
- Introduction to Google Cloud and AWS
- Market Share and Popularity
- Core Services and Offerings
- Pricing and Cost Comparison
- Performance and Scalability
- Security and Compliance
- Ease of Use and Management
- AI, Machine Learning, and Big Data Capabilities
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Support
- Customer Support and Service Reliability
- Use Cases and Industry Adoption
- Future Trends and Predictions
- Conclusion
Introduction to Google Cloud and AWS
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and Amazon Web Services (AWS) are leading cloud computing providers, offering various infrastructure, platform, and software services to businesses worldwide. AWS, launched in 2006, has long been the dominant player in the cloud space. Google Cloud, introduced in 2008, has rapidly gained traction, particularly in AI, data analytics, and hybrid cloud solutions. In 2025, both platforms will continue to evolve, providing businesses with cutting-edge cloud solutions to meet diverse computing needs. As companies increasingly shift toward cloud computing, understanding the key differences between AWS and Google Cloud is crucial for making informed decisions.
Market Share and Popularity
- AWS: AWS remains the market leader, holding a significant portion of the global cloud market and having a strong presence across enterprises and startups.
- Google Cloud: Google Cloud has gained market share in recent years, particularly among companies leveraging AI/ML and hybrid cloud architectures.
- Growth Trends: While AWS continues to lead, Google Cloud’s aggressive expansion in enterprise solutions has fueled its increasing adoption.
- Regional Adoption: AWS dominates in North America and Europe, whereas Google Cloud sees strong adoption in regions focused on AI-driven workloads.
- Enterprise Adoption: AWS is widely used by large enterprises due to its extensive service portfolio and strong compliance framework. Google Cloud has seen growth among digital-native businesses and organizations focusing on analytics and AI.
Core Services and Offerings
AWS and Google Cloud offer a broad range of services covering computing, storage, networking, databases, AI/ML, and security. AWS provides an extensive catalog, including Amazon EC2 (compute), Amazon S3 (storage), and AWS Lambda (serverless computing). AWS excels in offering a mature ecosystem with deep integrations for enterprises. It also provides high-performance networking solutions, advanced database management systems, and security tools tailored to various industries. Google Cloud, on the other hand, focuses on AI/ML and data processing capabilities with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), BigQuery (data analytics), and Vertex AI (machine learning). Businesses prioritize AI-driven applications and multi-cloud strategies, and they favor Google Cloud. Additionally, Google’s global fiber-optic network provides low-latency connections for data-intensive applications.
Security and Compliance
- AWS Security: Offers IAM, encryption, and compliance with industry standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
- Google Cloud Security: Provides identity and access management, encryption, and strong security analytics tools like Security Command Center.
- Compliance: Both platforms are highly secure, but AWS has a broader range of compliance certifications due to its extended presence in the market.
- Threat Detection and Response: Google Cloud’s Chronicle Security Operations and AWS’s GuardDuty both offer advanced threat detection capabilities, helping businesses protect their cloud environments from cyber threats.
Pricing and Cost Comparison
- AWS Pricing: Offers pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and savings plans, allowing flexibility but requiring optimization to control costs.
- Google Cloud Pricing: Competitive pricing with sustained use discounts, offering more straightforward cost structures for long-term use.
- Billing Models: AWS typically charges per second or minute of usage, whereas Google Cloud provides automatic discounts based on sustained usage.
- Free Tiers: Both platforms offer free-tier services, but Google Cloud often provides more extended trial credits for new users.
- Cost Optimization: AWS provides tools like AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Budgets to help businesses manage costs efficiently. Google Cloud’s cost optimization features include recommendations for idle resources and preemptible VM instances.
Performance and Scalability
AWS has a vast global infrastructure with multiple availability zones, providing high scalability and performance for large-scale applications. Google Cloud offers lower latency in specific workloads due to its private fiber-optic network, making it ideal for high-performance AI and data processing applications. Additionally, Google Cloud’s advanced containerization technologies provide efficient workload distribution across hybrid cloud environments.
Ease of Use and Management
- AWS: Offers an extensive set of tools and management consoles, but the complexity of its services can make onboarding challenging.
- Google Cloud: Features a more user-friendly UI with seamless integrations into Google Workspace, making it easier for new users to adopt.
- APIs and SDKs: Google Cloud is preferred for AI-based development, while AWS provides more robust enterprise integrations.
- Automation and DevOps: AWS provides AWS CloudFormation for infrastructure automation, while Google Cloud offers Terraform and Deployment Manager to simplify cloud management.
AI, Machine Learning, and Big Data Capabilities
Google Cloud has a clear advantage in AI/ML due to its TensorFlow framework, Vertex AI platform, and BigQuery for real-time analytics. While also strong in AI/ML with SageMaker and Redshift, AWS is often seen as more complex for data science workflows. Additionally, Google Cloud’s AutoML solutions simplify AI model development for businesses without deep machine learning expertise.
