
- What is a Private Cloud?
- Key Features of Private Cloud
- Private Cloud Providers (VMware, OpenStack)
- Private Cloud vs. Public Cloud
- Benefits of Using Private Cloud
- Security Considerations in Private Cloud
- Conclusion
Private cloud computing offers organizations enhanced control, security, and customization for their infrastructure. It provides dedicated resources within an isolated environment, reducing risks associated with shared platforms. With greater regulatory compliance, businesses can tailor security policies to protect sensitive data. Private clouds support scalability while maintaining strict access controls, ensuring data sovereignty. Advanced encryption, network segmentation, and intrusion detection strengthen defenses against Cloud Computing Course . Organizations benefit from flexible resource allocation, optimized performance, and seamless integration with on-premises systems. Automated monitoring tools enhance visibility, allowing proactive risk management. Private cloud computing delivers agility, reliability, and fortified protection for critical workloads.
Dive into Cloud Computing by enrolling in this Cloud Computing Online Course today.
What is a Private Cloud?
A Private Cloud is a cloud computing environment dedicated to a single organization. Unlike public clouds, where resources are shared among multiple users, private clouds offer greater control, customization, and security. A private cloud can be hosted on-premises within an organization’s data center or by a third-party service provider. It provides the scalability, flexibility, and efficiency of Load Balancing while maintaining a higher level of control over data, security, and resources. In a private cloud, the infrastructure is entirely private to the organization, which means that resources such as servers, storage, and networks are not shared with other tenants. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses with strict security and compliance requirements, as it allows them to customize and manage the cloud environment according to their specific needs.
Key Features of Private Cloud
- Dedicated Resources: Unlike public clouds, private clouds allocate resources specifically for the use of a single organization, ensuring higher performance and control over the cloud environment.
- Customization: Private clouds offer the flexibility to customize the architecture, security protocols, and Ansible Tower to meet the specific needs of the organization.
- Enhanced Security: With dedicated infrastructure, private clouds offer superior security measures, including more stringent access controls, firewalls, and data encryption, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.
- Compliance: Private clouds are often preferred by organizations with strict regulatory requirements, as they can meet the necessary compliance standards, including HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS.
- Virtualization: Private cloud environments make extensive use of virtualization technologies to provide scalable and efficient resource allocation. This allows multiple virtual machines to run on the same physical hardware.
- High Availability and Reliability: With dedicated resources and advanced management, private clouds often provide higher availability and reliability, with failover mechanisms and redundancy built into the infrastructure.
- Private Cloud: Resources are dedicated to a single organization, providing more control and customization.
- Public Cloud: Resources are shared among multiple tenants, which can lead to less control over resource allocation. Security:
- Private Cloud: Offers a higher level of security due to dedicated resources and more control over security configurations.
- Public Cloud: Security is managed by the cloud service provider, and while providers implement robust security measures, organizations may have less control. Cost:
- Private Cloud: Generally more expensive to set up and maintain due to the need for dedicated infrastructure and hardware. However, Understanding Terraform can be cost-effective for large organizations with high-demand computing needs.
- Public Cloud: Typically more affordable on a pay-as-you-go model, as resources are shared, and businesses only pay for what they use. Scalability:
- Private Cloud: Scalability is limited by the organization’s hardware and infrastructure, although it can still be quite flexible.
- Public Cloud: Offers virtually unlimited scalability, as resources can be dynamically allocated across a vast pool of servers. Compliance and Control:
- Private Cloud: Provides greater control over data management and can be more easily tailored to meet compliance requirements.
- Public Cloud: While public cloud providers offer compliance certifications, organizations may face challenges in meeting specific regulatory requirements due to shared infrastructure.
- Increased Security and Privacy: Private clouds offer enhanced security features, such as advanced firewalls, encryption, and isolated networks, which help protect sensitive data and applications.
- Customization: Organizations have full control over the private cloud environment, allowing them to customize their infrastructure, software, and services to meet specific business needs.
- Compliance: Private clouds provide a solution for organizations with strict regulatory requirements. The isolated nature of private clouds makes it easier to adhere to compliance standards.
- Performance and Reliability: With dedicated resources, private clouds can offer better performance, ensuring faster processing times and more reliable service. They are also less affected by resource contention that can occur in shared environments like public clouds.
- Cost Efficiency for Large Organizations: While private clouds may have a higher upfront cost, Essential Cloud Computing Tools and Beyond with substantial computing needs can find private clouds more cost-effective over time, especially when it comes to long-term scalability and maintenance.
- Flexibility in Integration: Private clouds can be integrated more easily with legacy systems and on-premises infrastructure, providing greater flexibility in how resources are managed.
- Scalability and Resource Optimization: Private cloud environments allow businesses to scale resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance without over-provisioning. This elasticity helps in better utilization of computing power while maintaining cost efficiency.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: Private clouds support robust disaster recovery mechanisms, enabling businesses to replicate critical data and applications across multiple locations. This ensures minimal downtime and quick recovery in case of unexpected failures.
