- Introduction
- Importance of Cloud Backup
- Types of Cloud Backup (Public, Private, Hybrid)
- Best Practices for Cloud Backup
- Leading Cloud Backup Providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
- Backup Security and Compliance Considerations
- Disaster Recovery and Cloud Backup
- Conclusion
Introduction
Data has emerged as one of the most significant resources for both individuals and enterprises in the current digital era. Protecting this data is no longer a luxury but a necessity. Cloud backup solutions offer a reliable and secure method for safeguarding critical information, ensuring that data is protected from loss, corruption, or theft. Whether you’re running a small business or managing a large enterprise, cloud backup offers flexibility, scalability, and enhanced disaster recovery options, all of which are key topics in a Cloud Computing Course. This article will explore the significance of cloud backup, the various types of cloud backup solutions available, and best practices for ensuring data security. We’ll also delve into the leading cloud backup providers, security and compliance considerations, and how cloud backup plays a key role in disaster recovery. By understanding the benefits and considerations surrounding cloud backup, organizations can make informed decisions to ensure the continuity and protection of their valuable data.
To Explore Cloud Computing in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cloud Computing Online Course To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Importance of Cloud Backup
Cloud backup is a vital part of any organization’s data management strategy, ensuring that critical data is securely stored and easily recoverable in case of unexpected events, such as data loss, hardware failures, or cyberattacks. Unlike traditional backup methods, which often involve physical storage devices, cloud backup leverages off-site servers to store data in a remote, scalable, and secure environment. This not only increases accessibility but also offers enhanced security and disaster recovery options.
The importance of cloud backup includes:
- Data Protection: Cloud backups ensure that all data, including important files, applications, and databases, is securely stored offsite and is easily recoverable if lost due to hardware failure, human error, or cyberattacks like ransomware.
- Scalability: Cloud backup solutions allow businesses to scale their backup requirements as needed, without the limitations of physical storage devices, which can be effectively managed using tools like Azure Data Studio A Complete Guide. Whether you need to store terabytes or petabytes of data, the cloud can accommodate it.
- Accessibility: Cloud backups can be accessed from anywhere, enabling users to restore data from any location as long as they have an internet connection. This increases flexibility, especially for remote workforces.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud backups typically operate on a pay-as-you-go model, which means businesses only pay for the storage they use, eliminating the upfront costs associated with purchasing and maintaining physical backup hardware.
- Business Continuity: In the event of a disaster, cloud backups ensure that critical business data remains available for recovery, minimizing downtime and enabling organizations to quickly restore operations.
- Definition: Public cloud backup involves storing data on third-party cloud service providers’ infrastructure, such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. It is the most common and cost-effective form of cloud backup.
- Benefits: Low initial costs since the infrastructure is maintained by the provider. Scalable, as you can increase storage space as your needs grow. Easily accessible from anywhere with internet connectivity.
- Drawbacks: Security concerns, as your data is stored on shared infrastructure. Limited control over the physical location of data. Private Cloud Backup:
- Definition: Private cloud backup involves backing up data on a dedicated infrastructure that is either on-premise or hosted in a private data center, which can be optimized with solutions like Azure Virtual Network Pricing. The organization has exclusive use of the infrastructure, ensuring complete control over security.
- Benefits: Greater control over security and compliance. More flexibility regarding configurations and storage. Improved performance due to dedicated resources.
- Drawbacks: Higher upfront costs, as the organization must maintain and manage the infrastructure. May require additional technical expertise for setup and management. Hybrid Cloud Backup:
- Definition: Hybrid cloud backup combines the benefits of both public and private clouds. Organizations use a private cloud for critical data while leveraging public cloud storage for less sensitive data or as a secondary backup option.
- Benefits: Flexibility to choose which data is stored in each environment. Enhanced disaster recovery capabilities by storing backups both on-premise and in the cloud. Greater control over sensitive data while benefiting from the scalability of the public cloud.
- Drawbacks: Complex setup and management, requiring integration of both public and private cloud solutions. May involve higher operational costs due to the dual infrastructure.
- Service: AWS offers Amazon S3 for scalable storage and Amazon Glacier for long-term archival storage.
- Features: Highly scalable and reliable storage options. Integration with AWS tools for data management, security, and automation. Advanced security features, such as encryption and IAM (Identity and Access Management). Microsoft Azure:
- Service: Azure Backup provides cloud-based data protection and disaster recovery solutions for businesses.
- Features: Integration with existing Microsoft services and tools like Azure Site Recovery. Advanced security features like encryption and role-based access control (RBAC) are crucial in cloud environments, and these features are also supported in platforms like Amazon Lightsail Uncovered Simplified Cloud Hosting. Supports both Windows and Linux-based virtual machines for backup. Google Cloud:
- Service: Google Cloud Storage and Google Cloud Backup and DR solutions are designed to back up enterprise data to the cloud.
- Features: Flexible storage options, including object and file storage. AI-powered tools for improved performance and management. High security, including encryption and compliance with global regulations. Backblaze:
- Service: Backblaze provides simple cloud storage and backup solutions, including unlimited backup plans for individual users and businesses.