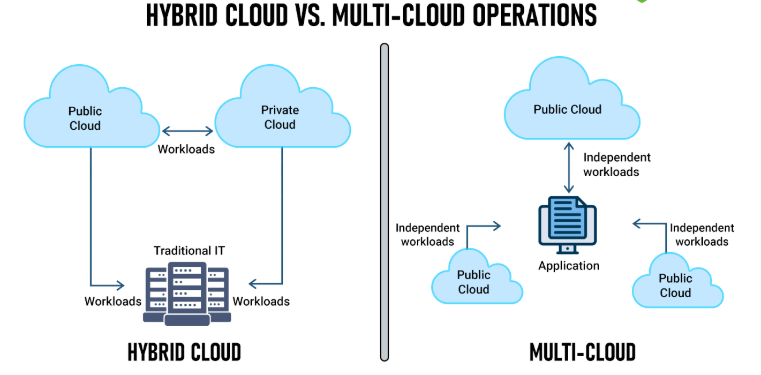
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Support
- AWS: Provides hybrid solutions like AWS Outposts and VMware on AWS.
- Google Cloud: Focuses heavily on multi-cloud strategies with Anthos, enabling seamless management across different cloud providers.
- Flexibility: Google Cloud’s Anthos gives it an edge for businesses adopting multi-cloud environments.
- Enterprise Cloud Strategy: Businesses with long-term hybrid cloud goals may benefit from Google Cloud’s focus on open-source tools and multi-cloud compatibility.
Customer Support and Service Reliability
AWS has a more established customer support ecosystem with various support plans for enterprises. Google Cloud provides substantial documentation and a growing support network, though it may not yet match AWS’s extensive enterprise-level support services. However, Google Cloud has improved customer engagement with dedicated support engineers and AI-powered support tools.
Use Cases and Industry Adoption
When evaluating cloud platforms, it’s essential to look at how industries are using them in real-world scenarios. Both Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offer a wide range of solutions, but their adoption patterns vary based on organizational needs, industry requirements, and platform strengths.
AWS: Use Cases & Industry Adoption Enterprise-Scale ApplicationsAWS is widely adopted by large enterprises for hosting and scaling mission-critical applications. Its broad range of services—from compute and storage to AI/ML—makes it a go-to choice for complex deployments.
Key Industries:- Finance: Banks and fintech companies rely on AWS for secure, scalable infrastructure.
- Retail & eCommerce: Amazon.com sets the standard, and many global retailers trust AWS for handling massive traffic and sales data.
- Media & Entertainment: Streaming platforms (like Netflix) use AWS for content delivery and global scalability. Popular Use Cases:
- Running large-scale web applications and APIs.
- Data warehousing and real-time analytics.
- Machine learning and AI services via SageMaker.
- Disaster recovery and backup solutions.
- Microservices and container orchestration (ECS, EKS). Google Cloud: Use Cases & Industry Adoption
- Technology & Startups: Startups and tech firms choose GCP for its innovation-first tools and pricing.
- Healthcare & Life Sciences: Leverages AI for medical imaging, genomics, and data sharing.
- Education & Research: Google Workspace integration and BigQuery support make it ideal for collaboration and large-scale research. Popular Use Cases:
- Big data analytics using BigQuery and Dataflow.
- Developing AI/ML models with Vertex AI.
- Kubernetes-based deployments (GCP created Kubernetes).
- Application modernization and CI/CD pipelines.
- Integrating with Google Workspace and third-party SaaS tools.
Data-Driven and AI-Centric Workloads
Google Cloud shines in data analytics, AI/ML, and open-source support. Companies that prioritize innovation and real-time insights often lean toward GCP.
Key Industries:Future Trends and Predictions
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, AWS is expected to continue dominating the cloud market with innovations in edge computing, serverless, and enterprise cloud solutions. Google Cloud will likely expand its AI/ML leadership, focusing on data-driven businesses and enhancing multi-cloud capabilities. The cloud industry will see increased adoption of hybrid solutions, automation, and cost-optimized cloud strategies. As regulatory requirements evolve, AWS and Google Cloud are expected to enhance their compliance frameworks and security features.
Conclusion
AWS and Google Cloud offer robust cloud computing services catering to different business needs. AWS remains the go-to platform for enterprises requiring extensive cloud capabilities, while Google Cloud is ideal for AI, data analytics, and multi-cloud deployments. Choosing between the two depends on a company’s priorities, whether scalability, cost, AI capabilities, or hybrid flexibility. As cloud technologies evolve, businesses must assess their long-term goals to select the provider that aligns best with their needs in 2025 and beyond. With both platforms constantly innovating, organizations can expect continued advancements in cloud computing efficiency, security, and automation.





