
- Introduction: Understanding On-Premise and Cloud Computing
- What is On-Premise Computing?
- What is Cloud Computing?
- Key Differences Between On-Premise and Cloud Computing
- Pros and Cons of On-Premise Solutions
- Pros and Cons of Cloud Solutions
- How to Choose Between On-Premise and Cloud Solutions
- Conclusion
On-Premise Computing refers to IT infrastructure, software, and services hosted and managed within an organization’s physical premises. It provides businesses full control over their systems, hardware, and data. On-premise solutions often require large upfront investments for servers, hardware, and maintenance costs. The organization is responsible for securing, updating, and maintaining the environment, which can be resource-intensive. Cloud Computing Course delivers computing resources like storage, processing, and networking over the internet. It enables businesses to use IT resources on-demand, typically through a service provider like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Cloud solutions reduce upfront costs, offer scalability, and provide flexibility. Organizations pay based on usage, with cloud providers managing infrastructure and updates, ensuring high availability and security.
Learn how to manage and deploy cloud services by joining this Cloud Computing Online Course today.
Introduction: Understanding On-Premise and Cloud Computing
As businesses continue to evolve in the digital age, one of the most important decisions they face is choosing between on-premise and cloud-based solutions. Both options have their own advantages, challenges, and use cases, which can make the decision-making process tricky.But what exactly do these terms mean? Simply put, on-premise refers to IT infrastructure that is physically housed within a company’s premises or data centers, while cloud computing involves using remote servers hosted over the internet to store and manage data. In this blog post, we’ll explore the differences between on-premise and cloud computing, help you understand the pros and cons of each, and guide you in choosing the right solution for your business. As businesses increasingly rely on technology for their daily operations, understanding the fundamental differences between on-premise and cloud solutions becomes crucial. The choice between the two often depends on factors such as cost, security, scalability, and ease of management. Each option offers unique benefits for different business needs, and in Virtualization in Cloud Computing blog, we will break down these factors to help you make an informed decision. Whether you’re looking for full control over your infrastructure or a flexible, scalable solution, understanding the trade-offs is key to finding the right fit for your organization. Let’s dive into the essential aspects of on-premise and cloud computing to guide you in this critical decision-making process.
What is On-Premise Computing?
On-premise computing refers to IT infrastructure that is physically located on a company’s property, whether that’s in the office, a dedicated server room, or a company-owned data center. This setup typically involves hardware such as servers, networking equipment, and storage devices that are owned, maintained, and managed by the organization itself.In an on-premise environment, businesses are responsible for purchasing the necessary hardware and software, setting up the infrastructure, and ensuring that everything runs smoothly. On-premise solutions are often considered more traditional, as companies have full control over their systems and data. Examples of on-premise infrastructure include internal servers for hosting websites and applications, local file storage, and internal email systems.
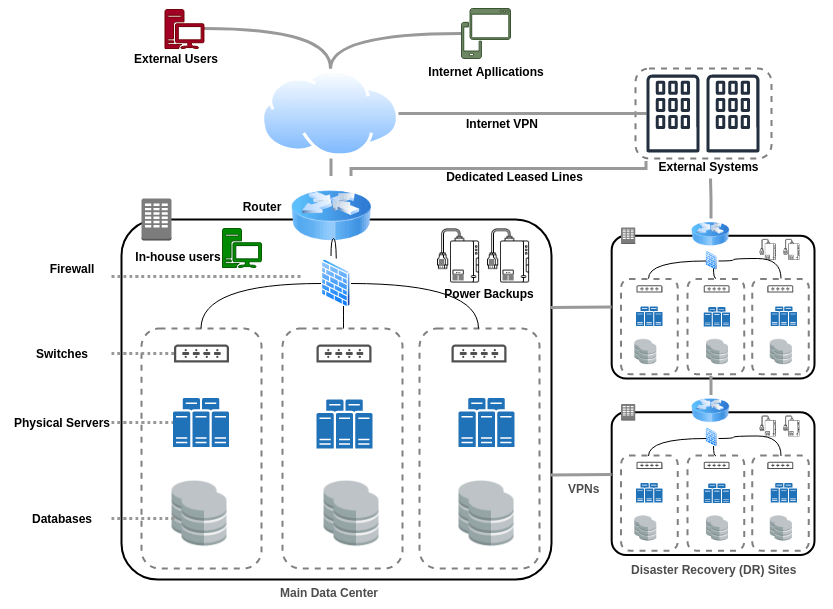
Additionally, on-premise setups allow businesses to customize their IT infrastructure to meet specific requirements, providing a high level of control over performance and security. However, this level of control comes with its own challenges, such as the need for skilled IT staff, ongoing maintenance, and potential hardware failures. Moreover, on-premise solutions can be more expensive upfront due to the need for purchasing and maintaining physical equipment. While they offer greater control, they may not be as scalable or flexible as cloud-based alternatives, especially when it comes to Cloud Computing Skills for Career Growth or fluctuating demand. Therefore, organizations must weigh the benefits of control against the resources required to maintain on-premise systems effectively.