- Features: Low-cost, unlimited data backup. Secure, encrypted storage Easy-to-use interface for backup and restoration.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): RPO defines the maximum amount of data an organization is willing to lose in the event of a disaster. Cloud backup solutions should be configured to meet the desired RPO, ensuring that backup intervals are aligned with business needs.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): RTO refers to the time it takes to recover data after a disaster. Cloud backup solutions with fast data retrieval options (like AWS Glacier or Azure Blob Storage) can help minimize downtime, which can be integrated with version control systems like Exploring AWS CodeCommit for seamless recovery and management.
- Geo-Redundancy: To ensure high availability, store backups across multiple geographic regions. This prevents data loss in case a single data center is affected by a disaster.
- Automated Failover: Many cloud providers offer automated failover capabilities, where backup data can be instantly restored to operational systems. This minimizes downtime and accelerates recovery.
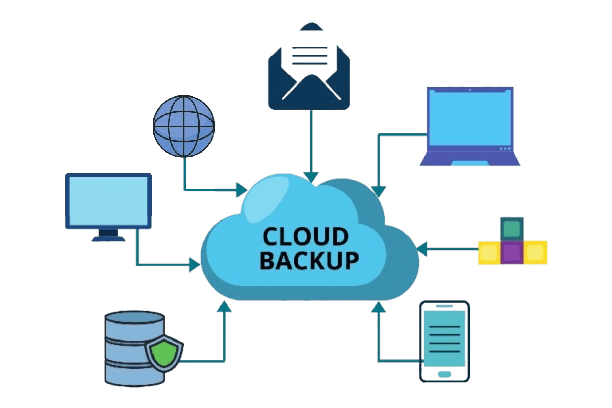
Types of Cloud Backup
Cloud backup solutions can be categorized into three main types based on their architecture and how they are implemented: Public, Private, and Hybrid.
Public Cloud Backup:Are You Interested in Learning More About Cloud Computing? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
Best Practices for Cloud Backup
To ensure that cloud backup is both effective and secure, it’s important to follow best practices. First, establish a regular backup schedule, performing backups according to the importance of the data; critical data may require daily backups, while less important data can be backed up less frequently. Automation is also essential to reduce human error set up automatic backup schedules to ensure data is consistently backed up without manual intervention. Encrypting data is another key practice; always encrypt your data before sending it to the cloud, both during transmission and while stored, to protect it from unauthorized access, a critical concept covered in a Cloud Computing Course. Regularly testing recovery procedures is necessary to ensure data can be restored quickly and accurately in the event of a disaster. Enable versioning for your backup files to allow restoring previous versions of data if needed, which is especially helpful in case of accidental changes or deletions. For additional protection, store backups in multiple locations both geographically and across different cloud providers helping to mitigate the risk of downtime if one provider encounters an issue. Finally, ensure compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements, such as GDPR or HIPAA, and maintain proper documentation of backup policies and recovery procedures.
Leading Cloud Backup Providers
Several providers offer reliable cloud backup solutions, each with unique features, scalability options, and pricing. Some of the leading cloud backup providers include:
AWS (Amazon Web Services):Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cloud Computing by Enrolling in Our Cloud Computing Masters Course.
Backup Security and Compliance Considerations
When implementing cloud backup, security and compliance are critical concerns, especially for organizations handling sensitive data. Data encryption is essential, ensuring that data is encrypted both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access. While many cloud providers offer built-in encryption, additional layers can enhance security, which can be effectively managed using tools like Azure Traffic Manager A Complete Guide.
Access control is also crucial implementing strict measures like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that only authorized personnel can access backup data. Compliance with industry standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS, is necessary, with some providers offering tools to assist with this. Additionally, backup integrity should be regularly tested to ensure that backup data has not been corrupted or tampered with. Regular audits and monitoring should be conducted to track potential vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with evolving security regulations. By maintaining strong security practices, organizations can protect their critical data and mitigate the risks of data breaches.
Disaster Recovery and Cloud Backup
Cloud backup plays a critical role in disaster recovery (DR) strategies. In the event of a disaster, whether natural (fire, flood, earthquake) or man-made (cyberattack, power failure), a well-implemented cloud backup system allows organizations to quickly restore lost data and resume business operations. Key aspects of disaster recovery include:
Are You Preparing for Cloud Computing Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud backup is an essential element of data protection and business continuity strategies, offering a robust solution to safeguard critical information in an increasingly digital and interconnected world. By choosing the right type of cloud backup, following industry best practices, and selecting a reliable and secure cloud backup provider, organizations can ensure that their data remains secure, easily accessible, and recoverable in times of need. This proactive approach not only helps protect against data loss but also minimizes downtime and operational disruptions, a key focus in any Cloud Computing Course. As businesses continue to rely more heavily on cloud environments, a well-implemented cloud backup solution becomes indispensable for mitigating risks associated with data breaches, hardware failures, cyberattacks, and other unforeseen events. In today’s fast-paced and data-driven landscape, ensuring the integrity and availability of business critical data is not just a precaution it is a fundamental aspect of long-term success and resilience.





