems. By processing data near its origin rather than relying solely on centralized cloud infrastructure, edge computing enhances performance, reduces bandwidth costs, and improves overall efficiency. Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and smart cities are increasingly leveraging edge computing for critical applications. As cloud computing evolves, the combination of hybrid, multi-cloud, and edge strategies will drive innovation, efficiency, and business agility in the digital era.
The Benefits of Adopting a Cloud-First Approach
Embracing a Cloud-First Strategy offers numerous advantages for businesses of all sizes, from cost savings to operational efficiency. Cloud services are typically billed on a subscription or pay-as-you-go model, eliminating the need for hefty upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure. By adopting a Cloud-First strategy, businesses can reduce their capital expenditures (CapEx) and transition to operational expenditures (OpEx), offering greater financial flexibility. The cloud also provides the ability to scale resources quickly and efficiently, allowing organizations to adjust infrastructure based on changing needs and ensuring they only pay for what they use, as detailed in the AWS Global Accelerator Guide for enhanced performance and availability. This agility is crucial for businesses with fluctuating demands or those expanding rapidly. Additionally, cloud solutions enable faster development cycles and greater agility, making it easier for businesses to innovate and respond to market changes. With cloud-native tools and platforms, organizations can deploy applications and features much faster, gaining a competitive advantage. Cloud services also support improved collaboration and remote work capabilities, providing secure, cloud-based tools accessible from anywhere. As remote work continues to rise, a Cloud-First strategy ensures employees can work seamlessly regardless of their location. Furthermore, cloud solutions offer built-in redundancy, data replication, and disaster recovery capabilities, safeguarding critical data even during hardware failures or disasters. A Cloud-First approach ensures businesses are better equipped to maintain operations during unforeseen events while enhancing efficiency, scalability, and resilience.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Cloud Computing? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
Challenges of Implementing a Cloud-First Strategy
While the benefits of adopting a Cloud-First Strategy are clear, there are challenges associated with its implementation. Some of the common obstacles organizations may face include:
Cloud-First vs. Traditional IT Strategy: A Comparative Overview
Understanding the differences between a Cloud-First Strategy and traditional IT approaches is key to recognizing the advantages of modernizing IT infrastructure. In a Cloud-First Strategy, the cost structure is typically based on a pay-as-you-go model (operational expenditures or OpEx), whereas traditional IT strategies require upfront capital investment in hardware and infrastructure (capital expenditures or CapEx). Cloud-based solutions are highly scalable and flexible, allowing businesses to adjust resources as needed, a concept that can be further explored through Cloud Computing Courses. On the other hand, traditional IT infrastructure has more limited scalability and often requires significant investment and effort to scale up. Cloud solutions offer faster deployment times, often with continuous integration and deployment capabilities, whereas traditional IT deployments can be slower due to manual updates and maintenance cycles. Cloud environments promote faster innovation, with cloud-native tools and platforms enabling businesses to iterate and release features quickly. Traditional IT strategies are often more limited by existing infrastructure and require significant resources to innovate. In a Cloud-First approach, maintenance is typically minimal, as the cloud provider manages most of the infrastructure. However, traditional IT strategies require extensive, ongoing maintenance and upgrades from in-house IT teams.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Cloud Computing Master’s Degree? Enroll For Cloud Computing Masters Course Today!
Steps to Successfully Implement a Cloud-First Strategy
Implementing a Cloud-First Strategy requires careful planning and a structured approach. Here are the key steps to guide successful adoption:
The Future of Cloud-First Strategies: Trends to Watch
As cloud computing continues to evolve, several emerging trends will shape the future of Cloud-First strategies:
Preparing for a Cloud Computing Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer
Conclusion
AWS DataSync is a powerful, fully managed service designed to simplify, automate, and accelerate data transfers between on-premises storage and AWS cloud environments. It ensures secure, efficient, and cost-effective data movement, making it ideal for enterprises handling large-scale migrations, backups, and real-time data replication. With built-in encryption, compression, and automation, AWS DataSync minimizes manual intervention and reduces operational complexity. It seamlessly integrates with AWS storage services like Amazon S3, Amazon EFS, and Amazon FSx, enabling businesses to optimize their hybrid cloud and data management strategies, which can be further enhanced through Cloud Computing Courses. The service’s ability to schedule and monitor transfers while ensuring high-speed performance makes it a reliable solution for enterprises with dynamic workloads. AWS DataSync also enhances disaster recovery capabilities by facilitating continuous data synchronization, ensuring minimal downtime and data loss. Its pay-as-you-go pricing model further adds cost efficiency, eliminating the need for expensive third-party solutions. Overall, AWS DataSync is an essential tool for organizations looking to enhance their data mobility, streamline cloud adoption, and improve operational efficiency. By leveraging its automation, security, and scalability, businesses can focus on innovation while ensuring seamless and reliable data movement across hybrid and cloud-native environments.