Unlock your potential in Cloud Computing with this Cloud Computing Online Course .
What is Cloud Computing?
- Cloud computing, on the other hand, refers to the use of remote servers, typically hosted by a third-party service provider, to store, manage, and process data.
- Rather than owning and maintaining hardware, businesses pay for cloud-based services on a subscription or usage-based model.
- Cloud services are accessed over the internet, meaning users can access their data and applications from virtually anywhere.
- Leading cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer a wide range of scalable solutions to businesses, including data storage, virtual machines, and software-as-a-service (SaaS) offerings.
- Examples of Cloud Computing Course include cloud storage solutions like Google Drive or Dropbox, software applications like Office 365 or Salesforce, and cloud hosting platforms for websites and databases.
- Cloud computing offers several advantages, such as reduced upfront costs, scalability, and the flexibility to quickly adapt to changing business needs. With cloud services, businesses only pay for what they use, allowing for more efficient cost management.
- Additionally, cloud providers typically handle maintenance, updates, and security, reducing the burden on internal IT teams.
- Cloud environments also provide enhanced collaboration features, enabling teams to work remotely and access shared resources easily.
- However, businesses must consider factors such as data privacy, security, and potential downtime when relying on third-party providers for their cloud infrastructure.
Key Differences Between On-Premise and Cloud Computing
The differences between on-premise and cloud computing are substantial, and understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision.
| Factor | On-Premise | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Company owns all hardware and software. | Services provided by third-party vendors; businesses pay for what they use. |
| Location | Resources are physically located within the company’s premises or data centers. | Resources stored in remote servers, managed by cloud providers, and accessed via the internet. |
| Cost Structure | High upfront investment for hardware, software, and infrastructure. | Subscription-based or pay-as-you-go model; businesses only pay for what they use. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability; requires additional hardware or upgrades. | Easy scalability; resources can be increased or decreased as needed without physical adjustments. |
| Maintenance | Business is responsible for ongoing maintenance, security updates, and hardware upgrades. | Cloud provider handles maintenance, updates, and security, reducing the workload for internal teams. |
| Security | Full control over security measures; responsibility lies entirely with the business. | Shared responsibility model; cloud providers offer robust security features but businesses share responsibility for securing their data. |
| Flexibility | More customization options, as the business controls the entire infrastructure. | Flexible in terms of scalability and access, but fewer customization options due to standardized third-party services. |
| Disaster Recovery | Requires the business to implement its own disaster recovery plans and backups. | Built-in disaster recovery options, with data backed up across multiple locations and streamlined recovery processes. |
This table highlights the main differences to help businesses decide which solution is best for their needs.
Looking to master Cloud Computing? Sign up for ACTE’s Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course and begin your journey today!
Pros and Cons of On-Premise Solutions
On-premise computing offers certain advantages but also comes with its own set of challenges.
Pros:
- Complete Control: On-premise solutions offer complete control over hardware, software, and data security. Businesses have the flexibility to configure their systems and security measures according to their needs.
- Data Security: Sensitive data is stored on-site, which can provide peace of mind, especially for organizations dealing with regulated industries or stringent compliance requirements.
- Customization: Companies have full control over their infrastructure, allowing them to customize everything to fit specific needs, whether that’s for performance, security, or specific applications.
Cons:
- High Initial Investment: On-premise systems come with high upfront costs for purchasing hardware, setting up the infrastructure, and ensuring everything is compatible and optimized.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Regular maintenance, including software updates, security patches, and hardware upgrades, can be Introduction to Cloud Storage its Benefits and costly for businesses.
- Limited Scalability: Scaling an on-premise solution can be cumbersome and expensive, as it typically requires purchasing additional physical hardware, which might not be as flexible or cost-effective as cloud-based scaling.