- Enhanced Control and Governance: Organizations using private clouds maintain full control over their infrastructure, enabling them to implement strict governance policies. This level of control ensures better management of user access, data protection, and IT compliance requirements.
Learn the fundamentals of Cloud Computing with this Cloud Computing Online Course .
Private Cloud Providers (VMware, OpenStack)
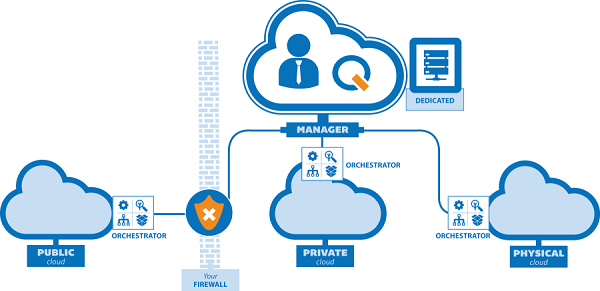
VMware is a leading provider of virtualization technologies, and its VMware Cloud Foundation enables organizations to build and manage private cloud environments. VMware offers a comprehensive suite of cloud solutions, including computing, storage, and networking, as well as cloud management and automation tools. VMware’s vSphere is widely used to build and manage virtualized private clouds, while VMware NSX provides software-defined networking (SDN) for better network management. VMware also offers a hybrid cloud solution with VMware Cloud on AWS, allowing organizations to extend their private cloud to a public cloud seamlessly. OpenStack is an open-source cloud computing platform that allows organizations to build and manage private clouds. It provides a set of software tools for deploying and Guide to Cloud Security, including computing, storage, and networking. OpenStack is widely used by organizations that prefer an open-source solution with flexibility and no vendor lock-in. It can be customized extensively to meet the needs of enterprises and service providers. OpenStack has a strong ecosystem, and various commercial distributions, such as those from Red Hat and Canonical (Ubuntu), offer support and additional tools for managing private cloud environments. Private cloud computing ensures enhanced security, control, and compliance for enterprises handling sensitive workloads. Organizations benefit from dedicated resources, reducing risks associated with multi-tenant environments. Scalable architectures allow seamless expansion without compromising data integrity or performance. Advanced automation tools streamline deployment, management, and monitoring, improving operational efficiency. With robust encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring, businesses can safeguard critical applications and data. Private clouds also enable seamless hybrid cloud integration, facilitating workload migration and business continuity strategies. Leveraging AI-powered analytics, predictive maintenance, and self-healing capabilities further enhances private cloud resilience and reliability.
Take charge of your Cloud Computing career by enrolling in ACTE’s Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course today!
Private Cloud vs. Public Cloud
The Private Cloud and Public Cloud differ in several key ways, including resource allocation, security, cost, and management:
Resource Allocation:Security Considerations in Private Cloud
One of the primary security concerns in a private cloud is ensuring that only authorized users and systems can access sensitive data and resources. This can be managed through advanced identity and access management (IAM) policies. To ensure that data is protected both in transit and at rest, private cloud environments should utilize strong encryption techniques. This prevents unauthorized access even if there is a breach or data theft. Network Security: In private clouds, network security is critical. Virtual networks should be segmented using firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and virtual private networks (VPNs) to prevent unauthorized access. Compliance: Many organizations use private clouds to meet regulatory compliance requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Private clouds give organizations the ability to control data storage and management in a way that meets these standards. Disaster Recovery and Backup: Private clouds should implement robust disaster recovery and backup strategies to ensure business continuity in the event of hardware failures, data loss, or natural disasters. Since the organization has full control over its private cloud infrastructure, regular patching, and updates are necessary to protect against known vulnerabilities and exploits. Private clouds offer businesses the ability to tailor security configurations based on Cloud Computing Course unique requirements. Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that users have the minimum necessary permissions to reduce risk exposure. Secure API gateways help manage application access, preventing unauthorized interactions with cloud services. Continuous monitoring with SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) solutions allows organizations to detect and respond to threats in real-time. Implementing zero-trust architecture (ZTA) strengthens authentication and authorization mechanisms, reducing insider threats. Private clouds also benefit from AI-driven security analytics, which enhances threat detection, anomaly identification, and automated response to cyber threats.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Benefits of Using Private Cloud
Conclusion
In conclusion, a private cloud provides organizations with the ability to leverage the benefits of cloud computing, such as scalability and flexibility, while maintaining control over data, security, and compliance. By carefully considering the features, benefits, and security aspects of private cloud environments, businesses can make informed decisions that best suit their needs and protect their sensitive information. Private clouds offer organizations enhanced customization, allowing them to configure infrastructure according to specific business requirements. Cloud Computing Course provide predictable performance by utilizing dedicated resources without external interference. Organizations can implement advanced monitoring tools to track system health, optimize resource allocation, and enhance operational efficiency. Private cloud solutions also improve application performance by reducing latency and ensuring seamless connectivity. With enhanced security mechanisms like multi-factor authentication and encrypted communications, businesses can safeguard sensitive workloads. Private cloud deployments support integration with existing IT infrastructure, enabling smooth migration of legacy applications. These advantages make private clouds an ideal choice for industries handling critical data.