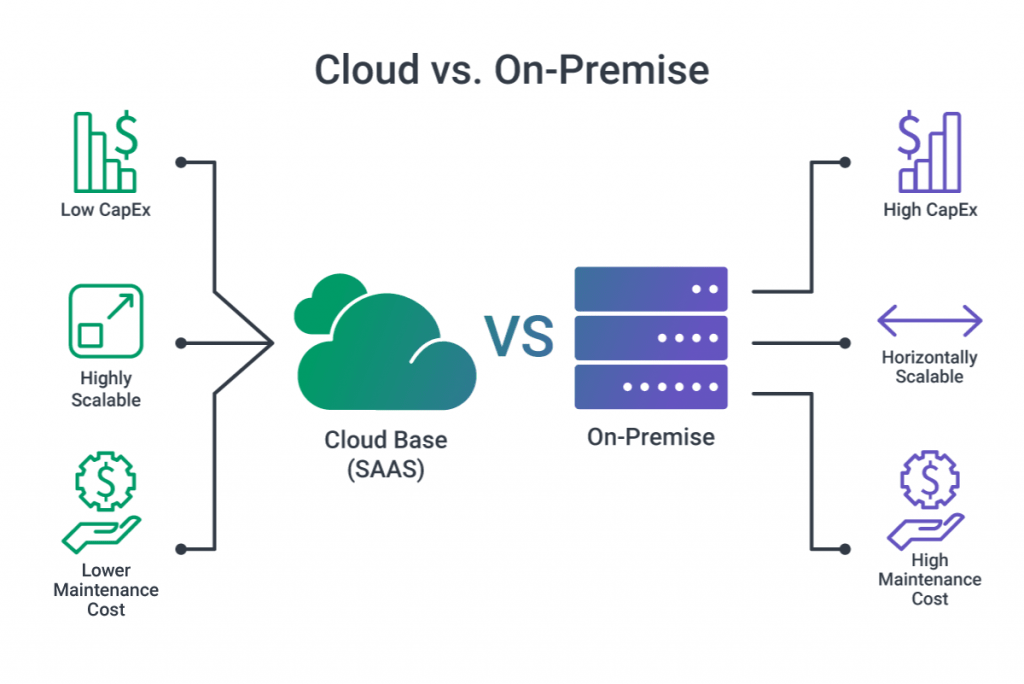
Pros and Cons of Cloud Solutions
Cloud computing offers a flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional on-premise systems. Here are some of the major benefits and challenges:
Pros:
- Cost-Effective: Cloud computing follows a pay-as-you-go model, reducing the need for large upfront investments. This makes it more affordable, especially for smaller businesses or those with fluctuating resource needs.
- Scalability: One of the biggest advantages of cloud computing is its scalability. Businesses can quickly scale up or down based on their needs, ensuring they only pay for the resources they actually use.
- Accessibility: Cloud Resource Management with Resource Pooling can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and global collaboration.
- Reduced Maintenance: The cloud provider is responsible for infrastructure maintenance, security, and software updates, which means businesses don’t need to worry about managing these aspects themselves.
Cons:
- Limited Control: With cloud computing, businesses have less control over their infrastructure and security measures, as they rely on the cloud provider to handle most of the operations.
- Security Concerns: Storing sensitive data in the cloud can raise security concerns, particularly if the provider doesn’t implement adequate data protection and compliance measures.
- Ongoing Subscription Fees: While cloud services have lower upfront costs, businesses will incur ongoing monthly or yearly subscription fees. Over time, these costs can add up, particularly for large-scale deployments.
Boost your chances in Cloud Computing interviews by checking out our blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers!
How to Choose Between On-Premise and Cloud Solutions
If upfront costs are a concern, cloud computing might be a better fit, as it generally requires lower initial investment. On-premise setups, on the other hand, involve significant capital expenditure. For businesses with rapidly changing needs, the cloud offers unparalleled scalability, making it easier to adjust resources on the fly. On-premise solutions are more limited in this regard and may require additional investment and effort to scale. If your organization handles highly sensitive data and needs to comply with strict security standards or regulatory requirements, an on-premise solution may provide more control over the security measures implemented. If your business has limited IT resources, the cloud might be a better option as it reduces the burden on internal teams for managing infrastructure and software maintenance. Cloud Computing Platforms and Services allows employees to access systems and data from virtually anywhere with an internet connection, making it ideal for remote work and collaboration. On-premise systems typically require VPNs or dedicated networks for remote access. Moreover, cloud solutions often offer automatic updates and patch management, reducing the need for manual intervention. Businesses with dynamic workloads can take advantage of the cloud’s pay-as-you-go model to optimize costs. Finally, hybrid cloud solutions offer a combination of both worlds, enabling businesses to balance control and flexibility.
Conclusion
On-premise and cloud computing both have their advantages and disadvantages, and the right choice depends on your organization’s specific needs and priorities. On-premise solutions offer more control and security but require higher upfront investments and ongoing maintenance. Cloud Computing Course , meanwhile, provide flexibility, scalability, and reduced maintenance but may involve less control over infrastructure and data security. For many businesses, a hybrid approach—combining the strengths of both on-premise and cloud systems—may be the most effective solution. By evaluating your business’s budget, scalability needs, security concerns, and IT resources, you can make an informed decision that best suits your goals. Additionally, assessing long-term growth projections and technology trends is crucial, as cloud services continue to evolve rapidly. Consider the potential for integration with existing systems and the expertise of your internal teams when making a choice. As businesses grow, the demands on infrastructure can change, so it’s essential to choose a solution that can scale accordingly. Regular reviews of your chosen solution will ensure that it continues to align with your organization’s goals. Finally, staying informed about emerging technologies will help you make strategic decisions for the future of your IT infrastructure.





